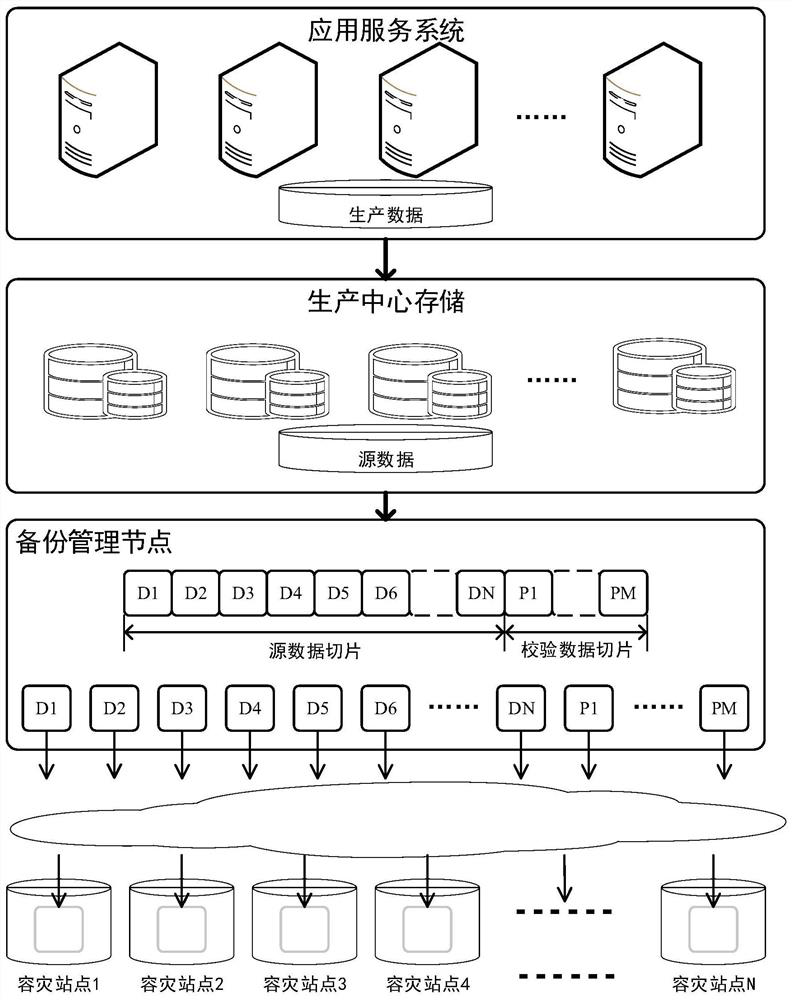
Multi-site disaster recovery backup method based on distributed raid slice
A disaster recovery backup, distributed technology, applied in response to the generation of errors, redundancy in operations for data error detection, input/output to record carriers, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
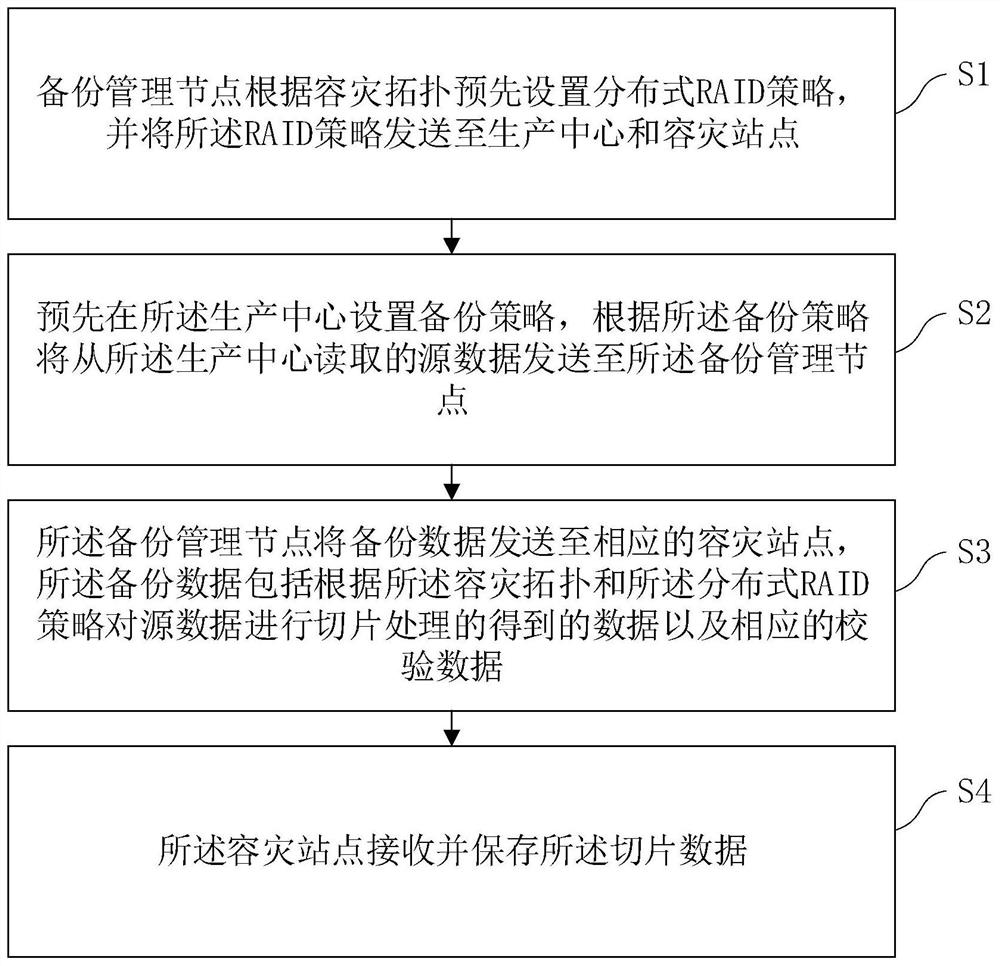
[0049] Embodiment 1: Data backup
[0050] S101, the data backup operation is carried out sequentially according to the sequence of events, for example, the three data backup events of backup data 0, backup data 1 and backup data 2 are carried out in sequence according to the order of 0, 1, and 2;
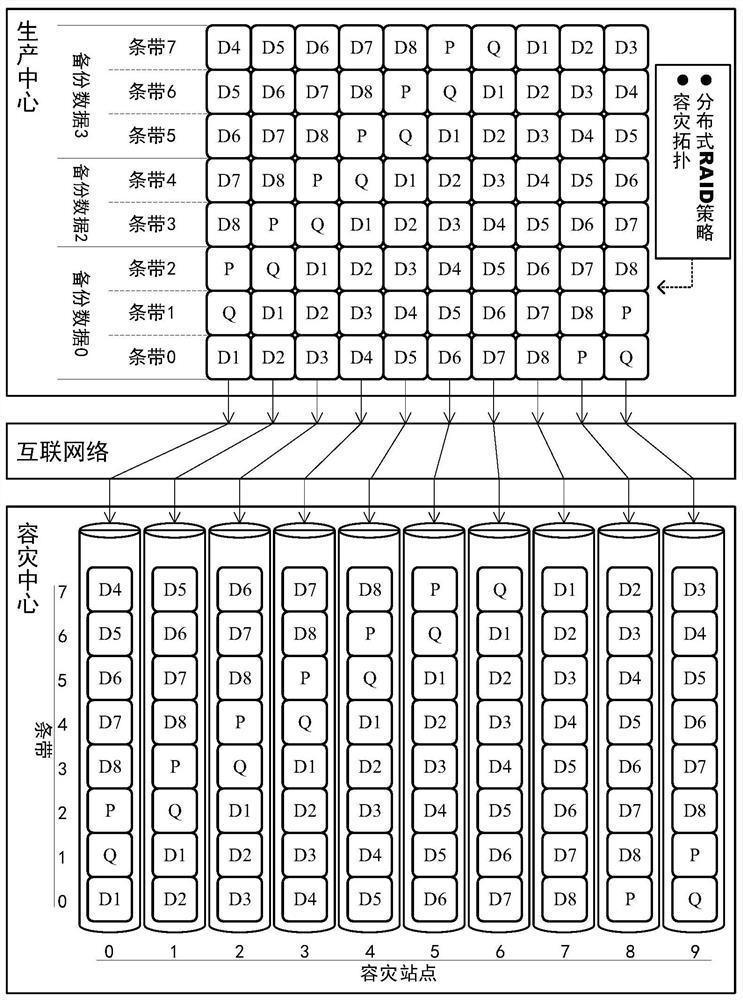
[0051] S102. When there is new data to be backed up, the production center divides the data to be backed up into data strips of a fixed size, such as image 3 Backup data 0 is divided into three stripes: stripe 0, stripe 1, and stripe 2;
[0052] S103. According to the disaster recovery topology and distributed RAID strategy, perform slice and check calculation on the data stripe, and send the check data and the source data slice to the disaster recovery site; image 3 Among them, 10 disaster recovery sites (disaster recovery sites 0-9) and the RAID strategy of RAID5+PQ verification are used to slice the data stripe into 8 data blocks D1-D8, and two verification data of P and Q are...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2: Data Recovery
[0056] When the data in the production center is damaged, the data needs to be restored to the recovery target center (it can be the original production center or another production center). The recovery steps are as follows.
[0057] S201. Data restoration in the production center takes stripes as a unit and restores one by one;
[0058] S202. The recovery target center reads the source data slice data block of stripe 0 in the disaster recovery site through the Internet, such as Figure 4 As shown, read disaster recovery site 0-7 when stripe 0 recovers;
[0059] S203. The recovery target center reorganizes the data according to the original data sequence (D1-D8) according to the RAID strategy;
[0060] S204. Save the reorganized data to the recovery target center storage, and complete the data recovery of stripe 0;
[0061] S205. Steps S202 to S204 are repeated according to stripes until data of all stripes is restored, that is, data resto...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Example 3: Data reconstruction
[0063] If PQ verification is adopted, data reconstruction and data recovery can be supported when the data of at most two disaster recovery sites is damaged at the same time. Such as Figure 5 As shown, assuming that disaster recovery sites 8 and 9 are damaged, the data reconstruction process is as follows.
[0064] S301. The process of data reconstruction, taking data stripes as a unit, restores data stripe by stripe;
[0065] S302. The production center reads the 8 data blocks stored in the disaster recovery site 0-7 in the stripe 0 through the Internet;
[0066] S303. The production center calculates the data blocks of the disaster recovery site 8 and the disaster recovery site 9 from the read 8 data blocks according to the RAID strategy and the PQ verification algorithm;
[0067] S304. The production center sends the calculated data blocks to the disaster recovery site 8 and the disaster recovery site 9 respectively through the In...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com