Antenna synchronous mobile electronic tag reading and writing method and system
A technology of electronic tags, reading and writing methods, applied in electromagnetic radiation induction, instruments, calculations, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in reading and writing, difficulty in equipment debugging, and inability to use small jump distances, and achieve miniaturization, Improve productivity and avoid cross-reading effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
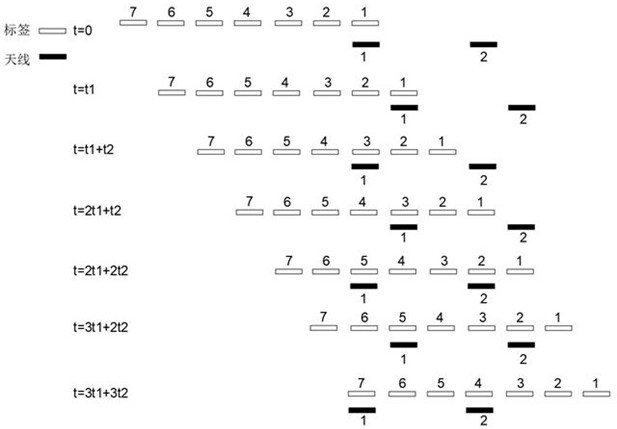
[0049] Such as figure 1 As shown, an antenna synchronous mobile electronic tag reading and writing system includes a label feeding line and two antennas beside the label feeding line.
[0050] The label feeding line is a straight line, and the labels are evenly spaced on the label feeding line. The jump distance of the label is P, and the reading and writing cycle of the label is set as T.
[0051] The two antennas are arranged along the label feeding direction, and the adjacent antennas are staggered by mq-1 hop distances, where q is a positive integer. In this example, the number of antennas is m=2, and if q=2, the adjacent antennas are staggered by 3 jump distances.
[0052] The reciprocating movement of the antenna is controlled by the mobile unit. When the antenna moves in the direction of material feeding, it remains relatively static with the corresponding label for reading and writing operations. When the antenna moves in the opposite direction of material feeding, it...
Embodiment 2
[0069] In this embodiment, on the basis of Embodiment 1, the reciprocating motion process of the antenna is further optimized.
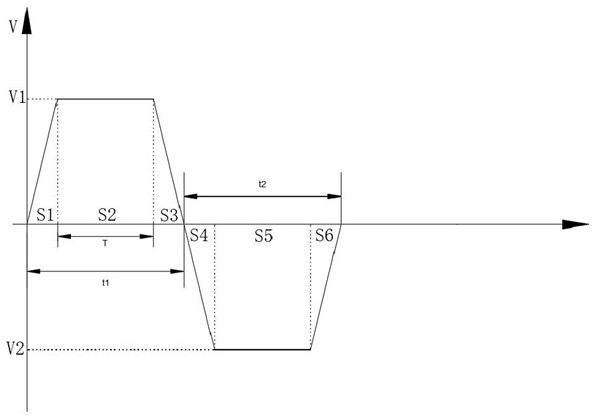
[0070] Such as image 3 Shown is the moving time-speed relationship diagram of the antenna. The movement of the antenna toward the feeding direction is divided into forward acceleration, uniform speed synchronization and forward deceleration in sequence. The speed V1 of uniform speed synchronization is the same as the feeding speed of the label feeding line. And the movement time of the uniform speed synchronization is T, and the antenna and the corresponding tag maintain a relatively static state for reading and writing operations during the uniform speed synchronization.
[0071] The movement of the antenna towards the opposite side of the feeding direction is divided into reverse acceleration, reverse constant speed and reverse deceleration in sequence, and the speed V2 of reverse uniform speed is greater than the speed V1 of uniform speed synchro...
Embodiment 3
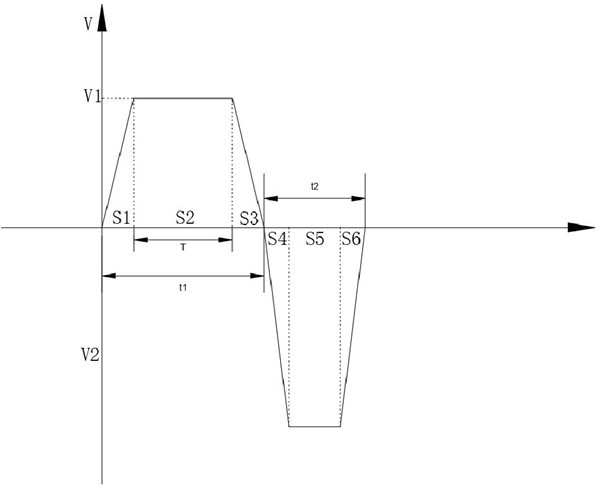
[0077] Such as Figure 4 As shown, this embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 2. It also optimizes the reciprocating motion of the antenna, unevenly distributes the time for antenna read and write operations and the time for returning to the initial position. The difference is that this embodiment is configured with four antennas. With one reciprocating movement, the label feeding line moves 4 jumps.
[0078] The four antennas are arranged along the feeding direction, and the adjacent antennas are staggered by mq-1 jump distances, where q is a positive integer. In this example, the number of antennas is m=4, and if q=1, the adjacent antennas are staggered by 3 jump distances.
[0079] In order to facilitate understanding and visually display the data relationship, assuming the optimized reciprocating motion period t1+t2=2T, the feeding speed of the label feeding line is V=mP / (t1+t2)=4P / 2T.
[0080] In order to visually display the working process of this embodiment,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com