Chemical exchange saturation transfer quantitative method and device for magnetic resonance and medium
A chemical exchange and magnetic resonance technology, applied in the field of biomedical engineering, can solve the problems of inaccurate and stable CEST quantification, underestimated CEST effect, and increased scan time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
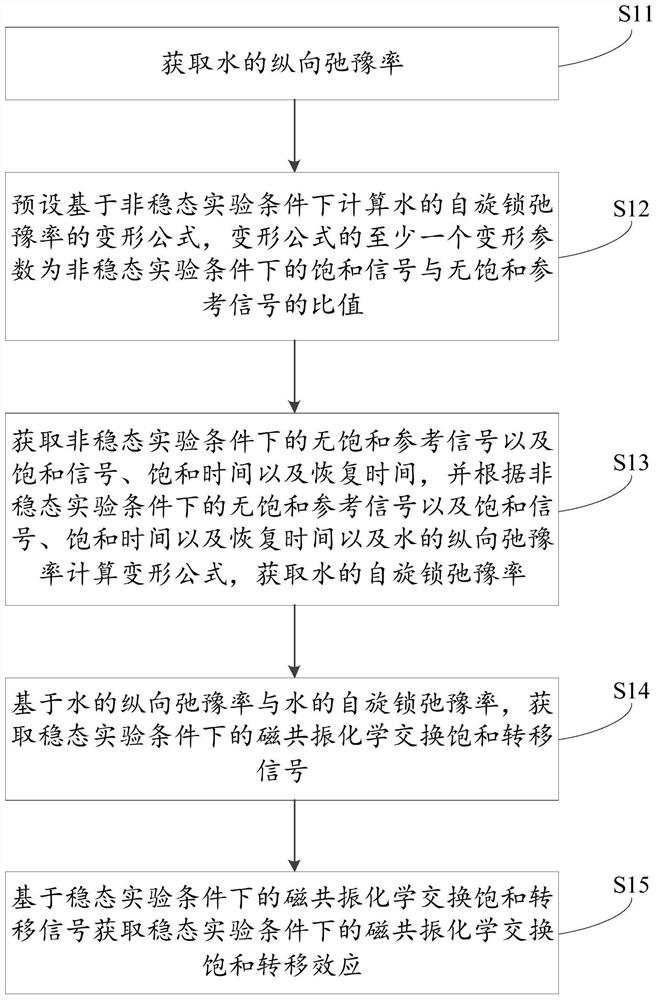
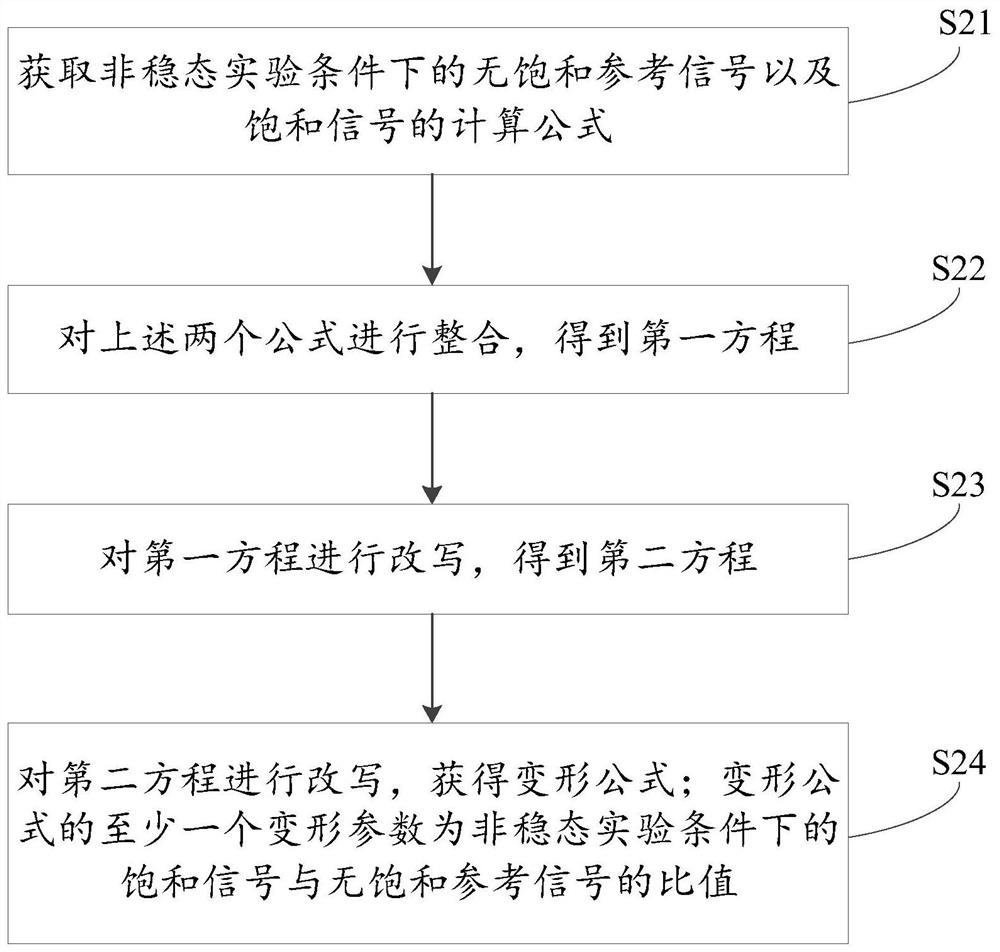
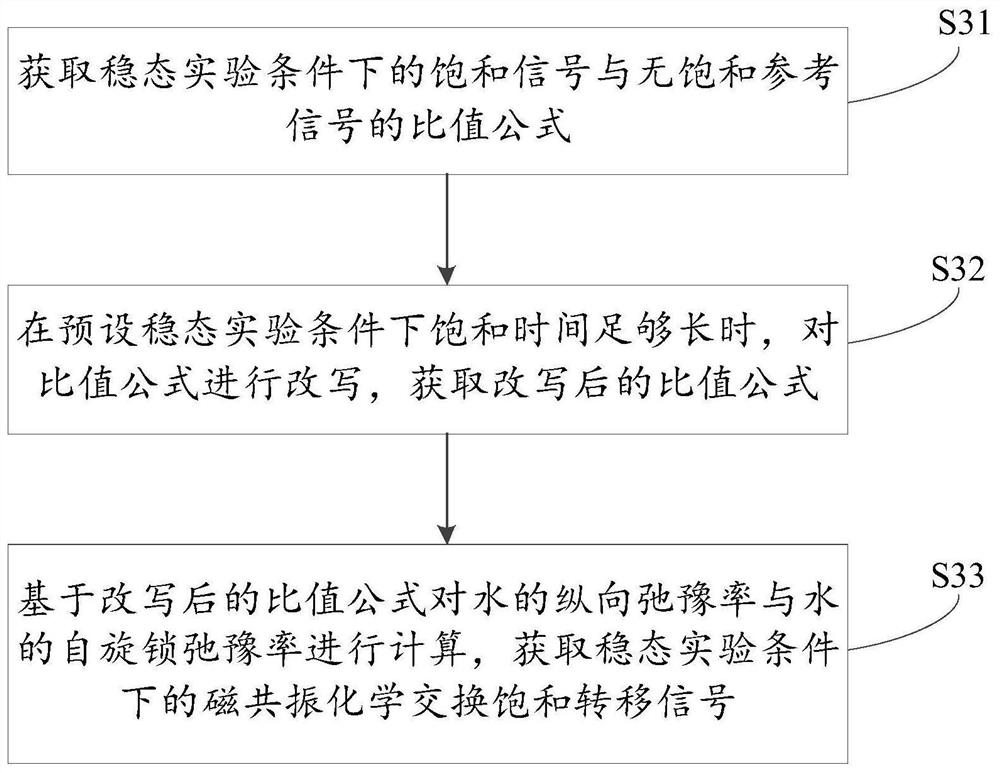
[0096] The chemical exchange process of water, semi-solid macromolecules and amide protons (amide) is simulated using the classic three-cell Bloch McConnell equation. Assuming a 11.7Tesla magnetic field environment, the longitudinal relaxation rate of water is 0.5Hz and the transverse relaxation rate is 30Hz; the longitudinal relaxation rate of amide protons is 1Hz and the transverse relaxation rate is 66.7Hz; Relaxation rate 105Hz. The proportions of amide protons (resonance frequency at 3.5 ppm relative to water) and semisolid macromolecules (resonance frequency at 0 ppm relative to water) relative to water were 0.1% and 13.9%, corresponding to exchange rates of 30 Hz and 23 Hz. Set the saturation energy amplitude (B1) to 1μT, the saturation time (Ts) / recovery time (Td) to 2s / 2s and 4s / 4s respectively, and simulate the CEST signal in the range of -4.5 to 4.5ppm with 0.1ppm as the step size. The CEST signal and the CEST effect are calculated by the chemical exchange saturati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com