Composition and methods for preventing or reducing the incidence of transient ischemic attacks
A technique for transient ischemia, morbidity, applied in the fields of neurology and cardiology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0152] Example 1: Neuroprotective effect of blocking calcium-permeable acid-sensitive ion channels on ischemia
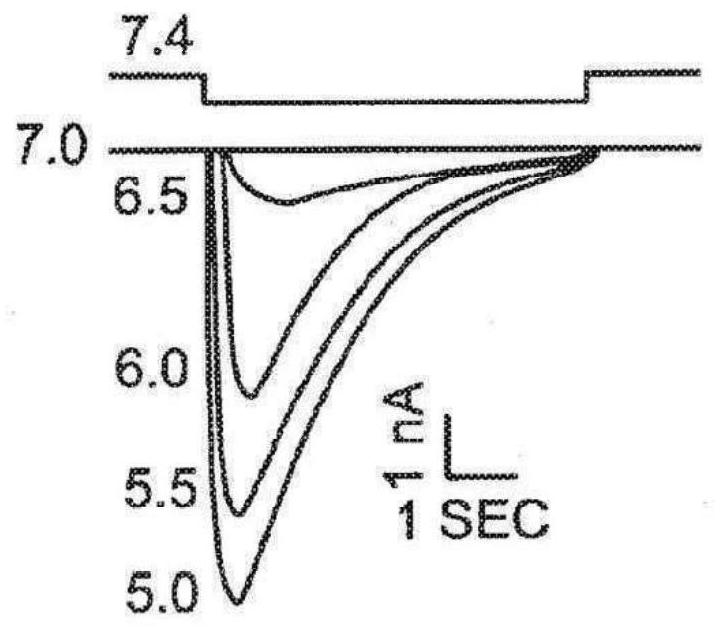
[0153] This example describes experiments showing the role of ASIC1a in mediating ischemic injury and the ability of ASIC1a inhibitors to attenuate ischemic injury; see Figure 2 to Figure 1 0. Ca 2+ Toxicity may play a central role in ischemic brain injury. Cytotoxic Ca 2+ The mechanisms by which loading occurs in the ischemic brain have become less clear as multiple human trials of glutamate antagonists have failed to show potent neuroprotection against stroke. Acidosis is a common feature of ischemia and plays a key role in brain injury. This example shows that acidosis activates Ca 2+ Permeable acid-sensitive ion channels (ASICs), which induce Ca 2+ dependent (but not glutamate receptor dependent) neuronal injury. Thus, cells lacking endogenous ASICs are resistant to acid damage, while Ca 2+ Transfection of permeable ASIC1a establishes sensitivity. In...
example 2
[0205] Example 2: The time window of PcTX neuroprotection (Time Window)
[0206] This example describes exemplary experiments to measure the neuroprotective effects of PcTX venom at various times after the onset of stroke in rodents; see Figure 11 . Briefly, cerebral ischemia (stroke) was induced in rodents by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). At indicated times after induction, artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF), PcTX venom (0.5 μl, 500 ng / ml total protein), or inactivated (boiled) venom was injected into the lateral ventricle of each rodent . Such as Figure 11As shown, administration of PcTX venom both 1 hour and 3 hours after stroke onset reduced stroke volume by 60%. Furthermore, a significant reduction in stroke volume was still achieved if treatment was discontinued 5 hours after the onset of MCAO. Thus, neuroprotection due to ASIC inhibition may have an extended treatment window after stroke onset, allowing stroke individuals to benefit from treatme...
example 3
[0207] Example 3: Exemplary Cystine Knot Peptides
[0208] This example describes exemplary cystine knot peptides, including full-length PcTxl and deletion derivatives of PcTx, which can be screened in cultured cells and tested in ischemic animals (e.g., rodents such as mice or rats) , and / or administered to an ischemic human subject.
[0209] Figure 12 The one-letter primary amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 1 ) of an exemplary cystine knot peptide PcTxl (indicated at 50) is shown, with various exemplary peptide features shown relative to amino acid positions 1 to 40 . Peptide 50 may include six cysteine residues that form cystine bonds 52 , 54 , 56 to create cystine knot motif 58 . The peptide may also include one or more beta sheet regions 60 and positively charged regions 62 . The N-terminal region 64 and the C-terminal region 66 may flank the cystine knot motif.
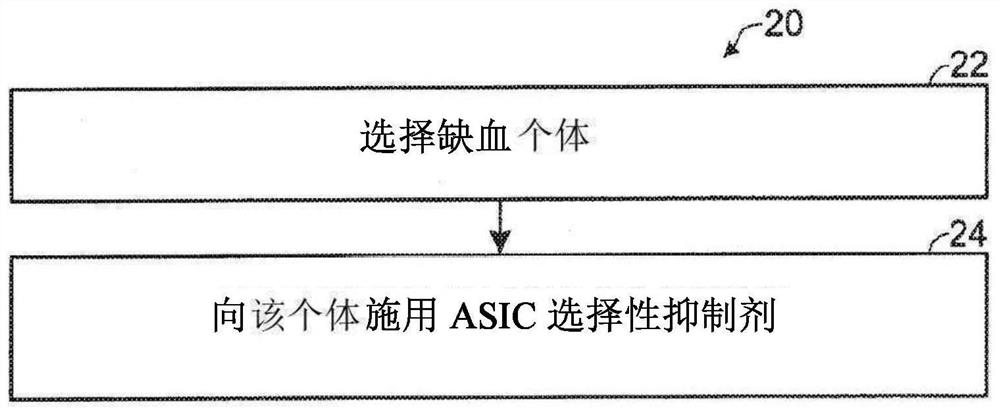
[0210] Figure 13 shown Figure 12 Comparison of the alignment of the PcTxl peptide 50 with various...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
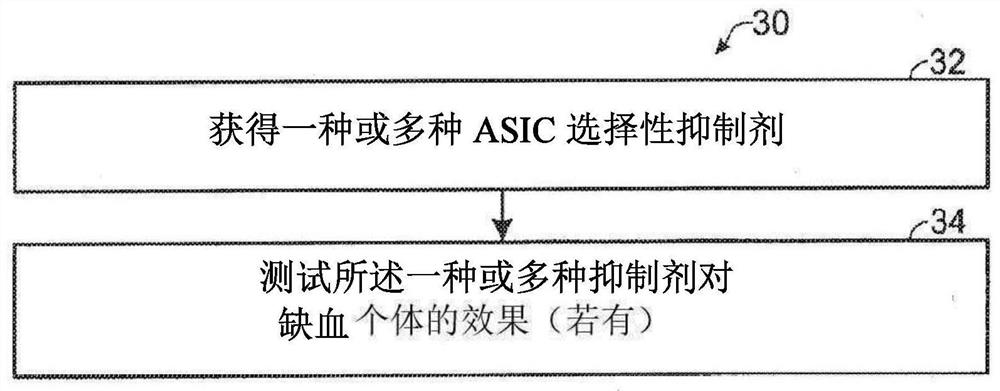
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com