A Quantitative Detection Method for Satellite Telescope Lens Surface Defects
A quantitative detection method and telescope technology, applied in measurement devices, optical testing flaws/defects, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of in-situ non-contact defect detection of large-sized optical components, size limitations of detection optical components, and complex equipment assembly, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of enhancing damage characteristics, improving robustness, and strong stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
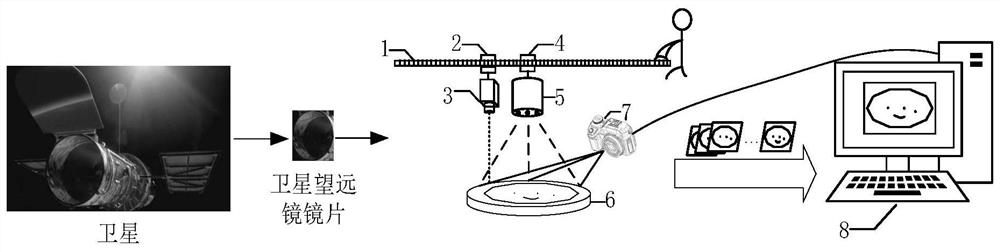
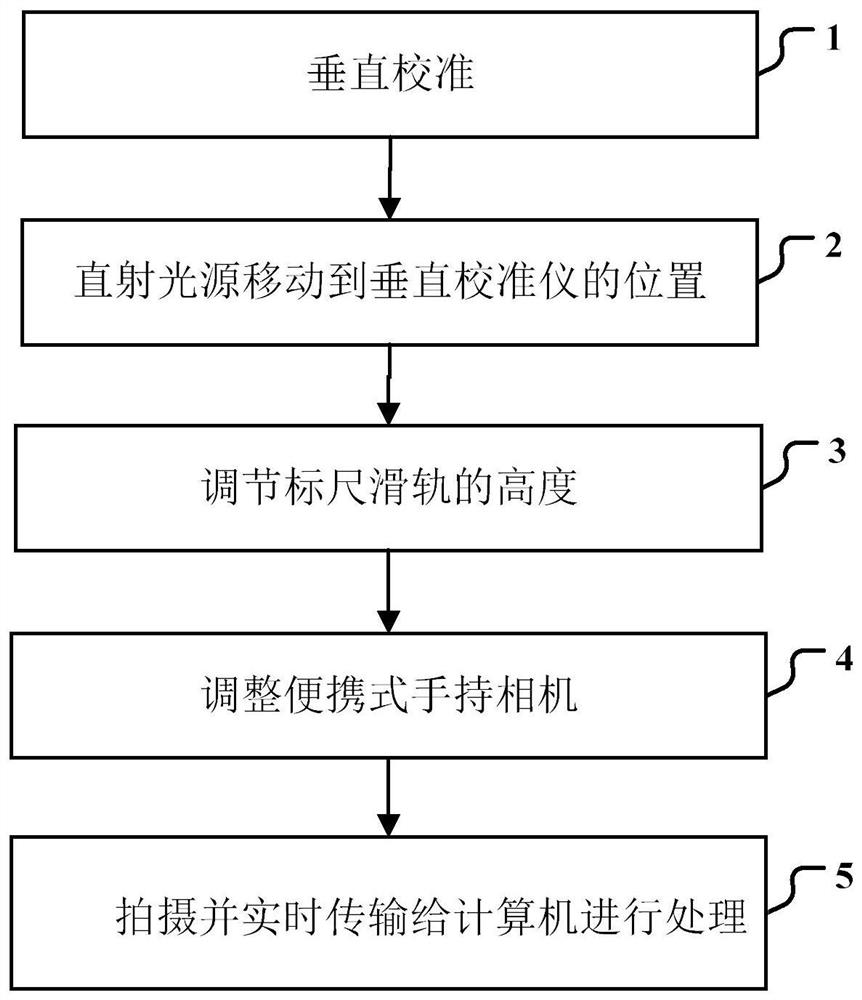
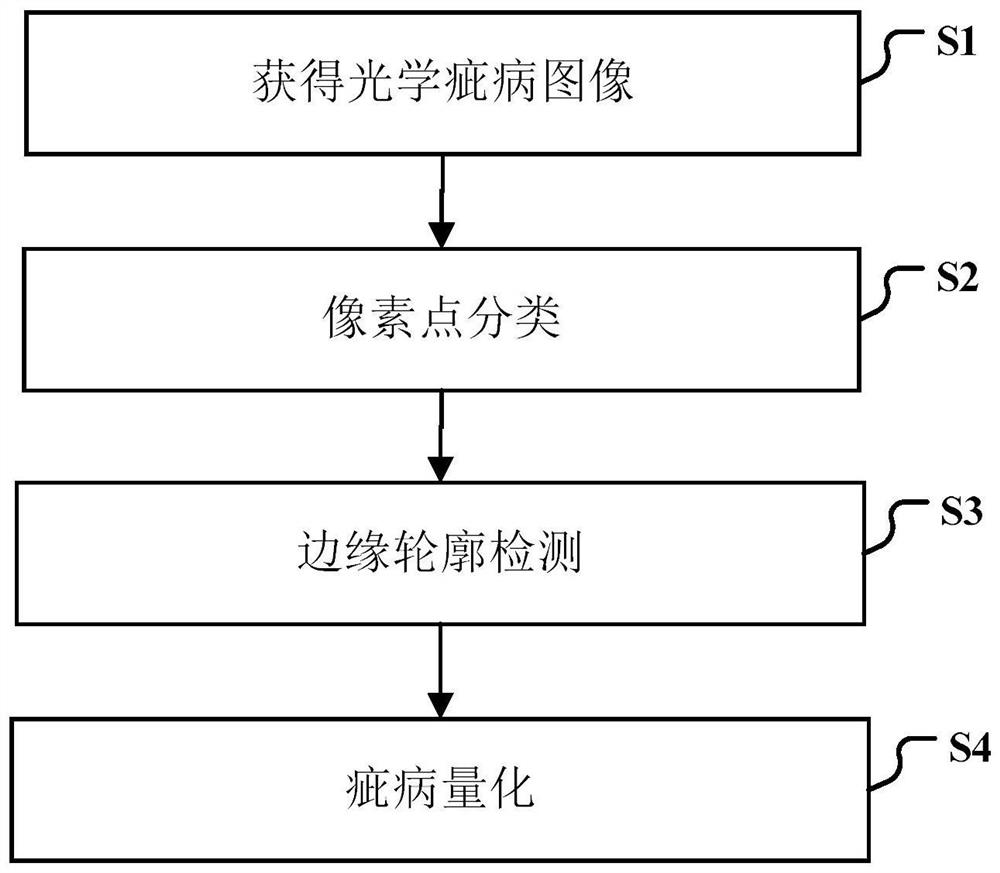
[0116] In this embodiment, there are scratches on the surface of the satellite telescope lens, Figure 6 There is a scratch at the upper left edge of the center, and particles formed by gas solidification adhere to the lens, and they are randomly and scatteredly distributed. use figure 1 The device shown collects images of defects on the surface of the satellite telescope lens, turns on the vertical calibrator, and irradiates the laser point on the geometric center of the lens under test placed horizontally, ensuring that the sliding track of the scale is perpendicular to the lens under test. Adjust the position of the sliding assembly on the scale rail, move the direct light source to the position of the vertical calibrator, so that the center of the direct light source and the center of the lens to be tested are on the same axis. Adjust the height of the ruler slide rail so that the lens under test can be completely irradiated by the direct light source. The portable hand-h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com