Inorganic energy storage ceramic noctilucent brick and preparation method thereof
An energy storage and ceramic technology, which is applied in the field of inorganic energy storage ceramic luminous bricks and its preparation, can solve the problems of reducing luminous effect, cumbersome manufacturing process, and cracks in brick adobe, and achieves improved cooling efficiency, uniform luminous performance, and enhanced bonding. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
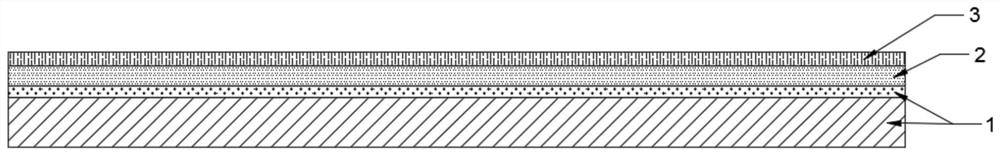
[0031] An inorganic energy storage ceramic luminous brick, comprising a bottom brick 1, a luminescent layer 2 and a protective layer 3 in sequence from the bottom surface to the top surface, and the bottom brick 1, the luminous layer 2 and the protective layer 3 are fired into an integrated structure through a kiln; the bottom brick 1 It is a finished ceramic tile with a glazed reflective layer, and the transparency of the protective layer 3 is 97%.
[0032] In this embodiment, the thickness of the light emitting layer 2 is 3 mm, and the thickness of the protective layer 3 is 1 mm.
[0033] Among them, the luminescent layer 2 is made of 25% rare earth luminescent material and 75% glass powder with a melting point of 750°C; the protective layer 3 is made of glass powder with a melting point of 750°C, and the transparency of the glass powder is 97%; The material is made by mixing type I rare earth luminescent material and type II rare earth luminescent material according to the ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The material and proportion of the inorganic energy storage ceramic luminous brick in this example are the same as in Example 1, and its preparation method is the same as in Example 1. The process parameters in the kiln sintering molding step are as follows:
[0040] During the sintering process, the temperatures on the upper table of the eight heating stages are 175°C, 255°C, 345°C, 455°C, 515°C, 615°C, 655°C and 770°C; 225°C, 275°C, 375°C, 495°C, 555°C, 635°C, 675°C and 795°C in sequence, the holding time of the first seven heating stages are 5min, 5min, 6min, 6min, 6min, 6min, 6min, The holding time of the eighth heating stage is 30 minutes, and the overall sintering time in this step is 70 minutes.
[0041] During the cooling molding process, the temperatures of the five cooling stages are controlled at 660°C, 520°C, 350°C, 180°C, and 20°C. The product is completely cooled and formed.
Embodiment 3
[0043] The materials and proportions of the inorganic energy storage ceramic luminous bricks in this example are the same as in Example 1, and the preparation method is the same as in Example 1. The process parameters in the kiln sintering step and the cold air channel cooling molding step are as follows:
[0044] During the sintering process, the temperatures on the upper table of the eight heating stages are 185°C, 265°C, 355°C, 465°C, 525°C, 625°C, 665°C and 780°C; 235°C, 285°C, 385°C, 505°C, 565°C, 645°C, 685°C and 805°C in sequence, the holding time of the first seven heating stages are 7min, 7min, 7min, 6min, 6min, 6min, 6min, The holding time of the eighth heating stage is 25 minutes, and the overall sintering time in this step is 70 minutes.
[0045] During the cooling molding process, the temperatures of the five cooling stages are controlled at 680°C, 540°C, 370°C, 200°C, and 30°C; Let the product cool completely.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com