Continuous fiber 3D printing path planning method based on parallel optimization of fiber orientation and structure
A continuous fiber and fiber orientation technology, applied in the field of continuous fiber 3D printing path planning, can solve the problems of restricted development, path jumping, and too small turning angle, and achieve the effect of improving printing efficiency, good applicability, and solving lightweight effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and embodiment the present invention will be described in further detail
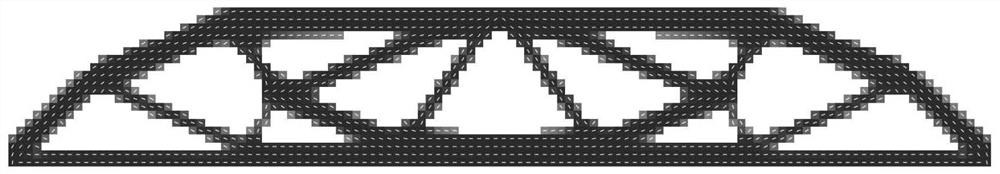
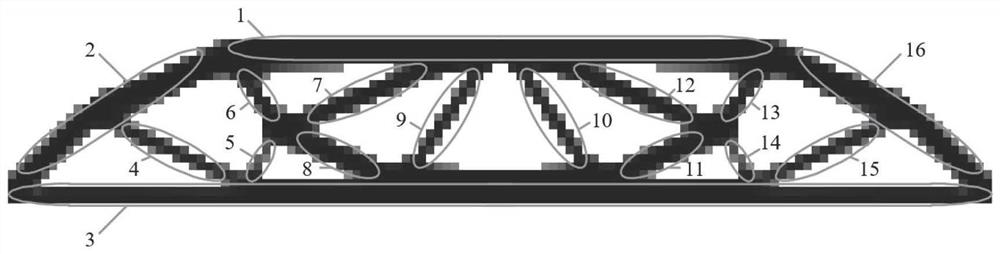
[0035] refer to figure 1 , a continuous fiber 3D printing path planning method for parallel optimization of fiber orientation and structure, comprising the following steps:
[0036] 1) Construct a parallel optimization model of fiber orientation and composite material structure, taking material density x and fiber angle θ as design variables, and its mathematical model is as follows:
[0037]
[0038]
[0039] In the formula, the objective function c represents the minimum compliance value; U and F represent the global displacement vector and the global load vector respectively; K represents the global stiffness matrix; u e and k e represent the element displacement vector and the element stiffness matrix respectively; x min Represents the relative minimum density; p represents the penalty factor; N represents the number of finite element gr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com