Visual SLAM method based on semantic segmentation dynamic points
A semantic segmentation and dynamic point technology, applied in the field of computer vision, can solve problems such as inaccurate camera pose estimation, reduced robustness of visual odometry, and inability to build a globally consistent map, achieving the goal of improving accuracy and accuracy Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
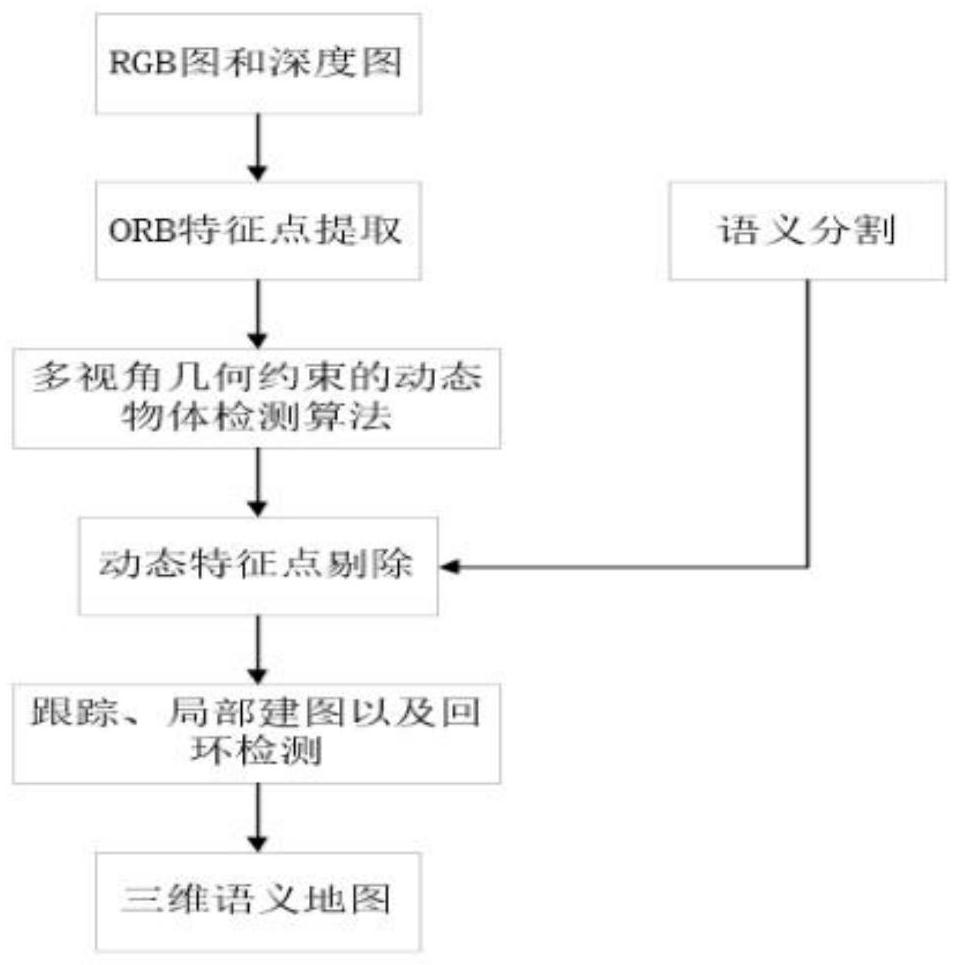
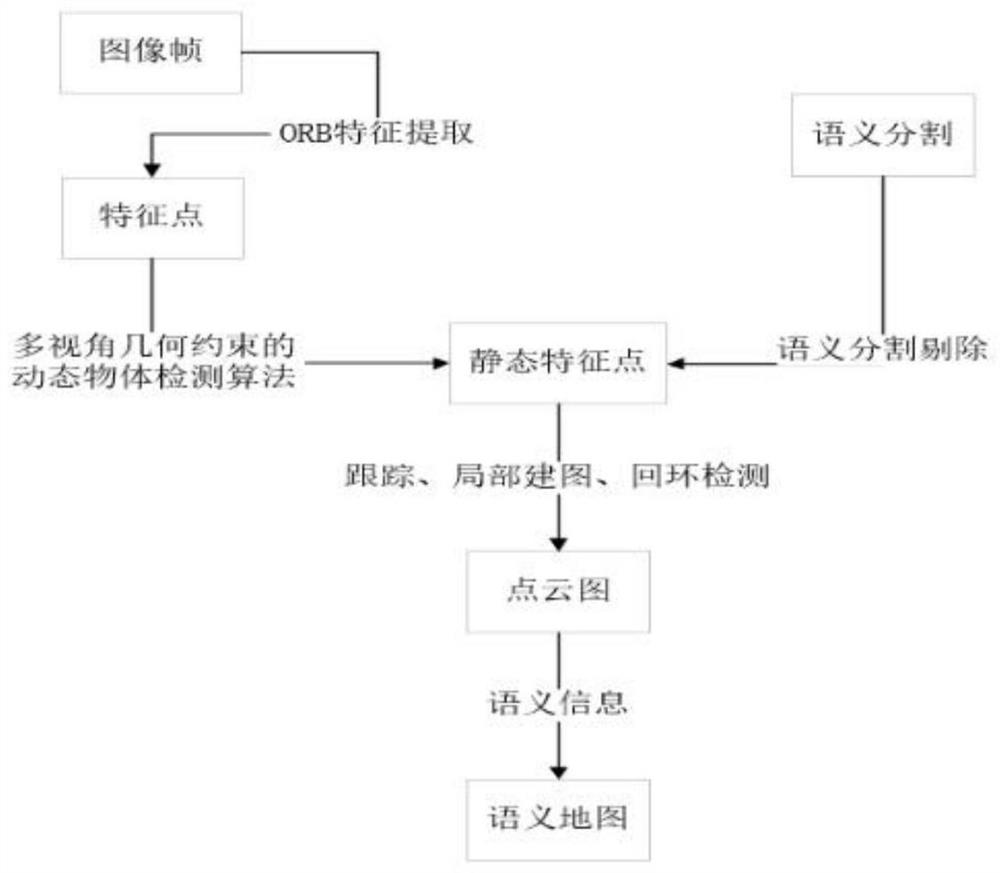
[0063] A visual SLAM method for semantically segmented dynamic points:
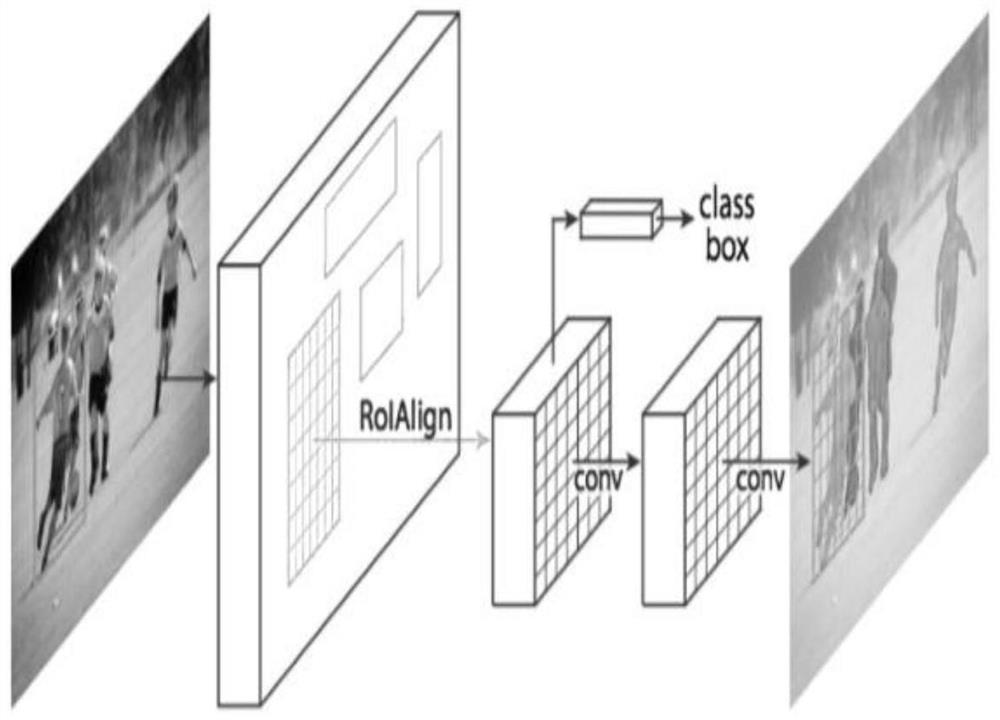
[0064] Step 1. After the camera collects the RGB-D image data, first pass the RGB image to the convolutional neural network (CNN), separate out all prior dynamic objects, complete the semantic segmentation task for the image, and obtain all the dynamic objects in a picture. The concealment of objects. Considering that feature points are easy to appear on the object boundary, the mask is expanded to expand the dynamic object boundary and eliminate the feature points of the dynamic object boundary. Then, on this basis, the ORB feature points of the image are extracted, and the camera pose is estimated by feature matching. Therefore, the mask obtained by using Mask R-CNN can retain the feature points of the static part of the image as input in the subsequent stage, thereby improving the system. Robustness in dynamic environments.
[0065] Step 2. Although most dynamic objects can be eliminated by using Mas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com