Zinc-aluminum-magnesium coating material and preparation method thereof
A zinc-aluminum-magnesium coating technology, which is applied in the field of zinc-aluminum-magnesium coating materials and its preparation, can solve problems such as potential safety hazards in downstream processes, component segregation, and high labor intensity, and achieve improved labor productivity, eutectic structure, and The effect of shortening the production time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] A preparation method for a zinc-aluminum-magnesium coating material, comprising the following steps:
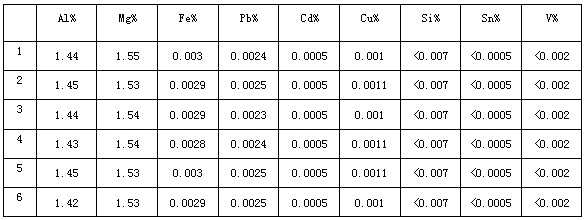
[0028] Step 1: According to the mass percentage of Al: 1.3%~1.7%, Mg: 1.3%~1.7%, and the balance is zinc (other impurities are inevitably brought in), weigh zinc ingots, aluminum ingots, and magnesium ingots.
[0029] Step 2: Weigh 0.8% of the total amount of Type II or III zinc slagging agent in the first step.
[0030] Step 3: Add the zinc ingots and aluminum ingots weighed in the first step to the coreless furnace.
[0031] Step 4: After the zinc and aluminum are melted, heat up to 480°C, add the slagging agent weighed in the second step, and stir to make it fully react, and scoop up the scum on the surface.
[0032] Step 5: Heat up to 480°C and add magnesium ingots, 3.5Kg each time, add magnesium ingots after the magnesium ingots added last time have melted, and stir for 10 minutes after adding all the magnesium ingots.
[0033] Step 6: Sampling and testing of al...
Embodiment 2
[0045] A preparation method for a zinc-aluminum-magnesium coating material, comprising the following steps:
[0046] Step 1: According to the mass percentage of Al: 1.3%~1.7%, Mg: 1.3%~1.7%, and the balance is zinc (other impurities are inevitably brought in), weigh zinc ingots, aluminum ingots, and magnesium ingots.
[0047] The second step: weigh 0.9% of the total amount of the slagging agent in the first step.
[0048]Step 3: Add the zinc ingots and aluminum ingots weighed in the first step to the coreless furnace.
[0049] Step 4: After the zinc and aluminum are melted, heat up to 480°C, add the slagging agent weighed in the second step, and stir to make it fully react, and scoop up the scum on the surface.
[0050] Step 5: Raise the temperature to 490°C and add magnesium ingots, adding 4Kg of magnesium ingots each time. After the magnesium ingots added last time are melted, add magnesium ingots again. After adding all the magnesium ingots, stir for 13 minutes.
[0051] ...
Embodiment 3
[0063] A preparation method for a zinc-aluminum-magnesium coating material, comprising the following steps:
[0064] Step 1: According to the mass percentage of Al: 1.3%~1.7%, Mg: 1.3%~1.7%, and the balance is zinc (other impurities are inevitably brought in), weigh zinc ingots, aluminum ingots, and magnesium ingots.
[0065] The second step: weigh 1% of the total amount of the slagging agent in the first step.
[0066] Step 3: Add the zinc ingots and aluminum ingots weighed in the first step to the coreless furnace.
[0067] Step 4: After the zinc and aluminum are melted, heat up to 480°C, add the slagging agent weighed in the second step, and stir to make it fully react, and scoop up the scum on the surface.
[0068] Step 5: Raise the temperature to 500°C and add magnesium ingots, adding 4.9Kg each time. After the magnesium ingots added last time are melted, add magnesium ingots again. After adding all the magnesium ingots, stir for 15 minutes.
[0069] Step 6: Sampling an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com