Low-boiling-point two-dimensional material layer-by-layer stacking forming method
A technology of two-dimensional materials and molding methods, applied in the field of additive manufacturing, can solve problems such as printing evaporation, and achieve the effects of improving stability, high precision, and reducing weld defects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0027] This embodiment provides a method for layer-by-layer accumulation of low-boiling point two-dimensional materials. The low-boiling point two-dimensional materials are 400-mesh magnesium alloy powder particles, and the weight percentages are 40% of paraffin, 40% of high-density polyethylene and stearic acid. 20% of the organic binder bonded to form a strip, the width is preferably 5mm, and the thickness is preferably 0.03mm. The mass of magnesium alloy powder accounts for 90%, and the organic binder accounts for 10%.
[0028] Its forming method comprises the following steps:
[0029] S1: Control the temperature of substrate 1 to 150°C;
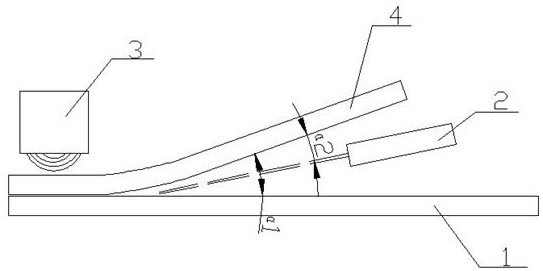
[0030] S2: if figure 1 , keep the first layer of two-dimensional material of the low-boiling point material and the substrate 1 at an angle α1 of 45°, and then preheat the first layer of two-dimensional material to 165°C, then use an energy gun 2 (preferably a laser energy gun or Electron beam energy gun) is incident between the first ...
Embodiment approach 2
[0041] This embodiment provides a method for layer-by-layer accumulation of low-boiling point two-dimensional materials. The low-boiling point two-dimensional materials are 300-500 mesh aluminum alloy powder particles, and the weight percentages are 40% of paraffin, 30% of acrylic resin, stearic acid 30% of the organic binder bonded to form a strip, the width is preferably 5mm, and the thickness is preferably 0.03mm.
[0042] Its forming method comprises the following steps:
[0043] S1: Control the temperature of substrate 1 to 130°C;
[0044] S2: if figure 1 , keep the first layer of two-dimensional material of the low-boiling point material and the substrate 1 at an angle α1 of 45°, and then preheat the first layer of two-dimensional material to 160°C, use an energy gun 2 (preferably a laser energy gun or Electron beam energy gun) is incident between the first layer of two-dimensional material and the substrate, and the incident angle α2 between the energy gun 2 and the t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Power density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com