Scanning protocol parameter determination method and magnetic resonance system
A scanning protocol and parameter determination technology, which is applied in the direction of magnetic resonance measurement, magnetic variable measurement, and measurement devices, can solve the problem of time-consuming and labor-intensive modification of scanning protocol parameters, and achieve the effect of reducing the time spent on magnetic resonance imaging and reducing the time spent
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
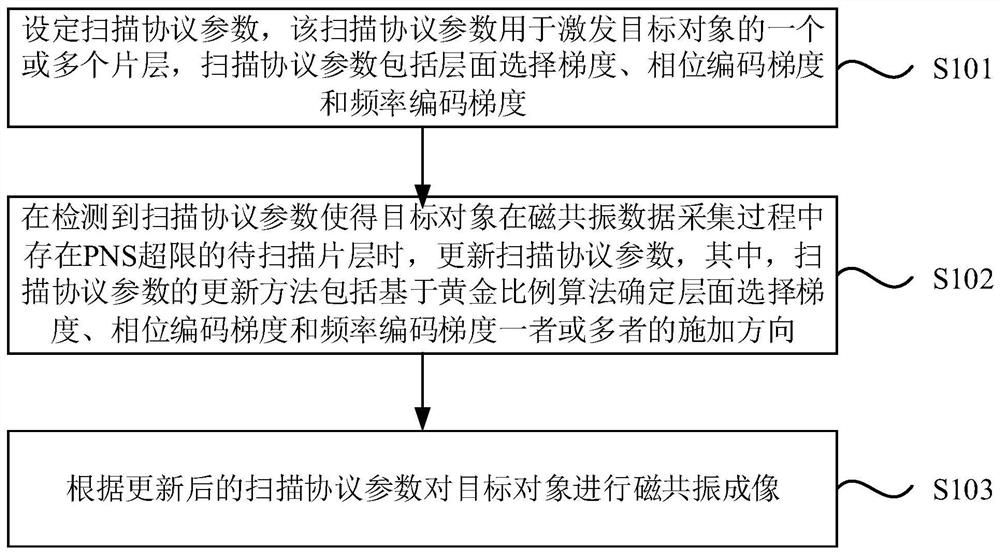
[0027] figure 1 It is a flow chart of the magnetic resonance scanning method provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention. The technical solution of this embodiment is applicable to the situation of quickly and automatically completing the modification of scanning protocol parameters. The method can be executed by the controller provided in the embodiment of the present invention. The method specifically includes the following steps:
[0028] S101. Set scan protocol parameters, the scan protocol parameters are used to excite one or more slices of the target object, and the scan protocol parameters include slice selection gradients, phase encoding gradients, and frequency encoding gradients.
[0029] Before performing a magnetic resonance scan on the target object, it is necessary to set corresponding scan protocol parameters on the parameter setting interface. The scan protocol parameters include slice selection gradients (parameters), phase encoding gradients (paramet...
Embodiment 2
[0059] On the basis of the method for determining the parameters of the above-mentioned scanning protocol, this application also proposes a magnetic resonance imaging method, which divides the scanning protocol into a plurality of visual sequence sub-modules: sequence routine sub-modules, sequence basic constituent modules, and these modules are visualized as modules The way exists in the toolbox. Among them, the conventional sub-modules of the sequence include, for example, the fat pressing module, the space saturation zone module, the inversion recovery module, etc.; the basic building blocks of the sequence include, for example, RF excitation pulse, refocusing pulse, slice selection gradient, phase encoding gradient, frequency encoding gradient, etc. These basic building blocks can be configured flexibly to meet the design requirements of the target sequence. Wherein, the parameter settings of the slice selection gradient, the phase encoding gradient, and the frequency enco...
Embodiment 3
[0063] An embodiment of the present invention provides a magnetic resonance system, such as Figure 5 and Image 6 As shown, the system includes a scanning device 110. The scanning device 110 includes a radio frequency transmitting coil 111, a gradient coil 112, a radio frequency receiving coil 113 and a controller 120. The radio frequency transmitting coil 111 is used to transmit radio frequency pulses to the scanning site of the target object to Excite the nuclear spin of the scanning part; the gradient coil 112 is used to apply the layer selection gradient field, the phase encoding gradient field and the frequency encoding gradient field to the scanning part to generate echo signals; the radio frequency receiving coil 113 is used to receive the echo signals to form Magnetic resonance scan data; the controller 120 is used to receive set scan protocol parameters, the scan protocol parameters are used to excite one or more slices of the target object, and the scan protocol par...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com