Whole genome association analysis algorithm based on parent genotypes and progeny phenotypes
A whole-genome, association analysis technology, applied in the field of bioinformatics, can solve the problems of large experiments and sequencing costs, consumption, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing manpower, material resources and time costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039]Next, the association analysis method based on parental genotype and offspring phenotype described in the present invention is described with grass carp sample data.
[0040] S1) Whole-genome resequencing was performed on the parent grass carp (15 females and 15 males) used for breeding in our laboratory in 2014. The sequencing platform was Illumina Xten with a sequencing depth of 20×.
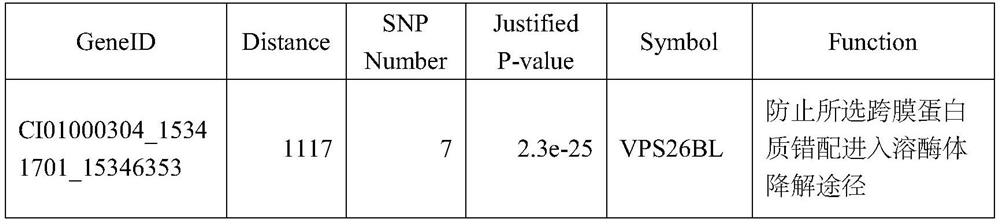
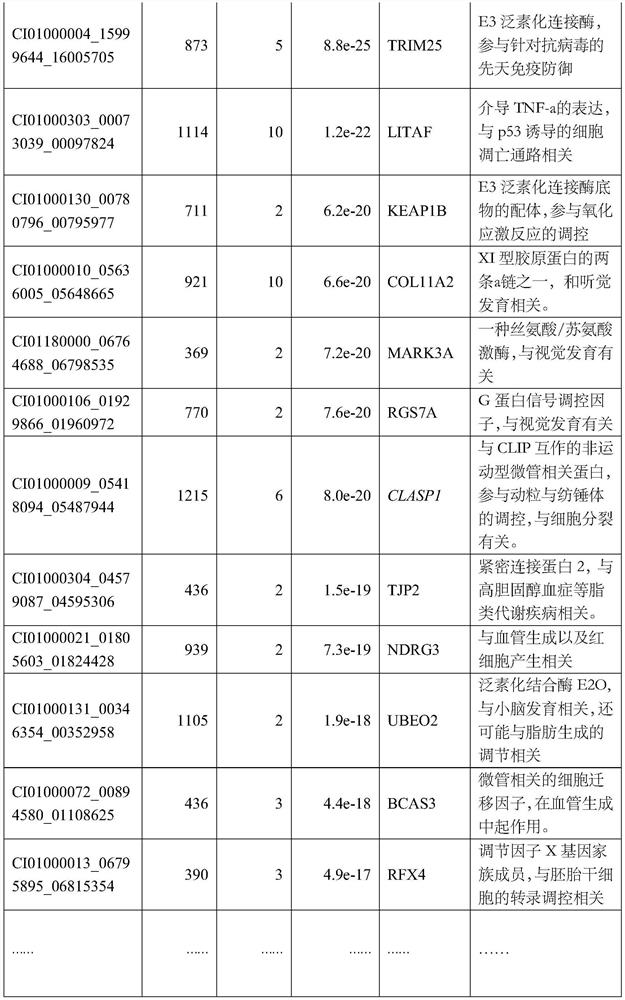
[0041] S2) Obtain the offspring body weight data of the parents described in S1), and collect 1729 tail phenotype data (example: Table 1) of 190 parent pairs (some parent pairs did not collect valid offspring phenotype data):
[0042] Table 1: Body weight data of 1729 offspring (example)
[0043] sample number female parent male parent weight(g) A1681 F14 M12 109.16 B0039 F5 x9 119.01 A1693 F14 2 99.95 A2479 F8 M9 134.84 … … … … A1664 F14 M9 87.39
[0044] S3) Using BWA software to compare the whole genome resequencing data o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com