A salt-tolerant bacterium and its application
A salt-tolerant and functional technology, applied in the field of agricultural microorganisms, achieves high agricultural application prospects and economic value, promotes rice growth, and has the effects of excellent strain resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1 Screening of salt-tolerant salt field bacteria
[0040] (1) Collect root soil samples of salinity-tolerant plants such as Suaeda salsa and reed from the saline-alkali land of the Yellow River Delta Nature Reserve, put them into clean sampling bags, mark them well, put them in an ice box and bring them back to the laboratory. Store at -20°C for later use. Weigh 1g of soil samples in a sterile ultra-clean bench and place them in 100mL conical flasks containing glass beads and 20mL of sterile water, and incubate them in a shaking incubator at 28°C and 180rpm for 1 hour to fully disperse and mix the soil samples. . Under sterile conditions, draw 0.5 mL of soil suspension and mix well with 4.5 mL of sterile water, and then successively dilute them successively to make 10 -1 , 10 -2 , 10 -3 For the sample solutions of different dilutions, draw 0.2 mL of the sample solutions and spread them on the salt-tolerant screening solid medium plate, and invert them in a c...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2 Morphological observation and identification of physiological and biochemical characteristics of strain JP11
[0046] The morphology of strain JP11 was observed using the oil lens of a Nikon inverted microscope.
[0047] The culture temperature of strain JP11 was set at 28°C for the identification of physiological and biochemical characteristics. At the same time, the optimum temperature, optimum growth pH and optimum salt concentration of strain JP11 when growing on LB solid medium were analyzed.
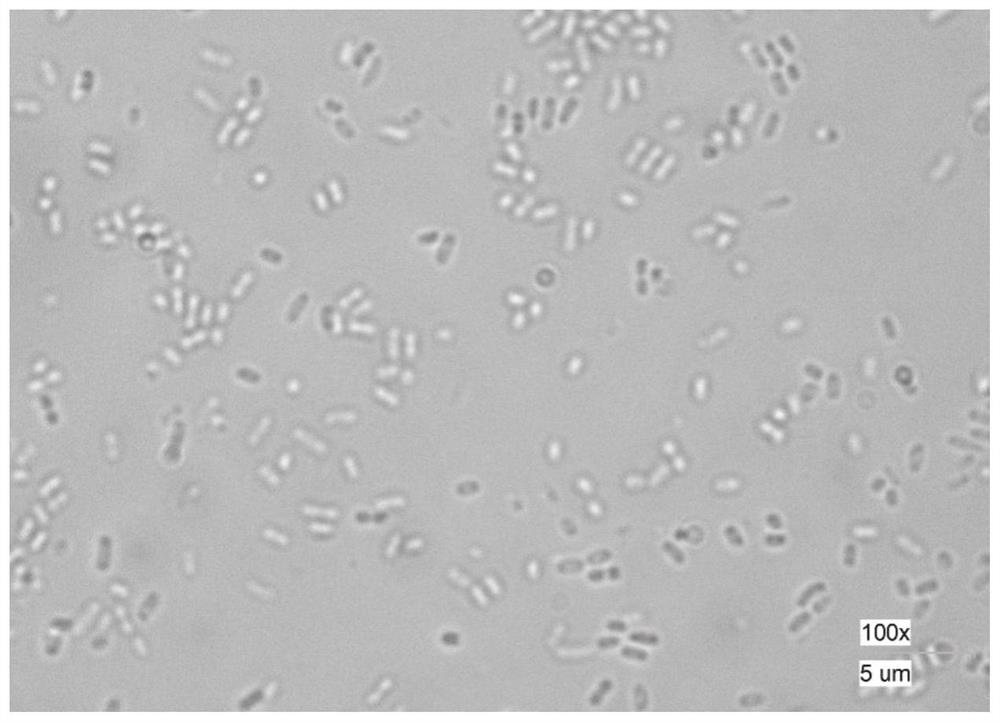
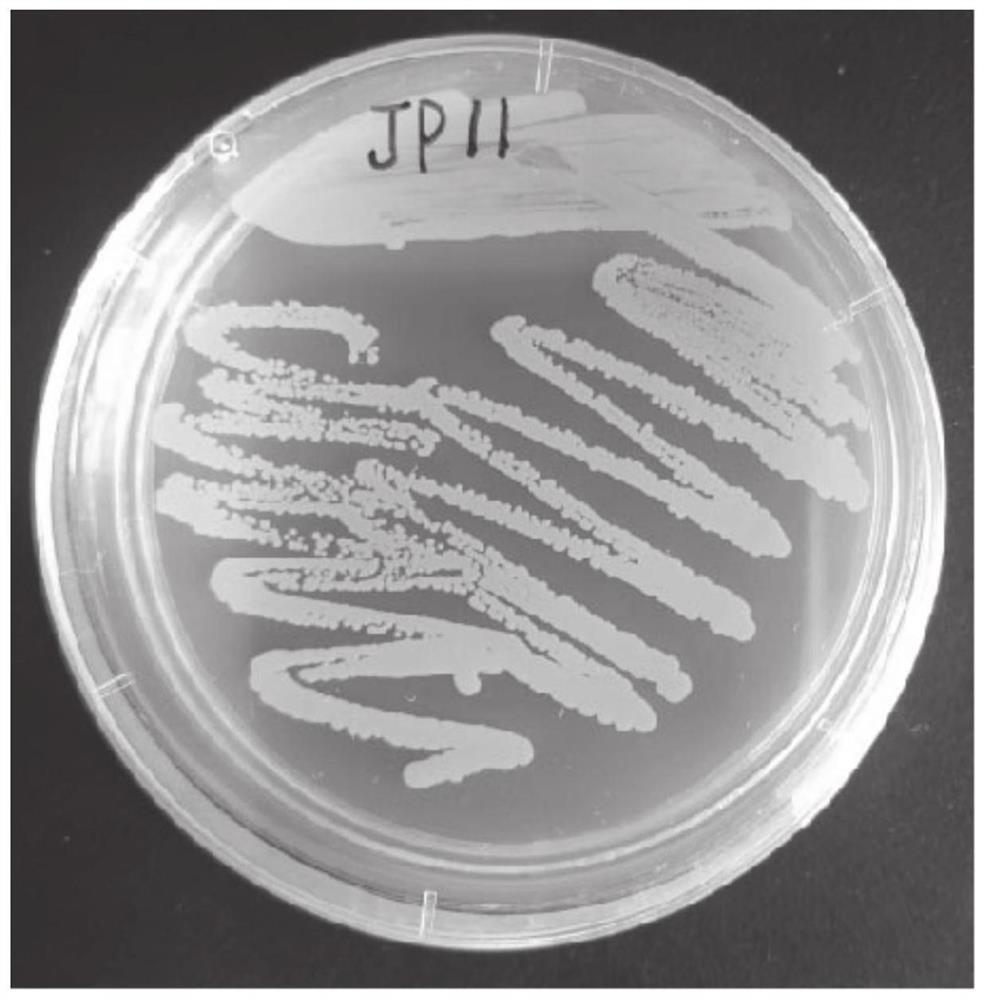
[0048] The biological characteristics of strain JP11 are: rod-shaped, single, cell size is (0.5μm ~ 0.8μm) × (1.0μm ~ 1.3μm), no spores ( figure 1 ). When cultured at 28°C, the colonies are regular circles, protruding, milky white, opaque, smooth and moist surface, easy to pick, and neat edges ( figure 2 ).
[0049] The physiological and biochemical characteristics of strain JP11 are: Gram staining negative, aerobic, positive for catalase, urease, phenylalani...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Example 3 Analysis of the growth-promoting effects of strain JP11 on potassium, phosphorus and phosphorus dissolution
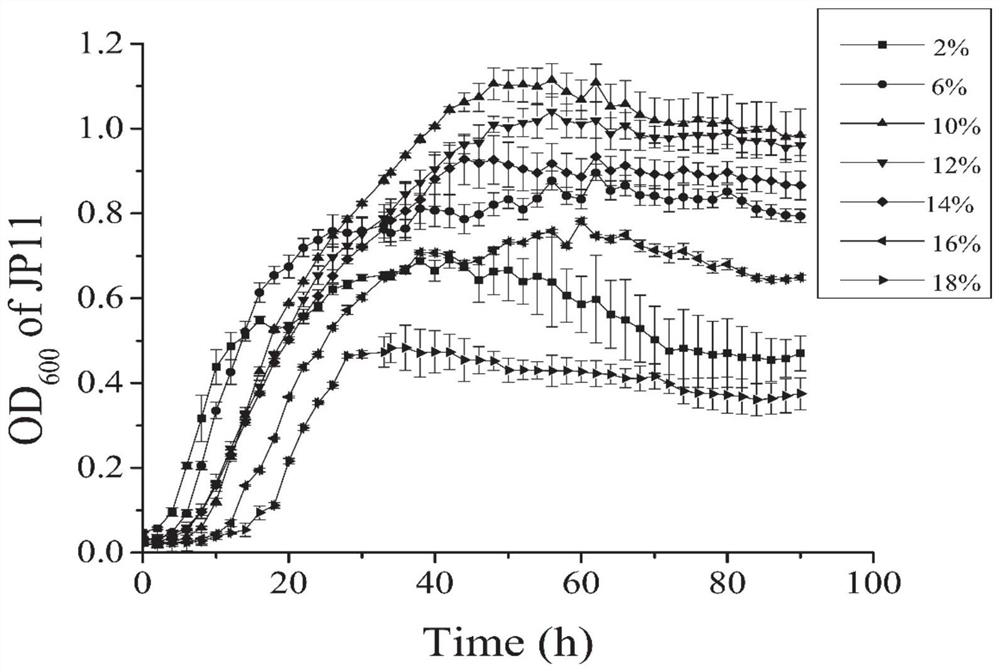
[0059] The isolated single colony of strain JP11 was transferred to a test tube containing 5 mL of liquid medium, and cultured with shaking at 28 °C and 180 rpm for 24 h. Cultivate in a constant temperature incubator for 3 days, and observe whether there are transparent oil droplet colonies on the silicate bacteria medium plate. The results showed that after the strain JP11 was cultured in the silicate bacteria solid medium for 2 days, transparent oil droplet-shaped colonies grew on the plate, indicating that the strain JP11 could dissolve potassium feldspar and had potassium-dissolving properties ( Figure 4 ).
[0060] The isolated single colony of strain JP11 was transferred to a test tube containing 5 mL of liquid medium, shaken for 24 h at 28 °C and 180 rpm, and 5 μL of seed solution was taken and placed on the Montkina organophosphorus solid cul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com