Semantic decoupling-based no-proposal time sequence language positioning method
A positioning method and semantic technology, applied in the field of cross-modal content retrieval, to improve user experience and improve accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0090] A non-proposed temporal language localization method based on semantic decoupling, comprising the following steps,
[0091] Step 1: Select the training data set;
[0092] Step 2: Load the model parameters of the pre-trained 2D or 3D convolutional neural network, and extract the original video features from the dataset in step 1;
[0093] Step 3: For the data set in step 1, given a natural language query Q, it has Words, first use GLoVE word embedding, express each vocabulary as a word vector with a dimension of 300, and then combine the obtained forward and backward features through two layers of bidirectional gated recurrent units to obtain the query text features;
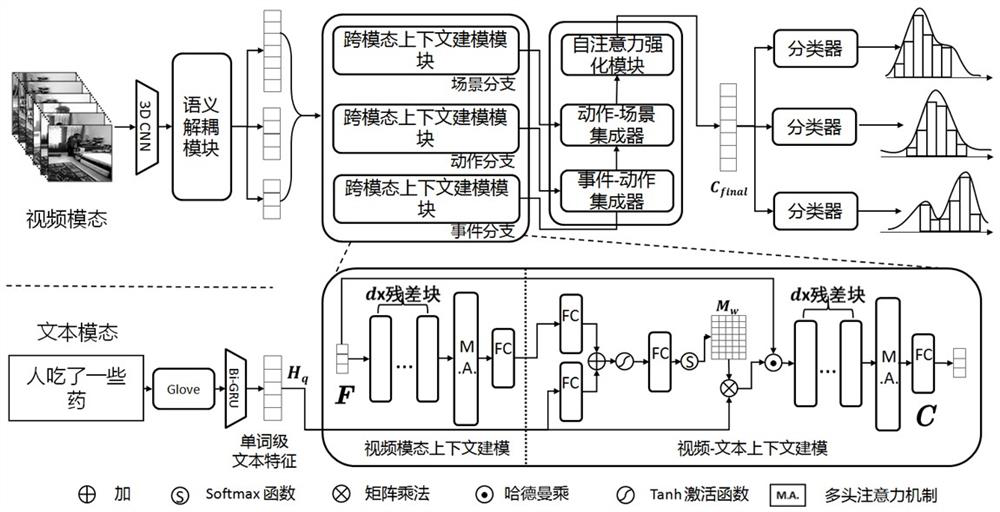
[0094] Step 4: Decouple the original video features in step 2 according to their latent semantics, obtain three semantic branches, and obtain three feature streams with different semantics;
[0095] Step 5: Perform feature interaction on the three feature streams in step 4 to obtain three different vide...
Embodiment 2
[0102] On the basis of Example 1, further, the step 5 includes in more detail,
[0103] Step 5.1: Perform feature interaction on the three feature streams to obtain three different video context features C S ,
[0104] Video Context Feature C S , obtained by the following formula:
[0105]
[0106]
[0107]
[0108] Step 5.2: Convert word-level text features H q Converted to a cross-modal specialized representation with strong resolution and compared to three different video context features C S Merge and get three cross-modal contexts;
[0109] Said step 5.2 comprises in more detail,
[0110] Step 5.21: Given a word-level textual feature H of a semantic branch q and video context feature C S , quantifying the word-to-per-video context feature C S The different contributions of the original word-level text features are weighted to obtain the updated text modality features;
[0111] Compute the intensity matrix:
[0112] ,in Represents the jth word pair aft...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com