MICRO LED chip transfer method
A chip transfer and chip technology, which is applied in the manufacture of electrical components, electrical solid devices, semiconductor/solid devices, etc., can solve the problems of MICROLED chip transfer difficulties, etc., so as to improve transfer yield, high transfer success rate, and ensure fixity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
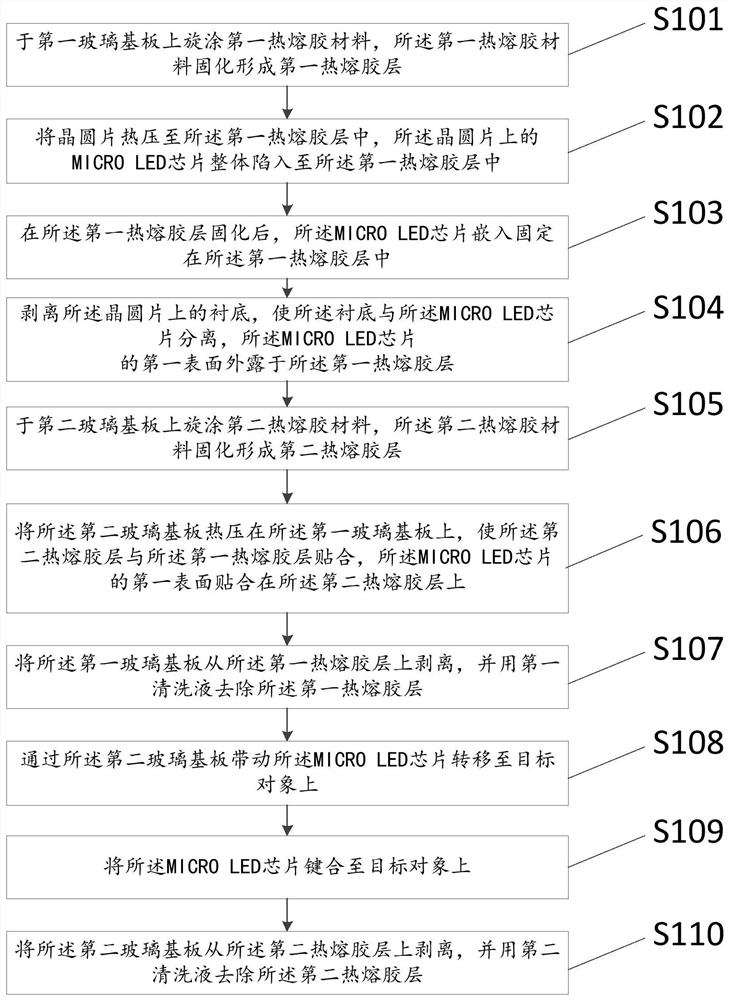
[0043] figure 1 It is a flow chart of the MICRO LED chip transfer method according to the embodiment of the present invention.
[0044] The present invention provides a kind of MICRO LED chip transfer method, comprises the following steps:
[0045] S101: Spin-coat a first hot-melt adhesive material on the first glass substrate 1, and the first hot-melt adhesive material solidifies to form a first hot-melt adhesive layer 2;
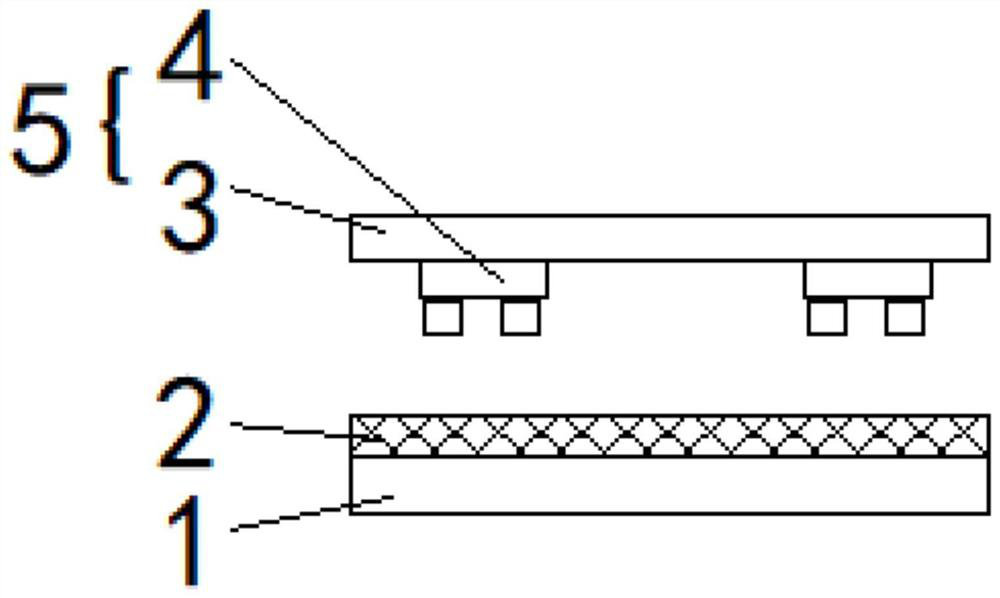
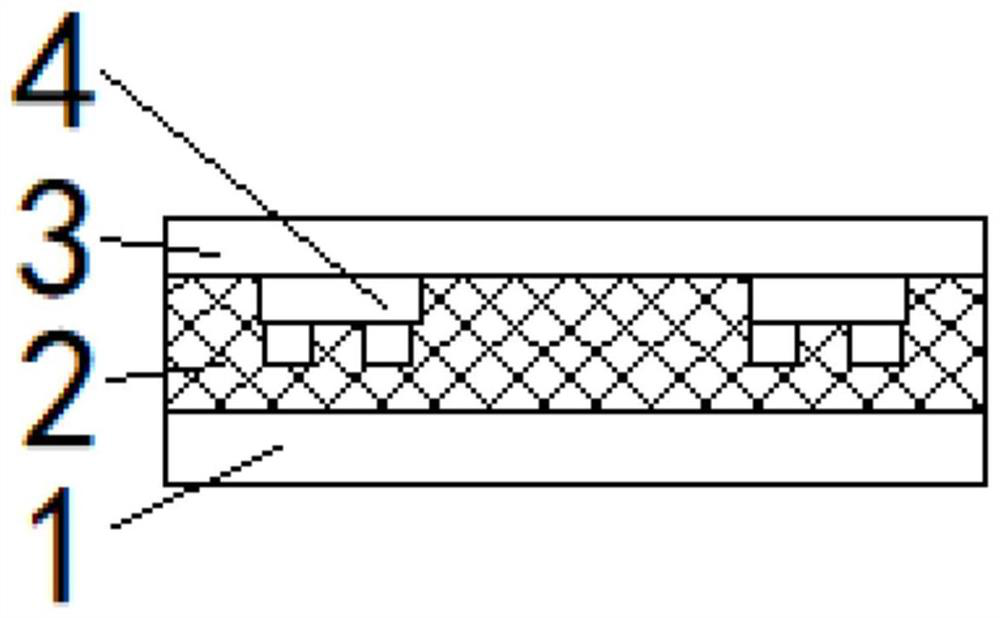
[0046] figure 2 It is a simplified schematic diagram of the principle of step S101 of the MICRO LED chip transfer method according to the embodiment of the present invention. Specifically, the top surface of the first glass substrate 1 is cleaned so that the surface cleanliness of the first glass substrate 1 meets the requirements, and then the surface of the first glass substrate 1 is cleaned. The first hot-melt adhesive material is spin-coated on the top surface of the substrate 1 . After the first hot-melt adhesive material is spin-coated, the desire...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Similar to the implementation of the second transition layer 7, specifically, since the first glass substrate 1 needs to be peeled off from the first hot melt adhesive layer 2 in step S107 of the first embodiment, in order to reduce the first The difficulty of peeling off the glass substrate 1, in the embodiment of the present invention, before the first hot melt adhesive material is spin-coated on the first glass substrate 1, the first transition material is spin-coated on the first glass substrate 1, The first transition material forms a first transition layer, the first hot-melt adhesive material is spin-coated on the first transition layer, and the first transition material is a photosensitive characteristic material;
[0078] Correspondingly, the peeling off the first glass substrate 1 from the first hot melt adhesive layer 2 includes:
[0079] The first transition layer is irradiated by a first light source matched with the first transition material to remove the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com