Electric vehicle driving range simulation method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
A driving range, electric vehicle technology, applied in computer-aided design, registration/indication of vehicle operation, registration/instruction, etc., can solve problems such as large data differences, achieve fast simulation calculation speed, reduce development risks, and reduce testing effect of cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
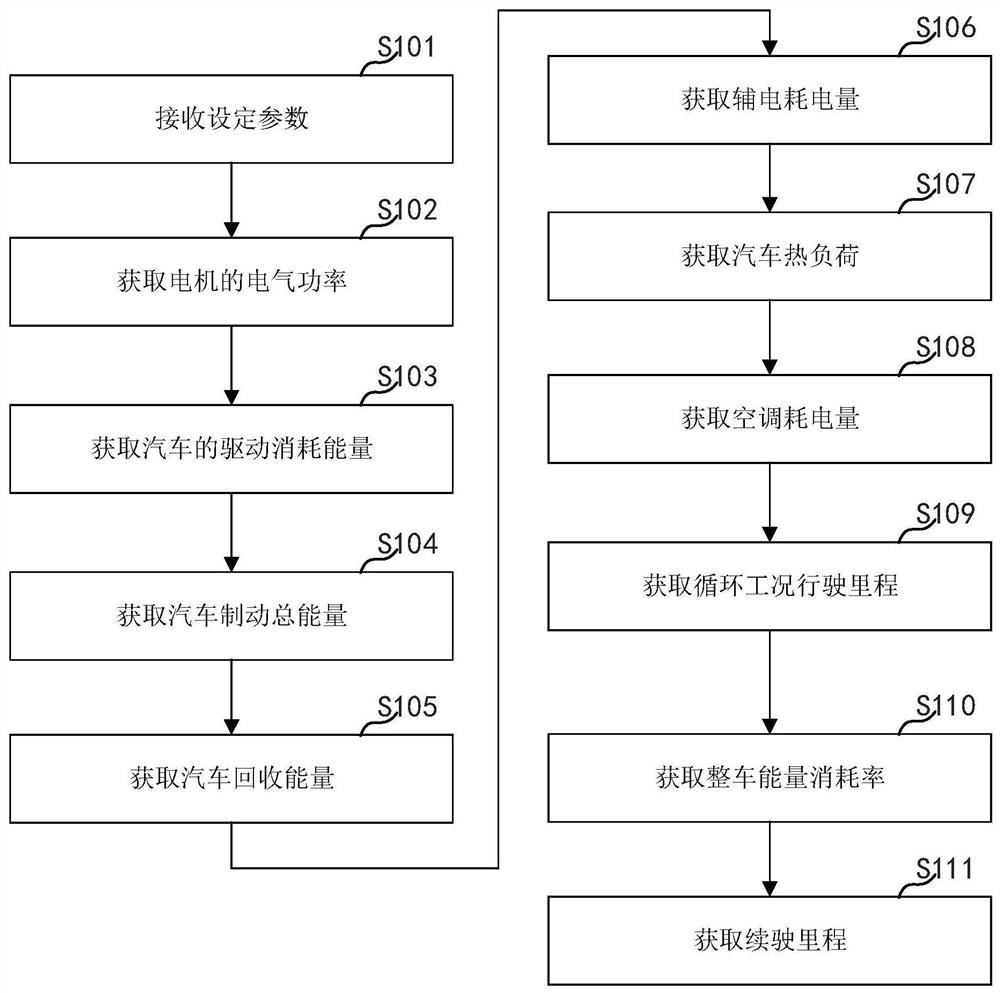
[0031] see figure 1 , figure 1 It is a schematic flowchart of a method for simulating the driving range of an electric vehicle provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. The method can be applied to electronic equipment. In the embodiment of the present invention, the electronic device includes a processor, a communication interface, a memory, and a communication bus, wherein the processor, the communication interface, and the memory complete mutual communication through the communication bus, which is not specifically limited in the present invention. Specifically, see figure 1 , the method includes the following steps S101-S111.
[0032] S101. Receive setting parameters, where the setting parameters include vehicle parameters, energy recovery parameters, motor parameters, air conditioning parameters, and driving condition parameters.
[0033] In a specific embodiment, the mileage simulation software for electric vehicles can receive any vehicle parameters, any en...
Embodiment 2
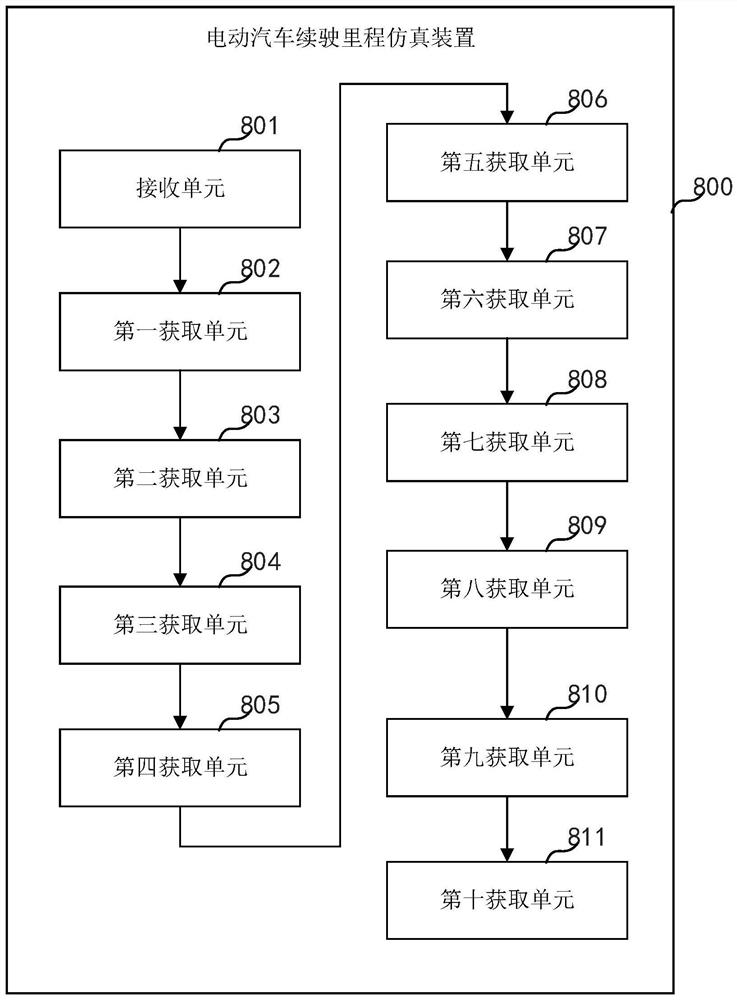
[0070] Such as figure 2 As shown, Embodiment 2 of the present invention also provides an electric vehicle driving range simulation device 800, the electric vehicle driving range simulation device 800 includes a receiving unit 801, a first obtaining unit 802, a second obtaining unit 803, a third An acquisition unit 804 , a fourth acquisition unit 805 , a fifth acquisition unit 806 , a sixth acquisition unit 807 , a seventh acquisition unit 808 , an eighth acquisition unit 809 , a ninth acquisition unit 810 , and a tenth acquisition unit 811 .
[0071] The receiving unit 801 is configured to receive parameters input by the user.
[0072] The first acquisition unit 802 is configured to receive vehicle parameters and driving condition parameters, and output electrical power of the motor.
[0073] The second acquisition unit 803 is configured to receive the electric power of the motor, and output the driving energy consumed by the vehicle.
[0074] The third acquisition unit 804...
Embodiment 3
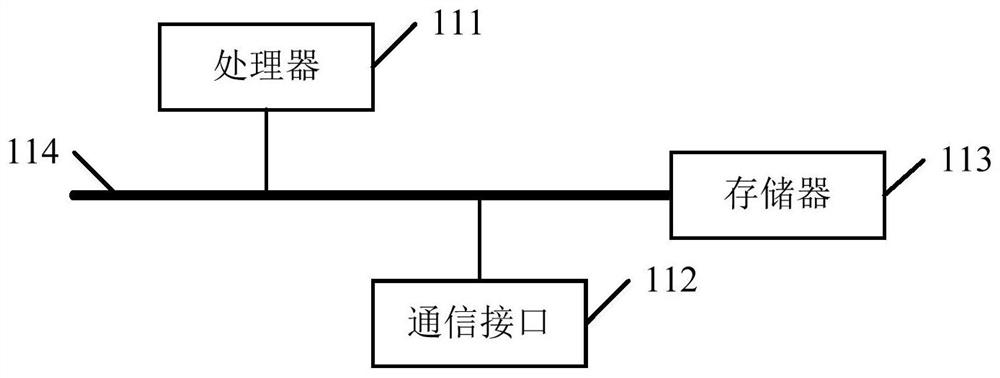
[0103] Such as image 3 As shown, Embodiment 3 of the present invention also provides an electronic device, including a processor 111, a communication interface 112, a memory 113, and a communication bus 114, wherein the processor 111, the communication interface 112, and the memory 113 complete the mutual communication through the communication bus 114. communication between
[0104] Memory 113, used to store computer programs;
[0105] The processor is configured to execute the program stored in the memory to realize the method for simulating the driving range of an electric vehicle provided in Embodiment 1.
[0106] The embodiment of the present invention also provides a computer-readable storage medium, on which a computer program is stored. When the computer program is executed by a processor, the steps of the method for simulating the driving range of an electric vehicle as provided in Embodiment 1 are realized.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com