Cytoplasm incompatibility factor CifA or CifB mutant gene and protein
A technique for mutating proteins and mutating genes, applied in genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, recombinant DNA technology, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0098] Construction of embodiment 1 pET-22b-CidAST
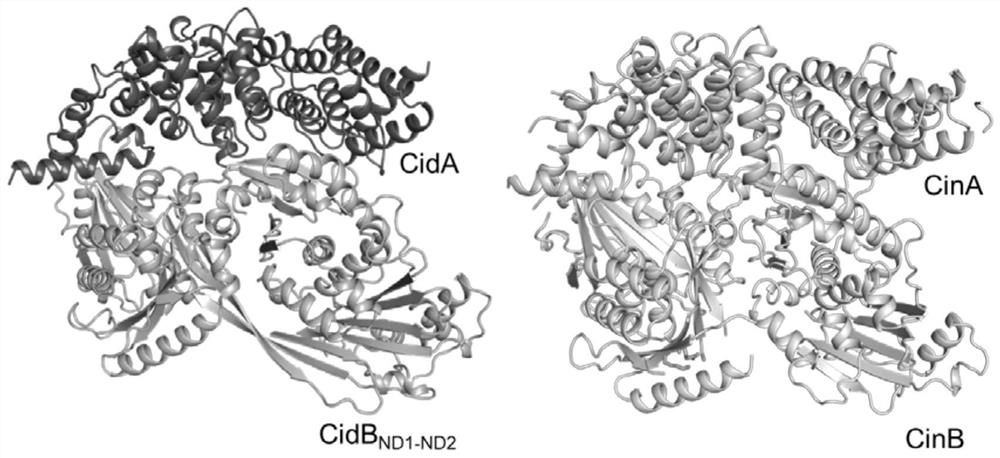
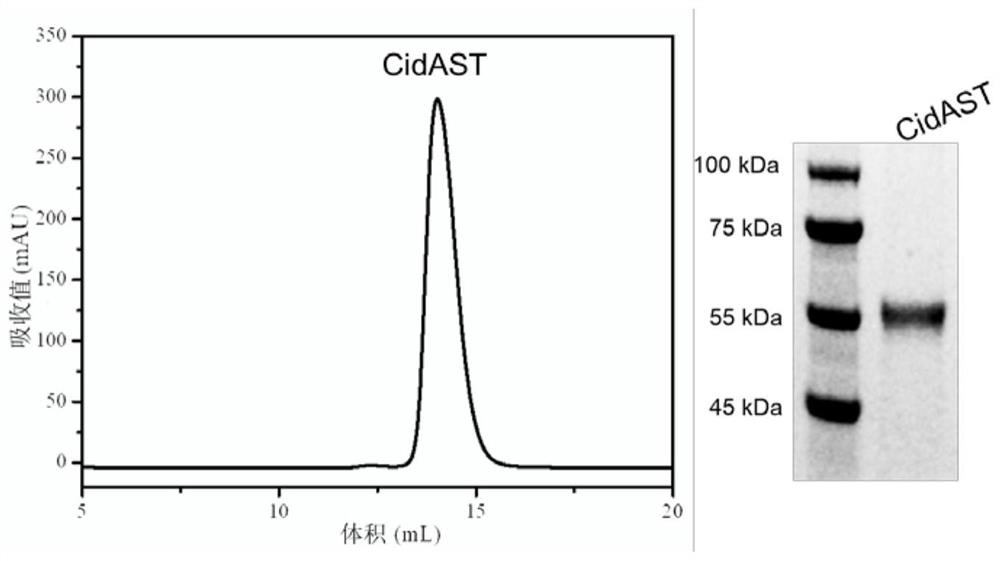
[0099] The wMel CidA nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.9 in Drosophila melanogaster and the wPip CidA nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.10 in Culex pipiens are: Template to wPip CidA-CidB ND1-ND2 (The nucleotide sequence of wPip CidB is shown in SEQ ID NO.11, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.12) and the structure of wMel CidA, wherein the A and B factor interaction interfaces can be divided into three, the The amino acid residues involved in the interaction between CidA and CidB in wPip CidA were replaced on wMel CidA, and the CidAST sequence was designed, as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. Using the above artificially synthesized SEQ ID NO.1 as a template, using F1 as a forward primer, and R1 as a reverse primer, the gene sequence containing CidAST obtained by PCR was digested and ligated with T4 DNA ligase to mutate The protein CidAST gene was constructed on the PET-22b vector to obtain the PET-22b-CidAS...
Embodiment 2
[0112] Example 2 Construction of pRS425-CidAST
[0113] The vector was selected as pRS425, the restriction sites were BamHI and SalI, primers were designed for PCR, and the primers were named F2 and R2 respectively, and the PCR system was shown in Table 3. Using the pET-22b-CidAST constructed in Example 1 above as a template, PCR can obtain the second sequence containing the mutant protein CidAST gene whose restriction sites are BamHI and SalI.
[0114] The PCR product and the vector pRS425 were double-digested with restriction endonucleases BamHI and SalI, respectively, so that sticky ends appeared on the target gene fragment and the vector. The specific enzyme digestion system is shown in Table 4.
[0115] The target gene fragment with cohesive ends and the vector pRS425 were ligated using T4 DNA ligase, and the ligation system was shown in Table 5 above.
[0116] After conversion and double enzyme digestion verification, the positive results obtained were verified by seque...
Embodiment 3
[0117] Construction of embodiment 3 pRS416-CidBST
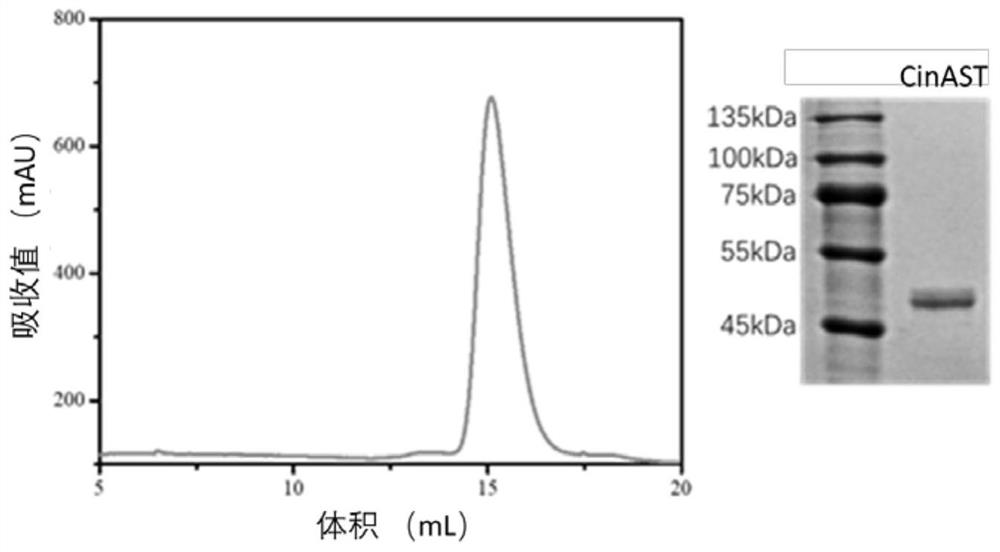
[0118] The wMel CidB nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.17 in Drosophila melanogaster and the wPip CidB nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.11 from Culex pipiens are: Template to wPip CidA-CidB ND1-ND2Based on the structure of wPip CidB, the amino acid residues involved in the interaction between CidA and CidB in wPip CidB were replaced on wMel CidB, and the CidBST sequence was designed, as shown in SEQ ID NO.3. Using the above-mentioned artificially synthesized SEQ ID NO.3 as a template, F3 as a forward primer, and R3 as a reverse primer, the gene sequence containing CidBST obtained by PCR was digested and ligated with T4 DNA ligase to mutate The protein CidBST gene was constructed on the PET-22b vector to obtain the PET-22b-CidBST plasmid; the PET-22b-CidBST plasmid was used as a template, F4 was used as a forward primer, and R4 was used as a reverse primer to perform PCR to obtain the second The sequence containin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com