A method for comprehensive recovery of valuable metals in waste lithium-ion battery black powder
A lithium-ion battery and valuable metal technology, which is applied in the field of comprehensive recovery of valuable metals in waste lithium-ion battery black powder, can solve the problems of ineffective recovery of lithium elements, long recovery time of wet technology, and large consumption of chemical reagents. Achieve the effects of less loss, efficient recovery and high recovery efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
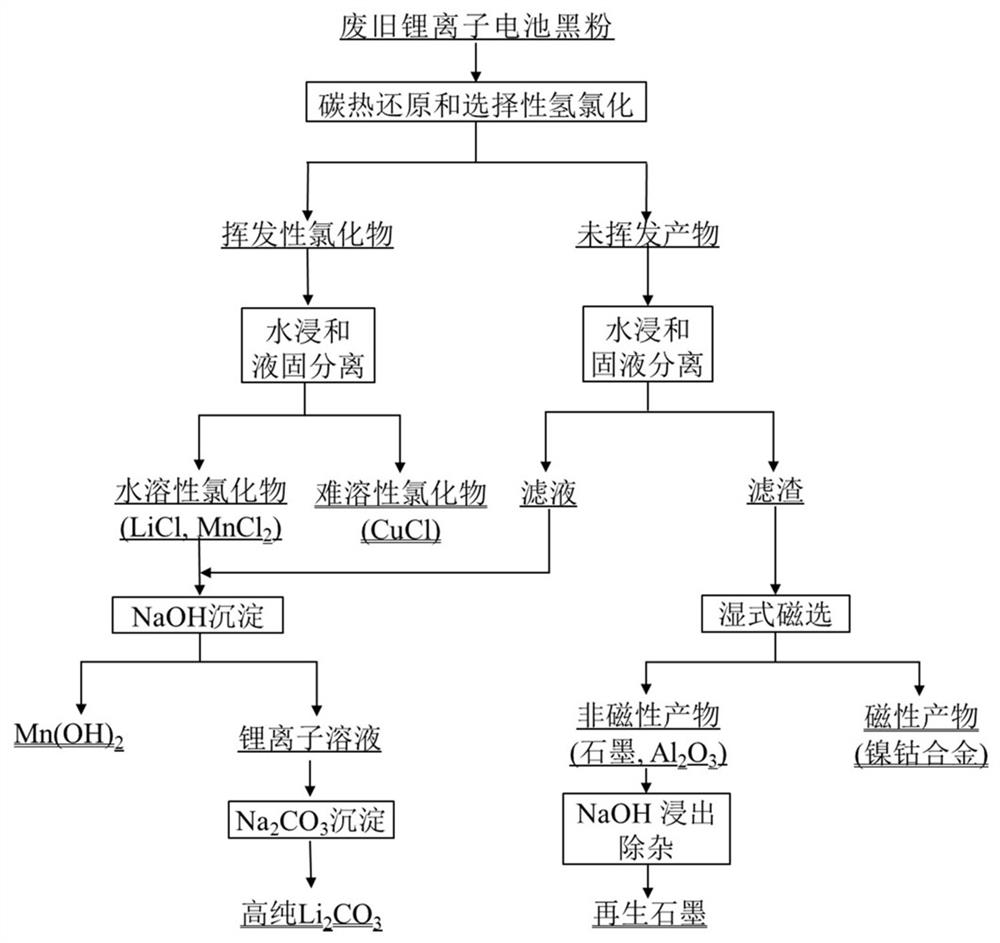
[0050] A method for comprehensively recovering valuable metals from waste lithium-ion battery black powder, the process flow diagram of which is as follows: figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0051] (1) Spread 5g of waste lithium-ion battery positive and negative mixed black powder in an alumina crucible, the thickness of the material layer is 9mm, put the alumina crucible into a reduction furnace, and carry out carbothermic reduction in an argon protective atmosphere. The temperature is 1000°C, and the reduction time is 30min; then hydrogen chloride gas is introduced into the reduction furnace to carry out selective hydrochlorination reaction, the hydrogen chloride gas flow rate is 50mL / min, the hydrogen chloride gas partial pressure is 50vol%, and the hydrochlorination reaction temperature is 1000 ℃, the reaction time is 30min, and CuCl, LiCl, MnCl are obtained 2 Such as volatile chloride fumes and solid products containing nickel-cobalt alloys, alumina, resi...
Embodiment 2
[0060] A method for comprehensively recovering valuable metals from waste lithium-ion battery black powder, the process flow diagram of which is as follows: figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
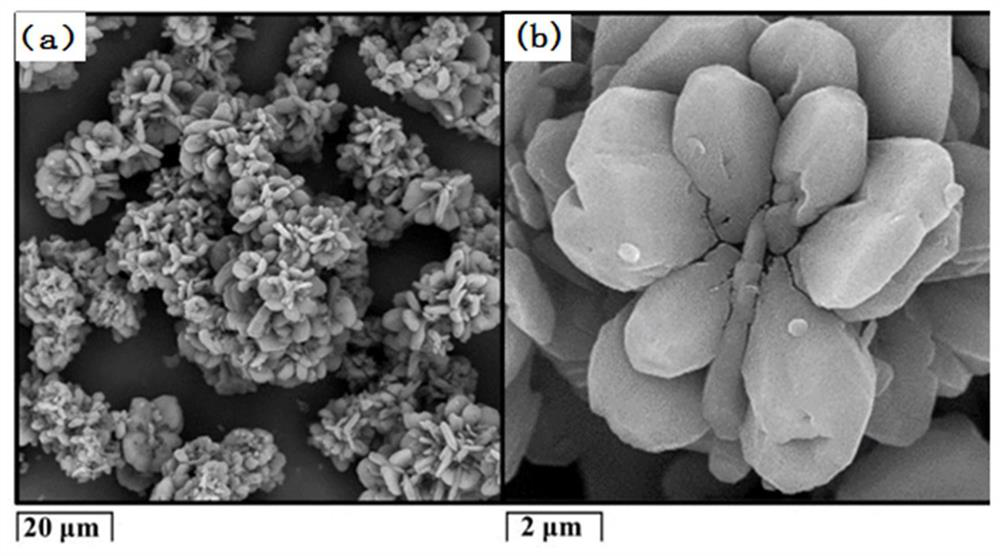
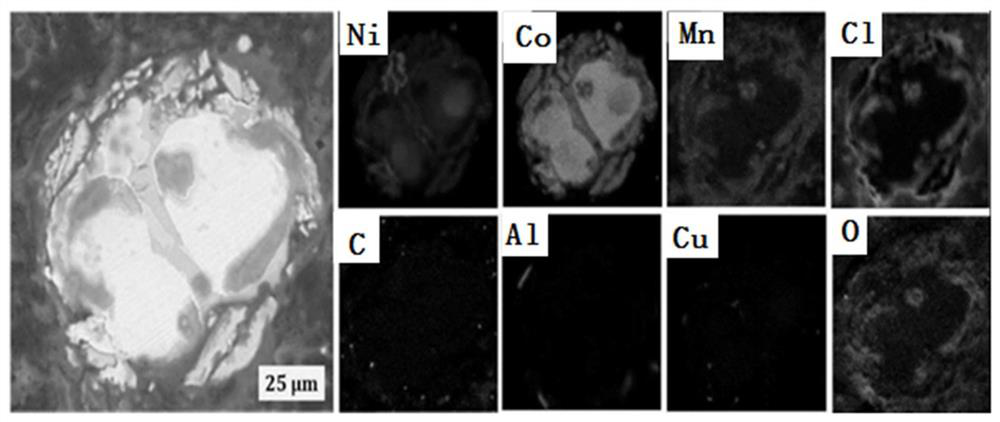
[0061] (1) Put 5g of waste lithium-ion battery positive and negative mixed black powder in an alumina crucible, the thickness of the material layer is 9mm, put the alumina crucible into a reduction furnace, and carry out carbothermic reduction in an argon protective atmosphere, The reduction temperature is 1000°C, and the reduction time is 30min; then hydrogen chloride gas is introduced into the furnace to carry out selective hydrochlorination reaction, the hydrogen chloride gas flow rate is 50mL / min, the hydrogen chloride gas partial pressure is 50vol%, the reaction temperature is 1000°C, and the reaction The time is 120min, and the volatile chloride fumes and solid products are obtained. The SEM micrographs and element distribution diagrams of the solid products are as foll...
Embodiment 3
[0070] A method for comprehensively recovering valuable metals from waste lithium-ion battery black powder, the process flow diagram of which is as follows: figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0071] (1) Put 5g of waste lithium-ion battery positive and negative mixed black powder in an alumina crucible, lay the material layer with a thickness of 9mm, put the alumina crucible into a reduction furnace, and carry out carbothermic reduction in an argon protective atmosphere, The reduction temperature is 1100°C, and the reduction time is 60min; then hydrogen chloride gas is introduced into the furnace to carry out selective hydrochlorination reaction, the hydrogen chloride gas flow rate is 50mL / min, the hydrogen chloride gas partial pressure is 50vol%, the reaction temperature is 1100°C, and the reaction The time was 30 min, and volatile chloride fumes and solid products were obtained.
[0072] (2) The volatile chloride dust collected in step (1) is subjected to wate...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com