Carrier
A carrier and precursor technology, applied in the direction of carriers, nucleic acid carriers, and the use of carriers to introduce foreign genetic material, can solve problems such as expensive
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
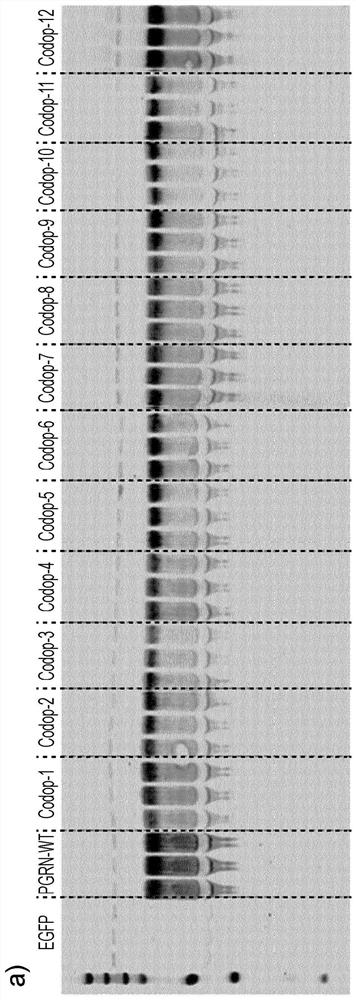
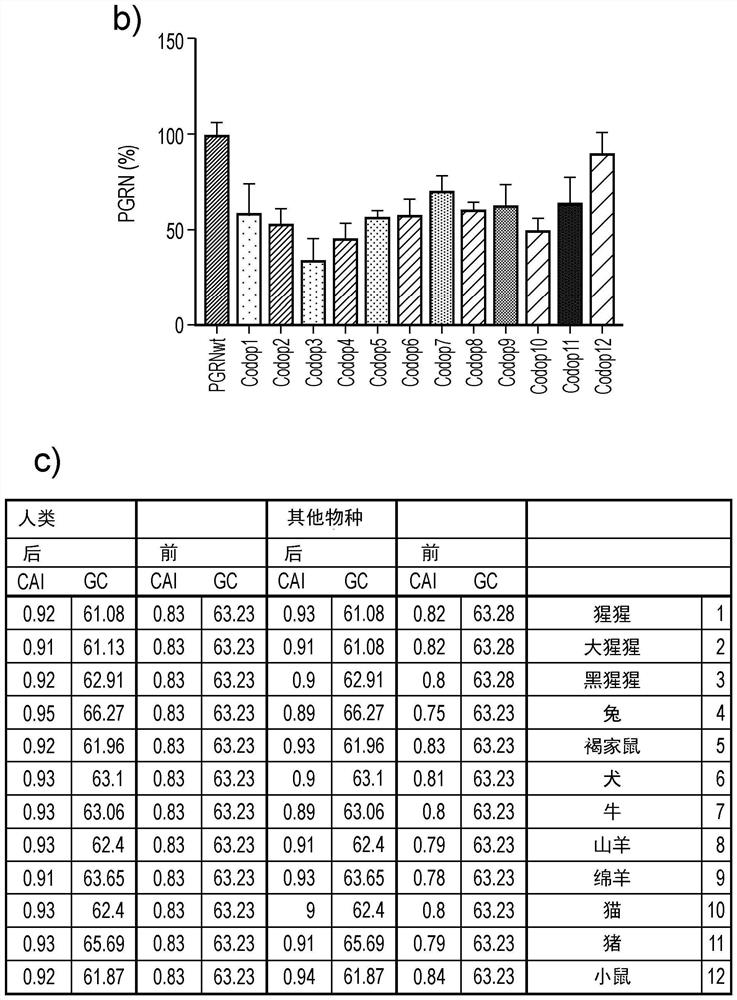
[0154] Example 1: Improve the efficiency of PGRN translation by codon optimization algorithm
[0155] The rate of protein translation from RNA transcripts can be increased by changing codons to use codons that are optimal for a particular species, and gene expression in a particular cell type can be increased. By optimizing protein production per transcript, fewer viral vectors are used, reducing toxicity risk and cost. Optimization of wild-type PGRN transcripts was modeled using three open source programs (IDT, Geneart and Genscript: see Materials and methods for details). The codon adaptation index (CAI; https: / / www.genscript.com / tools / rare-codon-analysis) was validated using the rare codon analysis tool. A CAI of 1.0 was considered ideal, while a CAI >0.8 was rated as good expression in the target expressing organism. The lower the number, the higher the likelihood of poor gene expression.
[0156] 1.1 Codon optimization design
[0157] Using a commercially available co...
Embodiment 2
[0192] Example 2: Development of intron enhancing elements to increase PGRN expression.
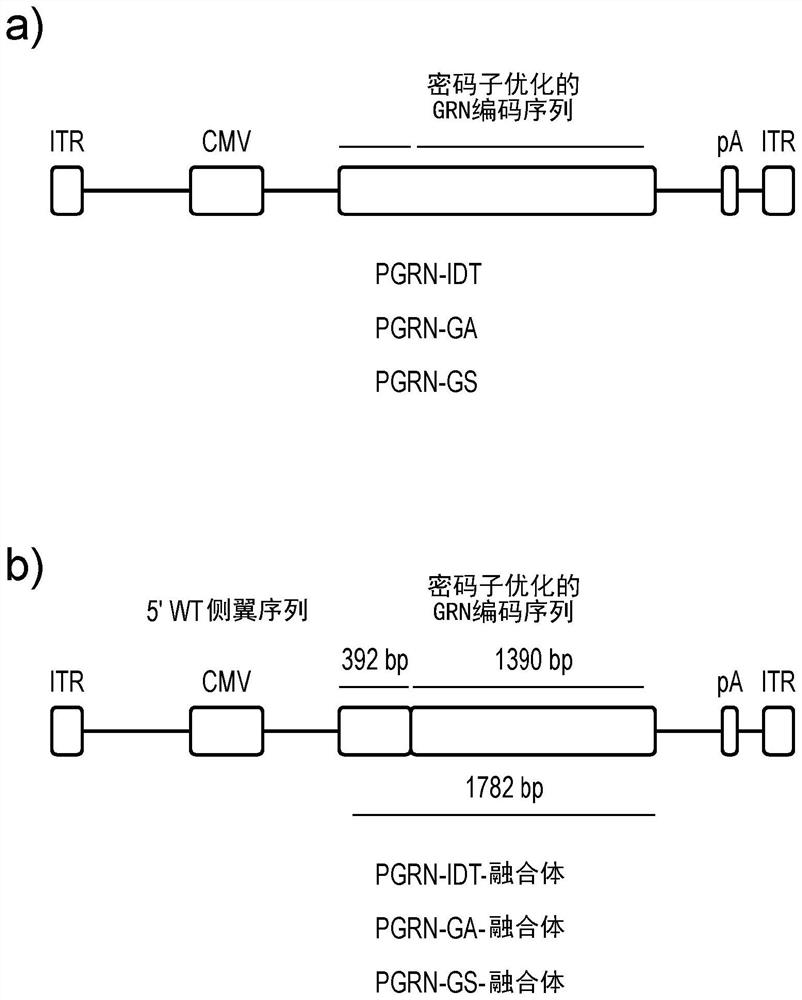
[0193] To further increase the expression and secretion of PGRN, the addition of an intron in the 5′ sequence of PGRN was explored to see if gene expression could be enhanced. Introns can increase transcription levels by affecting transcription rate, nuclear export, transcript stability, or mRNA translation efficiency, a phenomenon known as intron-mediated enhancement (IME) ( Shaul O. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2017 Oct;91(Pt B):145-155). A search was performed for intron sequences smaller than 300 bp that could be used to test for intron-mediated enhancement. Introns within the human growth hormone (hGH) gene were selected as suitable candidates (see Figure 5 a).
[0194] The wild-type GRN sequence was genetically synthesized and cloned into pAAV plasmid (Addgene; 99280) using BamH1 and Xho1 restriction sites. These constructs were used as a master vector (pAAV-CMV-PGRNwt) to sub-clon...
Embodiment 3
[0216] Example 3: Combining intronic and exonic enhancer elements.
[0217] To test the intron-mediated enhancement of codon-optimized PGRN-GS by hGHi3, the hGHi3 element was subcloned into the 5' position of PGRN-GS.
[0218] Surprisingly, hGHi3 did not enhance PGRN-GS expression (see Figure 8 a and 8b), because inclusion of intron 3 slightly lowers PGRN. This suggests that the action of hGHi3 may require an exonic splicing element (ESE) within the wild-type PGRN sequence to exert a cooperative effect on splicing. Use the software ESE finder 3.0 to search for ESE elements in wild-type PGRN and codon-optimized PGRN-GS sequences (see Figure 8 c). The ESE distribution pattern was significantly altered in codon-optimized PGRN-GS compared with wild-type PGRN. Thus, attempts to codon-optimize PGRN by including hGHi3 inadvertently removed the ESE required to provide enhancement.
[0219] Therefore, the intronic enhancer hGHi3 was combined with a PGRN fusion construct carrying...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com