Dual-aptamer functional nucleic acid constant-temperature micro-fluidic chip sensor for microbiological detection
A technology of microfluidic chips and biosensors, which is applied in the fields of biomaterial analysis, laboratory containers, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of inability to detect on-site, take a long time, and have high dependence on antibody genomes, and achieve efficient on-site detection and improve The effect of capture ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0089] Example 1 Composition, Installation Instructions and Uses of Each Part of Microfluidic Chip Biosensor
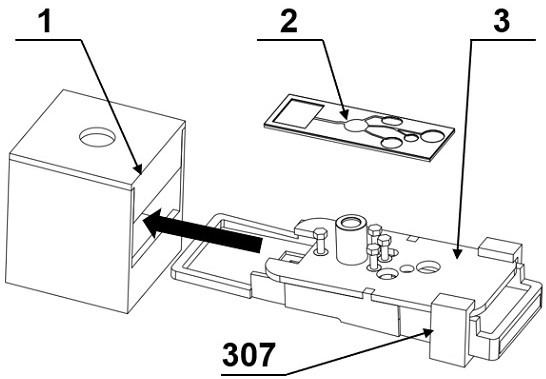
[0090] Microfluidic chip sensors consist of figure 1 As shown, it includes an observation dark box 1 for observing fluorescence, a microfluidic chip 2 for detecting Bacillus cereus, and a capillary microvalve control device 3 for controlling liquid flow in the microfluidic chip. Insert the microfluidic chip capillary microvalve control device 3 with the microfluidic chip 2 installed into the fluorescence collection dark box 1 .
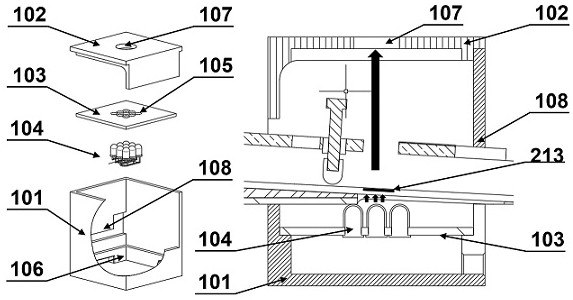
[0091] Obscura 1 for observing fluorescence figure 2 As shown, it is composed of a box body 101, a dark box top cover 102, a lamp bead partition 103 and a lamp bead 104. The lamp beads 104 are installed in the 9×9 array holes 105 reserved on the lamp bead partition 103 , and welded to form the lamp bead array 104 that produces sufficient fluorescence intensity. Install the lamp bead partition 103 with the lamp bead array 104 installed int...
Embodiment 2
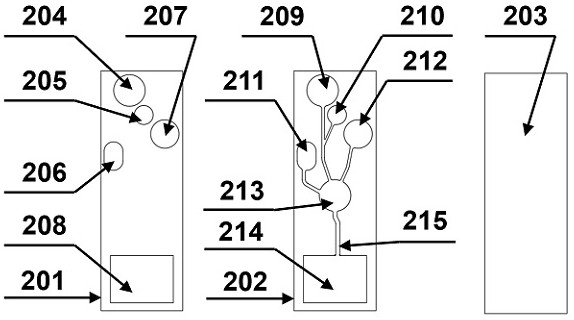
[0095] Example 2 Screening of recognition elements in microfluidic chip biosensors
[0096] The nucleic acid aptamer of Bacillus cereus was obtained by whole-cell screening technology, and then the specific recognition of Bacillus cereus in this application was realized. The nucleic acid sequences used in the experiment are shown in Table 1. The specific whole-cell screening process is as follows: (a) Take 1nmol of the synthetic random library, denature at 95°C for 5 minutes, place it on ice immediately, and let it stand for 5 minutes. Add 600 μL of bacterial suspension, and excess tRNA and BSA to the processed library. Incubate with shaking at 35°C and 120rpm for 90min. (b) After incubation at 8000rpm, centrifuge at 4°C for 5 minutes, the ssDNA combined with the target bacteria will be sedimented along with the bacteria, while the ssDNA not combined with the target bacteria will be in the supernatant, discard the supernatant as much as possible, and use Wash the pellet twic...
Embodiment 3
[0102] Example 3 Tailoring optimization of recognition elements in microfluidic chip biosensors
[0103] On the basis of the results in Example 2, carry out tailoring optimization, use IDT to predict the secondary structure of the preferred aptamer, select the predicted result with the lowest minimum free energy for subsequent cutting operations, and reserve 2-3 nt on both sides of the hairpin structure At the end, the trimmed aptamers are called trimmed aptamers. Then perform secondary trimming on the tailoring aptamer. The purpose of the secondary trimming is to disassemble and subdivide the complete stem-loop structure in the trimming aptamer, so as to accurately locate the core sequence of the aptamer involved in the interaction, and Aptamers that are trimmed twice are called secondary trimmed aptamers. Use the IDT website to predict the secondary structure of the tailoring aptamer and the secondary tailoring aptamer, and select a sequence with a suitable cutting length a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com