Application of ZmHIR3 protein or coding gene thereof in regulation and control of maize rough dwarf virus resistance
A technology that encodes genes and rough dwarf disease, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as environmental pollution, labor and time-consuming, poor control effect, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the ability to resist rough dwarf disease
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 ZmHIR3 Gene Overexpression Vector and Editing Vector Construction and Transformation
[0035] The vector used for overexpression in the present invention is pCUB-eGFP-3×FLAG, which is based on the pCUB vector (Song Pan, 2015, construction and genetic transformation of corn ZmPOT gene TALEN knockout and overexpression vector) using BamHI restriction enzyme point, the GFP protein and 3×FLAG tag were inserted between the promoter and terminator on the pCUB vector to construct.
[0036] Insert the ZmHIR3 gene (the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2, which can encode the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1) into the promoter and GFP tag protein on the pCUB-eGFP-3×FLAG vector between. Carry out transformation, pick a single spot, sequence, and use the heat shock method to transform the overexpression vector plasmid pCUB-ZmHIR3-eGFP-3×FLAG into Agrobacterium EHA105 competent cells, pick a single colony of recombinant Agrobacterium, and extract the plasmid...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2 Molecular detection of ZmHIR3 gene overexpression T2 generation strain
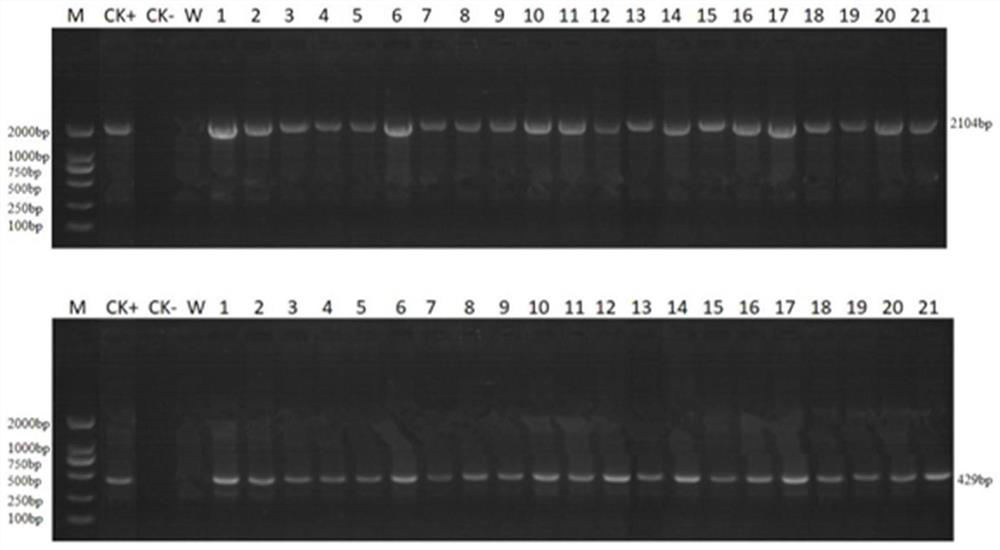
[0041]From the transgenic lines of the T1 generation, the plants that were positive in both PCR and test strip detection were selected for strict selfing, and the grains were harvested, and the T2 generation lines were obtained by planting in ear rows in the second year. Using the total leaf DNA of the T2 generation transgenic plants, design specific primers (SEQ ID NO.6-7) according to the sequence of the promoter plus the target gene plus the terminator, using the recipient control maize leaf DNA as a negative control, and the plasmid DNA as a positive control, Two rounds of PCR testing were performed. The result is as figure 2 Shown: There are 21 positive transgenic plants and the plasmids can amplify the 2104bp gene fragment and the 429bp Bar gene fragment, and no amplified bands are seen in the negative control and water control.
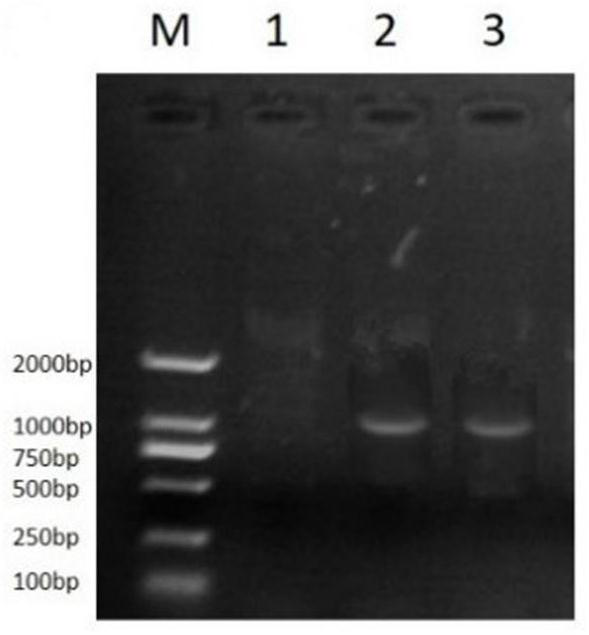
[0042] The leaves of different T2 generation tran...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3 Molecular detection of ZmHIR3 gene edited T2 generation strains
[0044] The total DNA of the two-leaf stage leaves of the gene-edited transgenic plants of the T2 generation obtained by the CTAB method was extracted. Design specific primers (SEQ ID NO.8-9) according to the edited target site, strictly self-cross the gene-edited plants of the T1 generation to harvest the ears, and plant all the ear rows in the second year to obtain the T2 generation plants, design according to the sequence of the target site Specific primers, with wild-type maize leaf DNA as a negative control and plasmid DNA as a positive control, two rounds of PCR detection were performed. Test results such as Figure 4 Shown: Both the positive transgenic plants and the plasmids can amplify a total of 618bp fragments including 3 targets, and carry out sequencing identification. There are 6 types of stable genetic homogeneity and variation.
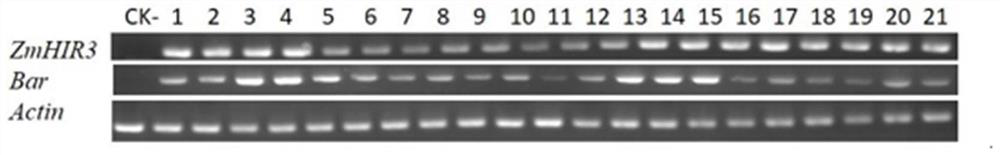
[0045] The leaves of the T2 transgenic line seedl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com