Application of ZmNuC gene and encoded protein thereof in resistance to maize rough dwarf disease
A protein-encoded, transgenic corn technology, applied in the application field of ZmNuC gene and its encoded protein in the resistance to corn rough dwarf disease, can solve the problem that corn germplasm resources cannot meet the needs of corn production, and achieve the effect supported by reliable data
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1ZmNuC gene analysis
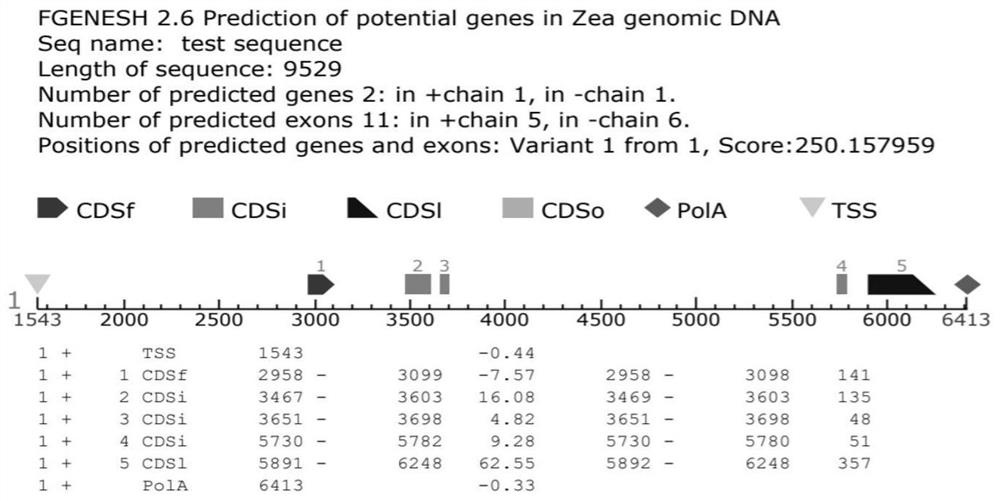
[0038] In this example, the full-length cDNA sequence of the corn ZmNuC gene was cloned, and the full-length sequence of the gene was obtained by sequencing technology, as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and based on this analysis, the ORF Finder software was used for comparative analysis. The gene structure of the ZmNuC gene was determined, and it was found through gene structure analysis that the gene contained four introns and five exons ( figure 1 ).
Embodiment 2
[0039] The subcellular localization of embodiment 2ZmNuC gene
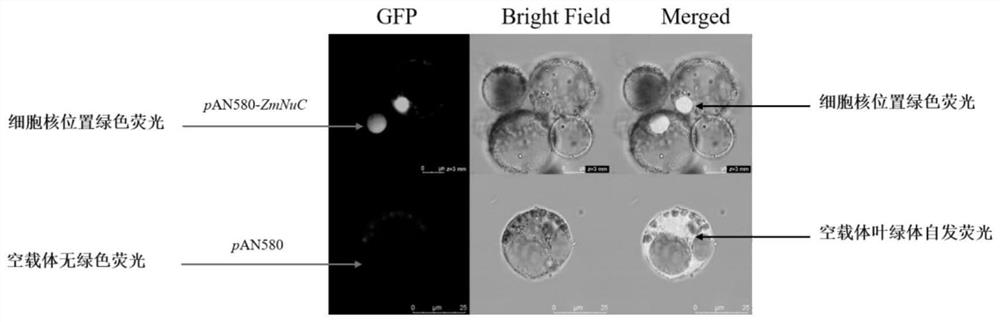
[0040] Digest the pAN580 empty vector with BamHI, recover the pAN580 vector fragment by gel, and then perform homologous recombination to connect the target gene ZmNuC (as shown in SEQ ID NO.1) to the vector to obtain pAN580-ZmNuC, transform and pick a single spot , sequencing; by transfecting maize protoplasts to clarify its subcellular location, laser confocal microscopy to observe the fluorescent signal, the green fluorescent signal of the control sample transformed with empty vector existed in the maize protoplast, while the green fluorescent signal of the ZmNuC fusion protein The signal appears in the nucleus region of the protoplast, indicating that the ZmNuC gene is localized on the nucleus ( figure 2 ).
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3 ZmNuC Gene Overexpression Vector and Editing Vector Construction and Transformation
[0042] The vector used for overexpression is pCUB-eGFP-3×FLAG, which is used on the basis of pCUB vector (Song Pan, 2015, Maize ZmPOT gene TALEN knockout and overexpression vector construction and genetic transformation, page 18, paragraph 3) The BamHI restriction site is constructed by inserting GFP protein and 3×FLAG tag between the promoter and terminator on the pCUB vector.
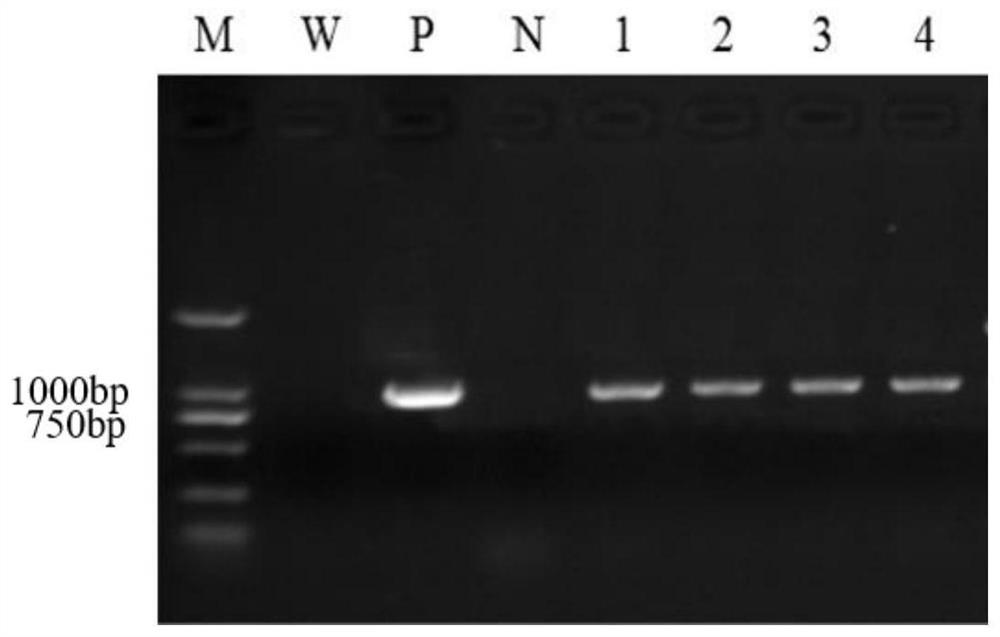
[0043]The ZmNuC gene (as shown in SEQ ID NO.1) was inserted between the promoter and the GFP tag protein on the pCUB-eGFP-3×FLAG vector. Carry out transformation, pick a single spot, sequence, and use the heat shock method to transform the overexpression vector plasmid pCUB-ZmNuC-eGFP-3×FLAG into Agrobacterium EHA105 competent cells, pick a single colony of recombinant Agrobacterium, and extract the plasmid DNA for PCR Identification. Escherichia coli positive plasmid was used as positive control. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com