Model predictive pulse mode control based on small signal pulse mode optimization
A pulse mode, small signal technology, applied in control systems, generator control, adaptive control, etc., can solve problems such as slow step response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
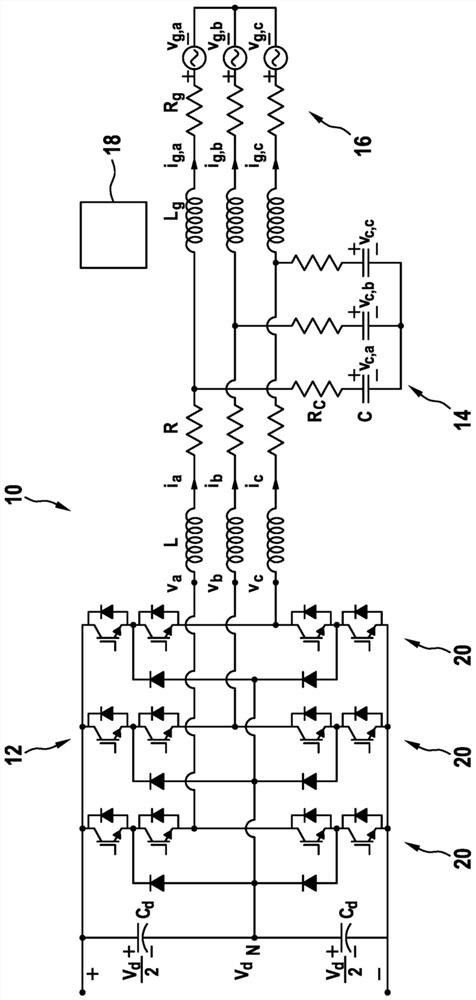
[0061] figure 1 A converter system 10 is shown that includes an electrical converter 12 and an LC filter 14 coupled to an electrical grid 16 . figure 1 The other corresponding quantities indicated are listed at the end of the description. figure 1 Also shown is a controller 18 adapted to carry out the method for controlling the converter system 10 as described herein.
[0062] The LC filter 14 may include a filter inductor L and a filter resistor R connected between the converter 12 and the grid 16 and a filter resistor R connected to the interconnection of the converter 12 and the grid 16 C and filter capacitor C.
[0063] As shown, the electrical converter 12 may be a midpoint clamped converter having a midpoint clamped phase leg 20 for each output phase. Other converters 12 such as T-converters, modular multilevel converters and / or converters with flying capacitors may be used as multilevel converters 12 . Also, a two-level converter can be used.
[0064] figure 2 is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com