Preparation method for preparing microcosmic porous structure material through freeze curing 3D printing
A porous structure, 3D printing technology, applied in the field of 3D printing, can solve the problems of limited pore size and porosity accuracy, and achieve the effect of improving the mechanical properties of materials, the variety of raw materials, and the range of solid phase content.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
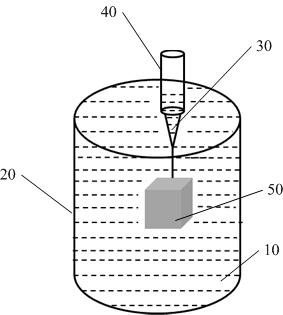
[0032] The present invention provides a preparation method for preparing microscopic porous structure materials by freezing and solidifying 3D printing. figure 1 Schematic diagram of the 3D printing scene when preparing microscopic porous structure materials, such as figure 1 As shown, the preparation method includes: preparing a supporting material 10, placing the prepared supporting material 10 in a mold 20; preparing a target material into a target slurry 30 for extrusion printing; 20 is placed on the printing platform, and the target slurry is put into the barrel 40 of the printing device; according to the target design model, the target slurry 30 is extruded in the supporting material 10 through the nozzle of the printing device to obtain printing a model 50; freezing and solidifying the printing model 50 to obtain a target model; and post-processing the target model to obtain a microscopic porous structure material.
[0033] The main components of the support material a...
Embodiment 1
[0051] In this example, carbomer 940, hydroxyapatite (with a particle size of 0.2 μm), deionized water, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, and Darvan CN were selected as raw materials, and sodium hydroxide solution (10 M). The volume fraction of hydroxyapatite was 40%, and the mass concentration of carbomer 940 was 1% w / v. 1) Preparation of support material Weigh 1 g of carbomer 940 powder, 100 mL of deionized water, and 0.1 mL of 10M sodium hydroxide. Add carbomer 940 powder to deionized water, stir well, and then gradually add 0.1 mL of 10M sodium hydroxide solution dropwise. After the carbomer gel is obtained, it is put into a centrifuge for defoaming, taken out and put into a plastic mold. 2) Preparation of target slurry Weigh 67 g of hydroxyapatite, 100 g of deionized water, and 0.2 g of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose. Add 0.2 g of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose to deionized water at 70°C, stir well, and then cool to room temperature. 1 g of Darvan CN and 67 g of hydroxyapat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com