Nucleic acid aptamer for detecting microglial cells and application of nucleic acid aptamer
A microglia and nucleic acid aptamer technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problem of not binding to microglia, and achieve the effects of no cytotoxicity, small molecular weight, and no immunogenicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
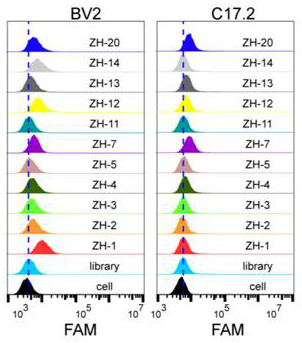
[0039] Example 1 Screening the nucleic acid aptamers by cell-SELEX technology.
[0040] (1) Design of nucleic acid library and primers used:
[0041] Random single-stranded DNA library:
[0042] 5'-ACCGACCGTGCTGGACTCA(N)42ACTATGAGCGAGCCTGGCG -3' (N represents four arbitrary bases of A, T, G, and C)
[0043] Upstream primer: 5'-Fluorescein isothiocyanate-ACCGACCGTGCTGGACTCA-3'
[0044] Downstream primer: 5'-Biotin-CGCCAGGCTCGCTCATAGT-3'
[0045] (2) Screening process:
[0046] In the present invention, mouse microglia BV2 is used as a positive screening target, and mouse neural stem cell C17.2 is used as a negative screening target.
[0047] 2.1 Positive screening:
[0048] a. Incubation: Dissolve the above random DNA library with binding buffer, denature at 95°C for 5 minutes, renature on ice for 10 minutes, and then mix with the pretreated mouse microglia BV2 cells that have been cultured for more than 24 hours and have a confluency of about 90%. Incubate for 1 h at 4°C...
Embodiment 2
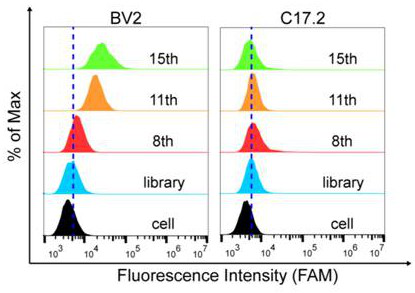
[0055] Example 2 Binding of nucleic acid aptamer ZH-1 obtained by flow detection to mouse microglia BV2 and mouse neural stem cells C17.2
[0056] First, mouse microglia BV2 and mouse neural stem cells C17.2 were cultured for 24 hours to make the cell density reach 90%, and then the adherent cells were digested from the culture dish with 0.2% EDTA. 250 nM of synthesized FAM-labeled ZH-1c was prepared with 200 μl binding buffer, denatured at 95°C for 5 min, and renatured on ice for 10 min. Incubate with 300,000 BV2 cells or C17.2 cells for 1 h at 4°C. The incubated cells were washed 2-3 times with wash buffer and then resuspended in 300 μl of wash buffer. Fluorescence detection was performed by flow cytometry, and the DNA initial random library served as a control. The nucleic acid aptamer only binds the target cell BV2, not C17.2, the results are as follows figure 2 shown.
Embodiment 3
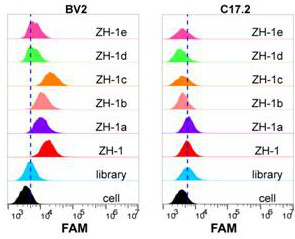
[0057] Example 3 The binding of the nucleic acid aptamer ZH-1 to mouse microglia BV2 after a series of deletions was detected by flow cytometry.
[0058] First, according to the secondary structure of ZH-1, the following sequence deletion optimization was performed on ZH-1:
[0059] The full-length sequence of ZH-1 is: ACCGACCGTGCTGGACTCATATGGTTAGTGTCAAAGAAATAGAAAGATTTACCGAGTTTTGACTATGAGCGAGCCTGGCG
[0060] ZH-1a: 4 bases are deleted in the 5'-end primer region, and 2 bases are deleted in the 3'-end primer region
[0061] ACCGTGCTGGACTCATATGGTTAGTGTCAAAGAAATAGAAAGATTTACCGAGTTTTGACTATGAGCGAGCCTGG
[0062] ZH-1b: 9 bases were deleted from the 5' primer region, and 7 bases were deleted from the 3' primer region
[0063] GCTGGACTCATATGGTTAGTGTCAAAGAAATAGAAAGATTTACCGAGTTTTGACTATGAGCGAG
[0064] ZH-1c: 16 bases are deleted at the 5' end, 12 bases are deleted at the 3' end, and the intermediate stem-loop structure is retained
[0065] TCATATGGTTAGTGTCAAAGAAATAGAAAGATTTACCGAGTTTTG...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com