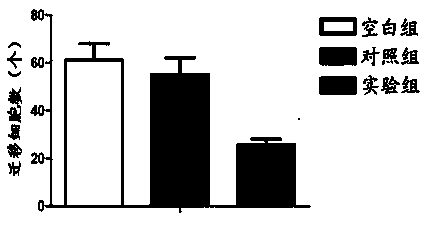Patents
Literature
237 results about "Microglial cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microglial cell. A small glial cell of the central nervous system and retina. Microglia have spiky branched processes and are arranged homogeneously throughout the brain and spinal cord. They are activated by disease and injury, after which they become phagocytic and sometimes resume their embryonic motility like a macrophage.
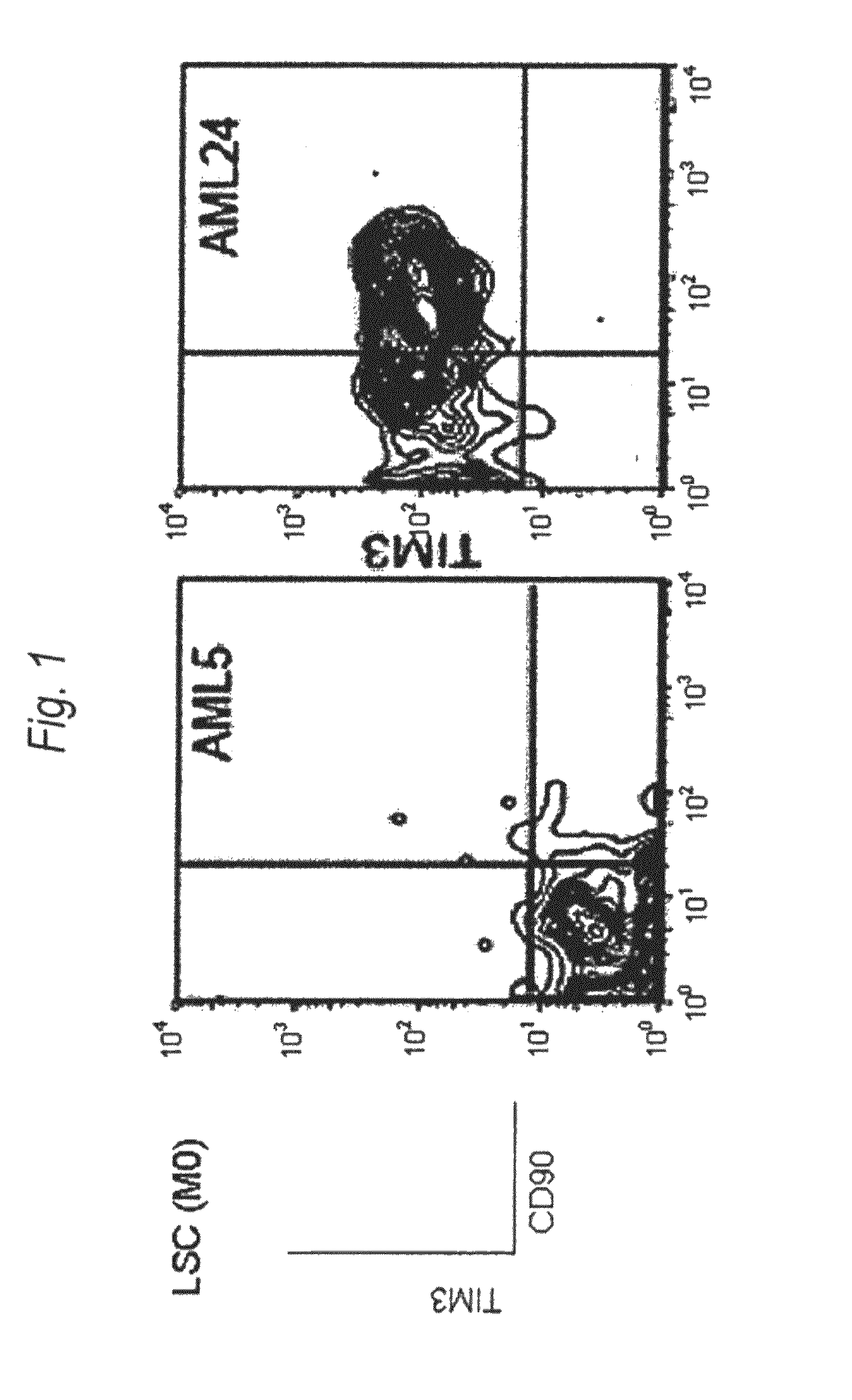
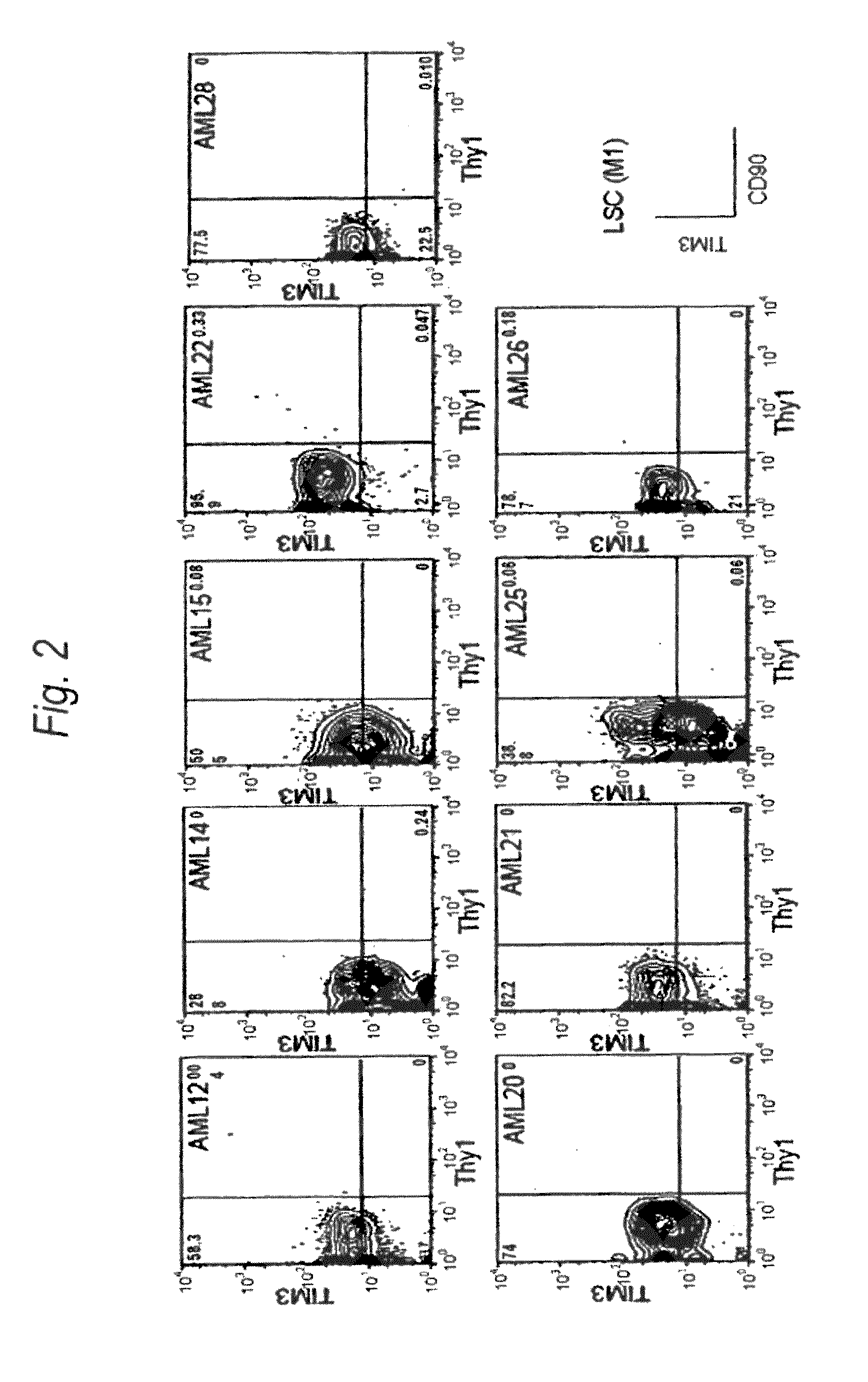
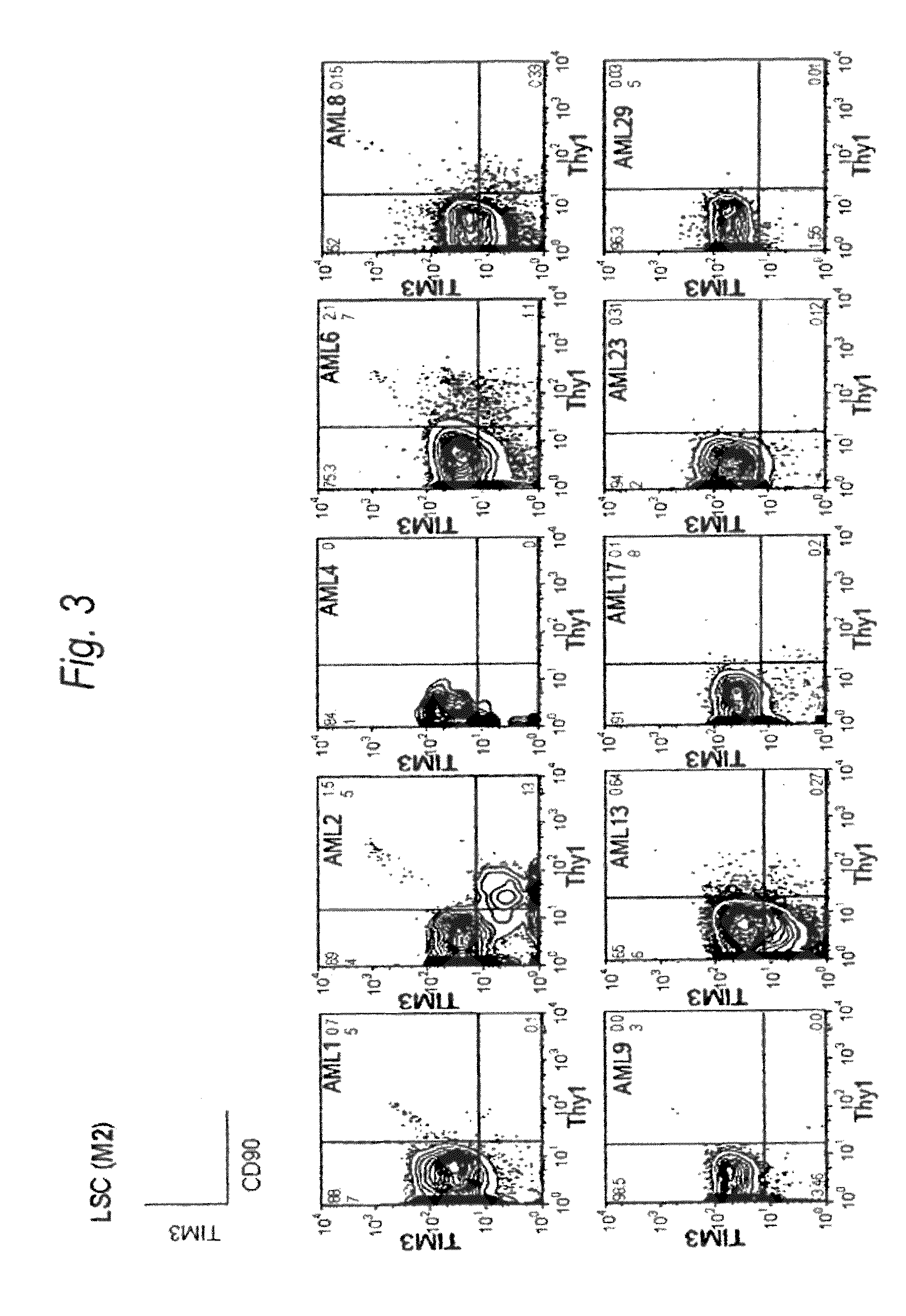
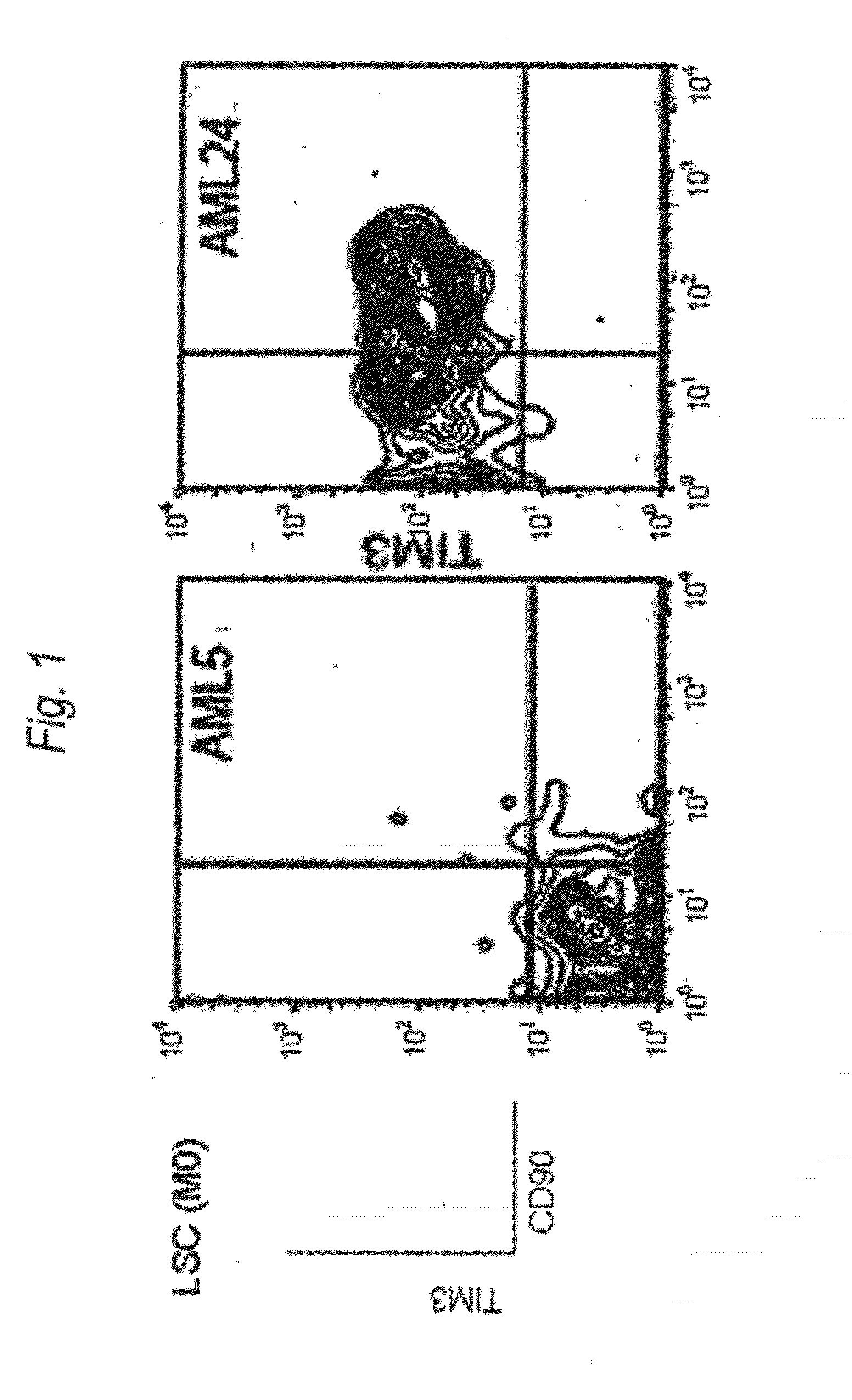
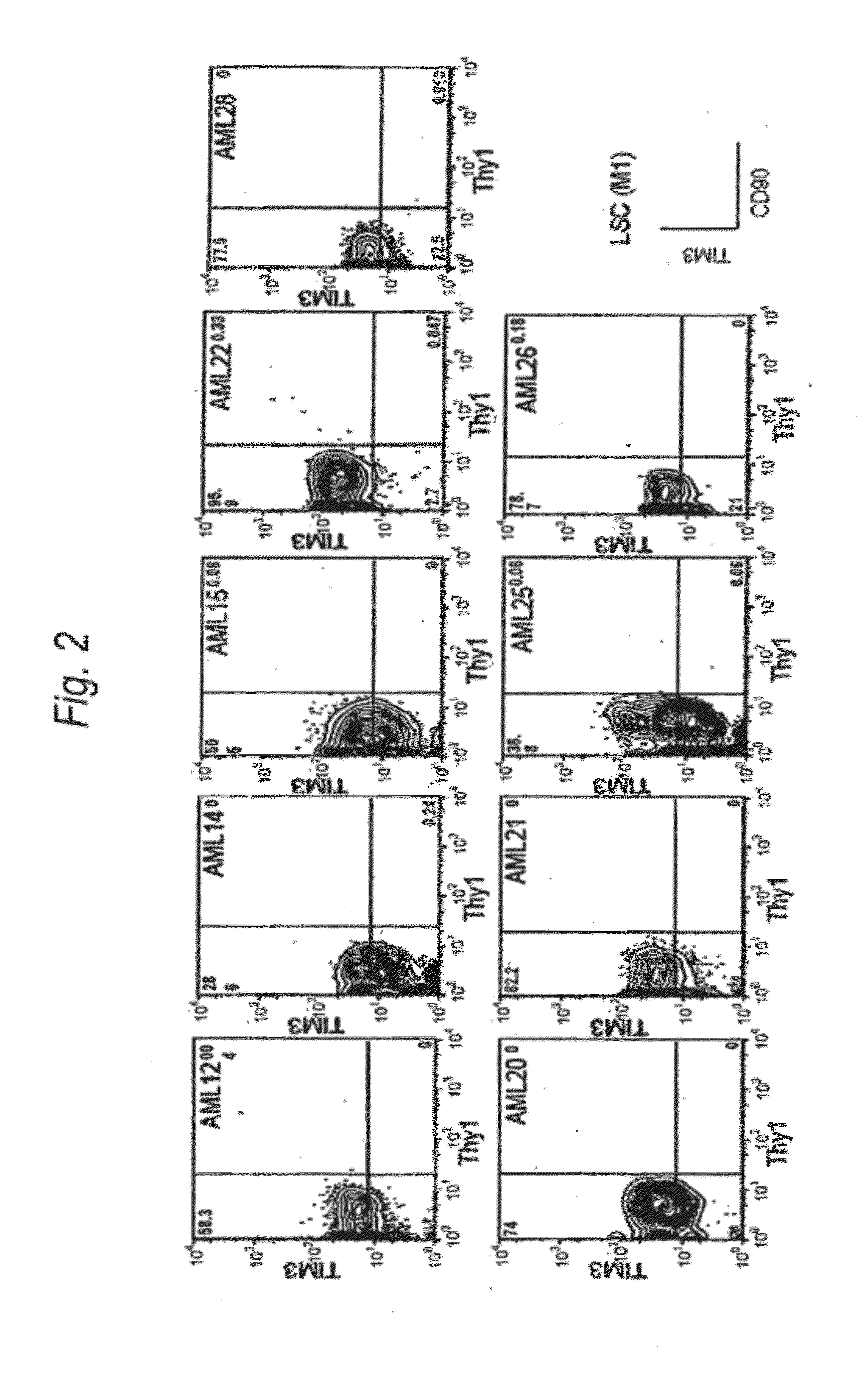
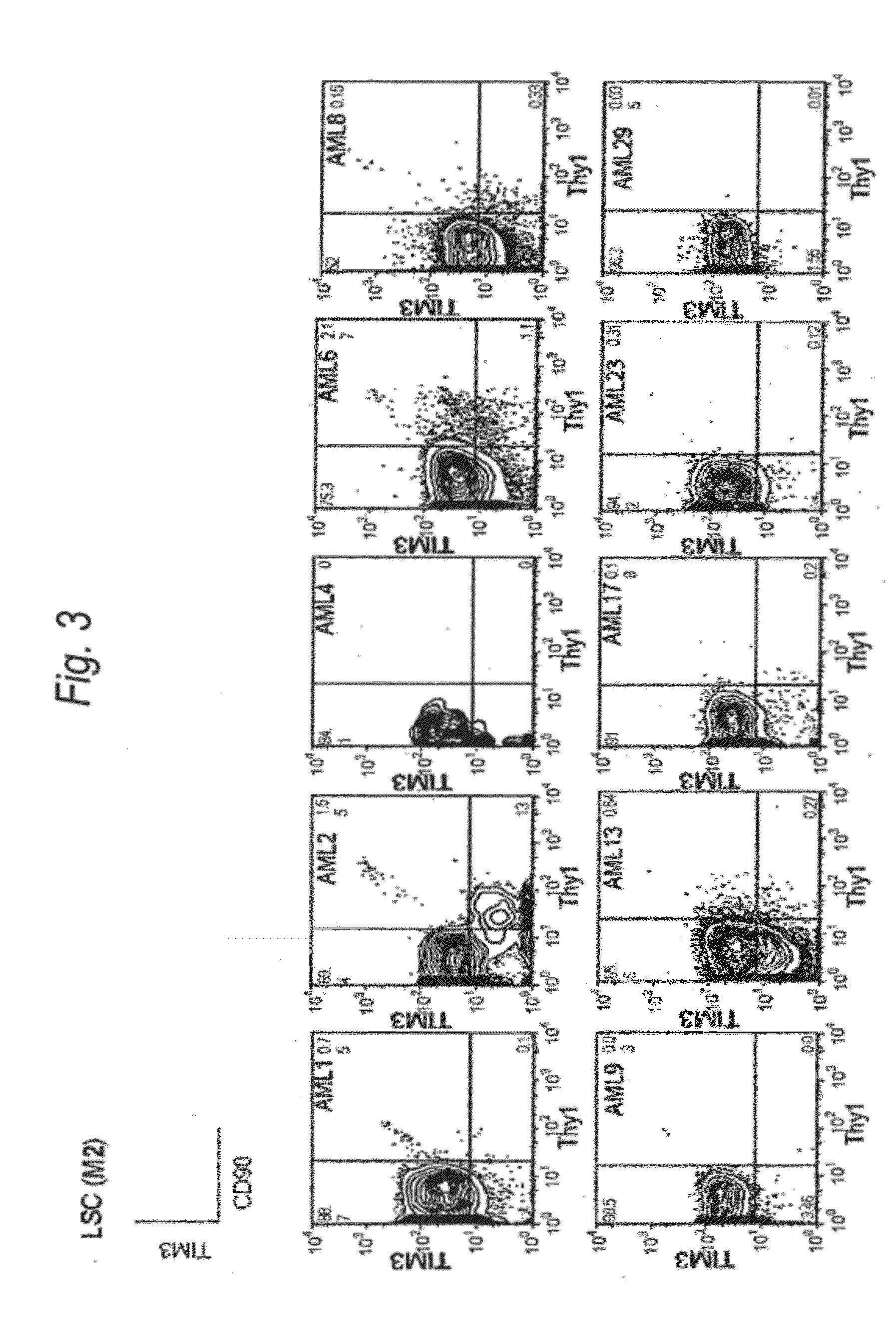
Method for treatment of blood tumor using anti-TIM-3 antibody
Disclosed is a therapeutic method comprising administering a TIM-3 antibody to a subject who is suspected to be suffering from blood tumor and in whom TIM-3 has been expressed in a Lin(−)CD34(+)CD38(−) cell fraction of bone marrow or peripheral blood or a subject who has been received any treatment for blood tumor. Also disclosed is a composition for preventing or treating blood tumor, which comprises a TIM-3 antibody as an active ingredient. Conceived diseases include those diseases which can be treated through the binding or targeting of the TIM-3 antibody to blood tumor cells (AML cells, CML cells, MDS cells, ALL cells, CLL cells, multiple myeloma cells, etc.), helper T cell (e.g., Th1 cells, Th17 cells), and antigen-presenting cells (e.g., dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages, and cells resembling to the aforementioned cells (hepatic stellate cells, osteoclasts, microglial cells, intraepidermal macrophages, dust cells (alveolar macrophages), etc)), all of which are capable of expressing TIM-3. The diseases for which the therapeutic use is to be examined include blood diseases in which the expression of TIM-3 is observed in bone marrow or peripheral blood, particularly blood tumor.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD +1
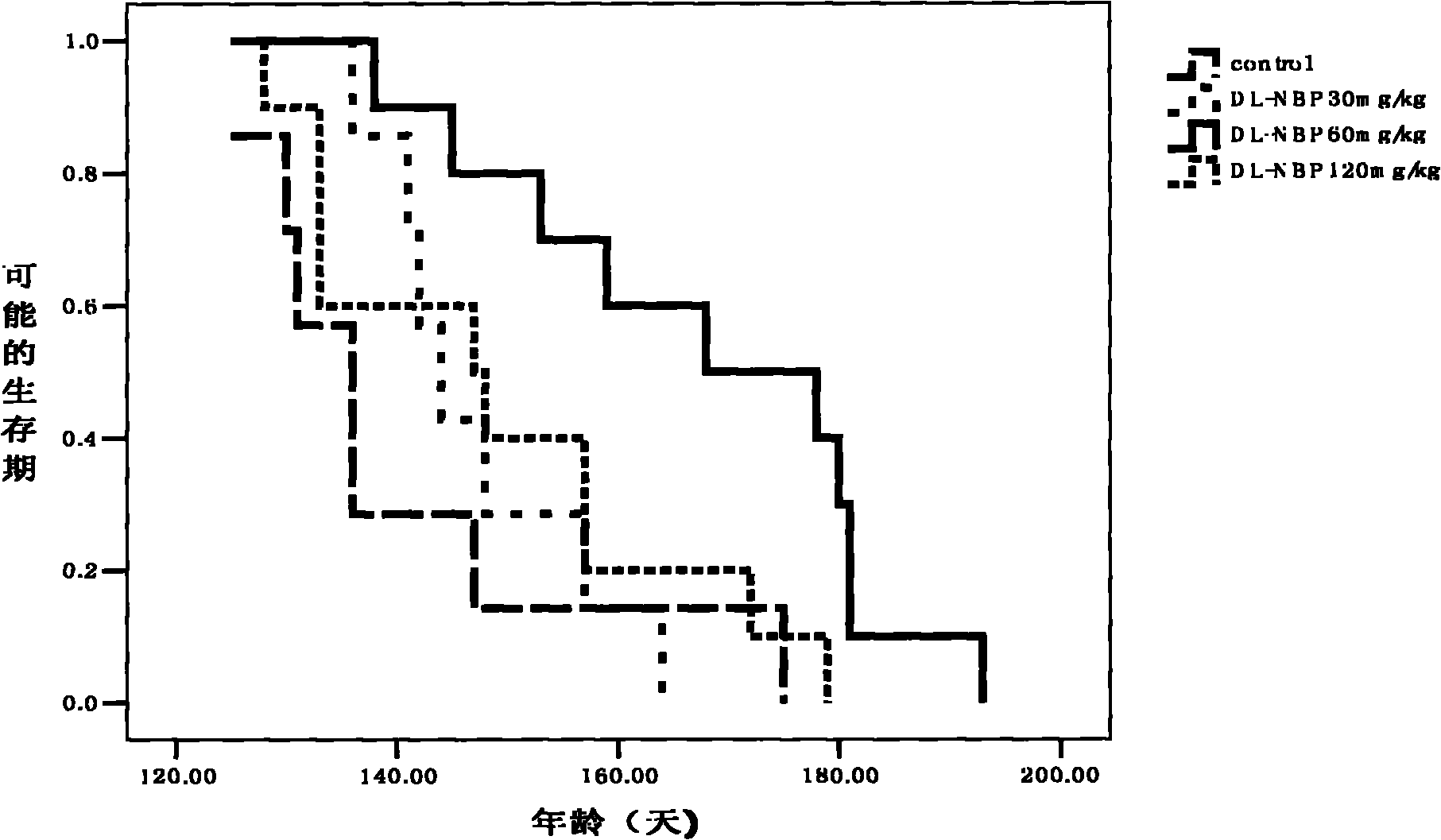
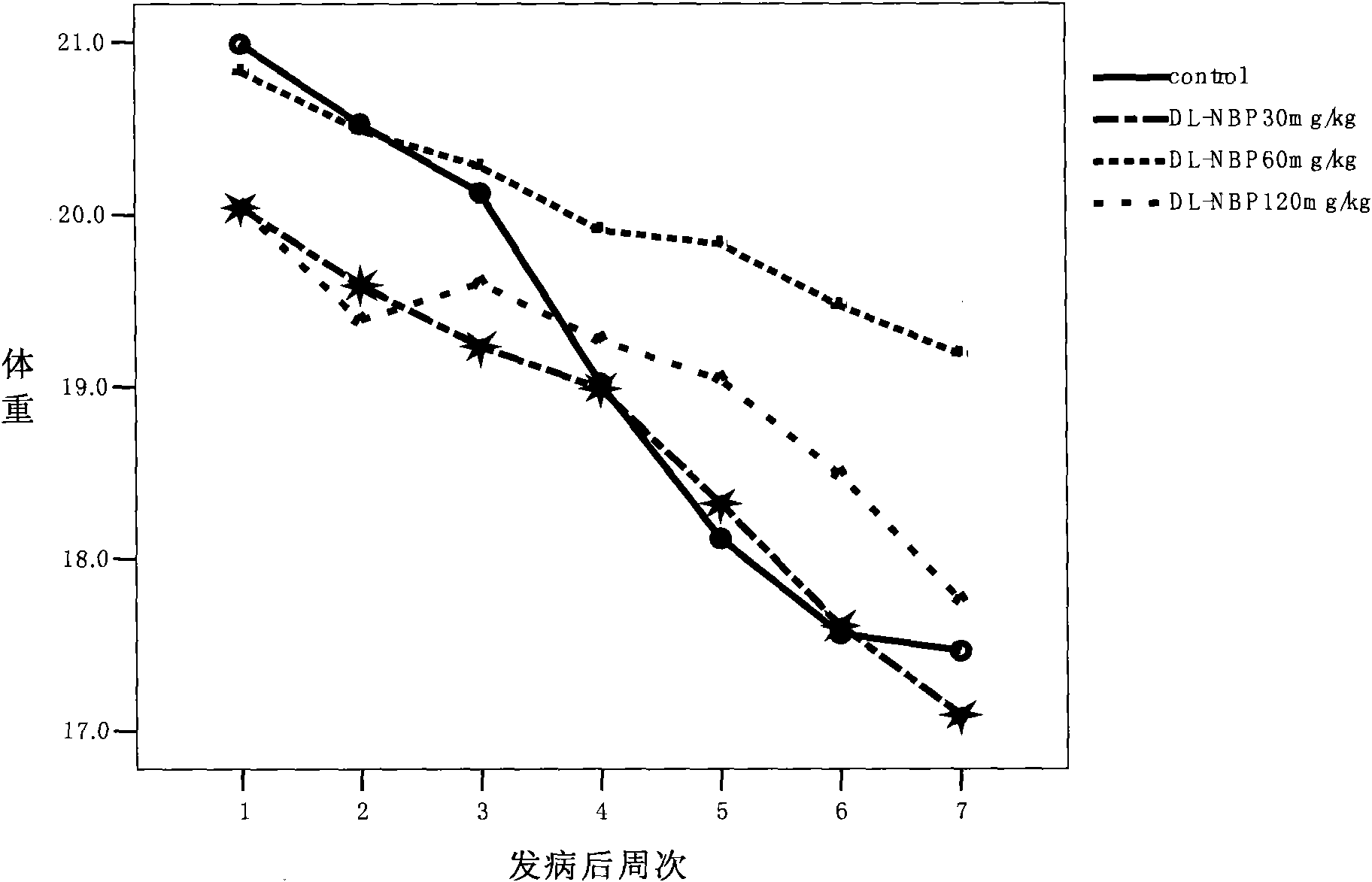
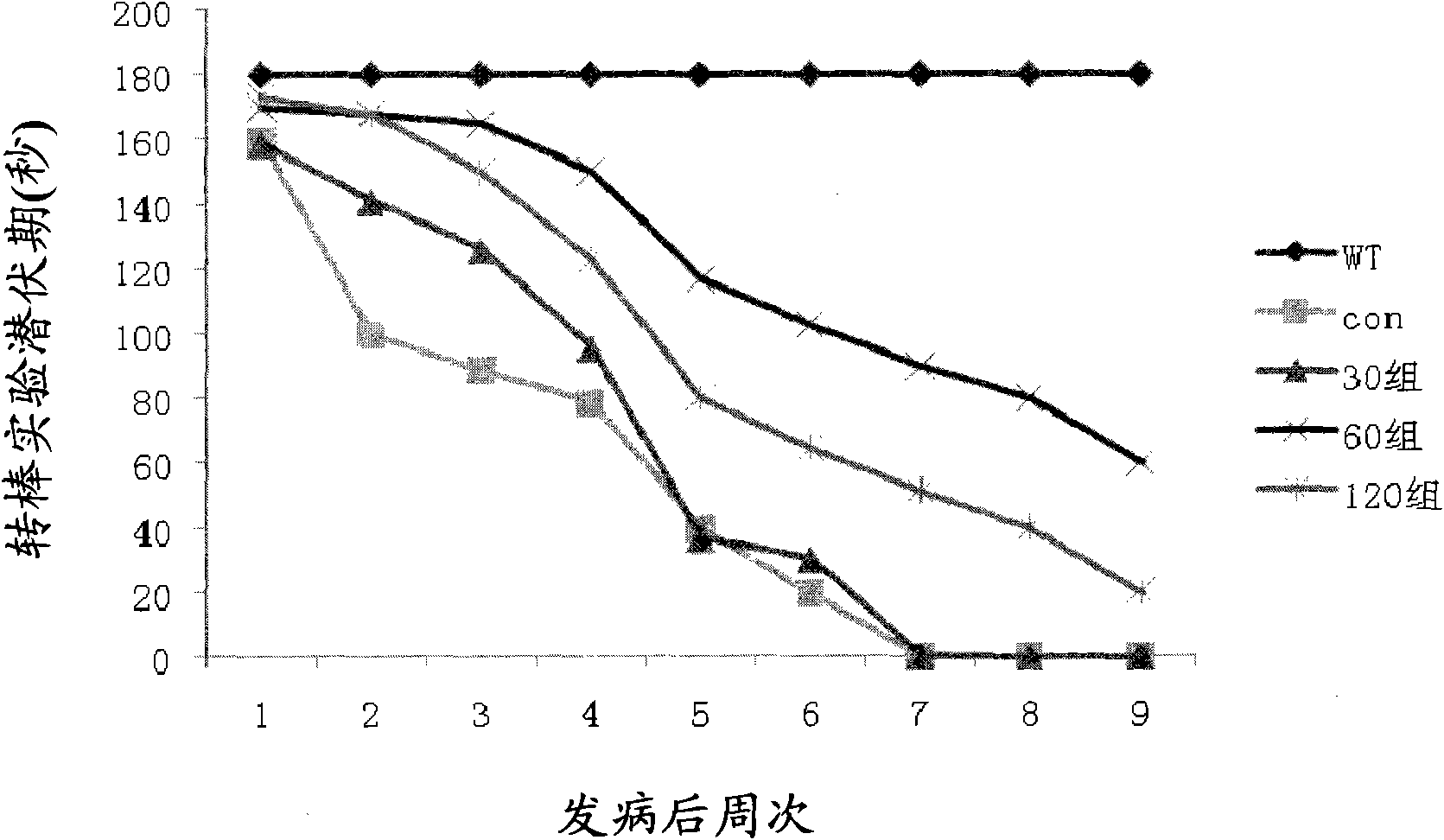
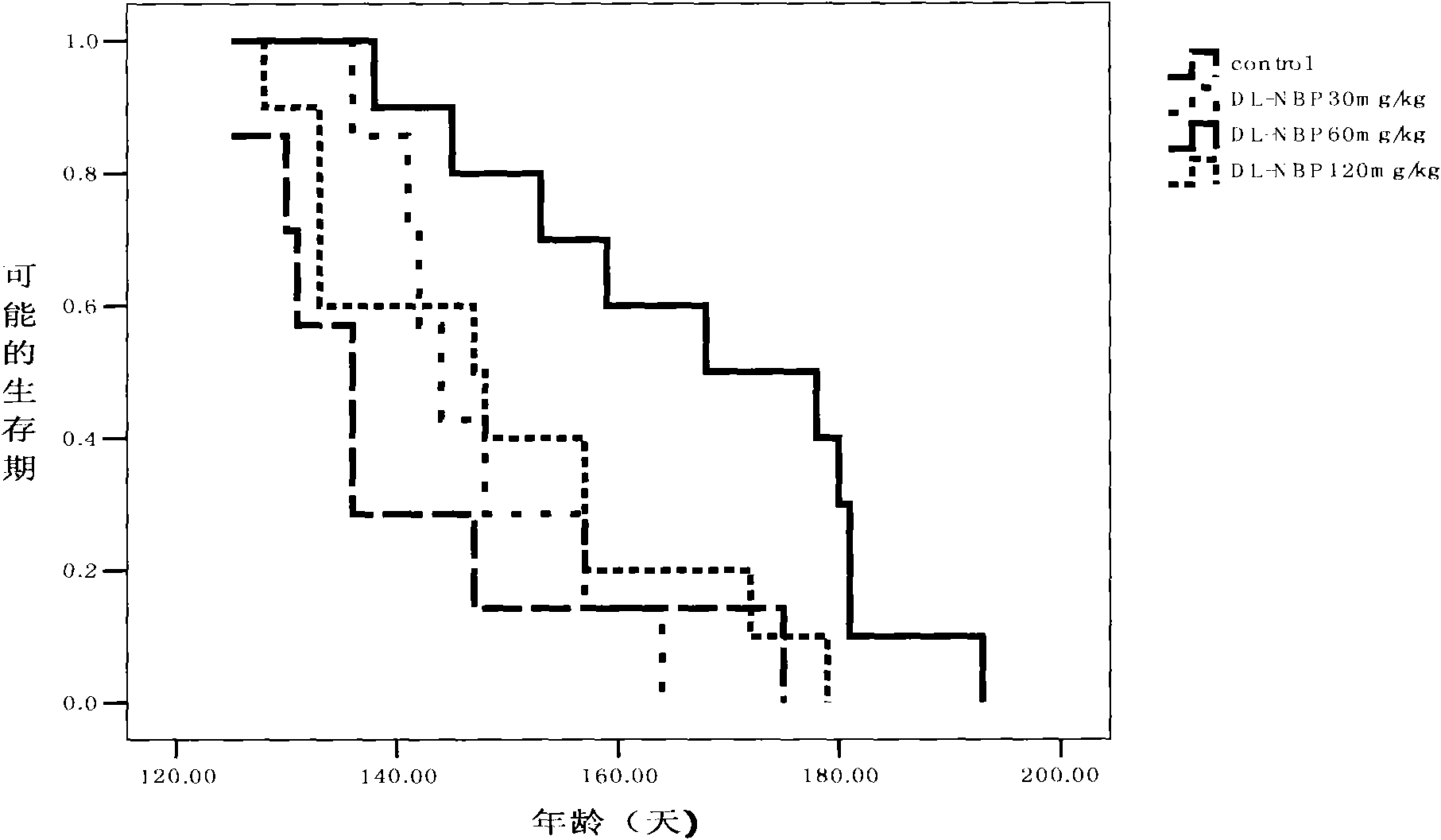
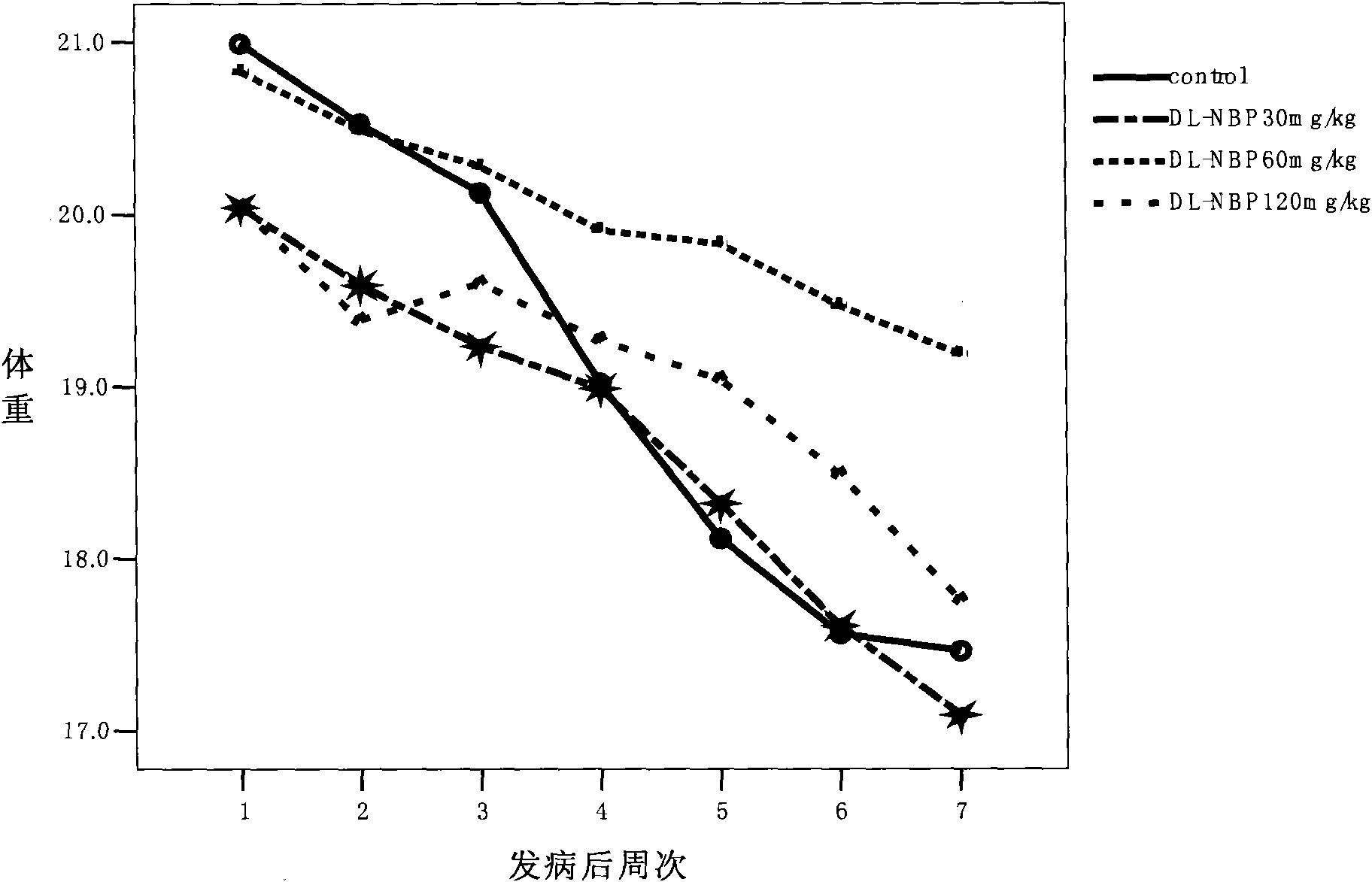
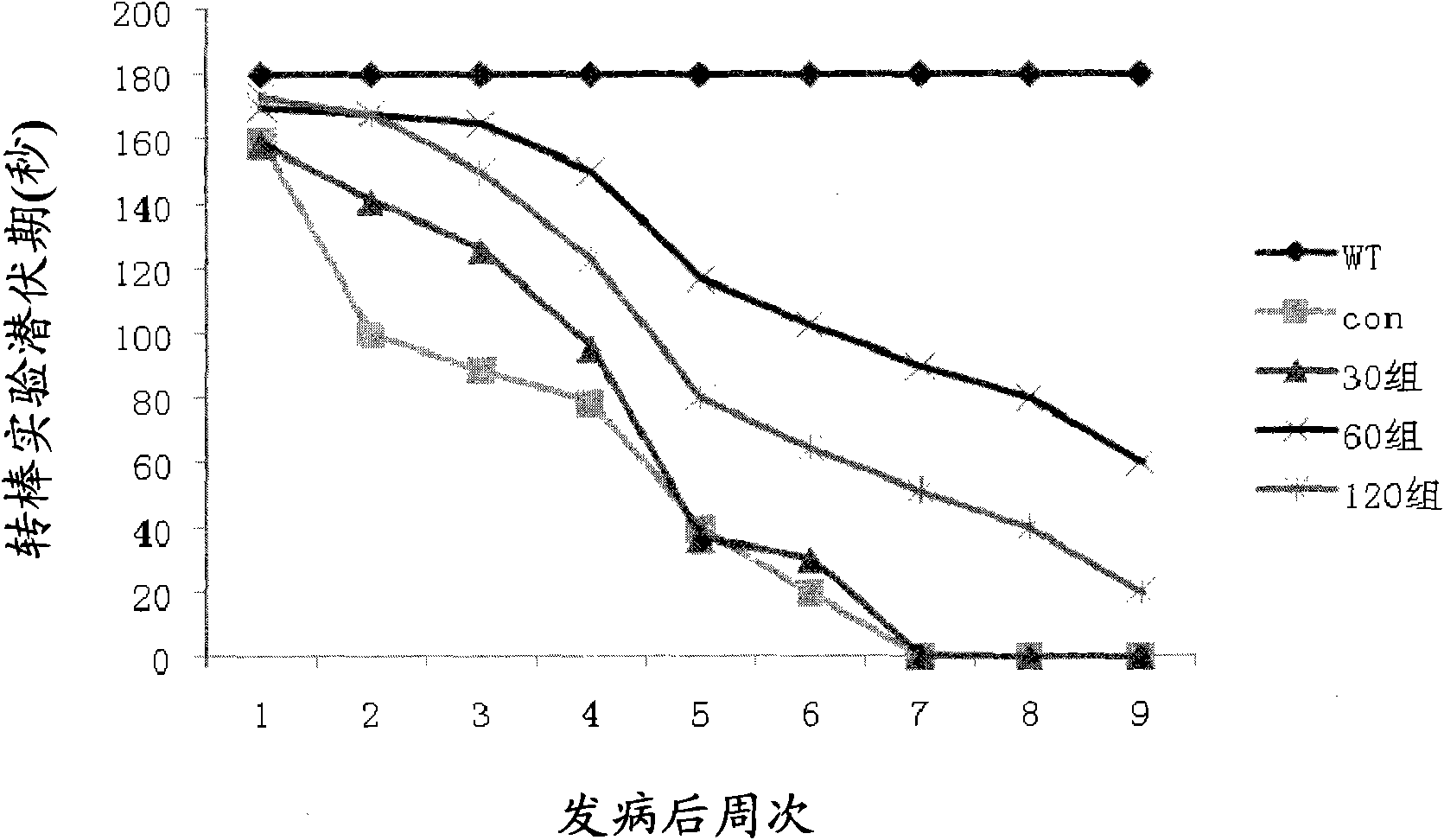
Application of butylphthalide and derivatives thereof in preparation of medicines for preventing and treating ALS
ActiveCN102397272ADelayed onset timeProlong lifeOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDegenerative changeButylphthalide
The invention which relates to the medicinal field discloses an application of butylphthalide and derivatives thereof in the preparation of medicines for preventing and treating ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis). Butylphthalide and the derivatives, which can delay the disease time of an SOD1-G93A transgenic mouse, prolong the lifetime of the mouse, reduce the degenerative change of spinal motorneurons, obviously increase the survival number of spinal anterior horn motor neurons of the mouse, reduce the electrophysiological abnormality of the transgenic mouse, obviously improve the action potential amplitude and the motion unit number of compound muscles, substantially inhibit the activation of astrocytes and microglial cells in the spinal cord of the mouse, and obviously reduce the expression level of iNOS and NF-kappaBp65, have good application prospects in the prevention and the treatment of the ALS.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG PHARMA GRP NBP PHARMA CO LTD
Method for treatment of blood tumor using Anti-tim-3 antibody
ActiveUS20120100131A1Use to establishBiological material analysisAntibody ingredientsDiseaseCell Fraction
Disclosed is a therapeutic method comprising administering a TIM-3 antibody to a subject who is suspected to be suffering from blood tumor and in whom TIM-3 has been expressed in a Lin(−)CD34(+)CD38(−) cell fraction of bone marrow or peripheral blood or a subject who has been received any treatment for blood tumor. Also disclosed is a composition for preventing or treating blood tumor, which comprises a TIM-3 antibody as an active ingredient. Conceived diseases include those diseases which can be treated through the binding or targeting of the TIM-3 antibody to blood tumor cells (AML cells, CML cells, MDS cells, ALL cells, CLL cells, multiple myeloma cells, etc.), helper T cell (e.g., Th1 cells, Th17 cells), and antigen-presenting cells (e.g., dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages, and cells resembling to the aforementioned cells (hepatic stellate cells, osteoclasts, microglial cells, intraepidermal macrophages, dust cells (alveolar macrophages), etc)), all of which are capable of expressing TIM-3. The diseases for which the therapeutic use is to be examined include blood diseases in which the expression of TIM-3 is observed in bone marrow or peripheral blood, particularly blood tumor.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD +1
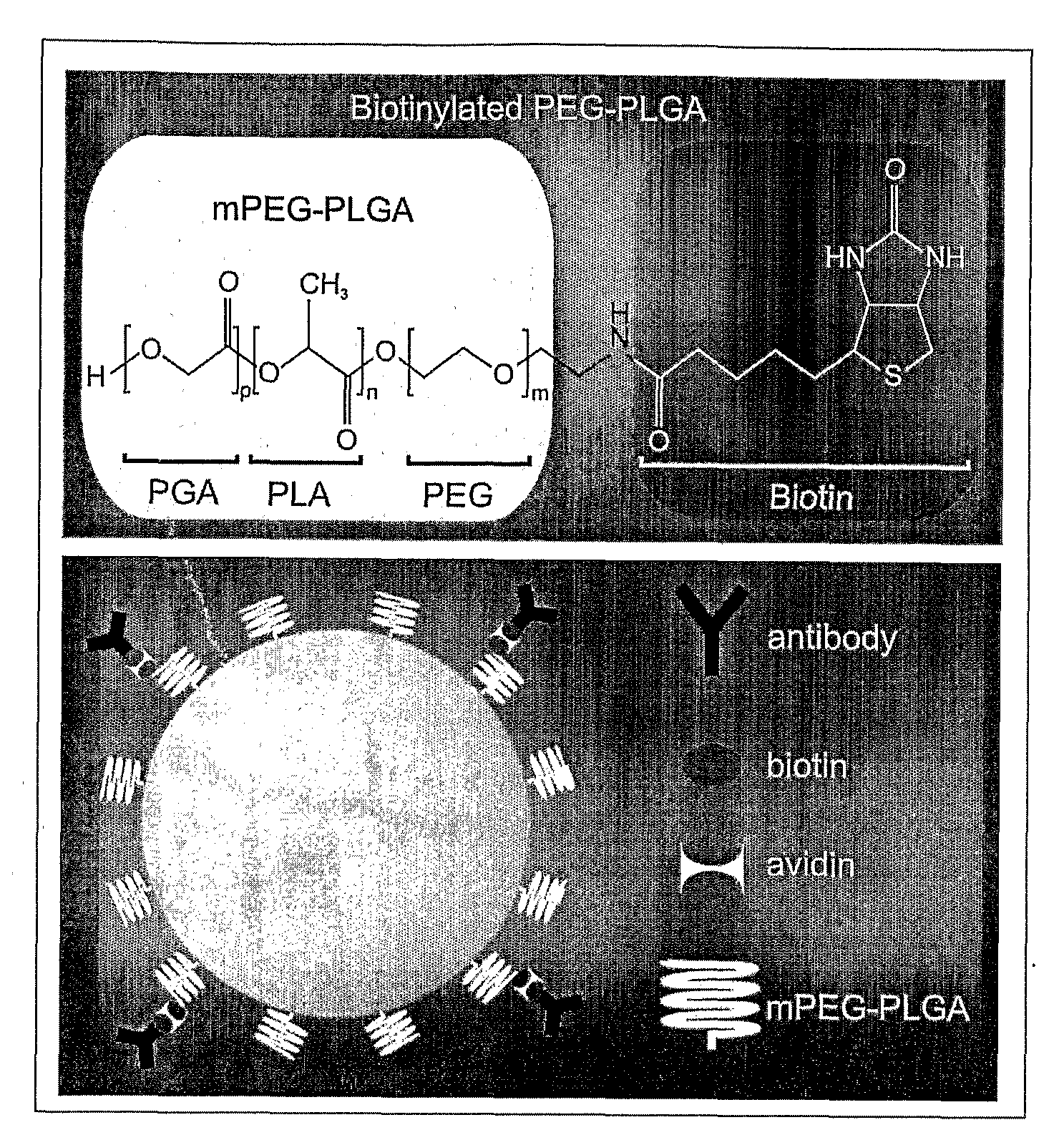
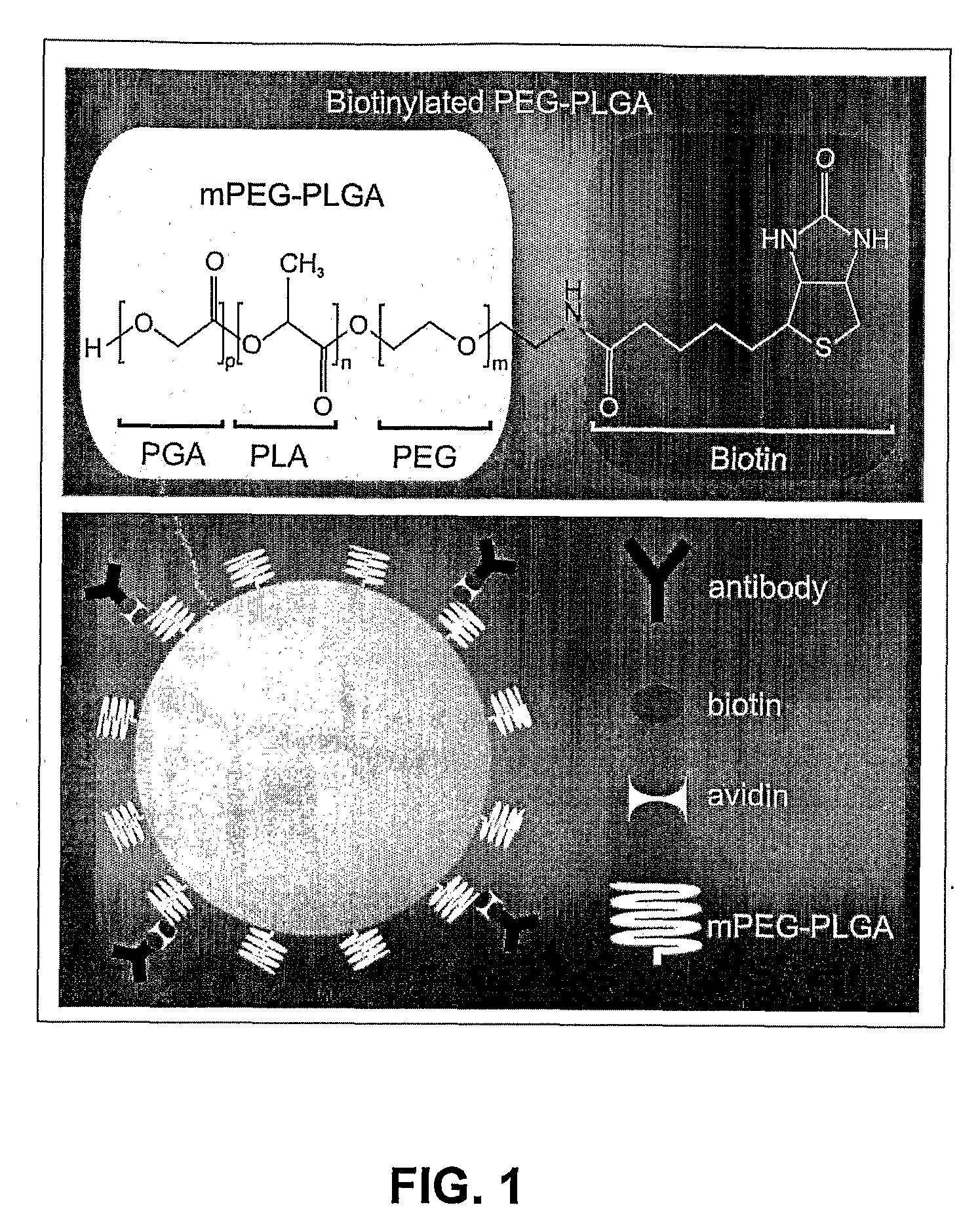
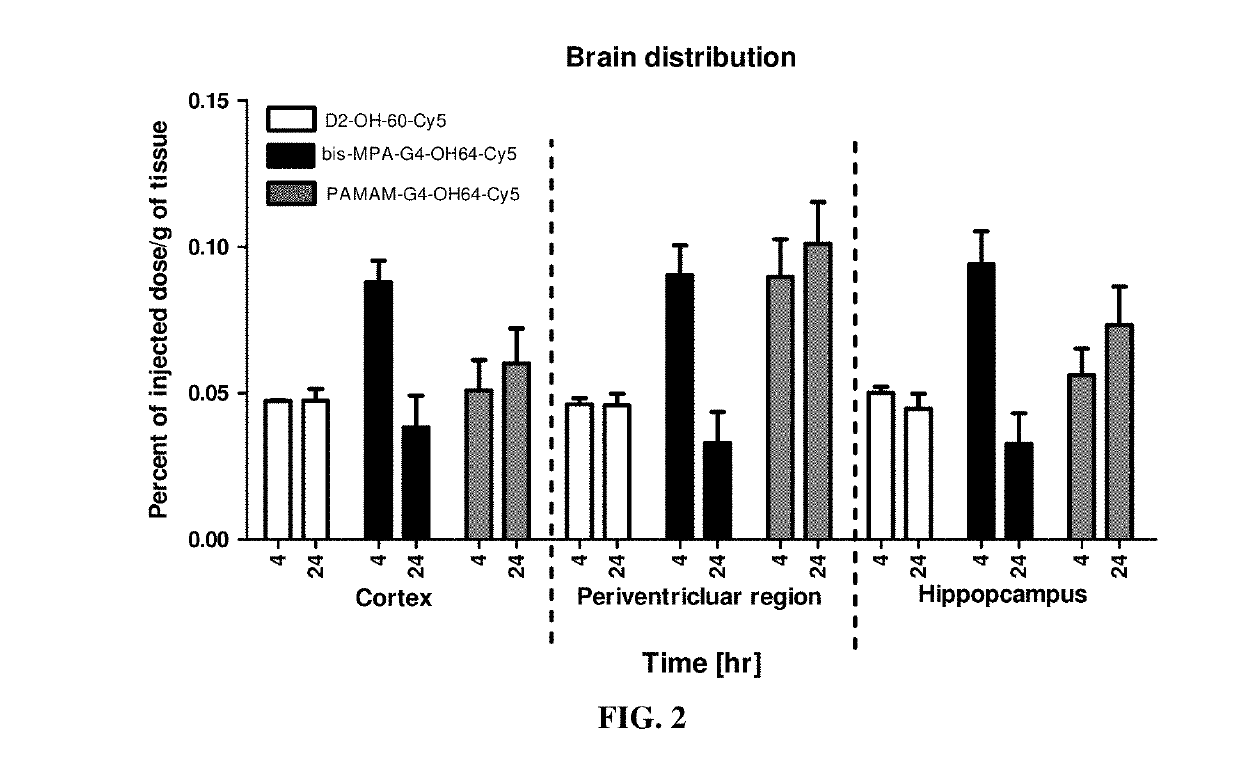
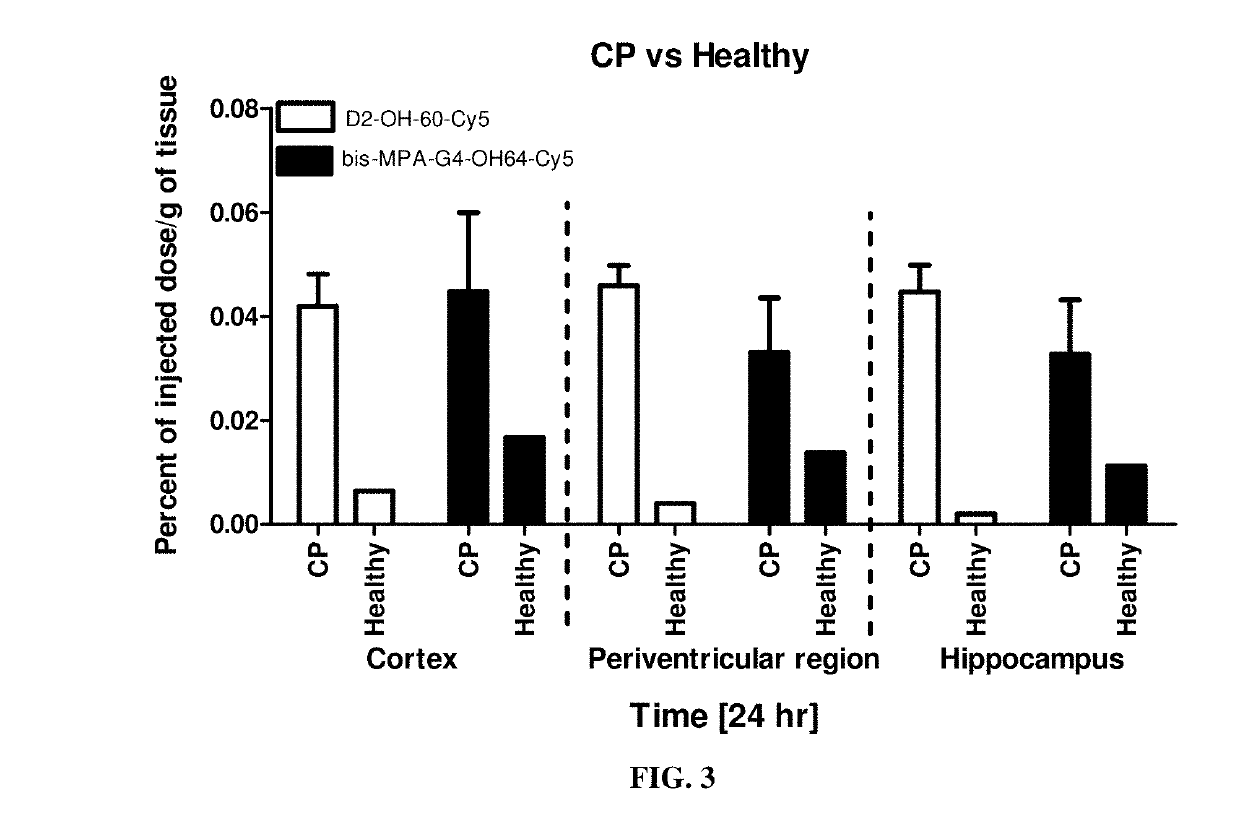
Compositions and Method for Brain Specific Targeted Delivery of Therapeutic Agents
Disclosed are methods and compositions for delivering a therapeutic agent to target organs or tissues, such as brain. The methods and compositions use bone marrow stem cells, monocytes, macrophages or microglial cells to deliver the therapeutic agent associated with nanoparticles to the target organ or tissue.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
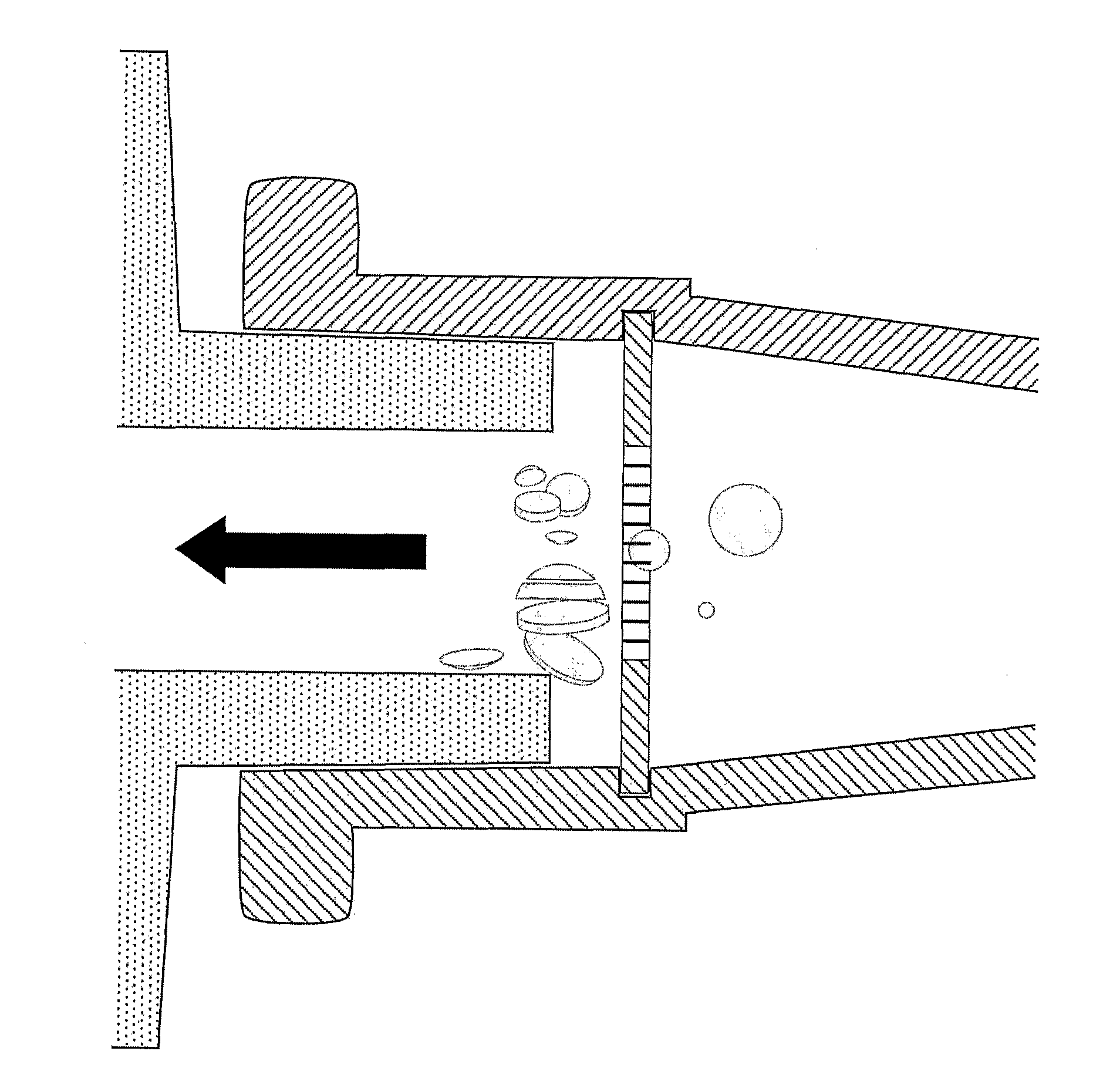
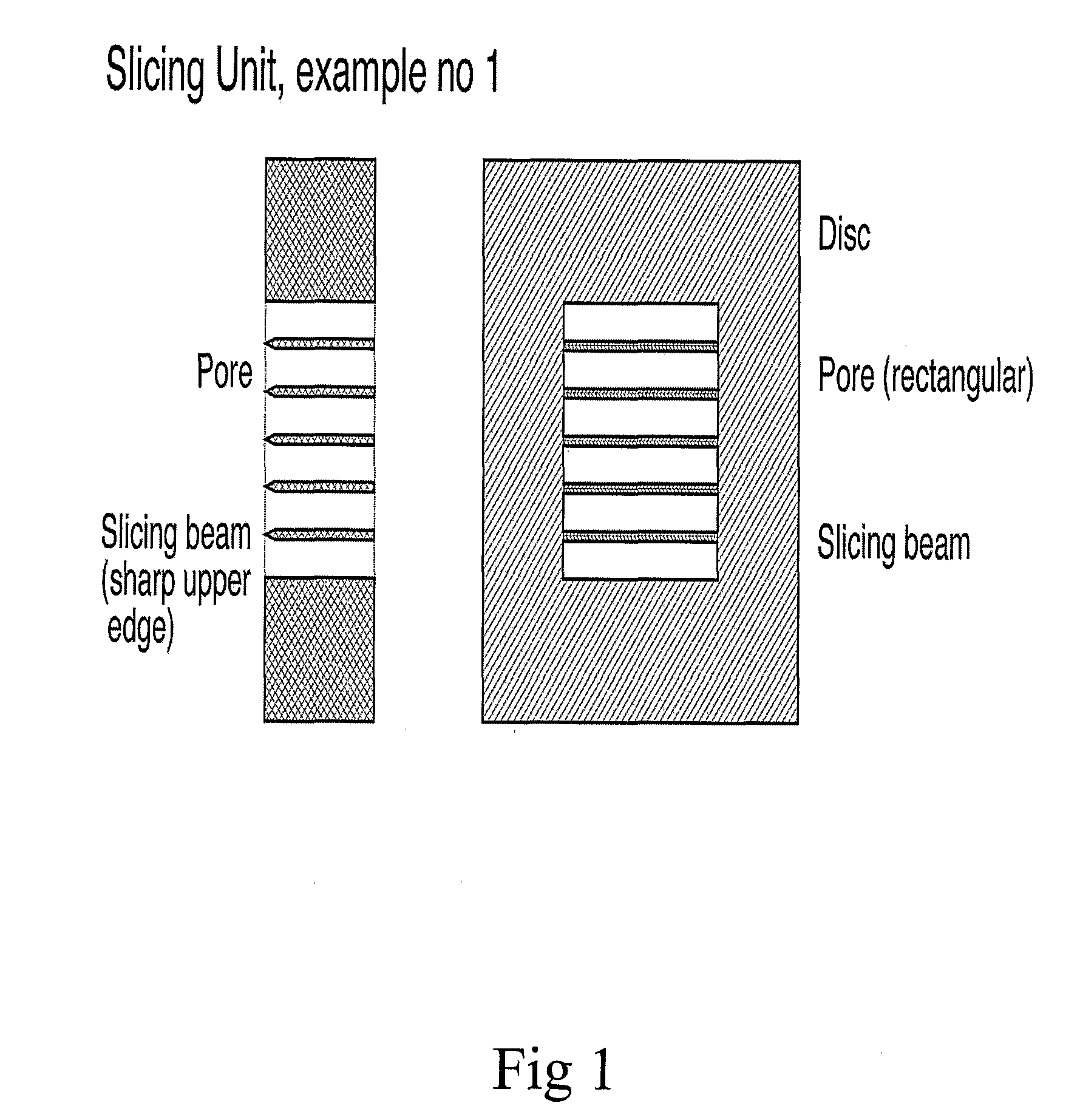
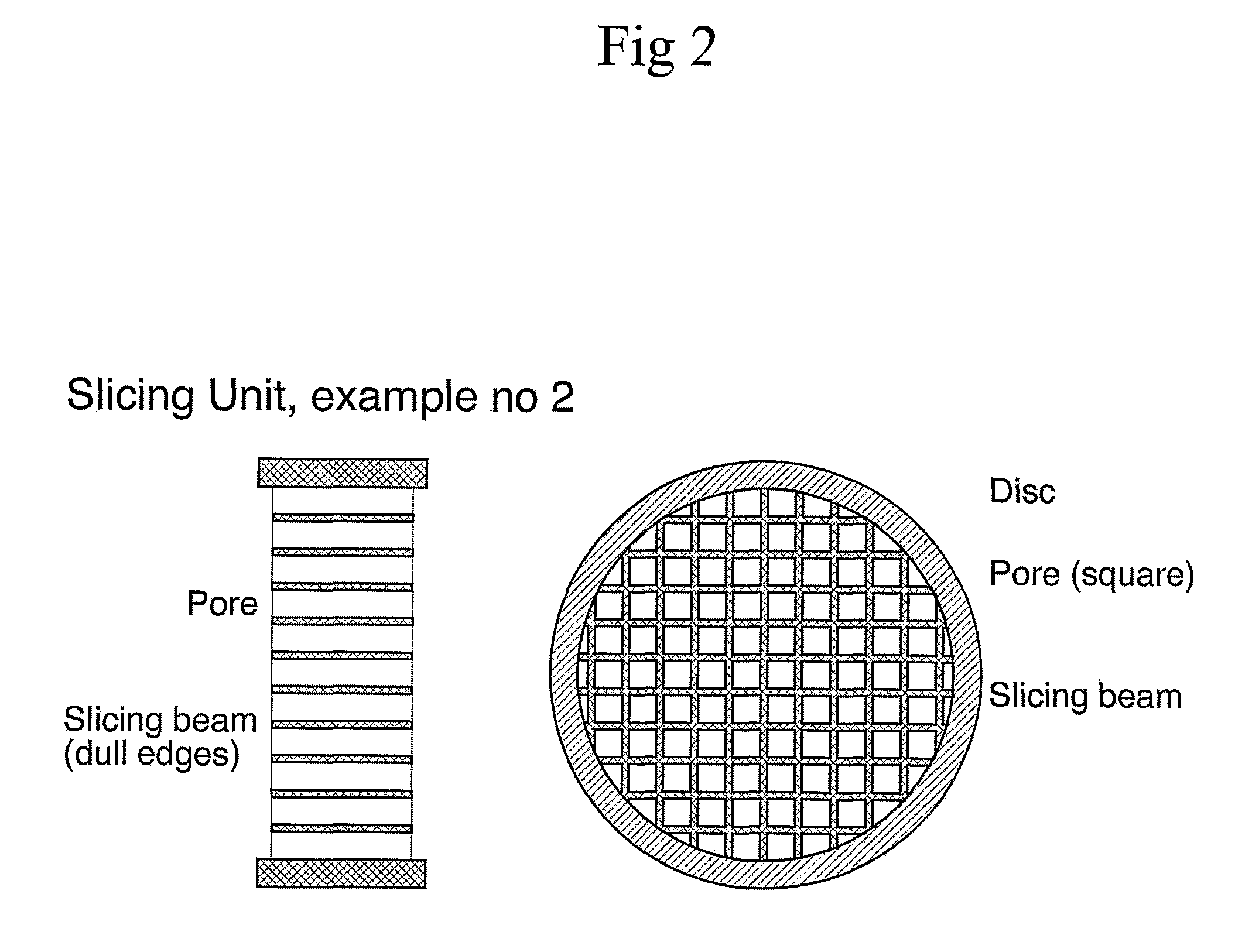
Slicing device
ActiveUS20100136690A1Easy to implementAvoiding enzymatic dissociationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological materialsMicroglia
The invention relates to a biological microglia comprising at least two pores having a size adopted to allow cells, cell aggregates, tissue or other biological material to pass through said pores, and one or several slicing beams separating said pores from each other, wherein biological material is split / sliced / cleaved into at least two parts when passing said microgrid, a slicing device, an apparatus comprising said slicing device as well as the use of said microgrid, slicing device and apparatus.
Owner:SUNDSTROM ERIK +3
Anti-alpha-synuclein monoclonal antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN110172098AFree from toxicityHigh affinityNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBeta-synucleinAutonomic symptoms
The invention relates to the technical field of antibody drugs, and specifically relates to an anti-alpha-synuclein monoclonal antibody and application thereof. The anti-alpha-synuclein monoclonal antibody provided by the invention can specifically bind to monomers and aggregates of alpha-synuclein, has high affinity to monomers and aggregates of a human alpha-synuclein, has no affinity to beta-synuclein and gamma-synuclein, can effectively inhibit the polymerization of the monomers of alpha-synuclein, promote microglial cells to clear formed alpha-synuclein aggregates, and protect neuronal cells from the toxicity of the alpha-synuclein aggregates, and can be used to prevent, treat and diagnose alpha-synuclein-related diseases and conditions such as Parkinson's disease, Lewy body dementia,Alzheimer's disease with Parkinson's disease, pure autonomic failure, and multiple system atrophy.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
Compound and application thereof
ActiveCN103922981AInhibit the inflammatory responsePrevent neurodegenerative diseasesOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseDrug compound
The invention provides a compound. The compound and pharmaceutically acceptable salt, various isotopes, various crystal forms or various isomers have the structure shown as a formula (I): A-L-B (I), wherein A is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug compound monomer, B is a hydrogen sulfide releaser or an antioxidant compound, and L is a group or a functional group which connects A and B. The invention further provides an application of the compound as a medicine for inhibiting neuroinflammation as well as a combined application of the compound and other drugs as medicines for inhibiting neuroinflammation. By applying the concept of double prodrugs, the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug and the hydrogen sulfide releaser or the antioxidant compound are covalently connected together to form a multiple-target point compound which can effectively inhibit inflammatory response of the microglial cell induced by lipopolysaccharide, so that the compound can be used for treating or preventing various neurodegenerative diseases.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
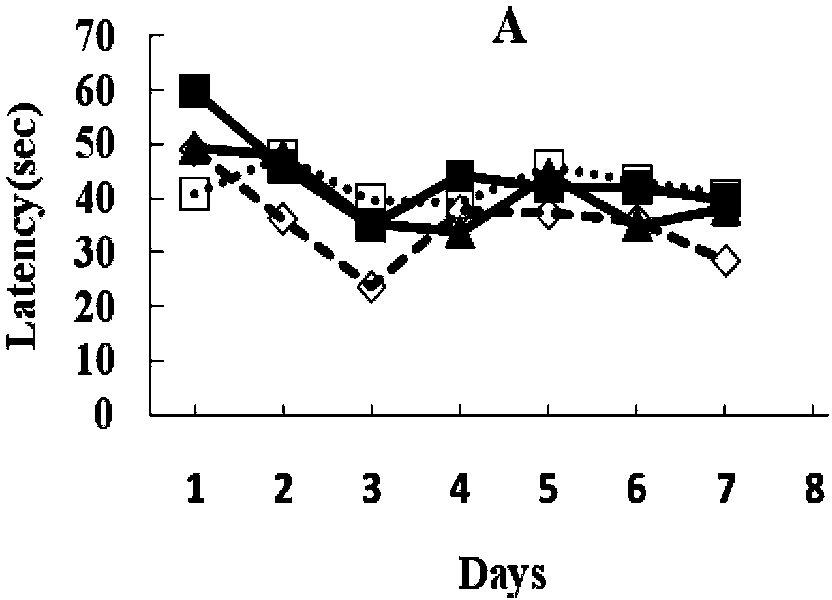
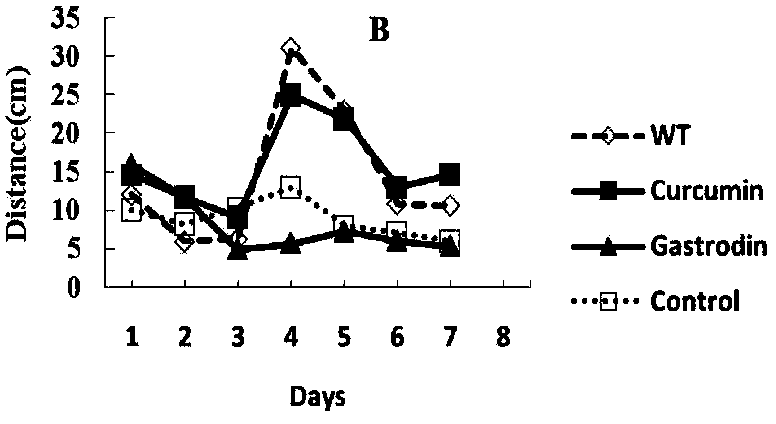
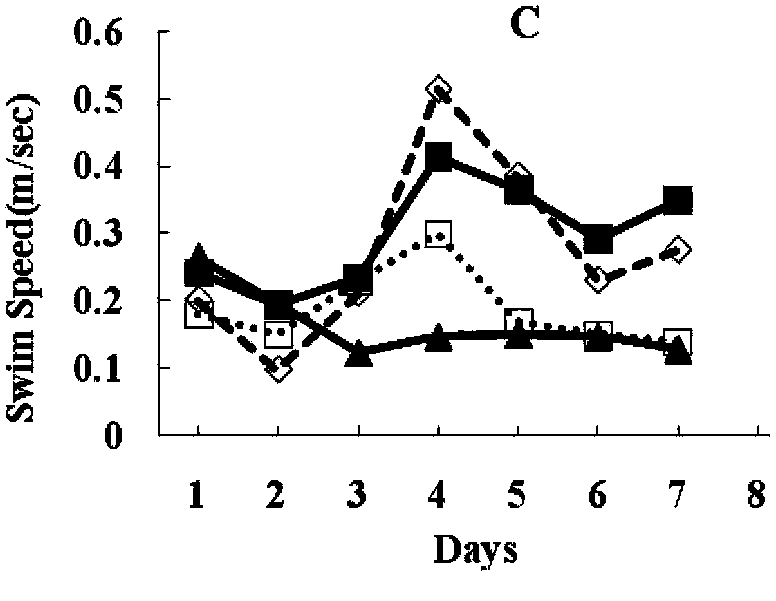
Application of gastrodin to preparing medicaments for preventing and treating Alzheimer's disease
InactiveCN103385884AReduce inflammationImprove toleranceOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseAmyloid
The invention discloses an application of gastrodin to preparing medicaments for preventing and treating Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease, and pathological characteristics comprise neuro fibrillary tangles formed in cells, hyperplasia of reactive microglia and glial cell, and the like, wherein the extracellular deposition of amyloid A beta is the main pathogenetic reason of AD. An AD small mouse taking a gastrodin-containing fodder is substantially improved in spatial-memory learning ability, substantially reduced in A beta level in brain and serum, and substantially reduced in amyloid plaques and microglia in brain tissue, and thus it is indicated that gastrodin is capable of preventing A beta deposition and decreasing active components causing AD mouse brain gastrodin.
Owner:KUNMING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Application of hexokinase 2-specific inhibitor in acute central nervous system injury diseases
InactiveCN106860867AInhibit neuroinflammationInhibit the inflammatory responseNervous disorderAntibody ingredientsDiseaseCerebral injury
Owner:GUANGZHOU CELLPROTEK PHARMA
Application of P2Y4 receptor stimulant in preparing medicaments for treating Alzheimer's disease
InactiveCN102058887AConvenient treatmentLow toxicityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseLower risk
The invention provides application of a P2Y4 receptor stimulant in preparing medicaments for treating the Alzheimer's disease. The application of the P2Y4 receptor stimulant in preparing medicaments for treating the Alzheimer's disease has the beneficial effects that the P2Y4 receptor stimulant can be used for effectively promoting the pinocytosis to beta-amyloid polypeptide of microglial cells so as to relieve and even cure the Alzheimer's disease; and the P2Y4 receptor stimulant has lower toxicity and low risk and is clinically applied to treating various diseases, thus the P2Y4 receptor stimulant has good application prospect in treating the Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Neuroprotective Ganoderma compositions and methods of use
Owner:PURAPHARM INT HK
Rhein supramolecular hydrogel as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106692037AImprove solubilityRetain biological activityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseSolubility
The invention discloses a rhein supramolecular hydrogel as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The rhein supramolecular hydrogel comprises rhein and a N3HCO3 solution, wherein the rhein is dissolved into the N3HCO3 solution. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving the rhein into the N3HCO3 solution, and performing ultrasonic dispersion, so as to obtain the rhein supramolecular hydrogel. The rhein supramolecular hydrogel has the characteristics of anti-inflammatory property, antibacterial property and antineoplastic property, can solve the problems of poor solubility and short half-life period of rhein, reserves the biological activity of the rhein, and has obvious treatment effect on the application of medicines for treating microglial cell mediated inflammatory encephalopathy, such as Alzheimer disease, Parkinson disease, cerebral trauma and cerebral edema.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
Application of polypeptide for preparing medicine for treating Alzheimer disease
ActiveCN109646668AFunction increaseHigh densityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideApoptosis
The invention discloses application of a polypeptide for preparing medicine for treating the Alzheimer disease. The amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The polypeptide is an extracellular section 41-81 amino acids of a TREM2 receptor protein, and the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The polypeptide has the application that the microglial mediated inflammation reaction is promoted, apoptosis of microglial cells is restrained, the migration capability of microglial cells is enhanced, Abeta endocytosis and degradation of the microglial cells are promoted, the density of microglial cells inside a brain is increased, and Abeta amyloid plaque deposition inside the brain is lowered.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
Coumarinolignoid and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109134486AInhibition releaseGood potential medicinal valueNervous disorderAntipyreticDiseaseBv2 microglia
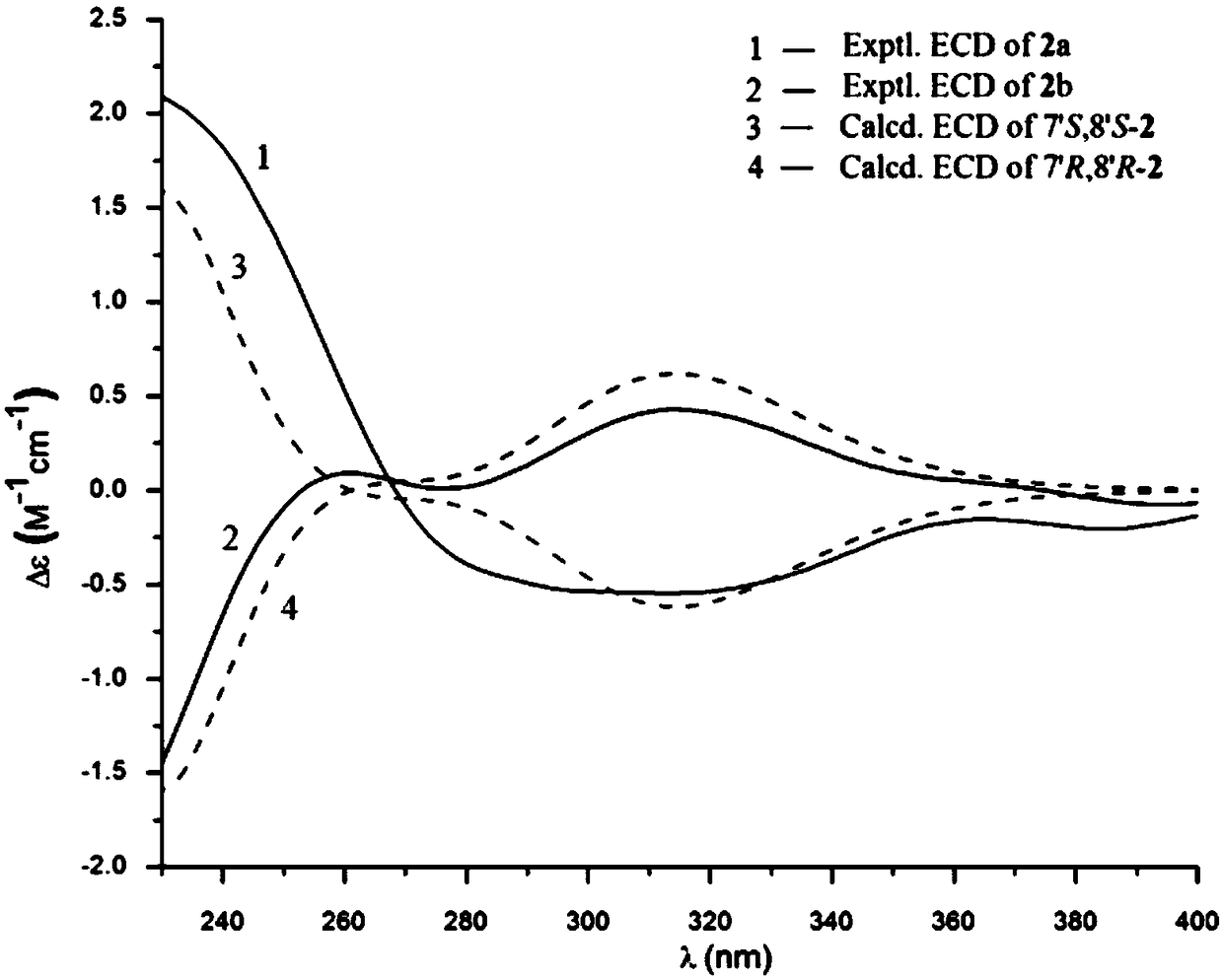
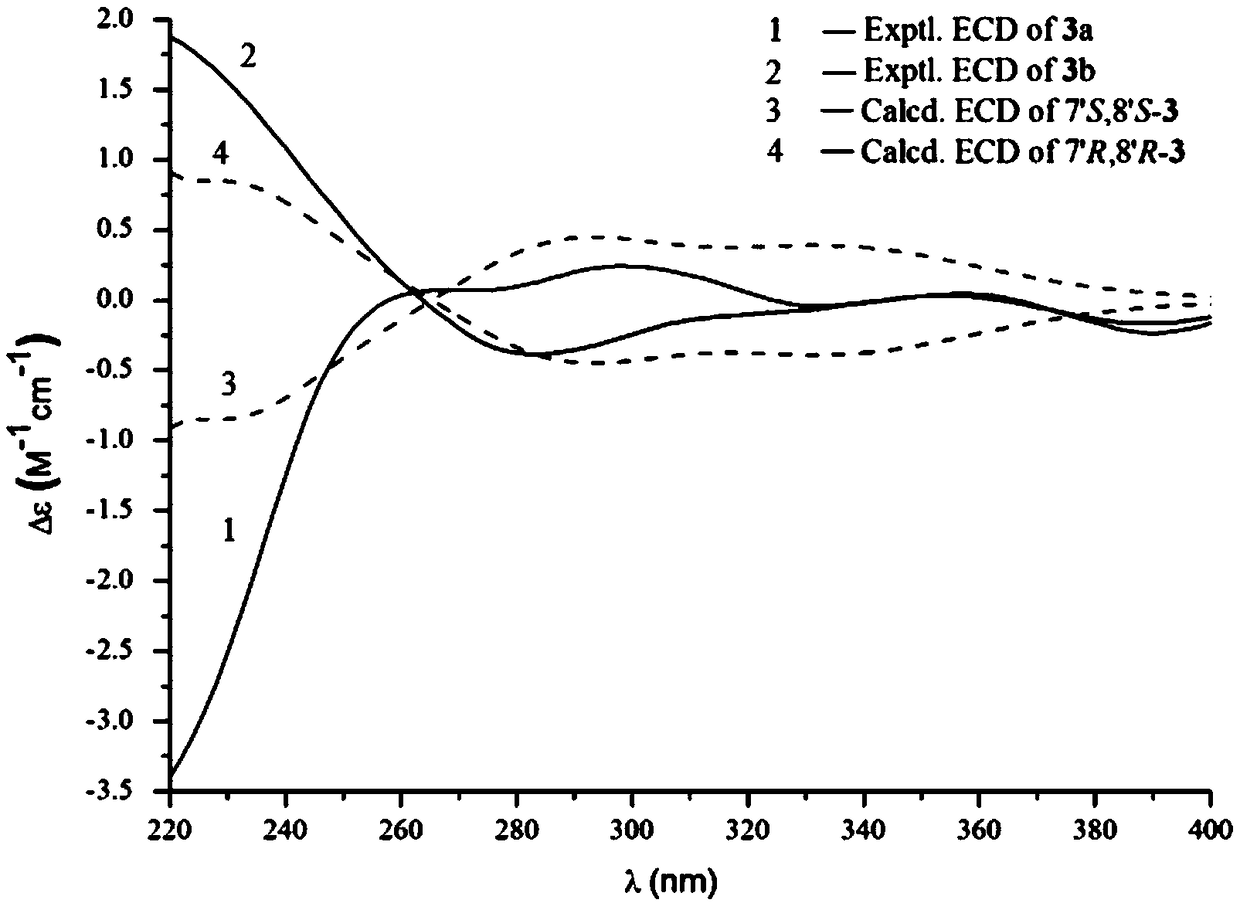
The invention discloses coumarinolignoid and a preparation method and application thereof. The coumarinolignoid specifically comprises six compounds obtained through separation of Sapium discolor (Champ.ex Benth.)Muell.Arg.). Experiments show that the compounds can remarkably inhibit NO release of BV2 microglial cells stimulated by LPS under the condition that the survival rate of the BV2 microglial cells is not influenced by the compounds. The inhibitory effect of the compound 2a is slightly stronger than that of clinically common medicine, namely minocyline, and the compounds are good in potential medicinal value and are expected to be used for preparing medicines for neurodegenerative diseases.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
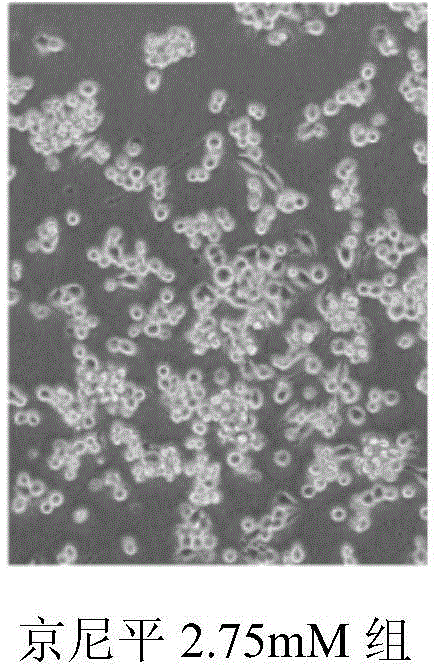
Application of genipin in prevention or treatment of ischemic brain injury
The invention relates to application of genipin in prevention or treatment of ischemic brain injury. Brain injury is particularly related to injury of microglial cells or human umbilical vein endothelial cells. The invention further relates to a medicine composition containing genipin for preventing or treating ischemic brain injury.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
Flexible electrode implantation system
PendingCN111990995AGood biocompatibilityControl implant depthDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBiocompatibilityNerve cells
The invention provides a flexible electrode implantation system. The flexible electrode implantation system comprises a foldable flexible electrode and an implantation guiding instrument, wherein thefoldable flexible electrode is used for extracting the discharge activity of neurons; and the implantation guiding instrument comprises an implantation guiding platform and an implantation guiding column and is used for sending the flexible electrode into a target brain region. The flexible electrode implantation system adopts an implantation mode of combining the flexible electrode with an implantation tool. The prepared flexible electrode has good biocompatibility, and does not cause excessive signal acquisition of astrocytes and microglial cells on nerve cells; and meanwhile, the electrodehas enough flexibility to move along with the movement of brain tissues, so that the generation of motion artifacts is reduced. The prepared implantation guiding instrument is used for in-vitro auxiliary flexible electrode implantation, the implantation depth of the flexible electrode can be controlled, additional implantation damage cannot be caused, and the interface environment of electrode recording points cannot be influenced.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
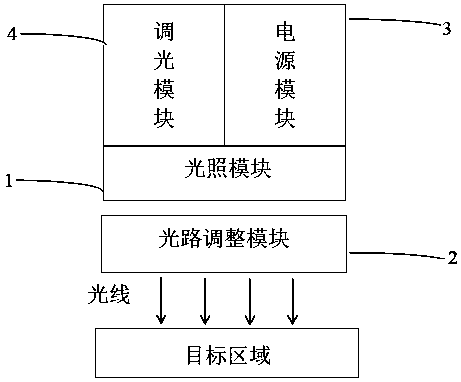
Phototherapy device for cervical spondylosis
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical instruments, and specifically relates to a phototherapy device for cervical spondylosis. The phototherapy device of the invention comprises a light illumination module, a light path adjustment module, a power supply module and a light adjustment module. The light illumination module is composed of a flexible circuit substrate and a light source for illuminating target cells. The light path adjustment module diffuses light emitted by the light source and distributes the light in a light illumination area uniformly. The light adjustment module is used to set pulse light wavelength, pulse light power and illumination time. Compared with existing therapeutic apparatuses, the phototherapy device of the present invention realizes higher-intensity illumination and has higher penetration depth in tissues. The phototherapy device of the present invention enhances activity of macrophages through an appropriate light mode, accelerates removal of necrotic debris of tissues and cells at lesions of a body while enhancing activity of microglial cells and promoting repair of the central nervous system. In addition, the phototherapy device ofthe present invention uses pulse width modulation to generate pulse light with an extremely strong transient power, thereby avoiding the problems such as small illumination area and reduced penetration depth of laser light in the tissues in infrared-type therapeutic instruments.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Application of dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells in preparing medicament for treating Alzheimer disease
PendingCN111973631ASuppress chronic inflammationReduce in quantityNervous disorderUnknown materialsMesenchymal stem cellDentistry
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, and in particular to application of dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of Alzheimer disease. According to the invention, through experimental research, it is found for the first time that transplantation of dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells can inhibit chronic inflammation of the brain, improve learning and memory capacity and movement capacity to a certain extent, reduce number of microglia in each region of the hippocampus, and effectively treat Alzheimer disease.
Owner:卡替(上海)生物技术有限公司
Compositions and methods for treating diseases and disorders of the central nervous system
PendingUS20200038439A1Improve efficiencyEnhanced drug releaseNervous disorderGenetic material ingredientsHematopoietic cellNervous system
The present invention provides compositions and methods for the treatment or prevention of a neurological disease or disorder of the central nervous system (e.g., a storage disorder, lysosomal storage disorder, neurodegenerative disease, etc.) by reconstitution of brain myeloid cell and microglia upon transplantation of hematopoietic cells enriched in microglia reconstitution potential. The invention also provides compositions and methods for ablating and reconstituting microglia.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP +3
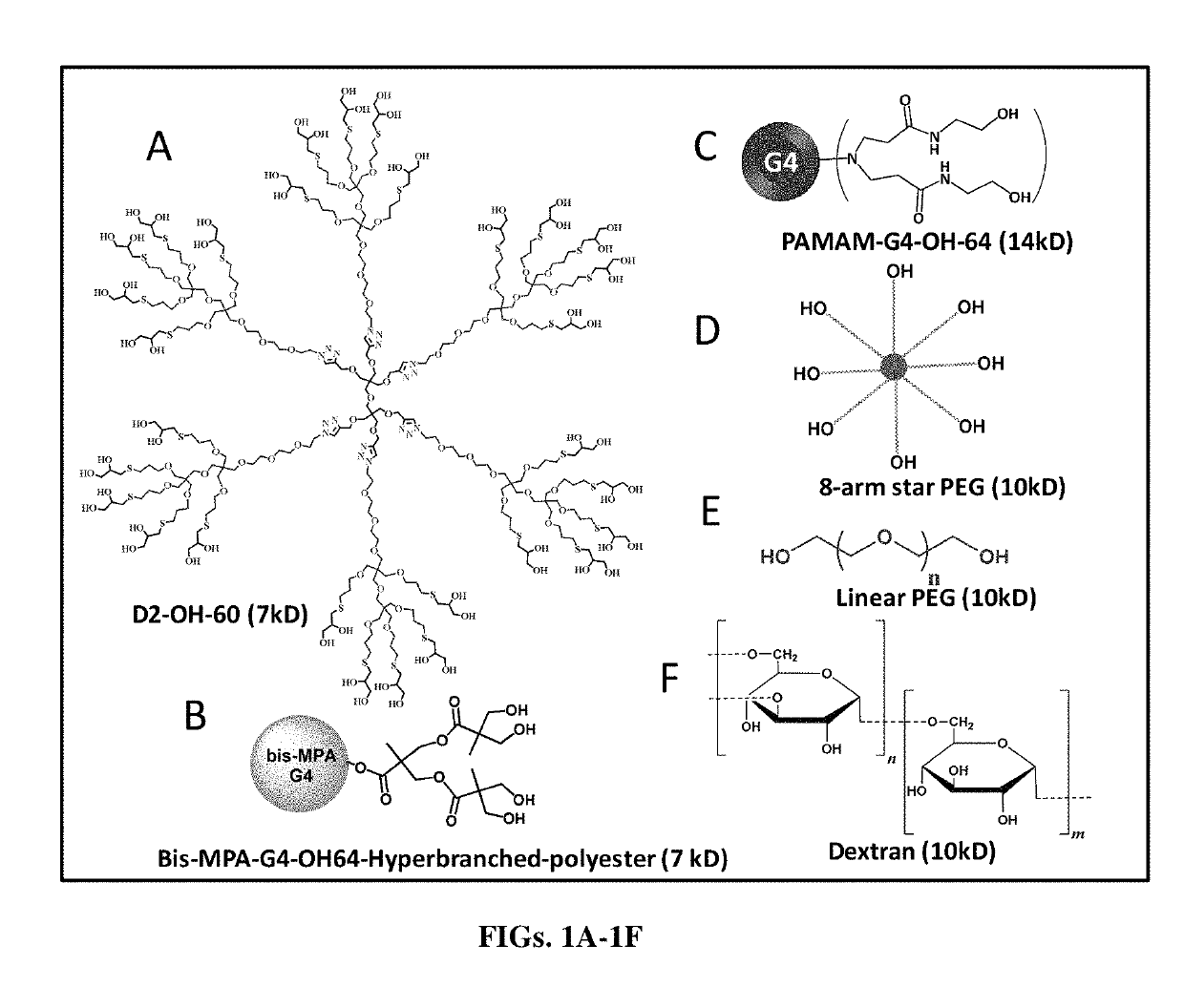
Dendrimer delivery system and methods of use thereof
PendingUS20190142964A1Many symptomPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDiseaseDendrimer
Low-generation dendrimers containing a high density of surface hydroxyl groups, and methods of synthesis thereof are provided. In particular, oligo ethylene glycol (OEG)-like dendrimers with a high surface functional groups at relatively low generations (e.g. ˜120 hydroxyls in the third generation, with a size of just 1-2 nm) is described. Dendrimer formulations including one or more prophylactic, therapeutic, and / or diagnostic agents, and methods of use thereof are also described. The formulations are suitable for topical, enteral, and / or parenteral delivery for treating one or more diseases, conditions, and injuries in the eye, the brain and nervous system (CNS), particularly those associated with pathological activation of microglia and astrocytes.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
TLR4 (Toll-like receptor) compound of targeting microglia as well as preparation method and application of compound
InactiveCN103933580AIncrease uptakeHigh transfection efficiencyNervous disorderGenetic material ingredientsCX3CR1Antiinflammatory drug
The invention discloses a TLR4 (Toll-like receptor) compound of targeting microglia as well as a preparation method and application of the compound in the pharmaceutical field, and belongs to the field of biomedicine. The compound is formed by binding fusion peptide of Q9 peptide (QQQKKKKKK) and T9 peptide (LTQQVVMKF) and TLR4RNAi through an electrostatic interaction; through a guiding function of the Q9 peptide, the compound can specifically target a specific CX3CR1 receptor on the surface of the microglia; when the T9 peptide acts with the CX3CR1 receptor, the TLR4RNAi is efficiently transfected into the microglia to inhibit activation of the microglia, so as to inhibit an inflammatory reaction after microglia mediated cerebral hemorrhage; the compound can be used for preparing microglia mediated anti-inflammatory drugs, and has good development and application prospects in the field of cerebral hemorrhage treatment.
Owner:中国人民解放军南京军区福州总医院四七六医院
Recombinant mutant adeno-associated virus capable of efficiently infecting primary microglial cells and related biological material of recombinant mutant adeno-associated virus
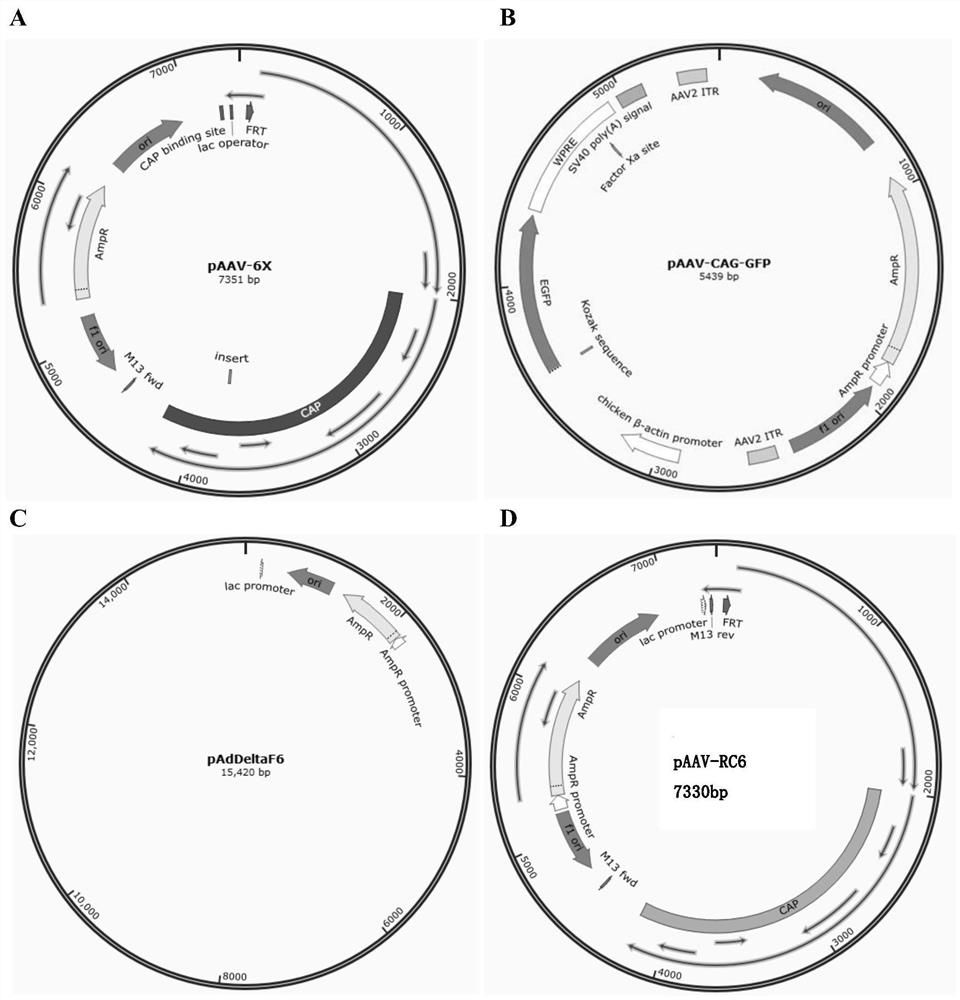
ActiveCN112813037AHigh infection efficiencyImprove infection abilityVirus peptidesMicroorganism based processesBiological materialsCapsid
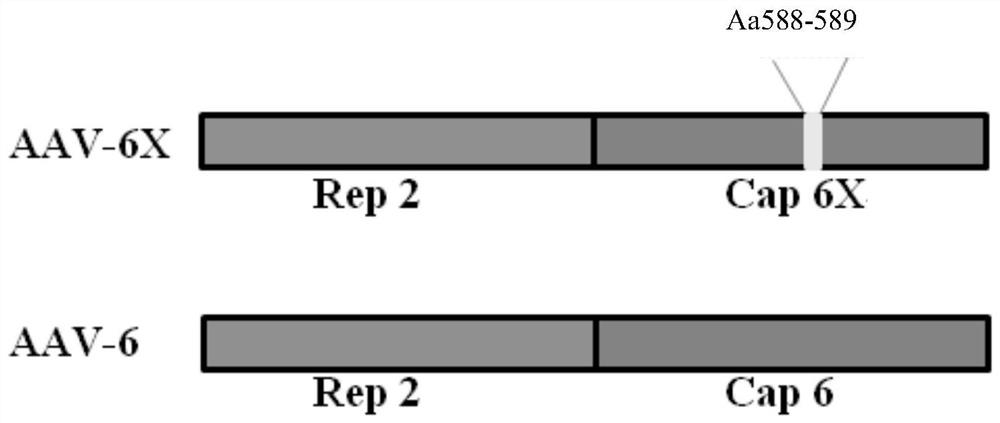
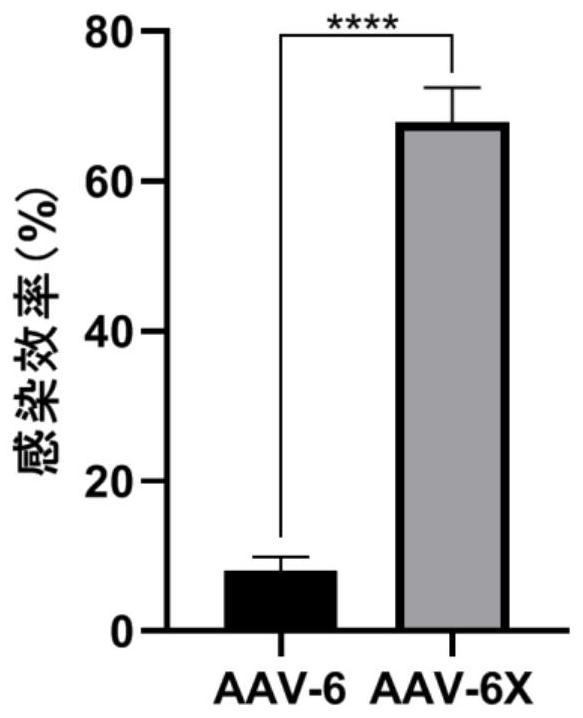
The invention discloses a recombinant mutant adeno-associated virus capable of efficiently infecting primary microglial cells and a related biological material of the recombinant mutant adeno-associated virus. The recombinant adeno-associated virus is an adeno-associated virus for expressing AAV-6X type capsid protein, and the AAV-6X type capsid protein is protein with an amino acid sequence as shown in a sequence 4 in a sequence table. According to the recombinant mutant adeno-associated virus, wild AAV-6 type capsid protein is subjected to the following mutation to obtain the mutated AAV-6 type capsid protein: seven amino acid residues are inserted between the 588 site and the 589 site of the amino acid sequence of the AAV-6 type capsid protein. The efficiency of in-vitro microglial cell infection of the recombinant adeno-associated virus rAAV-6X (expressing the AAV-6X type capsid protein) is 8 times that of the recombinant adeno-associated virus rAAV-6 (expressing the wild type AAV-6 type capsid protein). The recombinant adeno-associated virus provided by the invention is an rAAV vector for efficiently transducing the microglial cells.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Targeting polypeptide-gene composite as well as preparation method and application of composite
InactiveCN103007293ADoes not affect natural activityInhibitionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseNervous system
The invention discloses a targeting polypeptide-gene composite. The composite is formed by a binding fusion protein of HIV-Tat (49-57) peptide (RKKRRQRRR) (Human Immunodeficiency Virus Trans-activator of Transcription) and V9 peptide (LTQQMKFVV) and an HIF-1alphashRNA (Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1alpha Short Hairpin Ribonucleic Acid) carrier by means of electrostatic interaction; the composite can use the guide effect of the V9 (CX3C-chemokine receptor 1) receptor on the surface of microglia, and, at the same time when the V9 peptide and the CX3CR1 receptor act with each other, the HIF-1alphashRNA is efficiently transfected into the microglia to interfere with the HIF-1alpha (Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1alpha) expression and inhibit the microglia activation so as to further inhibit the occurrence and progression of a microglia-mediated central nervous system disease. The composite can be applied to the preparation of a medicine for treating the microglia-mediated central nervous system disease and has good development and application prospect in the field of treating the nervous system disease.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
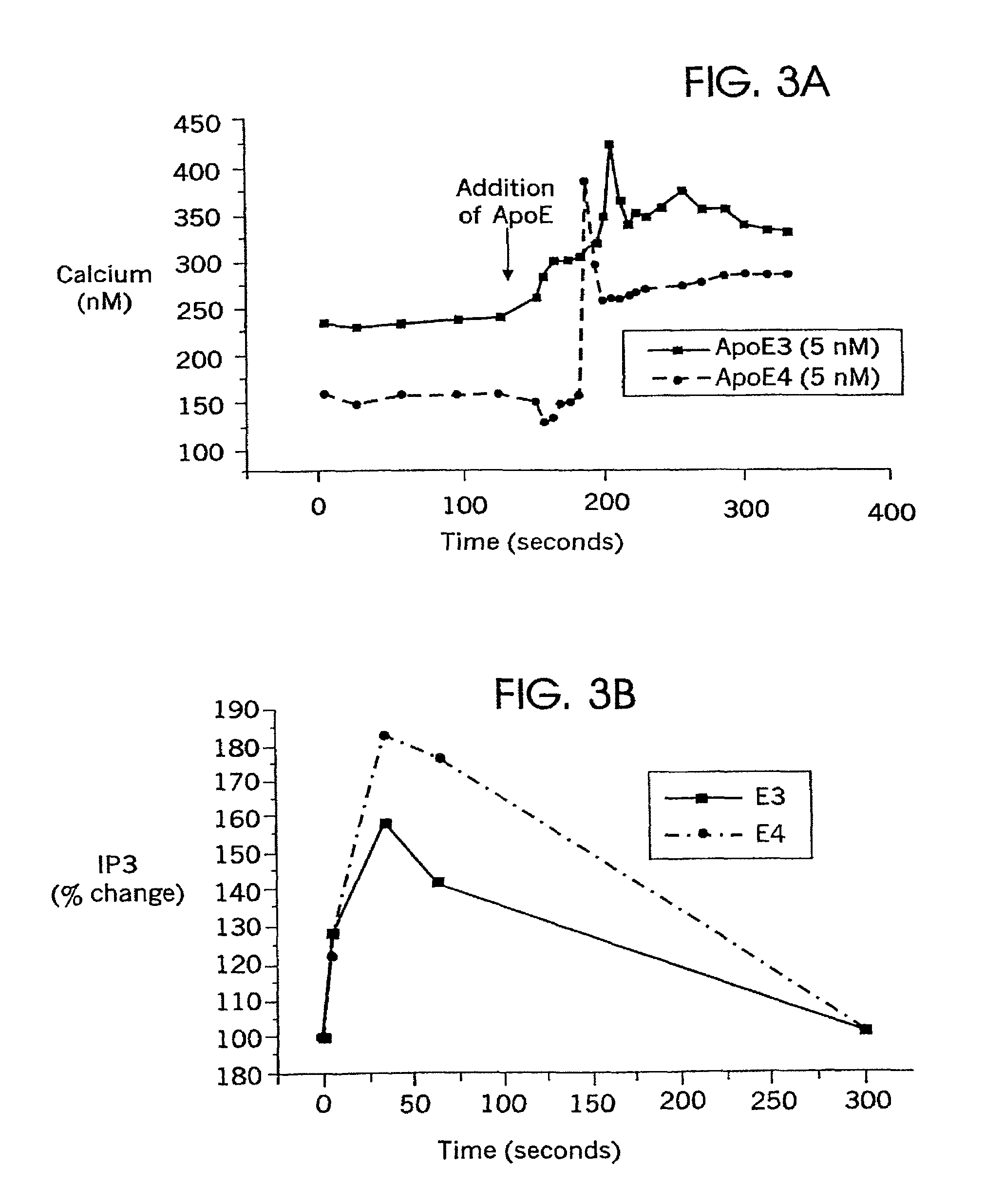
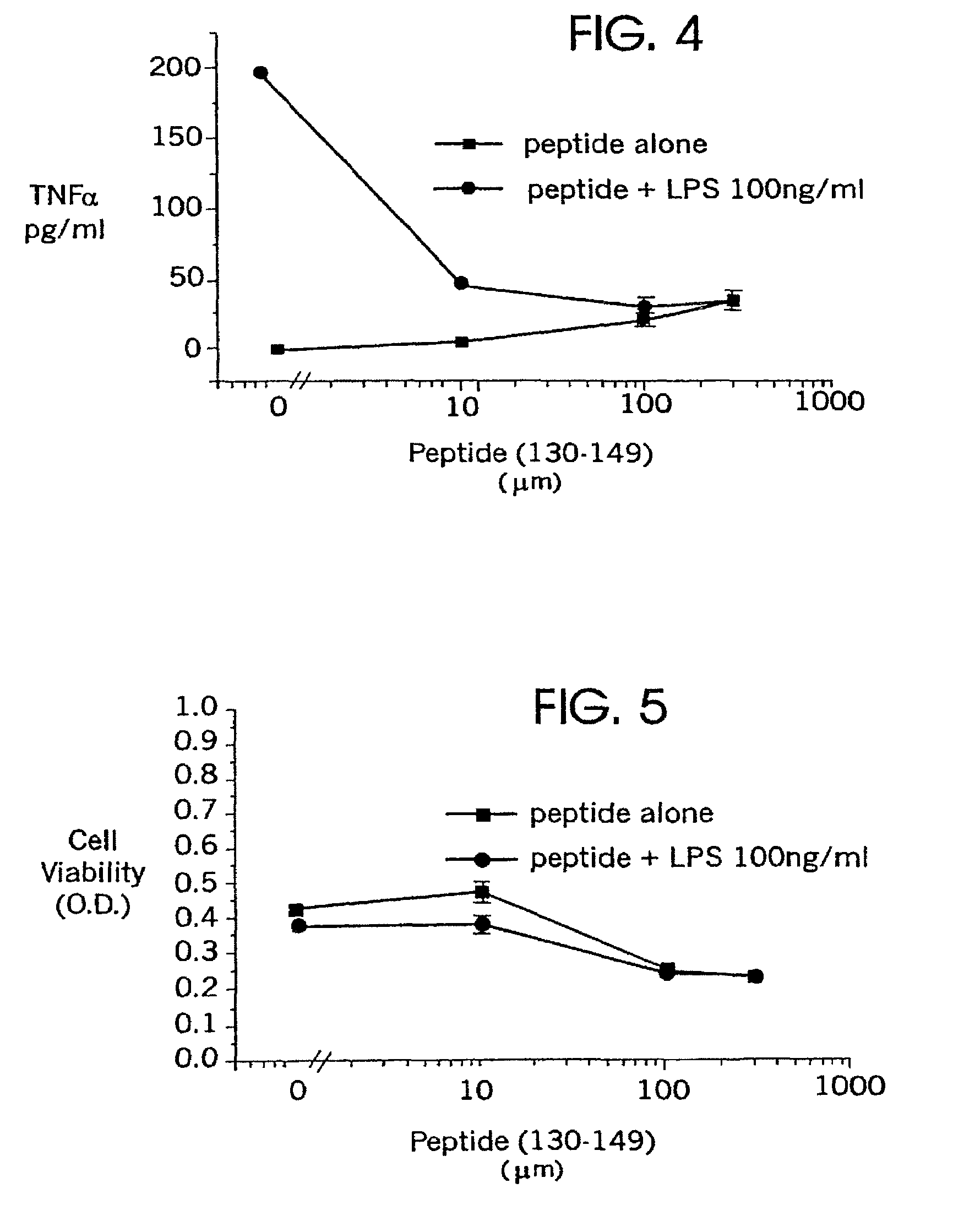
Methods of suppressing microglial activation and systemic inflammatory responses
Methods of suppressing the activation of microglial cells in the Central Nervous System (CNS), methods of ameliorating or treating the neurological effects of cerebral ischemia or cerebral inflammation, and methods of combating specific diseases that affect the CNS by administering a compound that binds to microglial receptors and prevents or reduces microglial activation are described. ApoE receptor binding peptides that may be used in the methods of the invention are also described, as are methods of using such peptides to treat peripheral inflammatory conditions such as sepsis. Also described are methods of screening compounds for the ability to suppress or reduce microglial activation.
Owner:CORNERSTONE BIOSCI INC
Zebra fish brain trauma model and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110178757APromote repairGood prospectsClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaDiseaseEmbryo
The invention discloses a zebra fish brain trauma model and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the zebra fish brain trauma model includes the steps that for an embryo in the 3dpf period, a needle is used for puncturing the hindbrain of a zebra fish, and microglial cells of the hindbrain of the zebra fish are labeled with fluorescent protein. After clinical first-line anti-inflammatory drugs are used for intervention, and more microglial cells can be activated to migrate and aggregate towards a wound part, so that injured hindbrain repairing is promoted; themicroglial-cell transgenic zebra fish brain trauma model can be used for rapid screening of drugs, so that an economical, convenient and reliable research model is provided for enterprise drug research and development and for evaluating the curative effect of the anti-inflammatory drugs in clinical brain trauma, encephalitis and other diseases, and the microglial-cell transgenic zebra fish braintrauma model has good application prospects and high application value.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGDONG MEDICAL UNIV
Application of butylphthalide and derivatives thereof in preparation of medicines for preventing and treating ALS
ActiveCN102397272BDelayed onset timeProlong lifeOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDegenerative changeButylphthalide
The invention which relates to the medicinal field discloses an application of butylphthalide and derivatives thereof in the preparation of medicines for preventing and treating ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis). Butylphthalide and the derivatives, which can delay the disease time of an SOD1-G93A transgenic mouse, prolong the lifetime of the mouse, reduce the degenerative change of spinal motorneurons, obviously increase the survival number of spinal anterior horn motor neurons of the mouse, reduce the electrophysiological abnormality of the transgenic mouse, obviously improve the action potential amplitude and the motion unit number of compound muscles, substantially inhibit the activation of astrocytes and microglial cells in the spinal cord of the mouse, and obviously reduce the expression level of iNOS and NF-kappaBp65, have good application prospects in the prevention and the treatment of the ALS.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG PHARMA GRP NBP PHARMA CO LTD
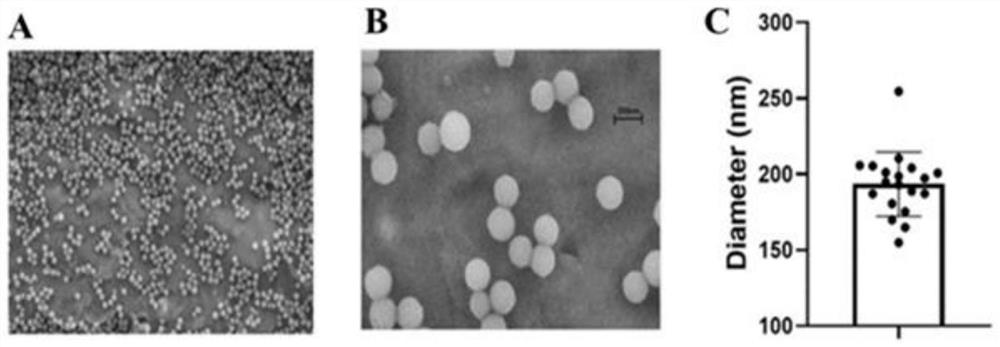
Nano-drug for preventing or treating cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury as well as preparation method and application of nano-drug
ActiveCN112370436AGood dispersionNo obvious aggregationOrganic active ingredientsMicrocapsulesDiseaseCerebral ischaemia
The invention relates to a nano-drug for preventing or treating cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury as well as a preparation method and application of the nano-drug. Cerebral ischemia is a cerebrovascular disease which has the greatest threat to human beings, and oxidative injury, inflammatory response and subsequent excitotoxic cell death can be caused by reperfusion as soon as possible. According to the nano-drug, dopamine is oxidized under an alkaline condition to form dopamine quinone, the dopamine quinone is further oxidized to form polydopamine nanoparticles with supramolecular structures, the formed particles are smooth and round in surface, good in sphericity degree and uniform in particle size distribution, a good dispersion state is kept in a solution, and through in-vitro and in-vivo experiments, the polydopamine nanoparticles prove the biological safety. Application of the polydopamine nanoparticles to a cerebral ischemia model shows that the polydopamine nanoparticles canrelieve cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury, inhibit inflammatory reaction, inhibit activation of an NF-kappa B signal channel and inhibit excessive activation of microglial cells, and have the potential of inhibiting cerebral inflammatory reaction and relieving cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Application of inhibitor SB (Sodium Butyrate) 203580 of p (phosphor) -p38
The invention aims to provide application of an inhibitor SB (Sodium Butyrate) 203580 of p (phosphor)-p38. Activation of phosphor-p38 mediated microglial cells contributes to pain correlated responses of a pain model of BmKI (Biomedical Knowledge Integration); the specific inhibitor SB 203580 of the p-p38 can inhibit the microglial cell and thus relieving the pain correlated responses in the pain model of the BmKI. The invention provides a theoretical basis for pain central sensitization induced by peripheral damages, a study carrier for studying cellular and molecular mechanisms and treatment strategies of nociception and an experimental basis for studying novel drugs for relieving the pain on clinic are provided. The SB 203580 has a prospect of becoming a tool medicine applied in studying correlated pain mechanism of p38 signal path and then has a potential prospect of developing drugs for treating and relieving pathological pain and maintaining corresponding drugs on clinic.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Application of saikoside compounds in preparation of drug for treating neurodegenerative diseases
ActiveCN105079016AInhibition releaseElevated preference indexOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMedicineNeuroinflammation
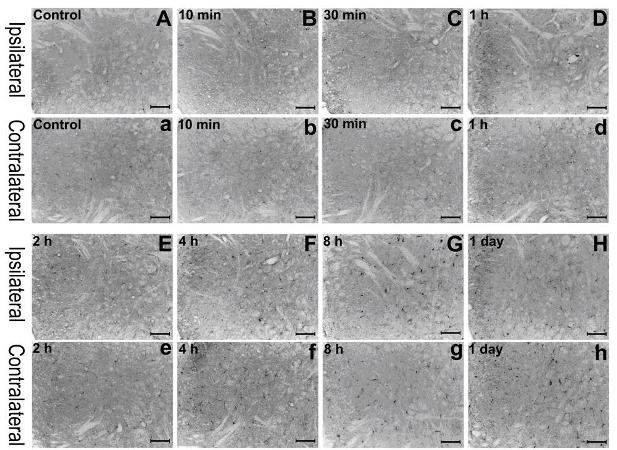
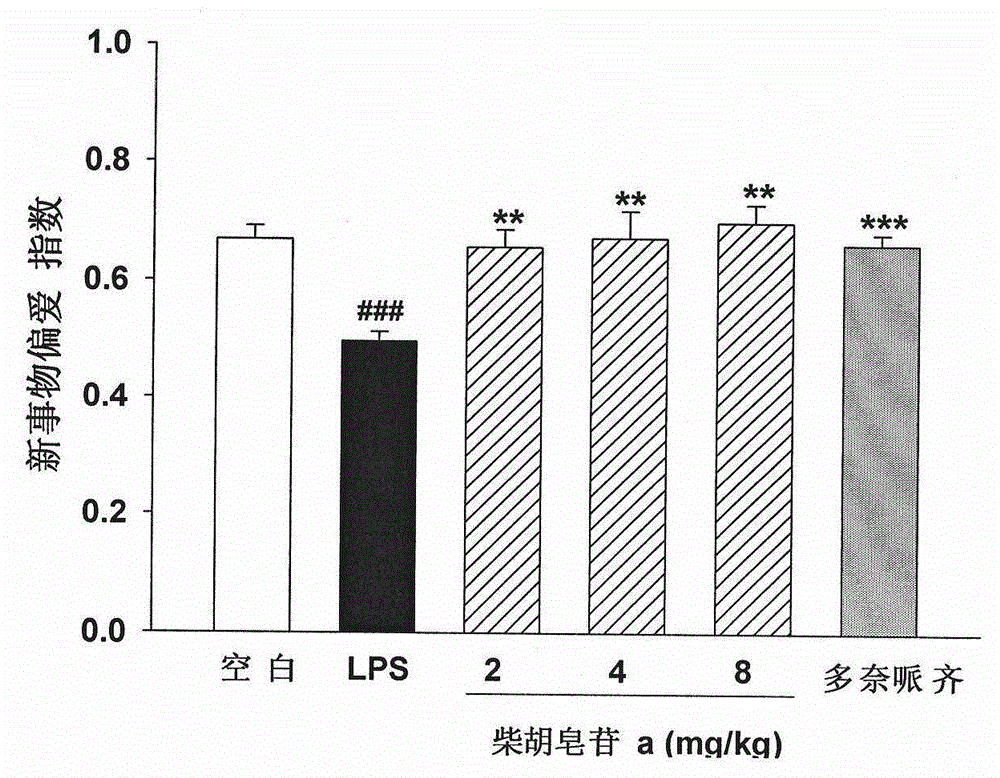
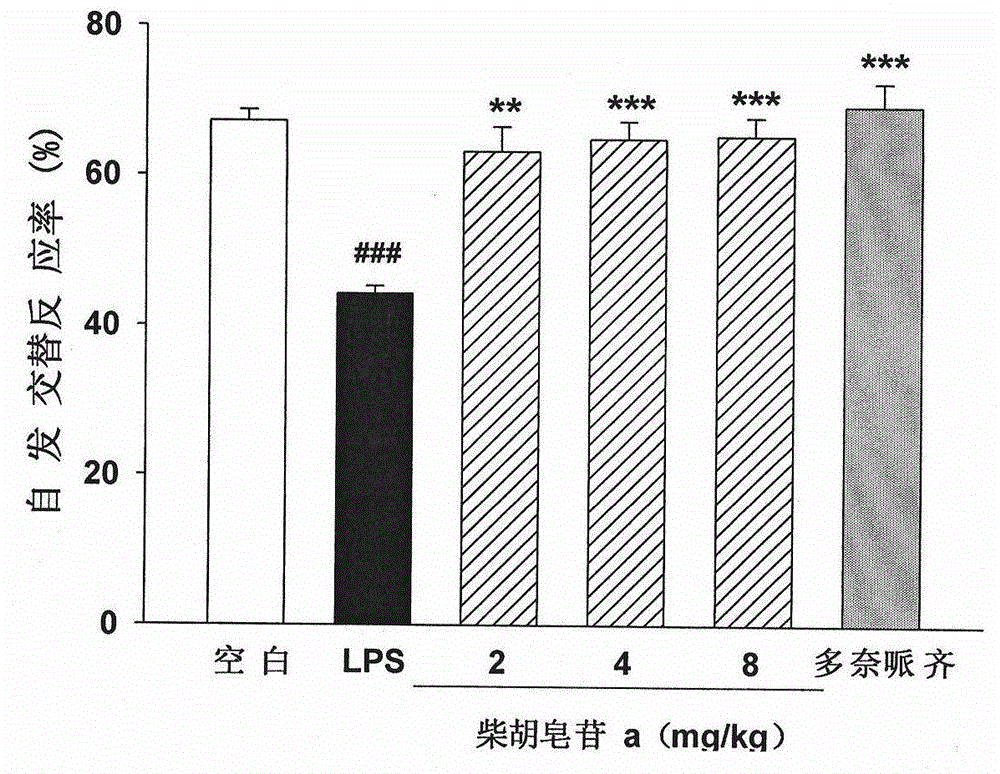
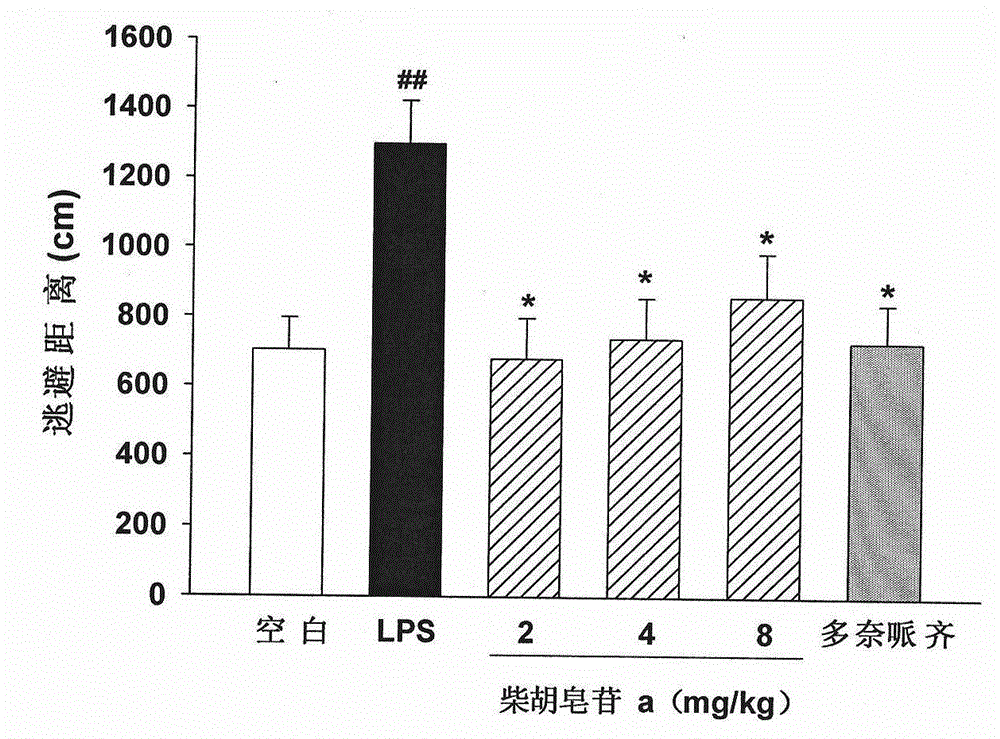
The invention discloses application of saikoside compounds in preparation of drug for treating neurodegenerative diseases. Five saikoside compounds are saikoside a, saikoside b1, saikoside b2, saikoside c and saikoside d which can remarkably inhibit release of LPS-induced microglial cell inflammation factors NO and ROS, and saikoside a can obviously shorten escape latency and escape distance of mice with LPS-induced learning memory impairment; in a nesting experiment, saikoside a can obviously enhance nesting ability of the mice with the LPS-induced mice with learning memory impairment. The above results show that saikoside a has obvious protecting effect on LPS-induced AD mouse learning memory impairment. Consequently, saikoside a, b1, b2, c and d can be used for treating the neurodegenerative diseases and inhibiting neuroinflammation.
Owner:NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
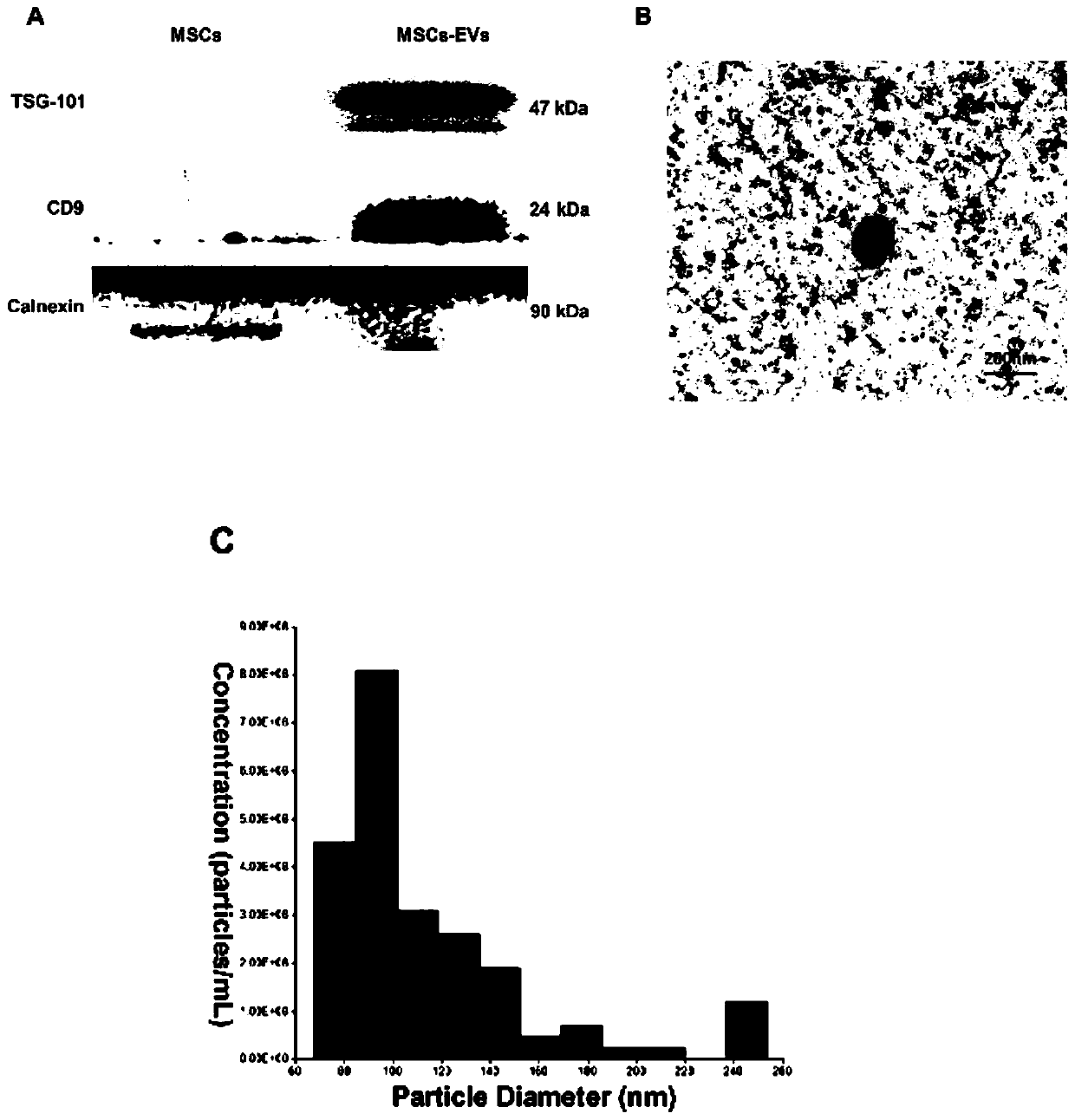
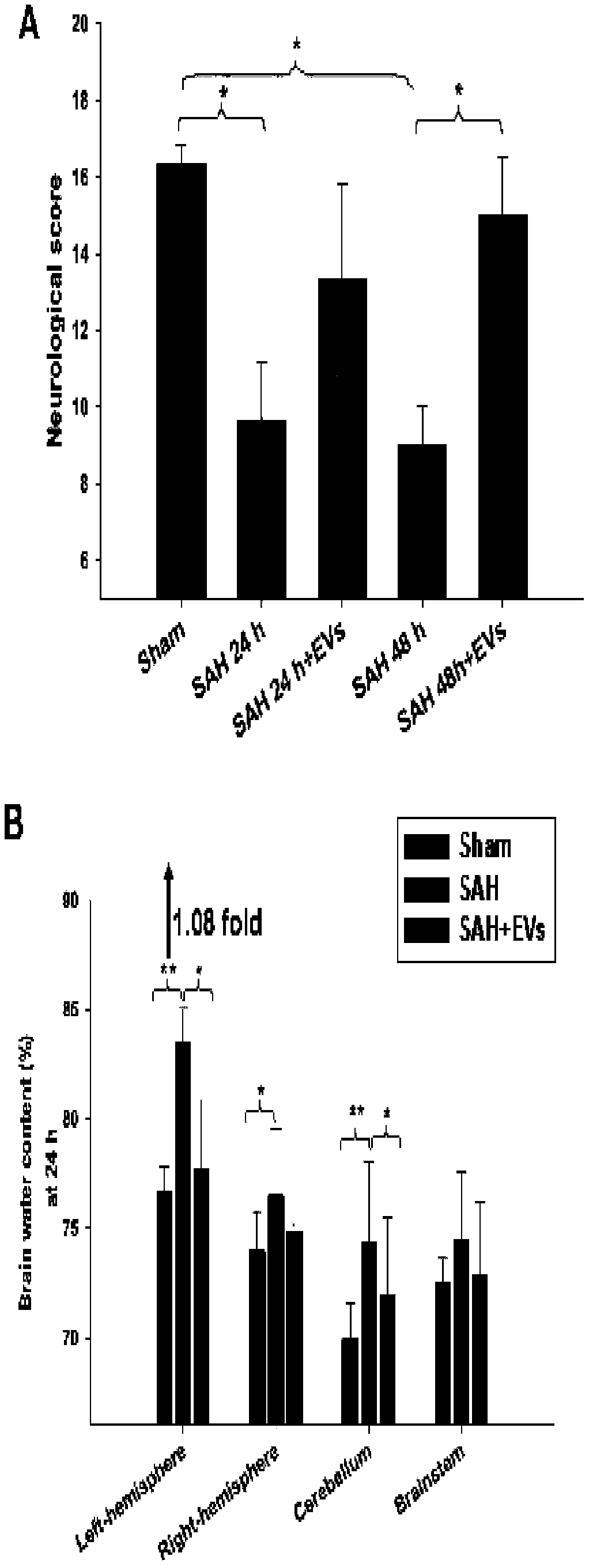
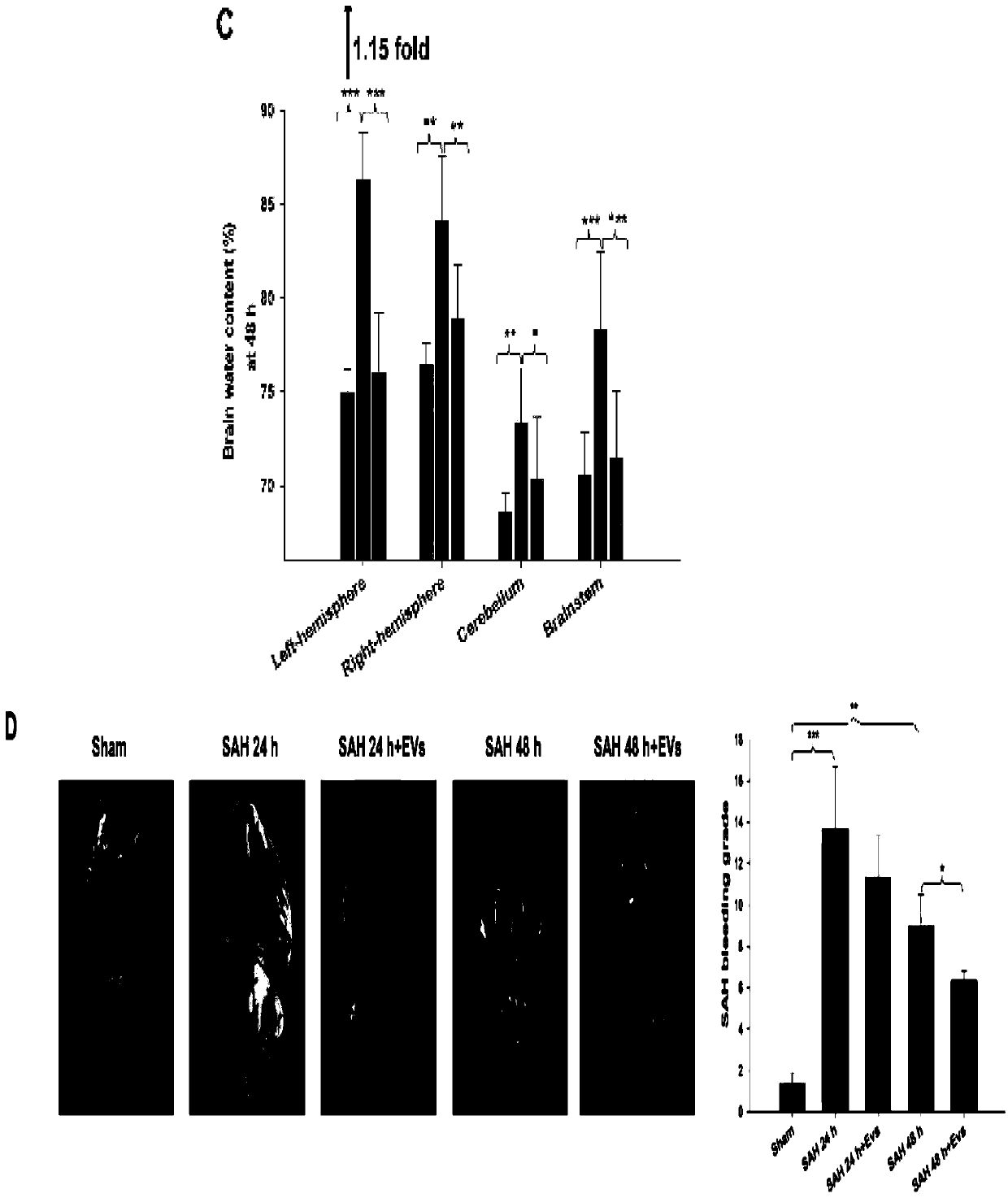
Application of extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of subarachnoid hemorrhage
ActiveCN110755450APromote phenotypic transformationImproved prognosisNervous disorderAntipyreticNeurological impairmentCell
The invention provides an application of extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of subarachnoid hemorrhage, which belongs to the technical field of molecular biology.The MSCs extracellular vesicles (MSCs-EVs) have the effects of relieving SAH complications, and improving prognosis and the like. Specifically, the MSCs-EVs can effectively improve the neuroinflammation reaction after subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), promote the phenotypic transformation of microglial cells to M2, and relieve the symptoms of neurological impairment, cerebral water content increase and the like caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV QILU HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com