Nitrogen gate containing silicon oxide layer structure of semiconductor device and preparation technique
A gate silicon oxide, manufacturing process technology, used in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, electrical components, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
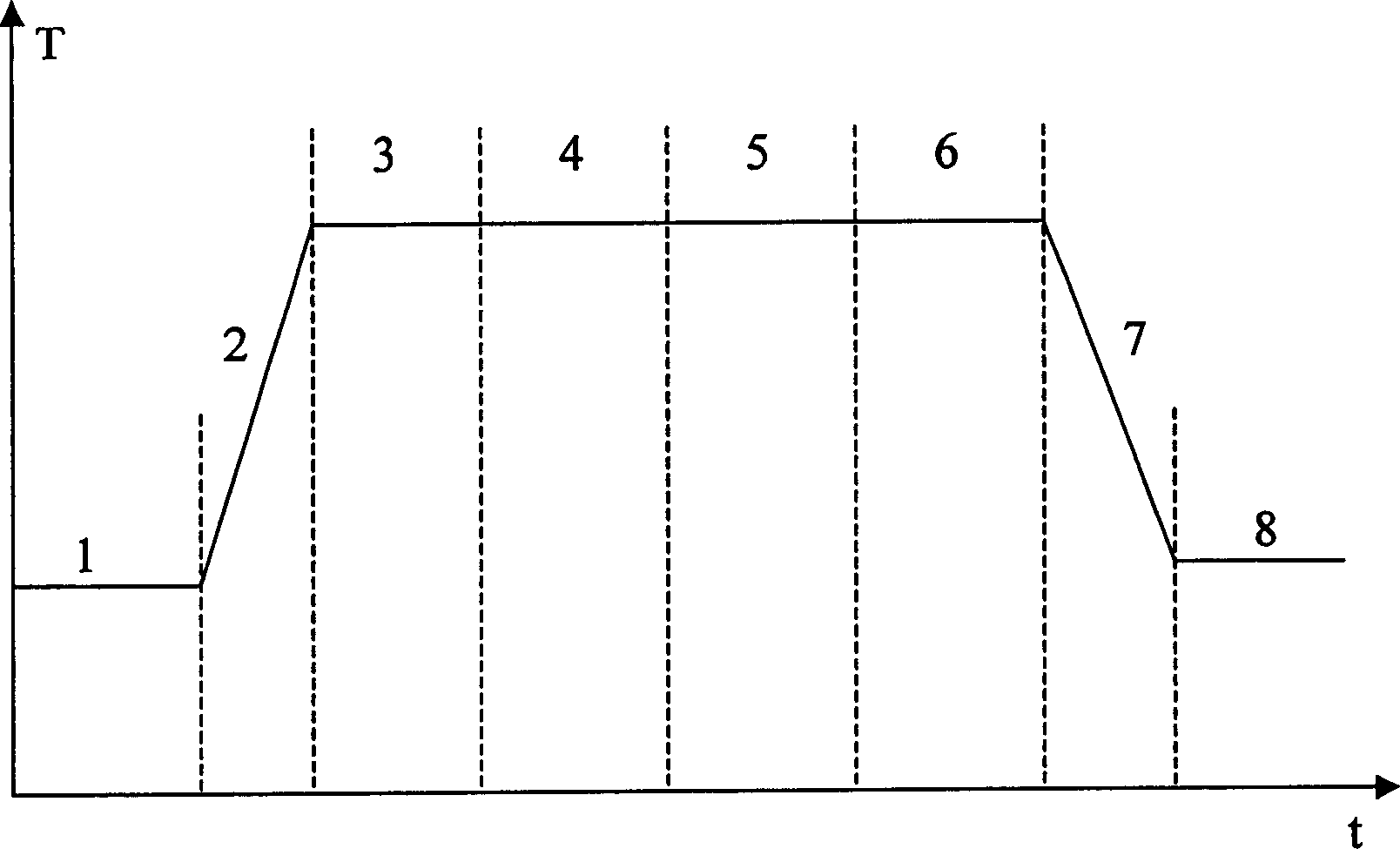
[0020] With rapid annealing oven (RTO), under normal pressure or reduced pressure
[0021] 1. In NO gas, at a temperature of 1000° C., grow a thin layer of silicon oxynitride (SiON) on the surface of a clean silicon wafer with a thickness of 8 Å.
[0022] 2. Turn off the NO gas and replace it with pure oxygen (O 2 ) gas, in this pure oxygen gas, the silicon wafer is further oxidized, that is, a thin silicon oxide (SiO) layer is grown under the newly grown SiON film, and its thickness is about 15 Å;
[0023] 3. Close O 2 Gas, then use NO gas, and anneal in this NO gas, so that a small amount of N in the NO gas diffuses to the interface between silicon oxide and silicon, forming a thin SiON interface layer with a thickness of about 3 Å;
[0024] 4. In order to further improve the quality of this gate silicon oxide, turn off the NO gas and replace it with O 2 Gas, so that the gate silicon oxide grown on it is further in O 2 Annealing in the gas for 30 seconds pushes the N ele...
Embodiment 2
[0026] 1. Using a rapid annealing furnace (RTO), under normal pressure or reduced pressure, in NO gas, at a temperature of 800°C, grow a layer of SiON on a silicon wafer with a thickness of 5 Å.
[0027] 2. Turn off the NO gas and replace it with O 2 gas to further oxidize the silicon wafer, and grow a layer of SiO under SiON with a thickness of 3 Å;
[0028] 3. Close O 2 Gas, and then replaced with NO gas, annealed in NO gas to form a SiON interface layer with a thickness of 7 Å;
[0029] 4. Turn off the NO gas and replace it with O 2 Gas, the grown gate silicon oxide will be further in O 2 Annealing in the gas for 10 seconds pushes the N element distributed on the silicon oxide-silicon interface away from the silicon surface by about 5 Å.
Embodiment 3
[0031] 1. Using a rapid annealing furnace (RTO), under normal pressure or reduced pressure, in NO gas, at a temperature of 1100°C, grow a layer of SiON on a silicon wafer with a thickness of 20 Å.
[0032] 2. Turn off the NO gas and replace it with pure oxygen gas, and grow a layer of SiO under the grown SiON film in oxygen, with a thickness of 10 Å;
[0033] 3. Close O 2 Gas, and then replaced with NO gas, annealed in NO gas, so that a small amount of NO gas diffuses to the interface between silicon oxide and silicon, forming a SiON interface layer with a thickness of 10 Å;
[0034] 4. Turn off the NO gas and replace it with O 2 or N 2 gas, making the gate silicon oxide further in O 2 or N 2 Annealing in the gas for 50 seconds pushes the N element distributed on the silicon oxide-silicon interface away from the silicon surface by about 3 Å.
[0035] The nitrogen-containing gate silicon oxide layers prepared by the above examples all have good performance, which can effec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com