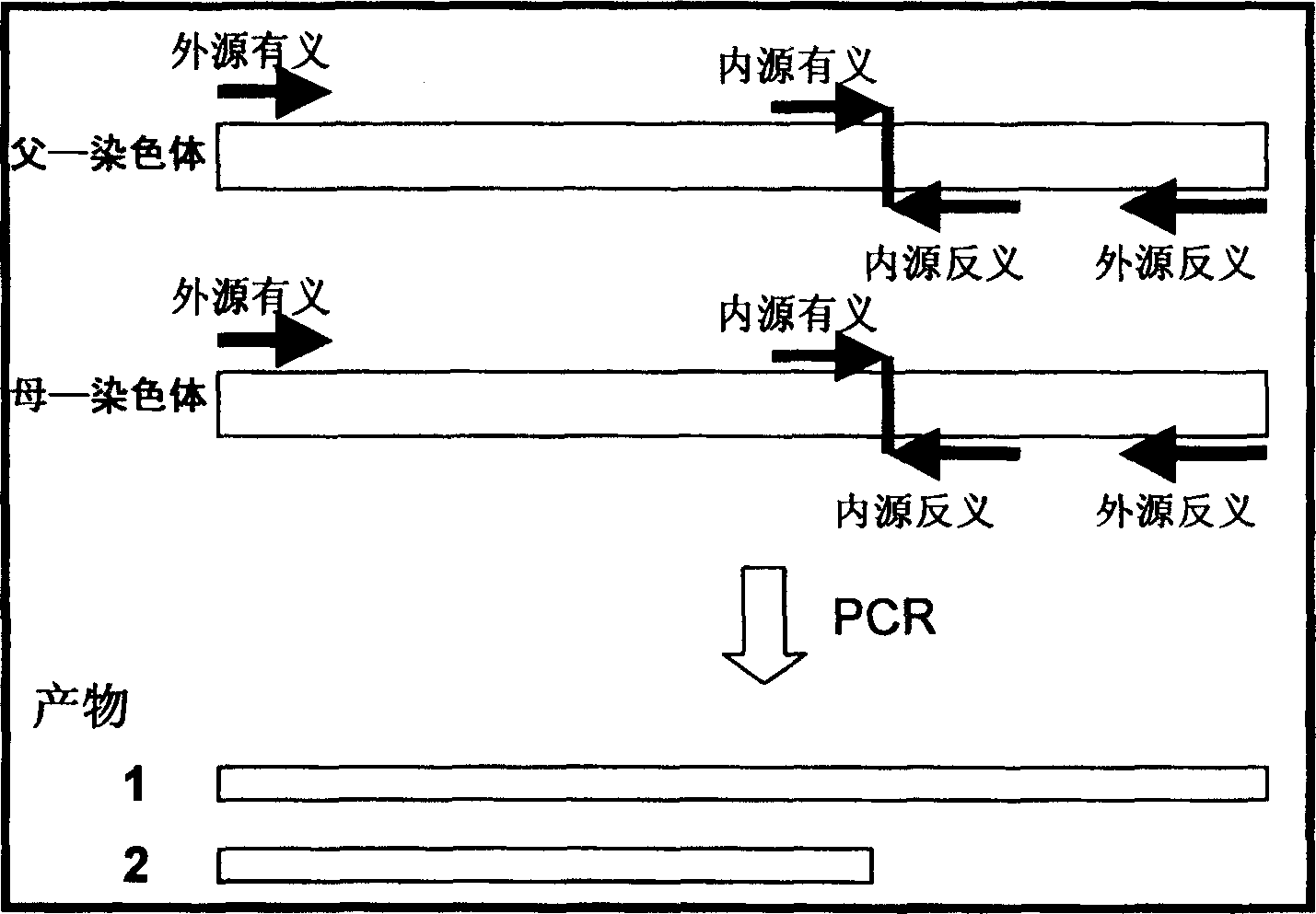
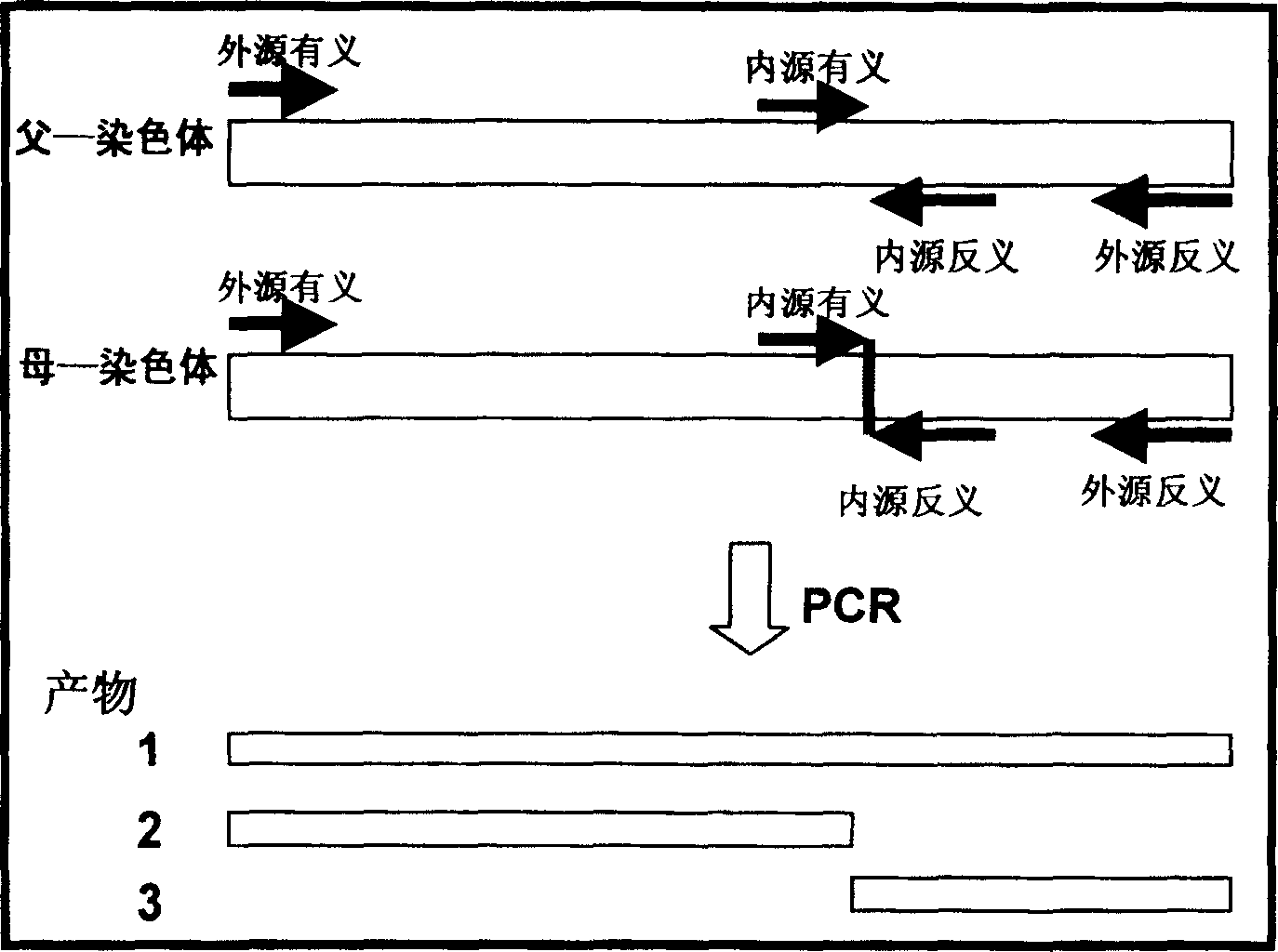
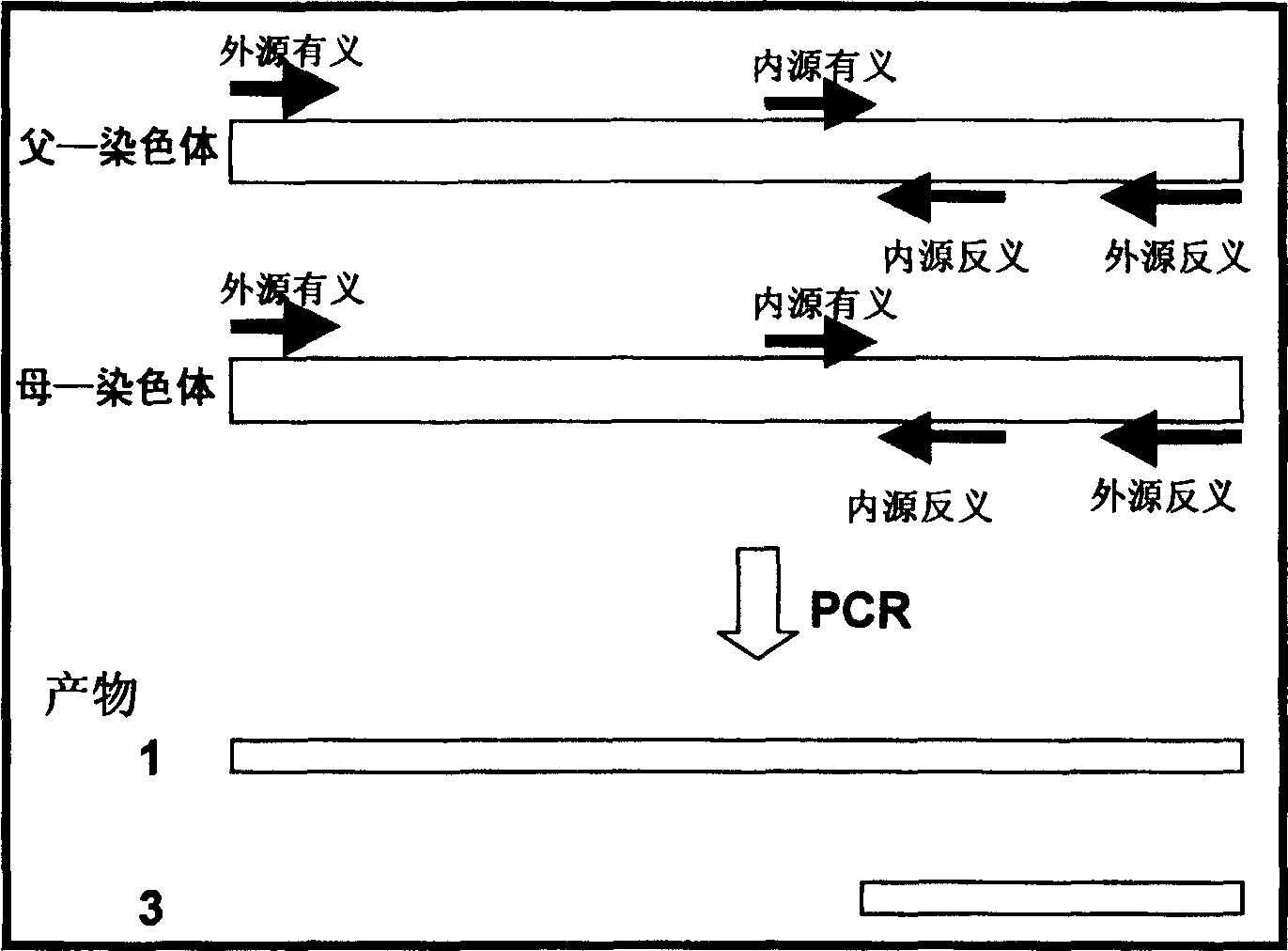
Fast method for detecting gene point mutation of receptor of epidermal growth factor lung cancer in non-cellule type
A technology of epidermal growth factor and non-small cells, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as time-consuming, difficult to popularize and apply, and expensive equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0077] Embodiment: a method for rapidly detecting a point mutation of epidermal growth factor receptor gene in non-small cell lung cancer, comprising the following steps:
[0078] The first step, tumor tissue genomic DNA sample preparation
[0079] The first fresh or formalin-treated tissue:
[0080] Reagent preparation:
[0081] Buffer solution: 50mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0
[0082] 20mM NaCl
[0083] 1 mM EDTA
[0084] 1% SDS
[0085] 10mg / ml proteinase K (Proteinase K): 10mg Proteinase K is dissolved in 1mlddH2O. Aliquot and store at -20°C. When in use, melt at 4°C. (It is best to use it now).
[0086] (1) Take a small amount of tissue (≤1 / 4 of the rice grain), add it to 20uL of the above solution (can be frozen), and then add 1uL of 10mg / ml proteinase K.
[0087] (2) Incubate at 55°C for 15 minutes, Vortex, and incubate for another 15 minutes. (PCR tubes can be used to complete on the PCR machine). Add double distilled water to 200uL.
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com