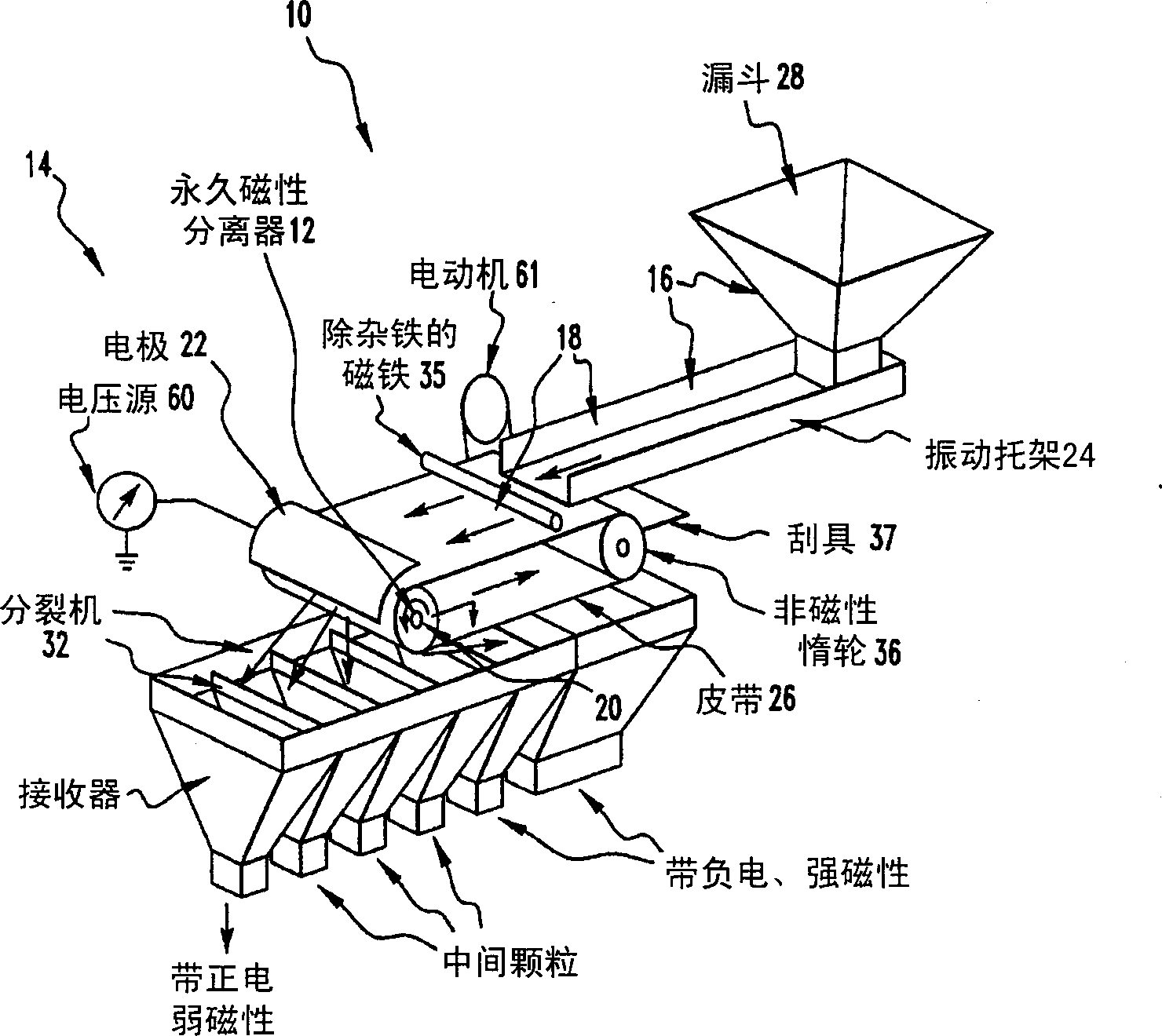
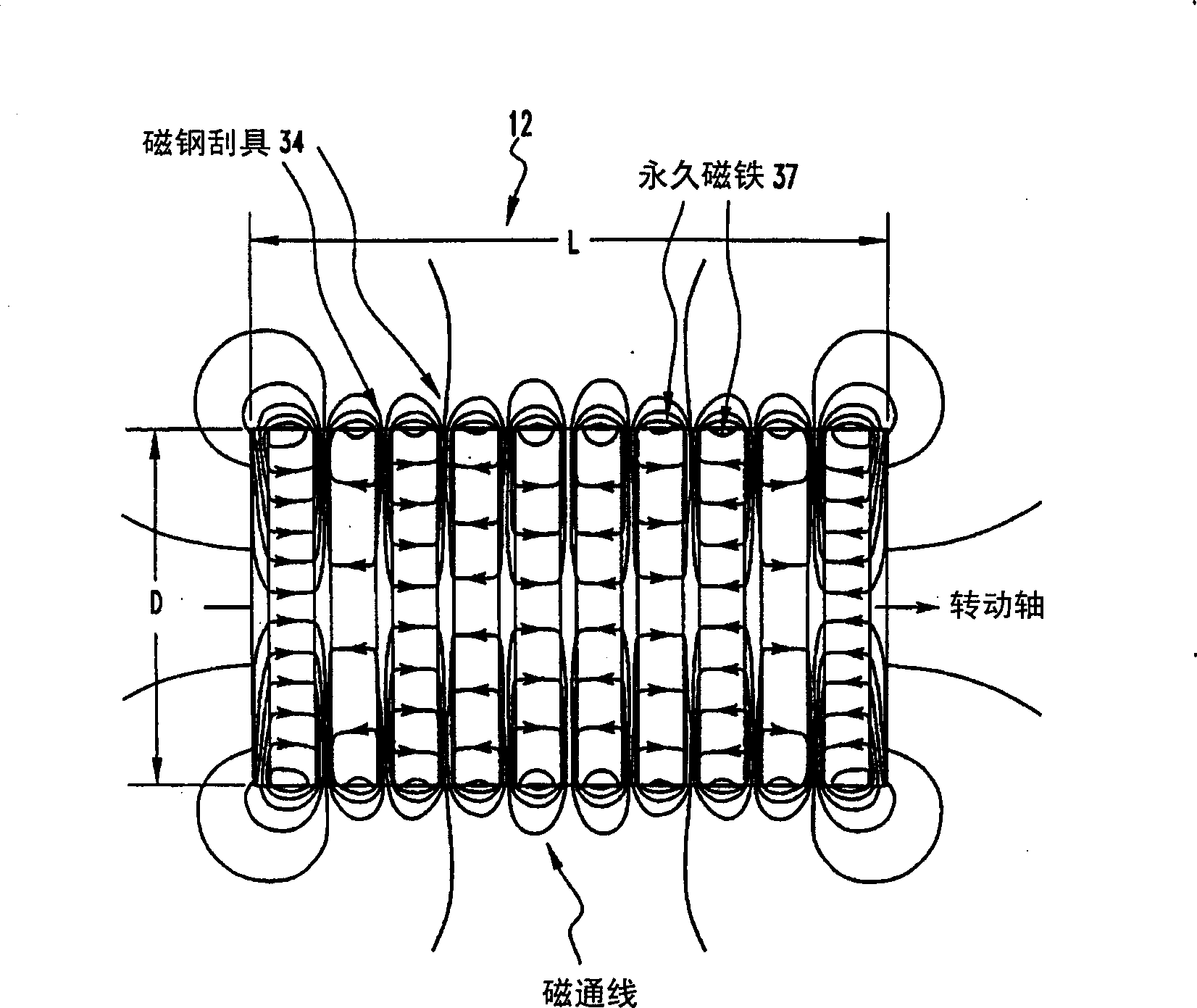
Method and apparatus for sorting particles with electric and magnetic forces
A magnetic separation and particle technology, applied in magnetic separation, chemical instruments and methods, Lorentz force separation, etc., can solve the problems that electrostatic technology cannot adapt to scale and limitations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0050] The magnetic susceptibility was measured using a modified Goyo balance. (The unit of magnetic susceptibility used below is 10 -6 cm 3 / g, the unit is multiplied by 4π×10 -3 can be converted into the international standard unit m 3 / kg. ) to measure unburned carbon and loss on ignition (LOI) by ashing using a muffle furnace. Sulfur content was determined using a Leco S32 sulfur determiner. ASTM procedures D-3174-82 and D-4239-83 were used for the measurement of ash and sulfur, respectively. Measurements of the LOI were performed according to standard procedure 2520. Determine the weight using an analytical balance with a resolution of 1 / 10 mg. Example 1: Effect of Charge
[0051] Coal particles with a nominal diameter of 0.3-0.6 mm are used to illustrate the effect of friction, triboelectric and capacitive charges, electric field strength, magnetic force and angular velocity on the magnetic separation of an electromagnetic separator. Individual particles can be ...
example 2
[0077] It is clear that the additional application of an electric field in addition to the magnetic force improves the performance of the magnetic separator. Polarity is determined by the triboelectric charge of the particles to be collected at the magnet surface. Example 2: Purified coal.
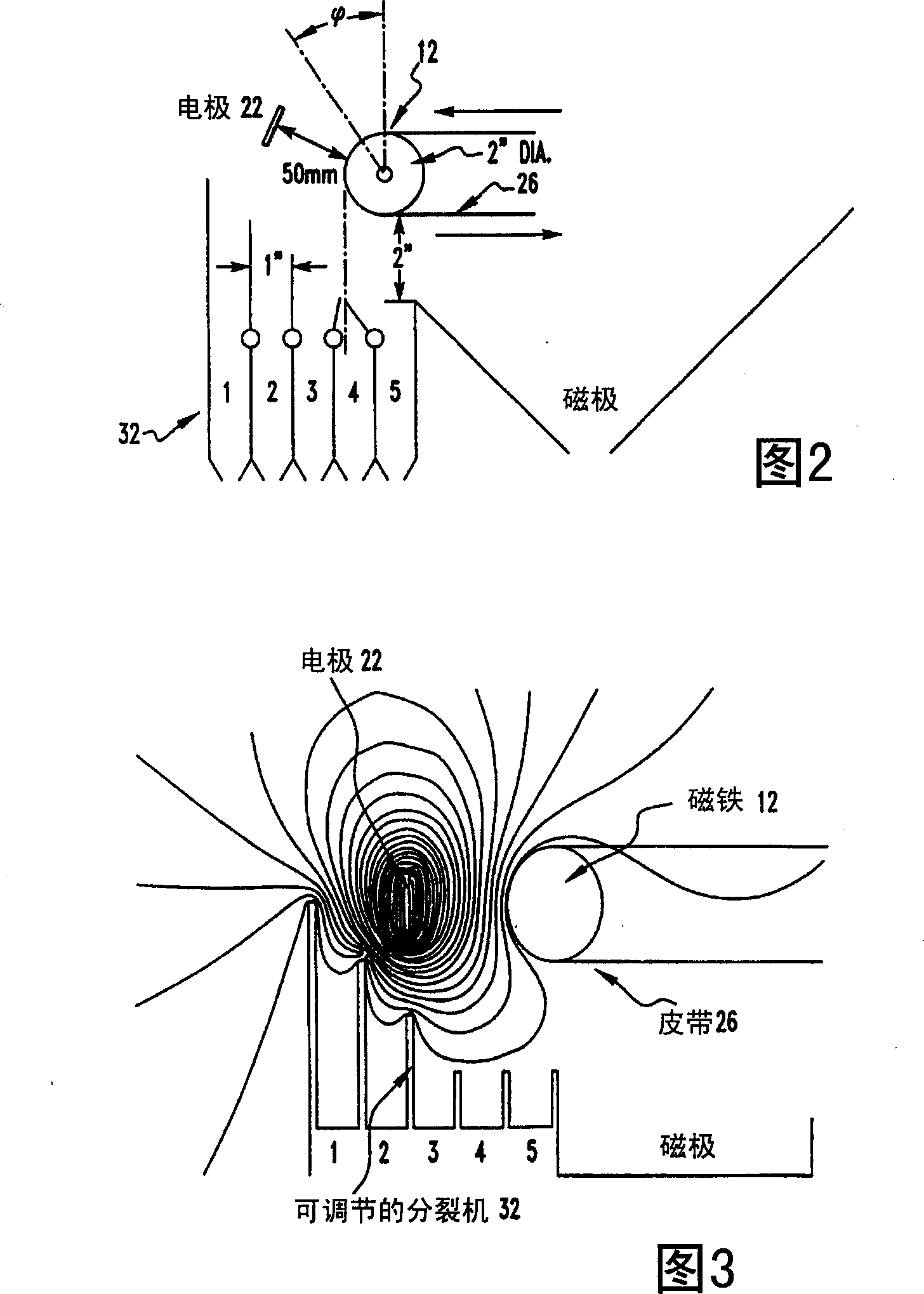
[0078] The test coal used was a low kittaning coal from Clearfield County, PA, containing 26.06% ash, 7.08% sulfur, a magnetic susceptibility of 133, and contained 0.58% moisture by weight. Particle sizes range from 0.074-1.19 mm in diameter. The coal was fed into an experimental electromagnetic separator at a rate of 116.3 pounds per hour and processed with 0 and ±5000 volts applied to a magnet rotating at 100 RPM. Splitter No. 1, which separates receivers 1 and 2, is 6.74 cm in front of this belt. Splitter No. 2, which separates receivers 2 and 3, is 1.66 cm in front of this belt. Splitter No. 3, which separates receivers 3 and 4, is 1.16 cm in front of this belt. Splitter No. 4, wh...
example 3
[0082] Applying a magnetic field such that the magnet surface is positive with respect to the outer electrode 22 results in a higher rate of reduction of ash and sulfur at a constant Btu recovery rate when compared to operation where the applied voltage difference is zero. When the magnet surface is negative with respect to the external electrode 22, the reduction rate of ash and sulfur is lower. The carbonaceous constituents of the test coal had a positive triboelectric charge while the mineral-rich constituents had a negative triboelectric charge. Applying a positive voltage differential to the surface of the magnetic separator improves the removal of undesirable ash and sulfur containing minerals without negatively affecting the recovery of the clean coal constituents. Example 3: Activated carbon-fly ash mixture.
[0083] Activated carbon was obtained from fisher scientific. Use traditional permanent magnets to sieve carbon particles with a diameter of 74um-297um to remov...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com