Method for measuring concentrations and molecular weights of glue and gelatin
A technology of molecular weight distribution and concentration, applied in chemical instruments and methods, material separation, analysis of materials, etc., can solve the problems of glue decomposition, non-quantitative collection of glue, and difficulty in correctly evaluating the existence of glue.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Take a sample from the copper electrolyte used in copper electrolytic refining, and dilute it twice with pure water immediately after sampling. Samples (diluted) were stored in the refrigerator until analysis.
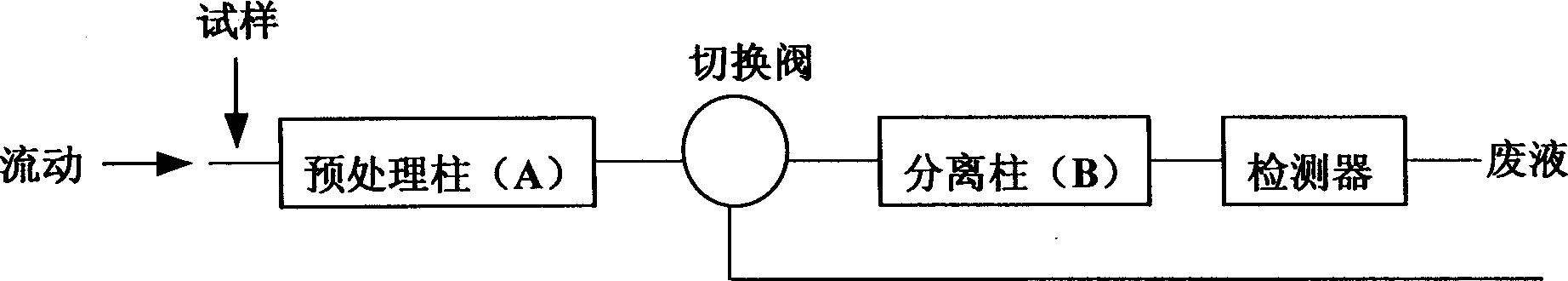
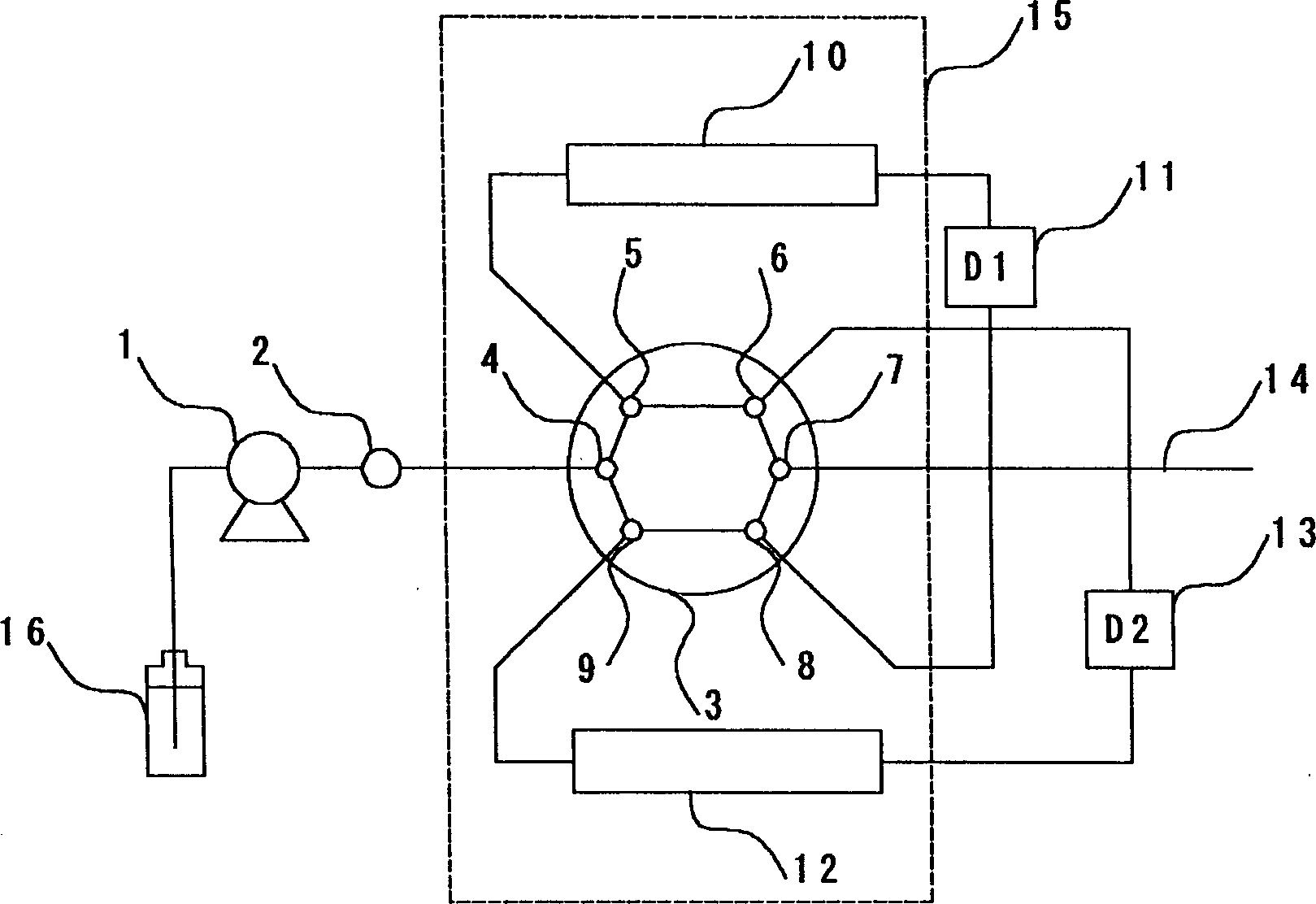
[0050] use figure 2 The instrumentation shown was analyzed where:
[0051] Mobile phase: 0.005M sulfuric acid / acetonitrile volume ratio of 95 / 5 solution.
[0052] Pretreatment column: polyetheretherketone PEEK column (inner diameter: 7.5mm, length: 250mm) filled with Sephadex G-15 filler (particle size: ≤66um; exclusion limit: 1500; product of Pharmacia Biosystems).
[0053] Separation column: SHODEX PROTEIN KW-802.5 column (exclusion limit: 50000; inner diameter: 8mm; length: 300mm; product of Showa Denko Co., Ltd.).
[0054] The two columns were thermostatted at 25°C. The mobile phase was delivered to the system at a constant flow rate of 0.6 mm / min. When the baseline was stable, 200 microliters of the sample was injected into the injector and flowed into...
Embodiment 2
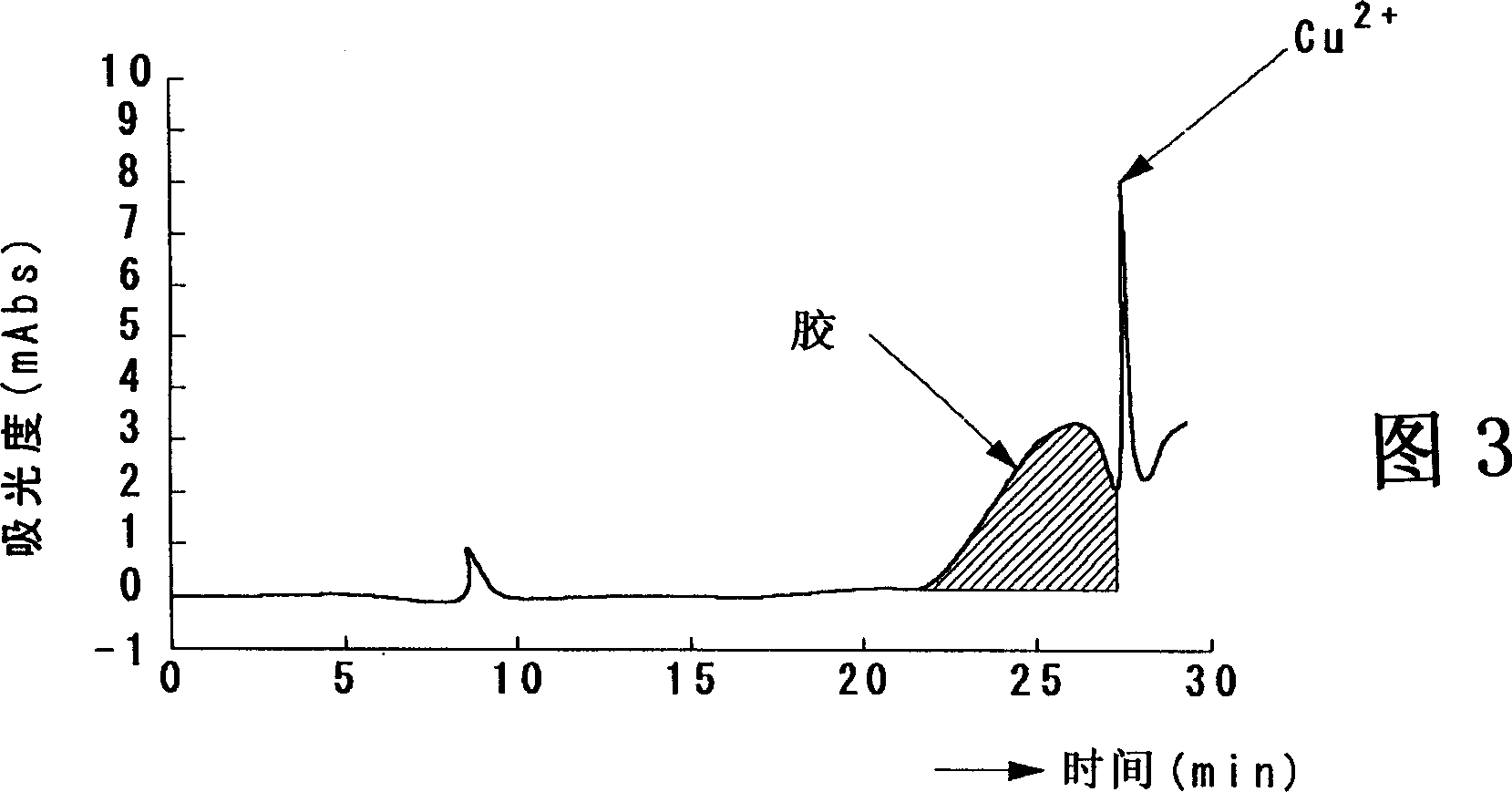
[0057] The test of the molecular weight of the glue in the copper electrolyte is carried out under the following conditions. The resulting chromatograms are shown in Figure 5 . The calculation of molecular weight is based on Figure 6 The calibration curve shown was performed. by just at Cu 2+ The peak area of the gum before ion elution gave a concentration of 0.9 mg / l of gum with a molecular weight above 790.
[0058] Test Conditions:
[0059] Pretreatment column: polyetheretherketone PEEK column (inner diameter: 7.5mm, length: 250mm) filled with Sephadex G-15 filler (particle size: ≤66um; exclusion limit: 1500; product of Pharmacia Biosystems).
[0060] Separation column: Asahipak GS-320HQ (exclusion limit: 40000; inner diameter: 7.6 mm; length: 300 mm; product of Showa Denko Co., Ltd.).
[0061] Temperature: 25°C.
[0062] Mobile phase: 0.005M sulfuric acid / acetonitrile volume ratio of 80 / 20 solution.
[0063] Mobile phase flow rate: 0.6ml / min.
[0064] Amount o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com