Catalytic conversion method for reducing olefine, sulfur and nitrogen contents in gasoline
A catalytic conversion method and a technology for olefin content, which are applied in the field of catalytic conversion of petroleum hydrocarbons, and can solve problems such as a decrease in liquid yield and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach A
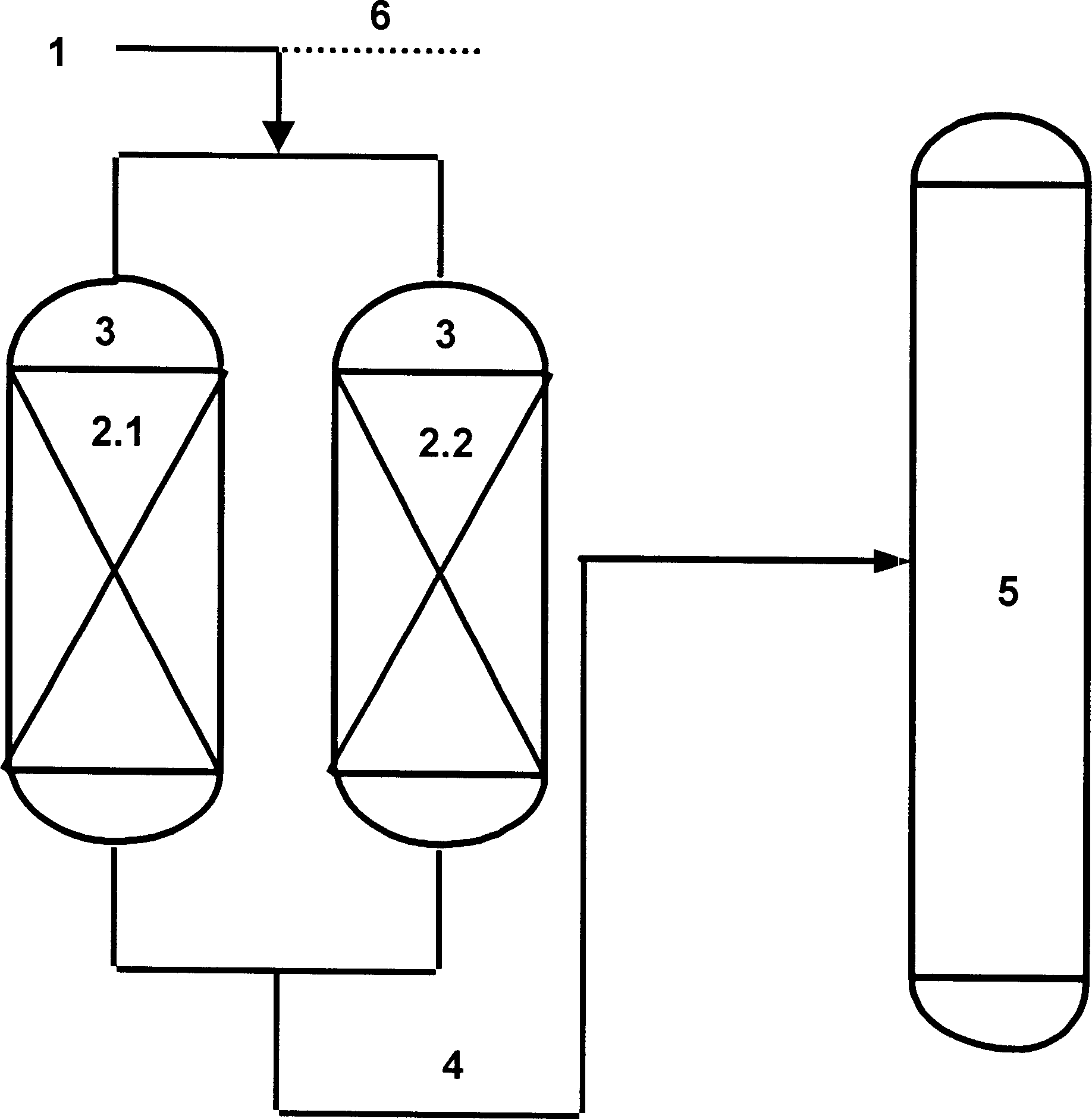
[0022]Embodiment A: For fixed-bed reactors, two or more fixed-bed reactors can be connected in parallel, wherein some reactors perform reaction, while the rest of the reactors perform regeneration. The preheated gasoline contacts and reacts with the catalyst in the reactor, and the reaction product flows out of the reactor and enters the separation system to separate gasoline and a small amount of dry gas, liquefied gas and diesel. After a reaction cycle, for example, after 0.05 to 60 minutes, the preheated gasoline raw material is cut into the next fixed-bed reactor to continue catalytic conversion, and at the same time, hydrogen is cut into the fixed-bed reactor, and the reactor The polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on the internal catalyst are hydrogenated and saturated to remove the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on the catalyst, and the regenerated catalyst is used for the next use.
Embodiment approach B
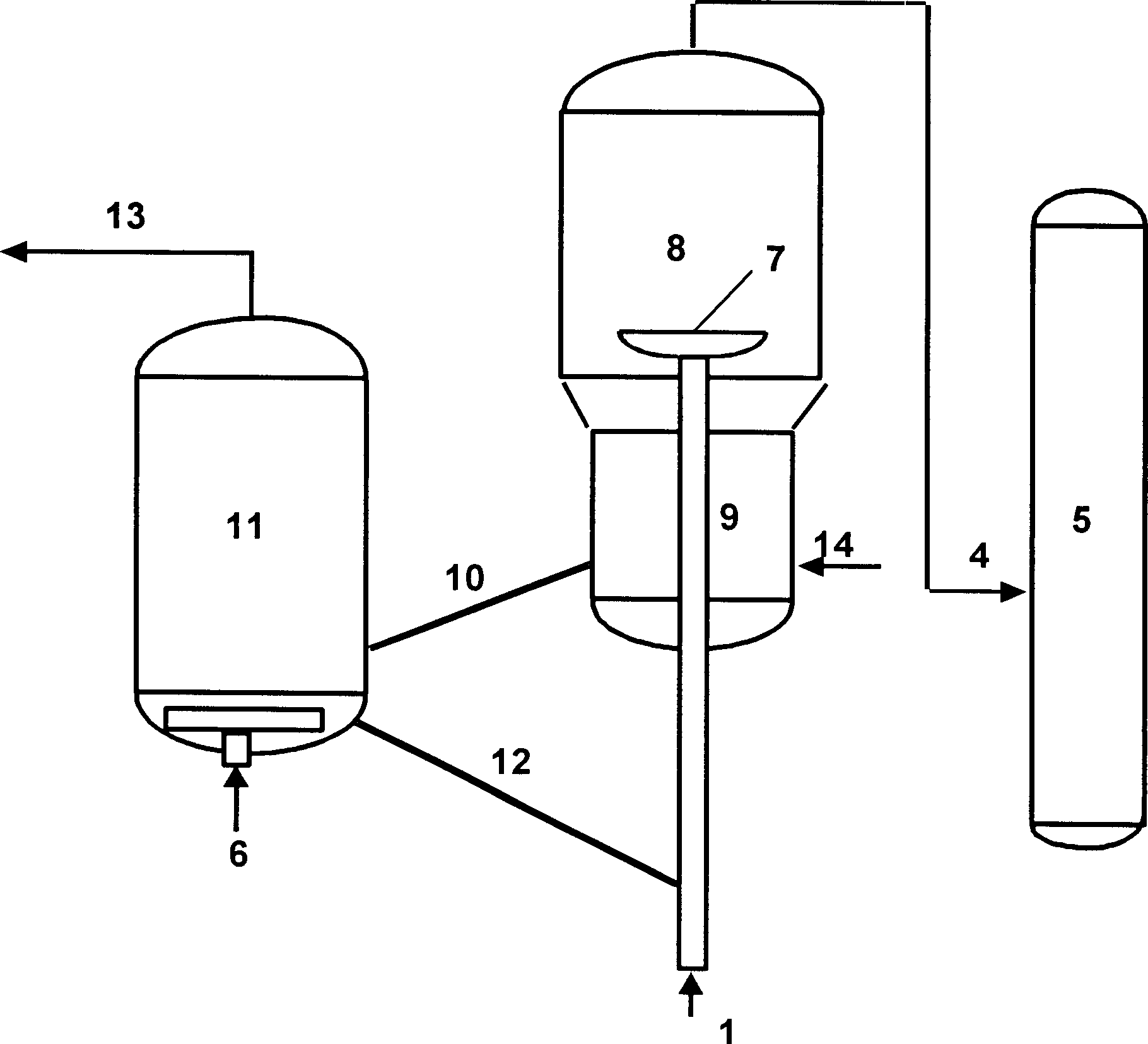
[0023] Embodiment B: For a fluidized bed reactor, the preheated gasoline contacts and reacts with the microsphere granular catalyst in the reactor, and the reaction product flows out of the reactor and enters the separation system to separate gasoline and a small amount of dry gas and liquefy Gas and diesel oil, the catalyst that deposits polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons is removed from the reactor and enters the regenerator. In the presence of hydrogen, the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on the catalyst are hydrogenated and saturated, and the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on the catalyst are removed. The regenerated catalyst is recycled to The reactor continues to be used.
[0024] The following examples will further illustrate the present invention, but do not limit the present invention thereby. The properties of the catalyst used in the embodiment and the feedstock oil are listed in Table 1 and Table 2 respectively. Catalyst A listed in table 1 is industrially produc...
Embodiment 1
[0026] This embodiment illustrates: low-quality gasoline can adopt the method provided by the invention on different types of reactors.
[0027] With the gasoline A listed in Table 2 as raw material, the reaction was carried out in a small-scale fixed-bed reactor, and 200 milliliters of catalyst A was housed in this reactor. The test procedure is briefly described as follows: gasoline fraction A is mixed with hydrogen and then enters a fixed-bed reactor. The reaction temperature is 350°C, the reactor pressure is 0.2 MPa, and the weight hourly space velocity is 10 hours. -1 , under the condition that the hydrogen-oil ratio is 0.2, contact with the catalyst for catalytic conversion reaction, the reaction product and hydrogen flow out of the reactor and enter the rear separation system, the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons generated during the reaction are deposited on the catalyst, and after 60 minutes of reaction, Stop injecting gasoline, cut into 8.0 MPa of hydrogen, and regen...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| denitrification rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com