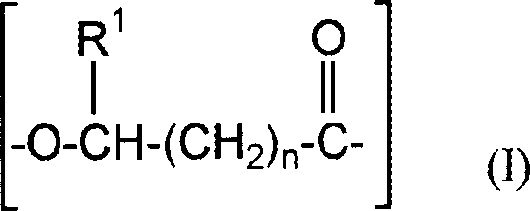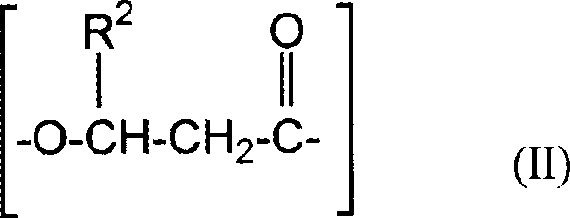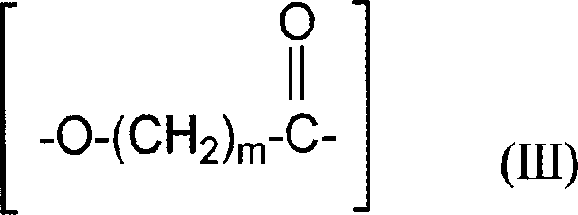Fibers comprising polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer/polylactic acid polymer or copolymer blends
A technology of polyhydroxyalkanoate and copolymer, which is applied in the field of fibers including polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer/polylactic acid polymer or copolymerization mixture, which can solve the problem of slow crystallization speed and limited production speed of polymer products, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0088] This example demonstrates the melt spinnability of a binary blend comprising a preferred polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer and PLA polymer. Specifically, a polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer comprising 3-hydroxybutyrate and about 12 mole percent 3-hydroxyhexanoate (hereinafter referred to as PHBH copolymer) and the PLA polymer from Example 1 were combined The mixture is first melted and formulated in a twin-screw extruder, and the temperature and screw speed of the extruder ensure the sufficient mixing of the two components, wherein the content of PHBH varies from 10 to 70% by weight based on the total weight of PHBH and PLA percentage. Each formulated PHBH / PLA blend was melt spun into fibers using the procedure described in Example 1. For PHBH levels of less than about 35 weight percent, no fiber rewinding or residual stickiness was observed and fibers 20 to 25 microns in diameter were collected. Comparing the tactile properties of these PHBH / PLA fibers with those of pure P...
Embodiment 3
[0090] This example demonstrates the melt spinnability of a ternary blend comprising a preferred polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer, a PLA polymer and a preferred moisture sensitive polymer. Specifically, a mixture of the PHBH copolymer of Example 2, the PLA polymer of Example 1, and polyethylene oxide (PEO) polymer was prepared by the melt formulation procedure in Example 2, wherein the PHA content was 20 weight percent , the PLA content is 64% by weight, and the PEO content is 16% by weight. The formulated PHBH / PLA / PEO blend was melt spun into fibers using the procedure described in Example 2, collecting fibers ranging in diameter from 14 to 25 microns. Comparing the tactile properties of these PHBH / PLA / PEO fibers with those of the PHBH / PLA blends of Example 2 with mixing ratios of 20 / 80 and 40 / 60, and those of pure PLA in Example 2, the results show that adding There was a noticeable increase in softness after a small amount of PEO was added to the PHBH / PLA blend, where the PH...
Embodiment 4
[0092] This example demonstrates the melt spinnability of bicomponent fibers using the PHA of Example 2 in the core. PLA resin from Biomer, L5000, was used as the sheath and PHA as the core at sheath / core ratios of 20 / 80, 40 / 60, 60 / 40 and 80 / 20. The fiber diameter is 20 to 35 microns. This example demonstrates that bicomponent fibers can be prepared using a high Tg polymer and PHA.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com