Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and control method thereof
A non-volatile, storage device technology, applied in the field of memory arrays of storage cells, can solve the problems of large dispersion of variable resistance elements, increased power consumption, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
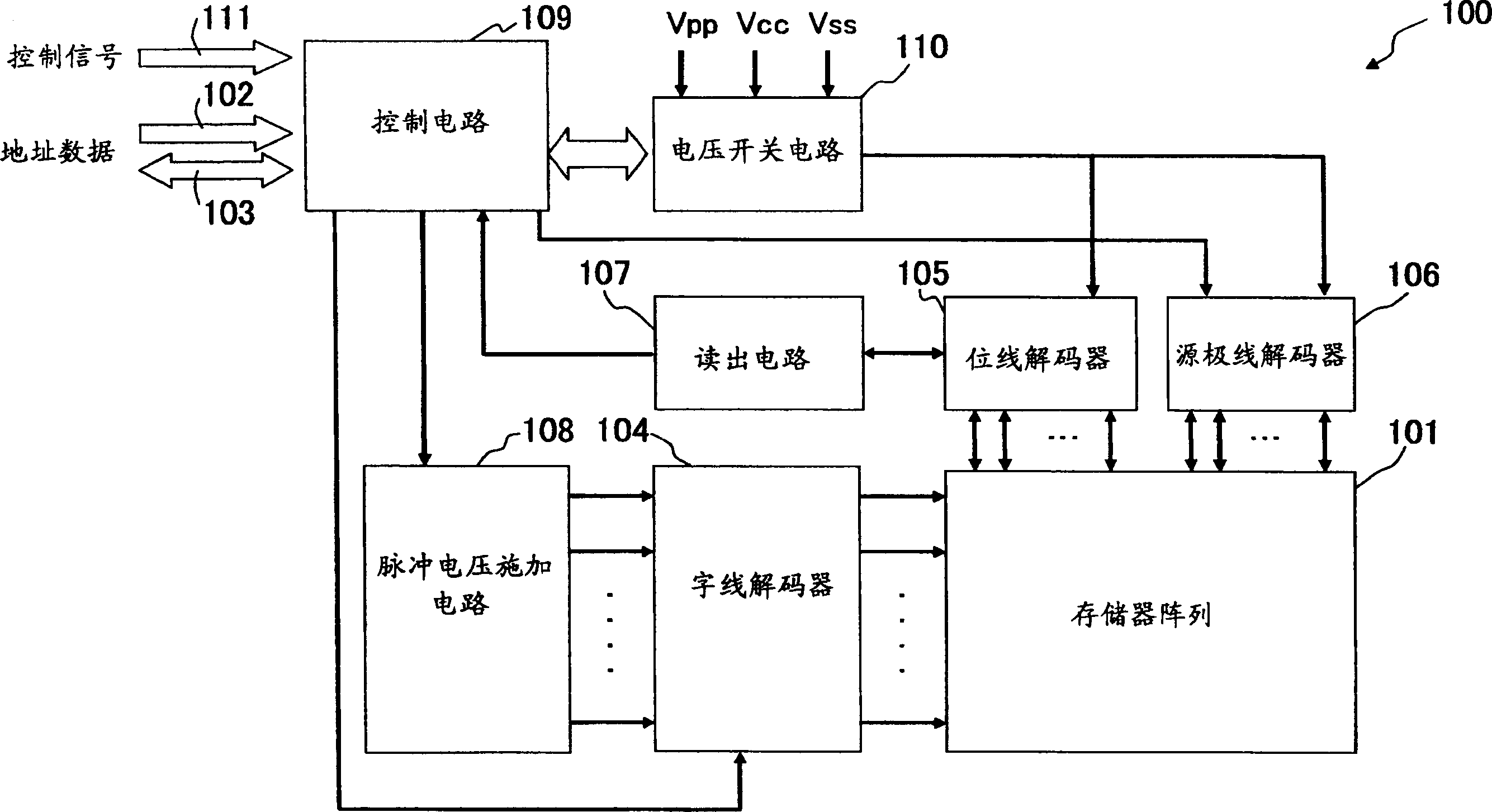
[0040] figure 1 A block diagram of an apparatus 100 of the present invention is shown. The device 100 of the present invention stores information in the memory array 101, and the memory array 101 adopts a structure configured with a plurality of storage units, and can store and read information in the storage units in the memory array 101.
[0041] Information is stored in a specific memory cell in the memory array 101 corresponding to an address input from the address line 102 , and the information is output to an external device through the data line 103 . The word line decoder 104 selects the word line of the memory array 101 corresponding to the signal input to the address line 102, the bit line decoder 105 selects the bit line of the memory array 101 corresponding to the address signal input to the address line 102, and the source The line decoder 106 selects the source line of the memory array 101 corresponding to the address signal input to the address line 102 . The...
Embodiment approach 2
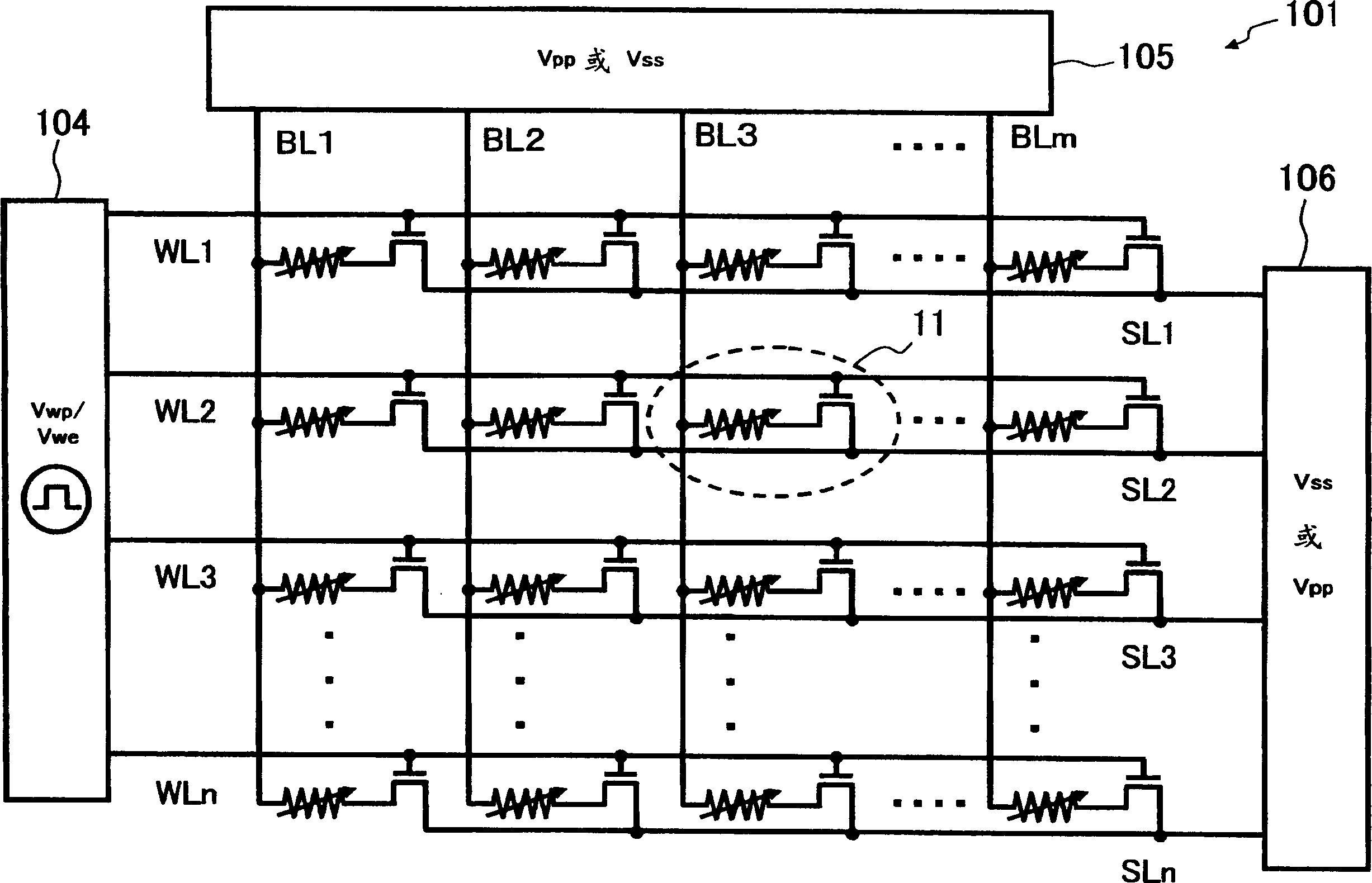
[0087] In the device of the present invention and the method of the present invention according to Embodiment 1, the amplitudes Vwp and Vwe of the pulse voltage applied to the gate electrode 5 of the selection transistor 6 of the memory cell 11 are independently adjusted for writing and erasing. Write and delete operations are explained. In Embodiment 1, the period during which the memory cell 11 is in the write or erase operation state is defined according to the pulse width of the pulse voltage applied to the gate electrode 5 . On the other hand, in the device of the present invention and the method of the present invention according to the second embodiment, a pulse voltage is applied to either the bit line or the source line connected to the memory cell to be written or erased. The programming voltage or erasing voltage between the bit line and the source line is applied in a pulse form, during which a predetermined word line voltage is applied to the word line connected t...
other Embodiment approach
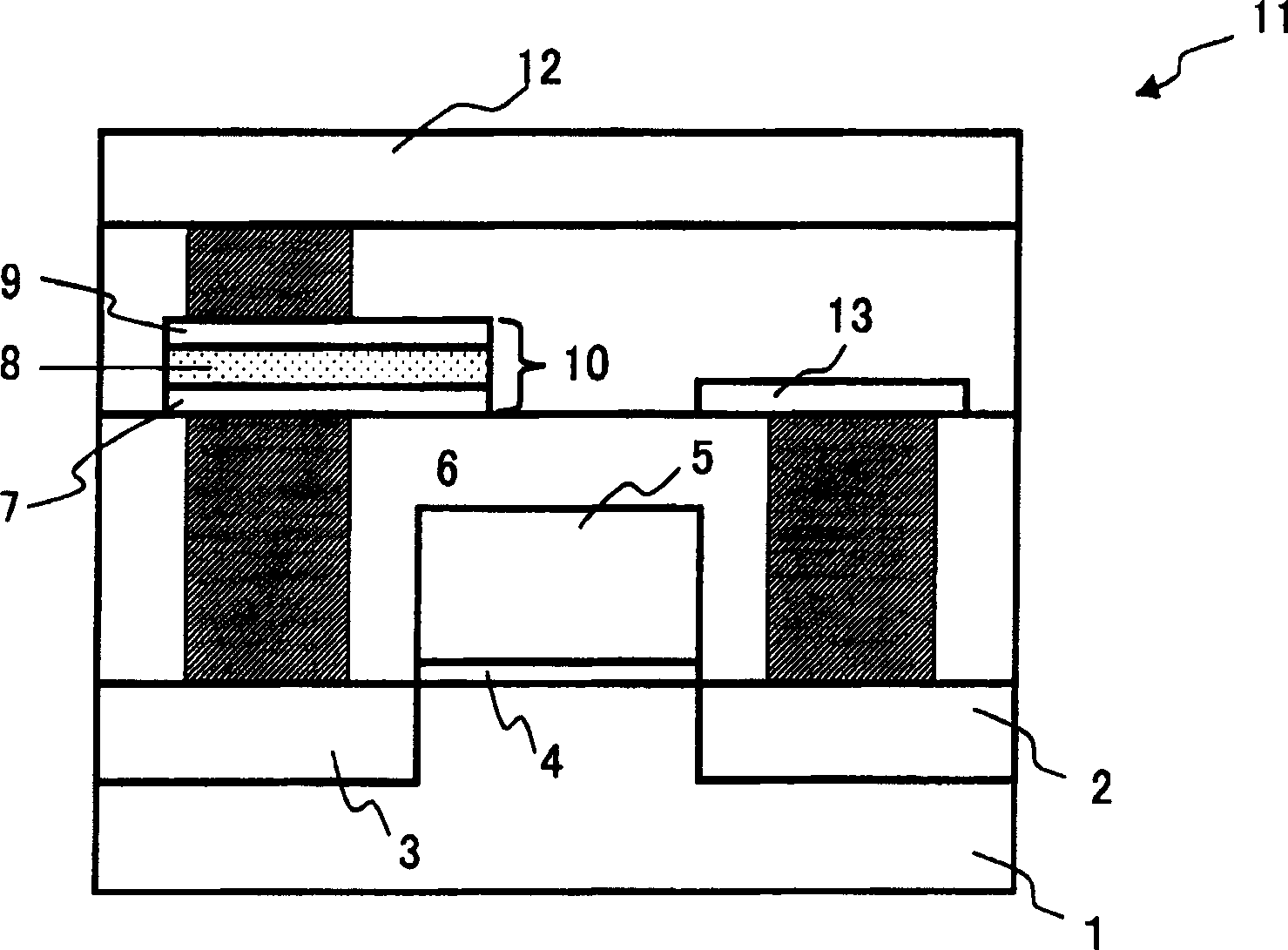
[0099] In each of the above-mentioned embodiments, the storage unit 11 is figure 2 and Figure 7 shown in the figure, but the memory cell 11 may also be configured as follows: the source region 2 of the selection transistor 6 is electrically connected to the lower electrode 7 of the variable resistance element 10, the upper electrode 9 is connected to the source line, and the drain region 3 is connected to the bit line to alternate the arrangement of the selection transistor 6 and the variable resistance element 10. By alternation of this arrangement, the voltage difference (Vpp-Vss) between the upper electrode 9 and the drain region 3 is divided into the voltage Vr across the variable resistive element 10 and the source-drain voltage Vds. under normal conditions with figure 2 and Figure 7 The memory cells shown are constructed identically.
[0100] In addition, the device of the present invention and the method of the present invention are not limited to the above-ment...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com