Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae vaccine and methods for reducing mycoplasma bovis pneumonia in cattle
A technology of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae and Mycoplasma bovis is applied in the field of treating or preventing diseases or diseases caused by Mycoplasma bovis infection in animals, and can solve problems such as unrecognized protective effects and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] Materials and Methods
[0075] animal
[0076] Healthy crossbred dairy calves are vaccinated at approximately 14 days of age. The calves were acclimated for 7 days before starting the study. All calves received a daily concentrated unmedicated diet without any known contaminants or pesticides, but had free access to water.
[0077] vaccine
[0078] The bacterin used to immunize calves contains an appropriate concentration of BEI-inactivated whole cells of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae per dose. Additionally, the vaccine preparation comprises phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and an oil-in-water adjuvant. Placebo contained PBS.
[0079] attack method
[0080] Each calf received 12 ml of fresh M. bovis culture (approximately 1 × 10 8 to 1×10 10 Colony forming units (CFU / ml)). Immediately after completion of each experimental challenge, the viable number (CFU / ml) of the challenge inoculum was determined.
[0081] Experimental procedure
[0082] Each calf is identifie...
Embodiment 2
[0092] In this example, the efficacy of the M. hyopneumoniae bacterin was assessed in young calves. Thirty healthy hybrid calves were randomly grouped according to age.
[0093] On day 0 (left neck) and day 21 (right neck), animals were inoculated subcutaneously with 2 ml of the vaccine or placebo. The experimental treatment groups and vaccines used are shown in Table 1.
[0094] therapy group
[0095] Calves were challenged as described above 3 weeks after the second inoculation. Each calf received 12 ml of fresh M. bovis culture for 3 consecutive days by the intranasal route.
[0096] Within 1 hour after completion of the M. bovis experimental challenge, the number of surviving inoculum per challenge (CFU / ml) was determined. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0097] Table 2
[0098] challenge culture
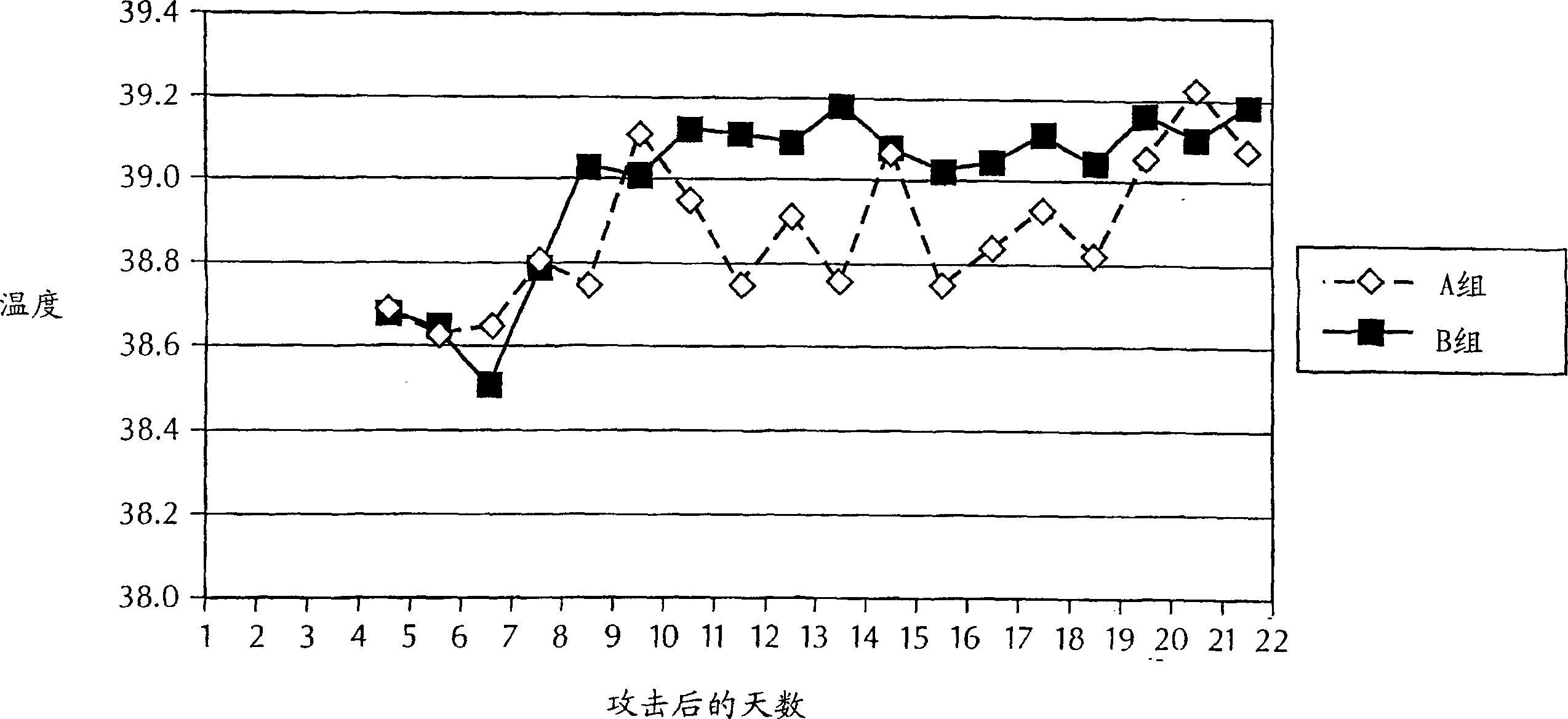
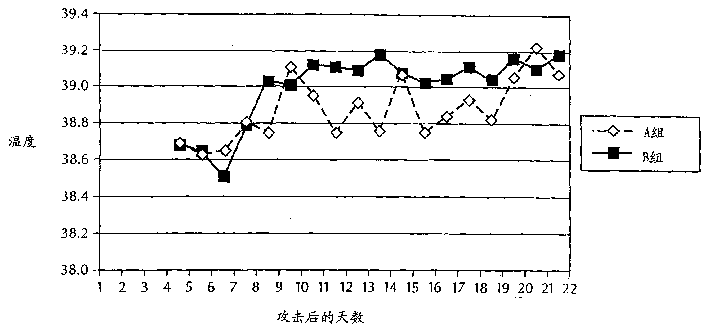
[0099] Rectal temperatures were measured every morning on the day before the experimental M. bovis challenge, immediately before the st...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com