Multi-path reflection fluorescent probe
A multiple reflective and fluorescent technology, applied in the field of multiple reflective fluorescent probes, can solve problems such as usage restrictions, errors, and low resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
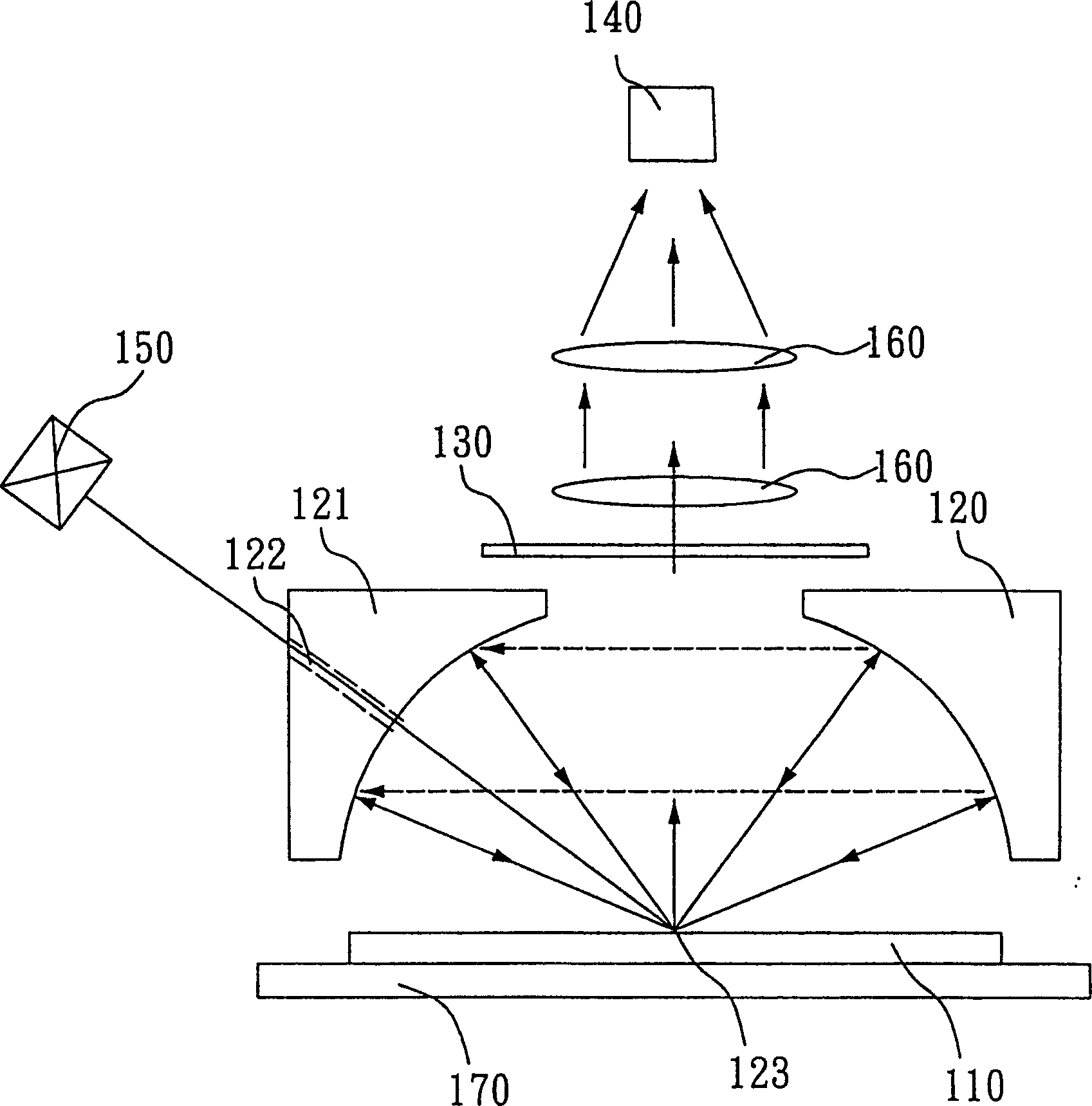
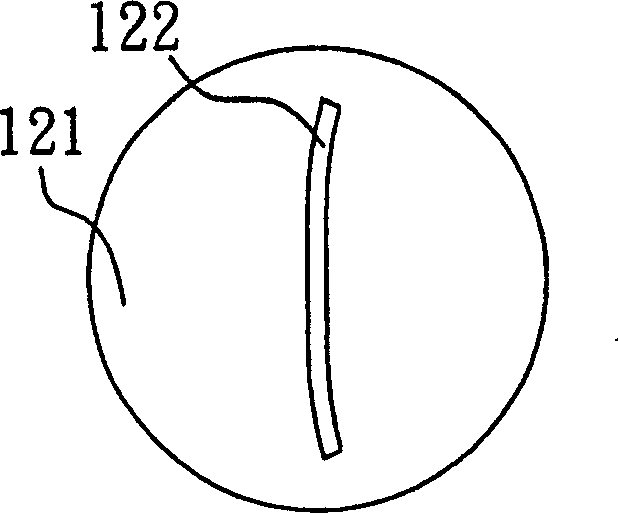
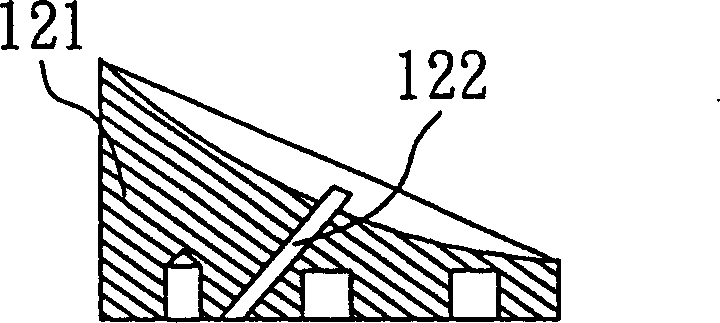
[0021] For the multiple reflection fluorescent probe in this example, see figure 1 , is to cooperate with the defect detection on the surface of a printed circuit board 110, using laser to excite the organic fluorescent material of the non-metal wire part, cooperate with the optical filter 130 to filter the excited laser, and then use the image detector 140 to retrieve the laser-induced fluorescence (Laser Induced Fluorescence, LIF) image. The multiple reflection fluorescence probe includes two off-axis parabolic mirrors 120 and 121 confocally arranged, and its shape is as follows: Figure 2(A) to 2(D) As shown, one of the off-axis parabolic mirrors 121 has a linear slit 122 inclined at 45 degrees; a linear laser light source 150 generates laser excitation light, and directly incident off-axis through the linear slit 122 at an angle of 45 degrees The position of the focus 123 of the parabolic mirrors 120 and 121; an image detector 140, to detect the fluorescence induced by t...
Embodiment 2
[0023] For the multiple reflection fluorescent probe in this example, see image 3 , is to cooperate with a defect detection on the surface of a printed circuit board 210, use laser to excite the organic fluorescence of the non-metal wire part, cooperate with the optical filter 230 to filter the laser, and then use the image detector 240 to retrieve the laser-induced fluorescence (Laser Induced Fluorescence, LIF) image. The reflective fluorescence probe includes two off-axis parabolic mirrors 220 and 221 confocally arranged, wherein one off-axis parabolic mirror 221 has a linear slit 222 parallel to the surface of the printed circuit board 210; a linear laser light source 250 generates laser light The excitation light passes through the linear slit 222, reaches the off-axis parabolic mirror 221, and then reflects to the focal point 223 of the off-axis parabolic mirror; Fluorescence; a filter 230, located between the printed circuit board 210 and the image detector 240, to fil...
Embodiment 3
[0025] For the multiple reflection fluorescent probe in this example, see Figure 4, which is matched with a biochip 310 implanted with nucleic acid probes of a plurality of fluorescent groups, which is excited by laser light and filtered by a dichroic mirror 330 , and then retrieved by an image detector 340 for its laser-induced fluorescence light image. The fluorescent probe includes two off-axis parabolic mirrors 320 and 321 confocally arranged; a linear laser light source 350 generates laser excitation light, which is reflected by a dichroic mirror 330 and reaches the focal point 323 of the off-axis parabolic mirror; an image Detector 340, to detect the position of the fluorescent substance; a dichroic mirror 330, located between the biochip 310 and the image detector 340, to filter the excitation light of the laser, so that the fluorescent light can penetrate and reach the image detector 340; a detection platform 370 that moves horizontally and vertically is used to plac...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle of incidence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com