Methods and compositions for generating a genetically modified animal using lentiviral vectors
A technology of lentiviral vectors and compositions, applied in the field of methods and compositions, capable of solving problems such as low embryo survival rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
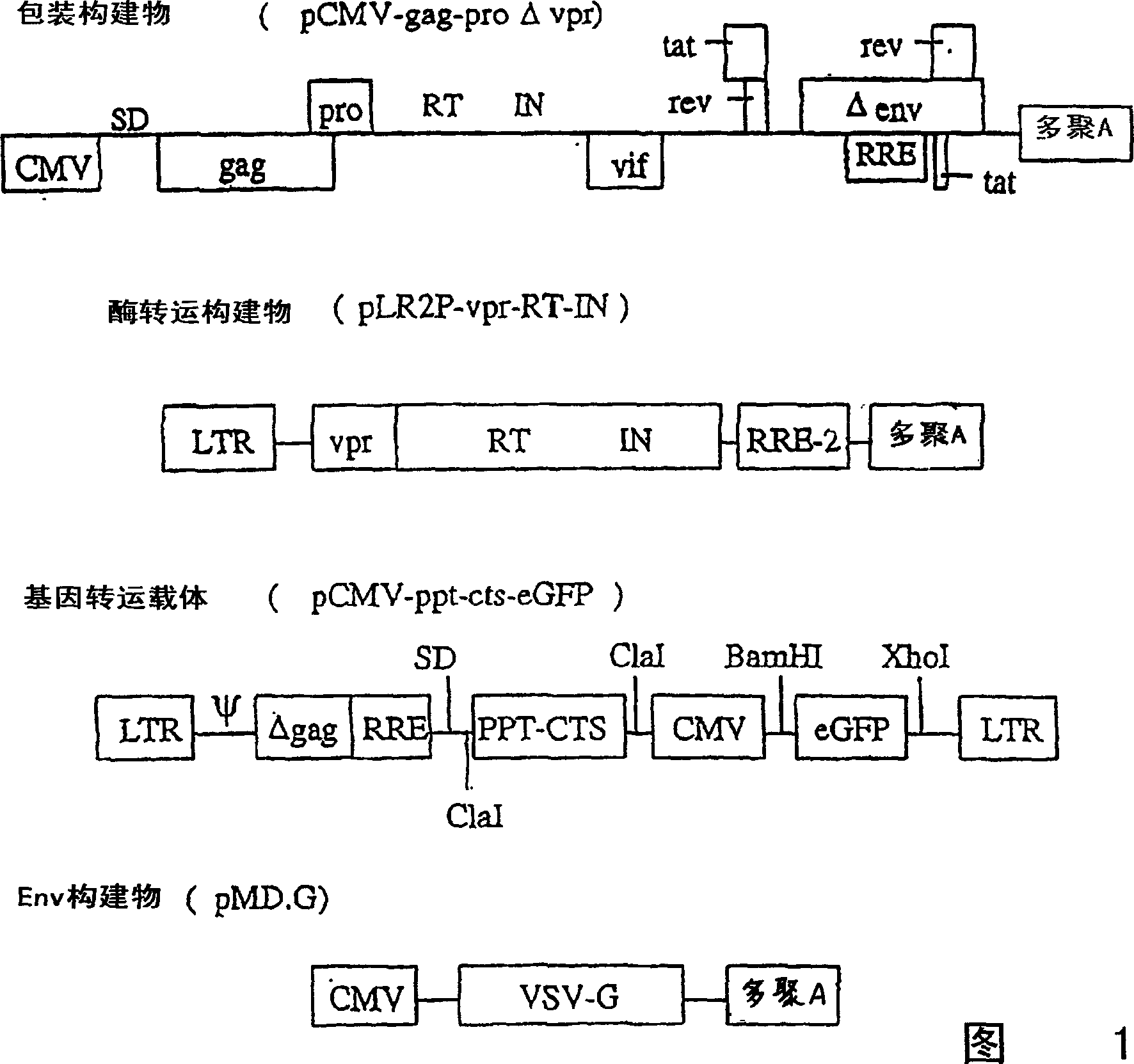
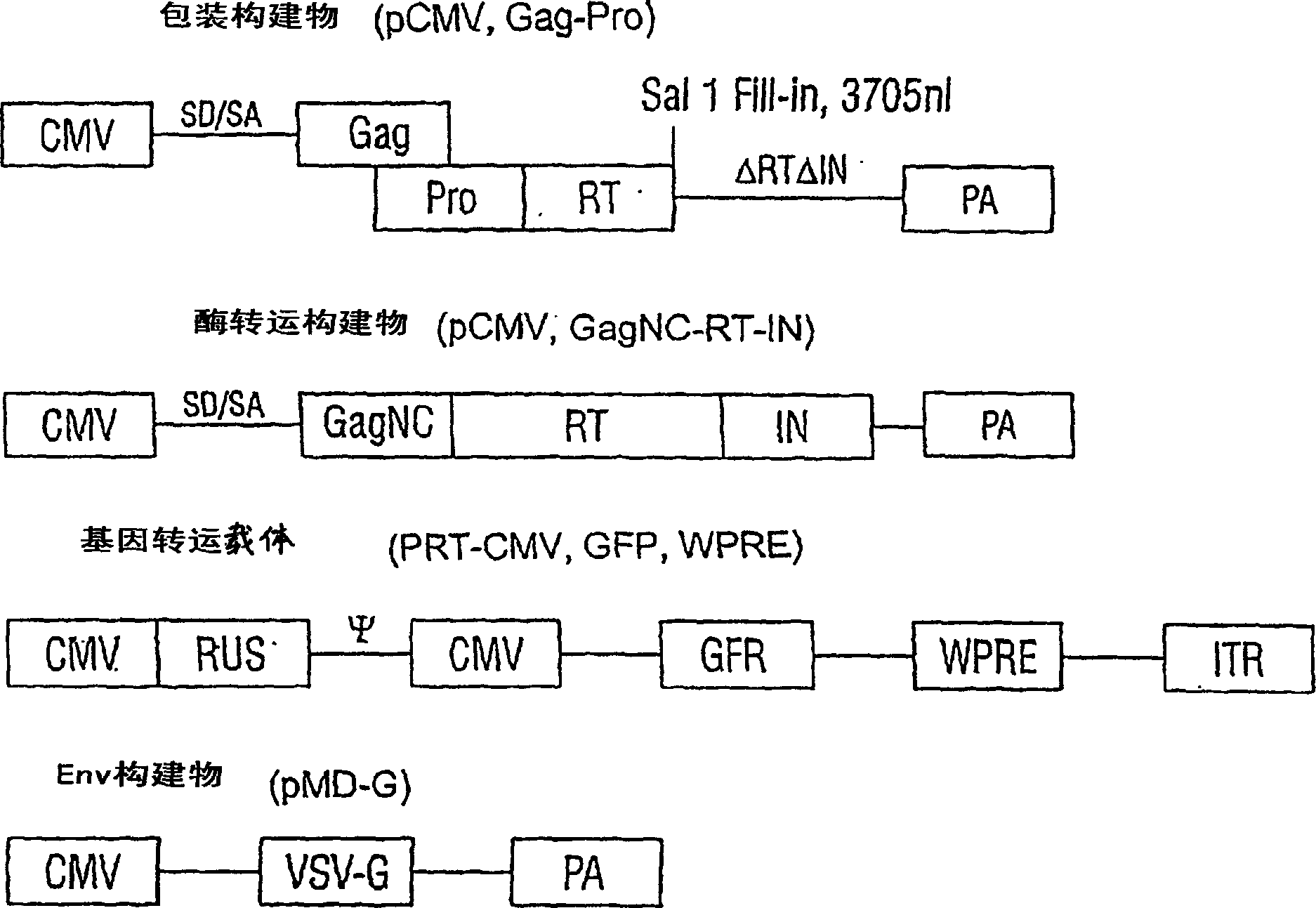
[0175] Example 1: Generation of Genetically Modified Mice by Exposure of Lentiviral Vectors to the Plasma Membrane
[0176] A. Lentiviral transfer vector
[0177] Plasmid:
[0178] To construct the pPCW-eGFP gene transfer vector, a PCR-amplified DNA fragment containing EGFP cDNA (derived from pEGFP-C1, Clontech) was ligated into the BamHI / XhoI site of the pHR-CMV-LacZ plasmid (Naldini et al., Science 272: 263-7, 1996), produce pHR-CMV-eGFP; then PCR amplify the 150bp DNA sequence (4327-4483) containing central polypurine sequence (PPT) and central termination site (CTS) of HIV-1 pSG3 molecular clone ( Ghosh et al., Virology 194:858-864, 1993), and ligated into the unique ClaI site of pHR-CMV-eGFP. To reduce eGFP expression (Zufferey et al., J. Virol. 7:2886, 1999), a post-transcriptional regulatory element derived from duck hepatitis virus (WPRE) was inserted downstream of eGFP, generating the pPCW-eGFP gene transfer vector. This construct was used in the cell experiments i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com