N-phase integrated buck converter
A converter and controller technology, used in output power conversion devices, instruments, and DC power input to DC power output, etc., can solve the problems of multi-phase converters, high switching losses, large time constants, etc. Achieve the effect of shortened response time, low total cost and fast switching
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
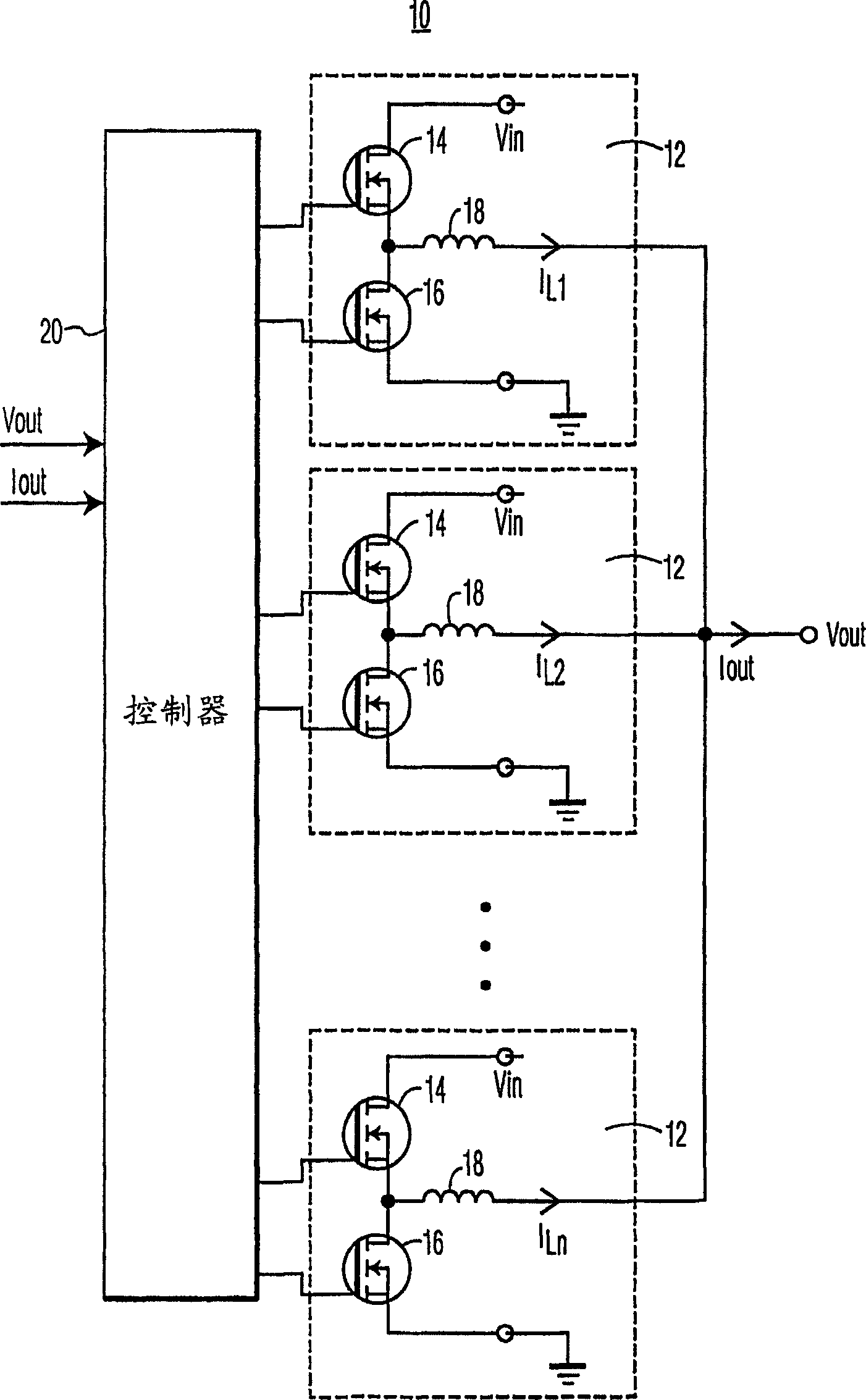
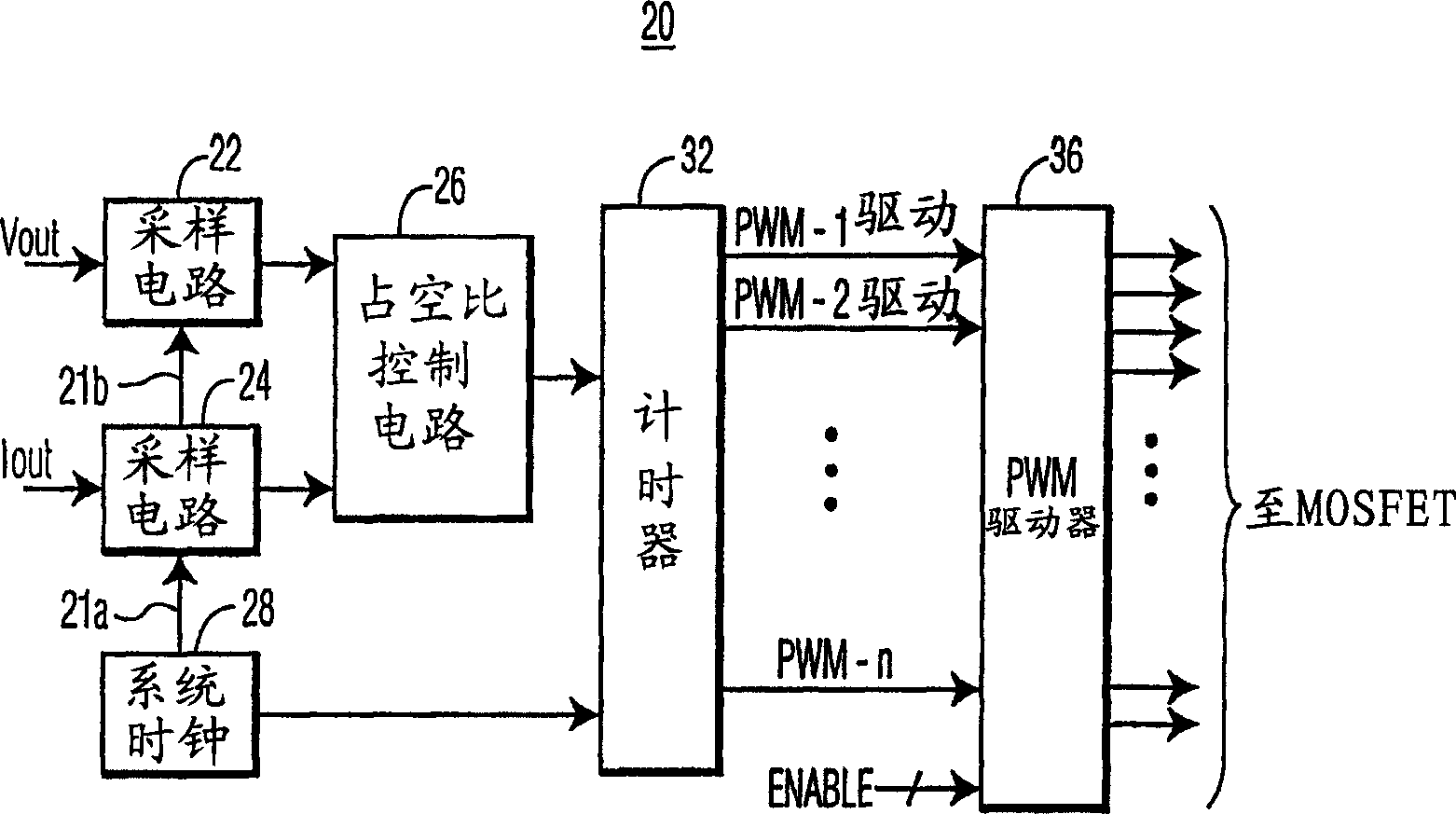
[0019] figure 1 An n-phase buck converter 10 according to an embodiment of the invention is shown. figure 1 In the example, the buck converter 10 includes a plurality (for example, n) of circuits 12 connected to an n-phase controller 20 . Each circuit 12 includes a control transistor such as MOSFET 14, a synchronous transistor such as MOSFET 16, and an inductor 18 to generate an output current IL representing one phase of the n-phase buck converter. Although MOSFETs 14 and 16 are shown as n-type MOSFETs, they could also be p-type MOSFETs.
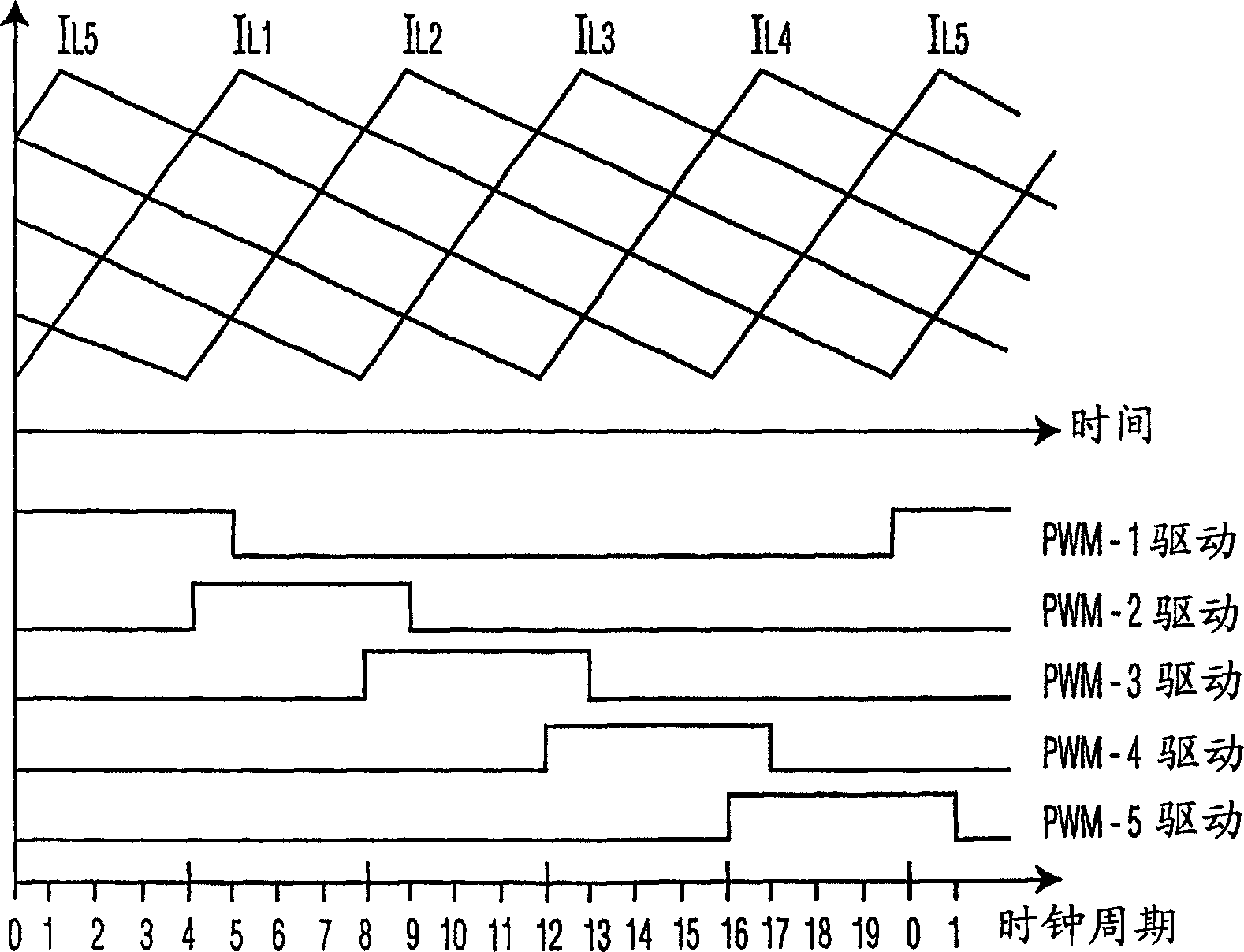
[0020] To operate each circuit 12, the controller 20 turns on the control transistor 14 to connect the input Vin to the inductor 18 to charge the inductor. After the inductor is charged, control 20 turns off control transistor 14 to disconnect Vin from inductor 18 and turns on transistor 16 to provide a current path and discharge the inductor current to the load. As detailed below, the inductor currents originating from n circuits 12 can...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com