Method for producing a semiconductor element
A technology for semiconductors and devices, applied in the field of manufacturing semiconductor devices, can solve the problems of limited thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity of adhesives, heat resistance, limited reliable temperature range, power loss, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
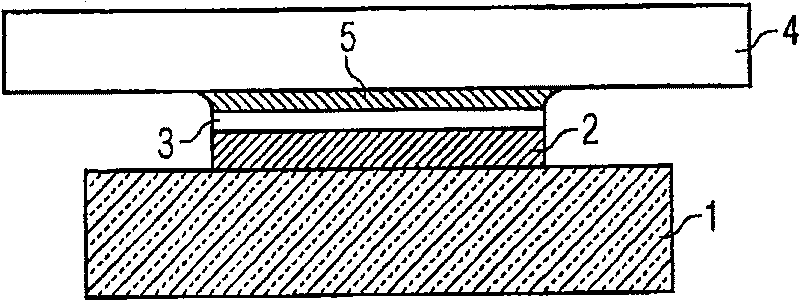
[0083] In the figures, identical elements or identically acting elements are marked with the same reference signs.
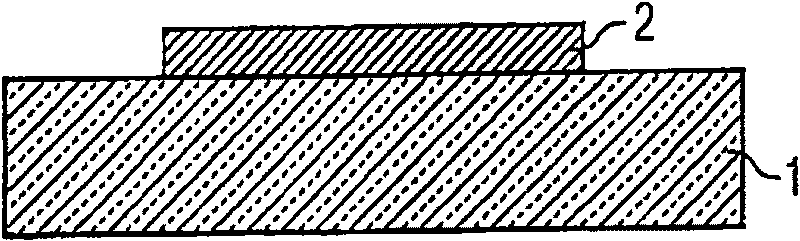
[0084] In the first step of the method shown in the figure, Figure 1A , a semiconductor layer 2 is provided on a substrate 1 . The semiconductor layer 2 may be a nitride compound semiconductor layer, such as an InGaN layer epitaxially grown on a sapphire substrate. Furthermore, the semiconductor layer 2 can also comprise a plurality of individual layers which can contain, for example, GaN, AlN, AlGaN, InGaN, InN or InAlNGaN and which are grown successively on the substrate 1 .
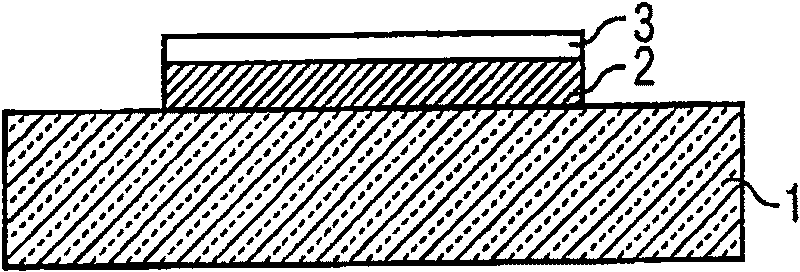
[0085] In the next step, Figure 1B , the semiconductor layer 2 is provided with a contact metallization layer 3 on the side facing away from the substrate. A very low contact resistance is achieved by means of the contact metallization layer 3 between the semiconductor layer 2 and an electrical connection, for example a connecting line, which is provided in a later method step. Fur...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap