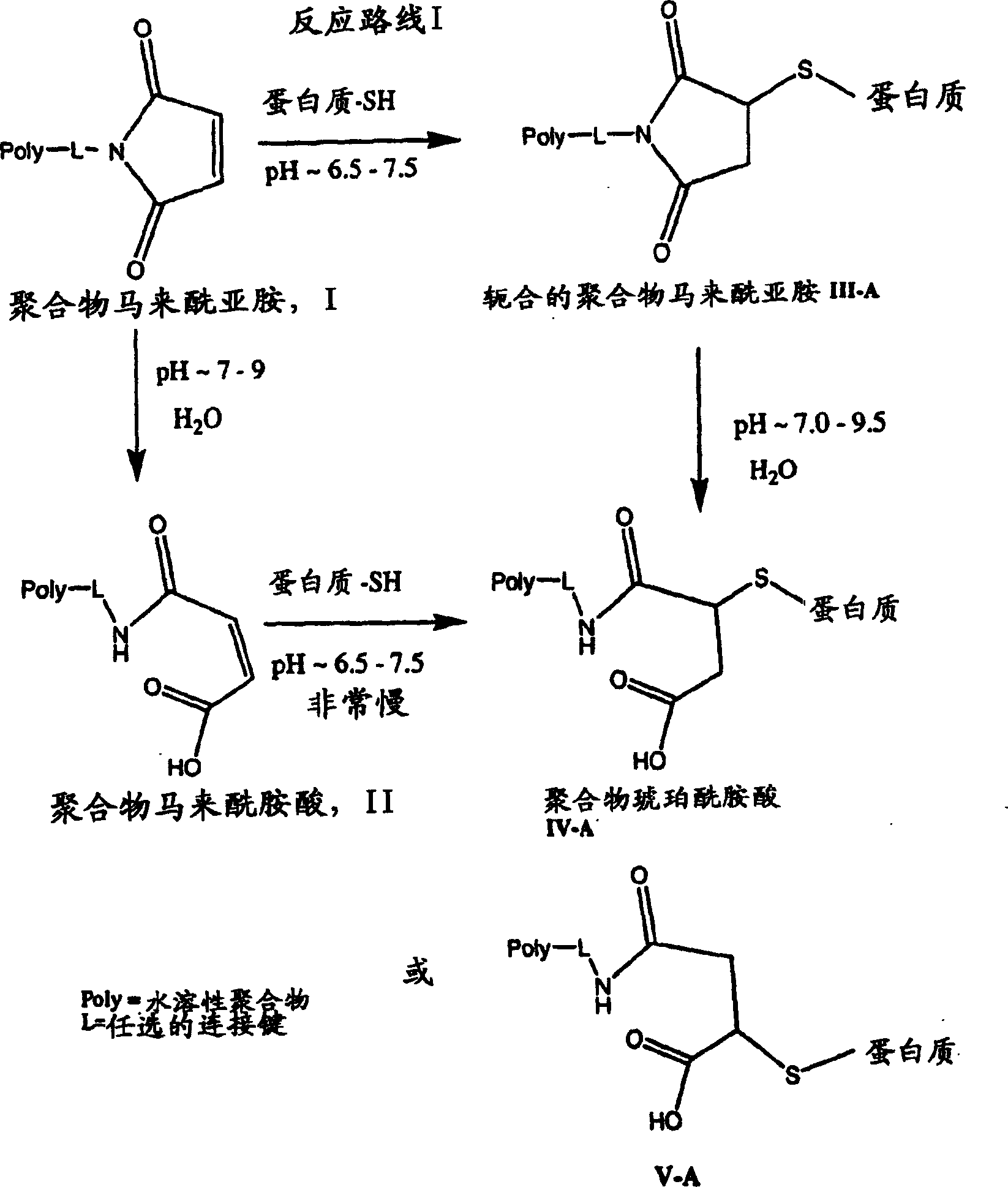
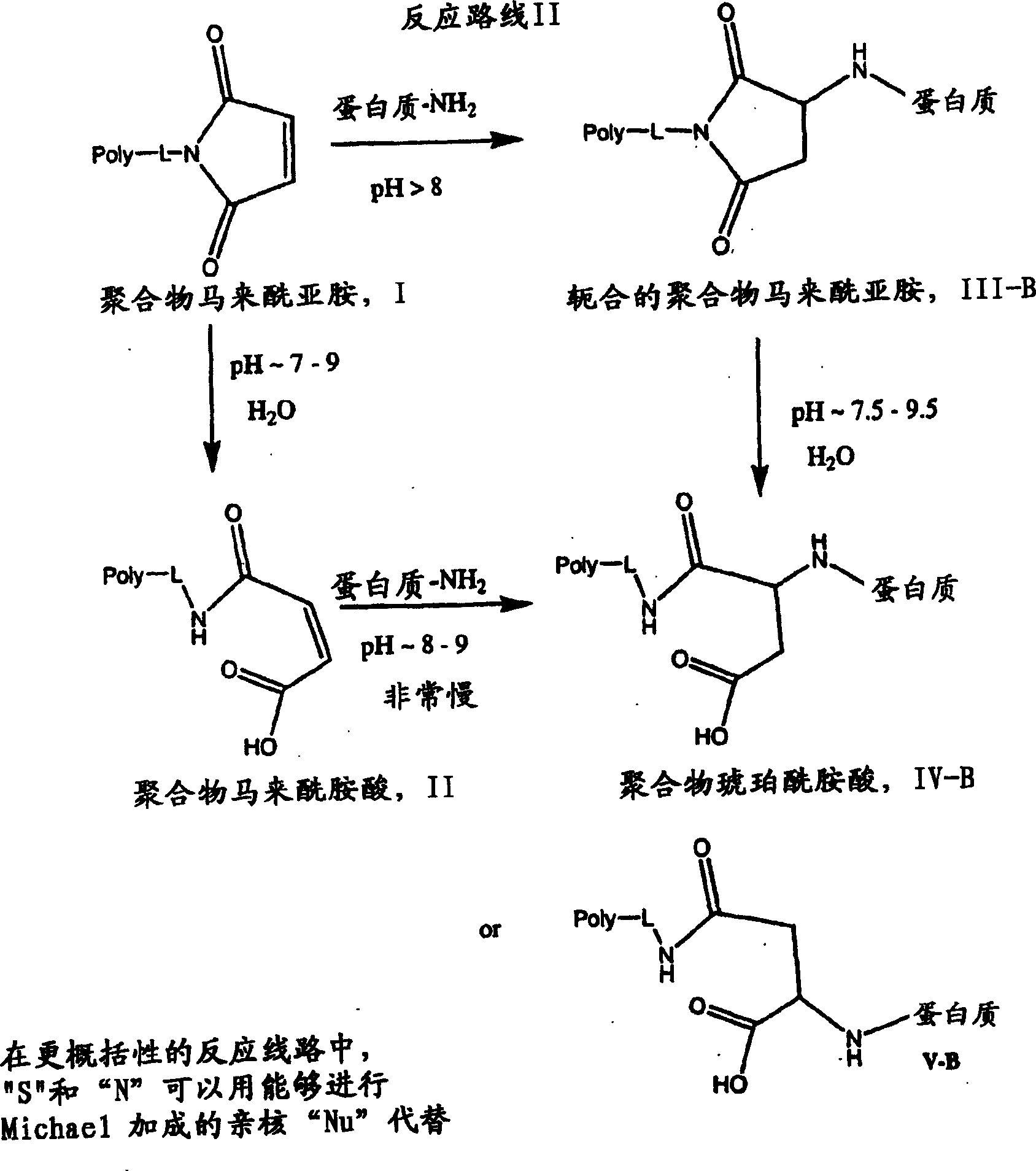
Maleamic acid polymer derivatives and their bioconjugates
A technology of maleimide, polymer, applied in the field of polymer chemistry
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0262] Hydrolysis rate of linked PEG maleimide examples
[0263] A series of representative methoxy-PEG maleimides with an average molecular weight of 5000 Daltons were synthesized and studied. Determine the maleimide for each of the following structures by measuring the UV absorption at 297 nm of a solution of mPEG maleimide at a concentration of 5 mg / mL in 50 mM phosphate buffer at a pH of approximately 7.5 Ring hydrolysis reaction kinetics. The general structure of polymer maleimide is shown below. The exact structure corresponding to each linker is provided in Table 1 above (L 1 , L 2 and L 3 ).
[0264]
[0265] Table 2, Hydrolysis rate of mPEG (5k-Da) maleimide (5 mg / mL) dissolved in 50 mM phosphate buffer (pH ~ 7.5) as determined by UV absorption at 297 nm
[0266] Structure Half-life Relative rate
[0267] (Hour)
[0268] L 1 -AMTR 8.8 3.66
[0269] L 1 -AMPE 19.4 1.66
[0270] L 1 -MCH 16.3 1.98
[0271] L 2 -BU 19.6 1.65
[0272] L...
Embodiment 2
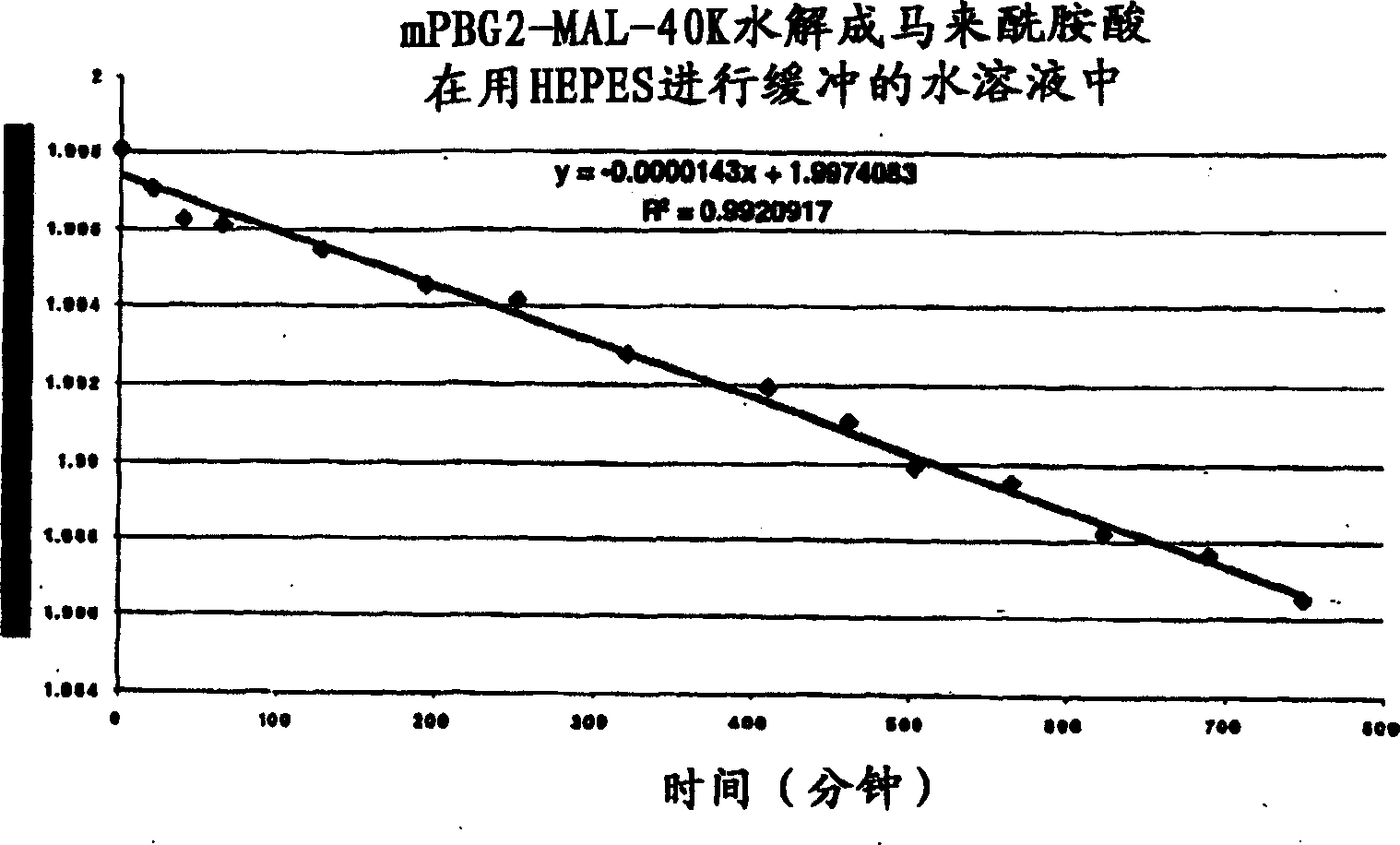
[0278] Hydrolysis of a branched linked polymer maleimide, mPEG2-MAL-40K
[0279]
[0280] The polymer maleimide drawn on hair, mPEG2-MAL-40K, was obtained from Nektar (Huntsville, AL). The maleimide ring of the polymer derivative undergoes limited hydrolysis under certain conditions to form the corresponding maleamic acid derivative described below.
[0281] The hydrolysis reaction was monitored analytically by HPLC to observe the decrease in the percentage of parent maleimide over time. The kinetics of the hydrolysis reaction were determined under the following conditions: a pH value of about 5.5, using a HEPES buffer solution at about 25°C.
[0282] By plotting the logarithm of maleamic acid or maleimide concentration versus time (the latter shown in image 3 ), a linear relationship can be obtained.
[0283] This data was then used to determine the half-life of the hydrolysis reaction, which was calculated to be approximately 34 days under the test conditions. Thus...
Embodiment 3
[0285] Study on the Hydrolysis Rate of Polymer Succinimide Conjugate
[0286] Hydrolysis rates of representative proteins and small molecule model conjugates were studied to examine the relationship between the polymer-terminated maleimide itself and the ring-opening tendency of its conjugates.
[0287] Since large biomolecular components such as proteins have a significant impact on the retention of linked molecules in typical LC columns, it is often more difficult to determine the kinetics of maleimide conjugates than the polymers themselves. In this analysis, the ring-opened acid form of maleamic acid could not be cleanly separated from the ring-opened or ring-closed form. However, combined analytical methods based on size exclusion chromatography (HPLC-SE) and protein analysis electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) have been successfully used to evaluate polymeric maleimide protein conjugates and those made with nonproteinaceous model compounds. The ring-opening properties of the c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com