Anode, cathode material conductive agent for lithium-ion secondary battery and preparation method thereof
A secondary battery and negative electrode material technology, applied in the direction of conductive materials, conductive materials, battery electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of high price and low practical value of carbon nanotubes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
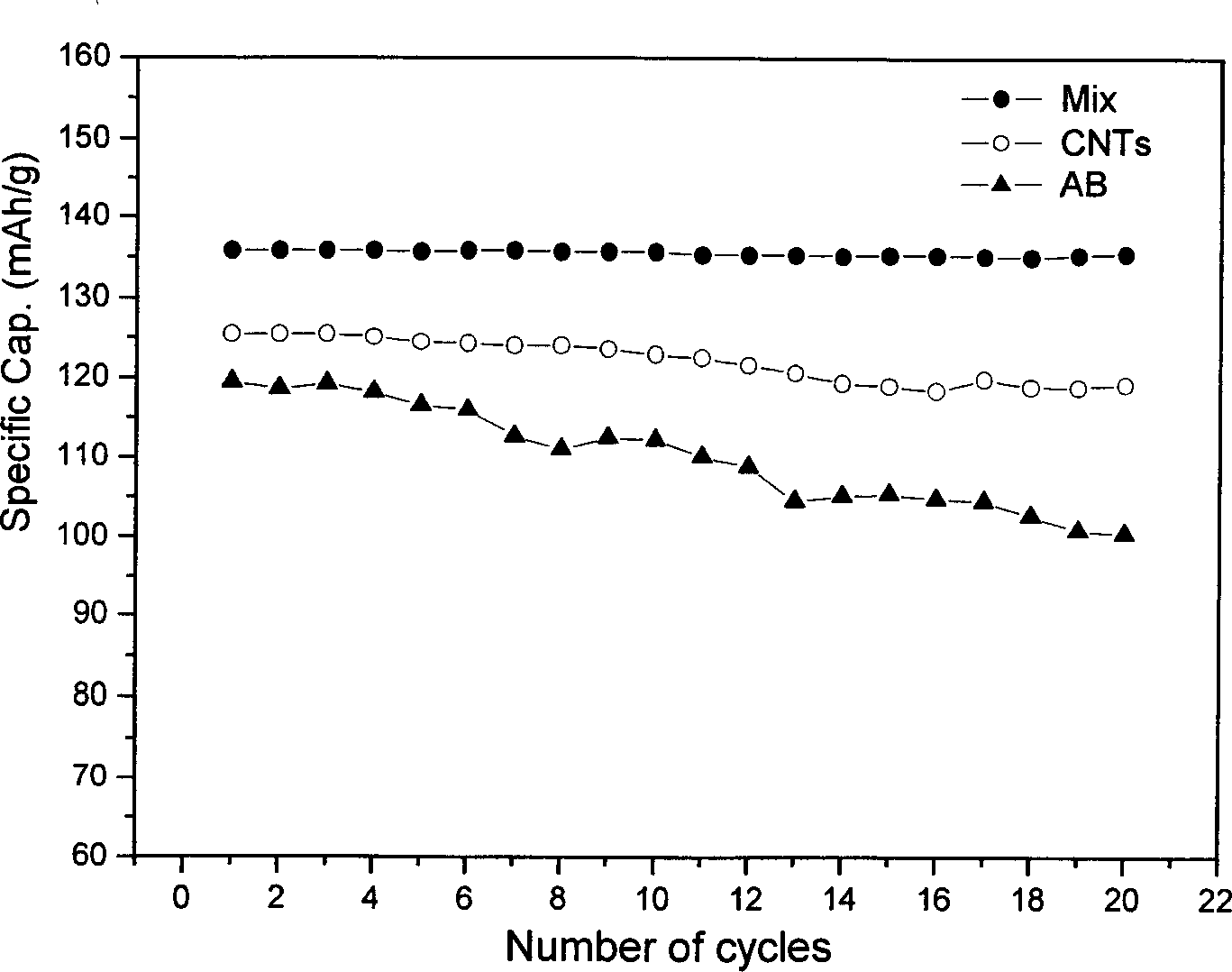
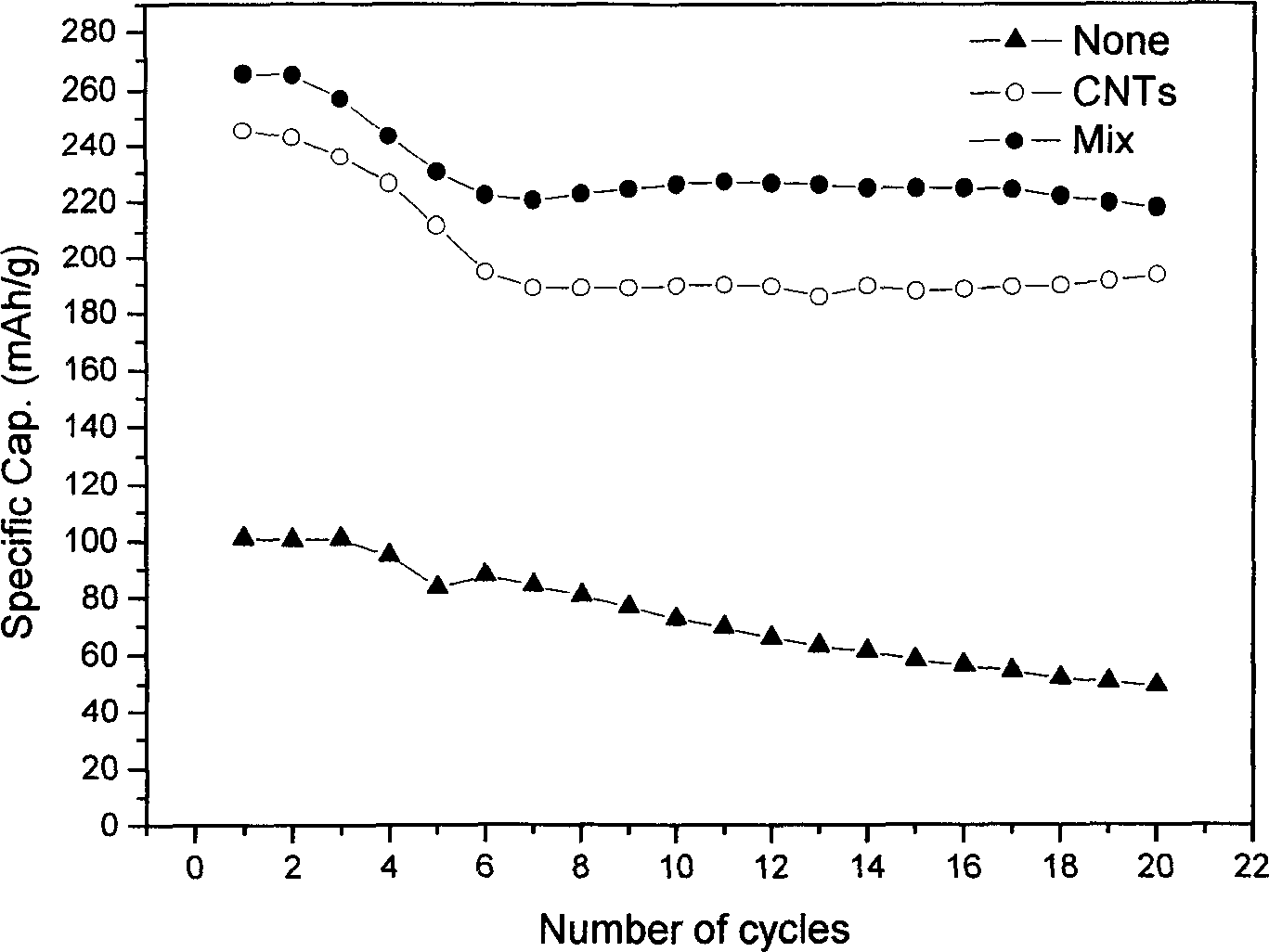
[0018] Add 2g of carbon nanotubes and 1.2g of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) to 100ml of deionized water or N-methylpyrrolidone; after ultrasonic dispersion, add 4g of acetylene black, and continue to mix by ultrasonic or high-speed stirring. The obtained mother liquor was suction-filtered into a sample with a dry weight of 20%. LiCoO as cathode active material for lithium-ion secondary batteries 2 4.7g, 0.75g of sample with a dry weight of 20%, 0.15g of LA132 positive electrode binder (provided by Chengdu Yindile Power Supply Co., Ltd.), disperse in a high-speed disperser for 30 minutes, and dry the mixed solution with a hair dryer to a certain viscosity The slurry is coated on the aluminum foil with a thickness of 60-80 μm. After drying at 100°C under vacuum, punch holes to make electrode sheets of φ16. A simulated battery was assembled with Cellgard2400 as the diaphragm and LiPF6 solution as the electrolyte. It was measured that it had a discharge specific capacity of 137mAh / ...
Embodiment 2
[0020] Add 0.6g of carbon nanotubes and 1.2g of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) to 150ml of deionized water or N-methylpyrrolidone; after ultrasonic dispersion, add 5.4g of acetylene black, and continue to mix by ultrasonic or high-speed stirring. The obtained mother liquor was suction-filtered into a sample with a dry weight of 6%. The preparation of the electrode sheets, the assembly and testing of the simulated battery are the same as in Example 1. It is measured that it has a discharge specific capacity of 129mAh / g when charging and discharging at 1C, which is 88% of that at 0.2C.
Embodiment 3
[0022] Add 3g of carbon nanotubes and 0.6g of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) to 100ml of deionized water or N-methylpyrrolidone; ultrasonically disperse for 5 minutes, then add 3g of acetylene black, and continue to mix by ultrasonic or high-speed stirring. The obtained mother liquor was suction-filtered into a sample with a dry weight of 15%. The preparation of the electrode sheets, the assembly and testing of the simulated battery are the same as in Example 1. It is measured that it has a discharge specific capacity of 141mAh / g when charging and discharging at 1C, reaching 0.2C
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Discharge specific capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Discharge specific capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Discharge specific capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com