Catalystic reforming method for hydrocarbons
A technology for catalytic reforming and hydrocarbons, applied in the direction of catalytic reforming of naphtha, etc., can solve problems such as catalyst activity decline, reformed product octane number reduction, catalyst acidity reduction, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
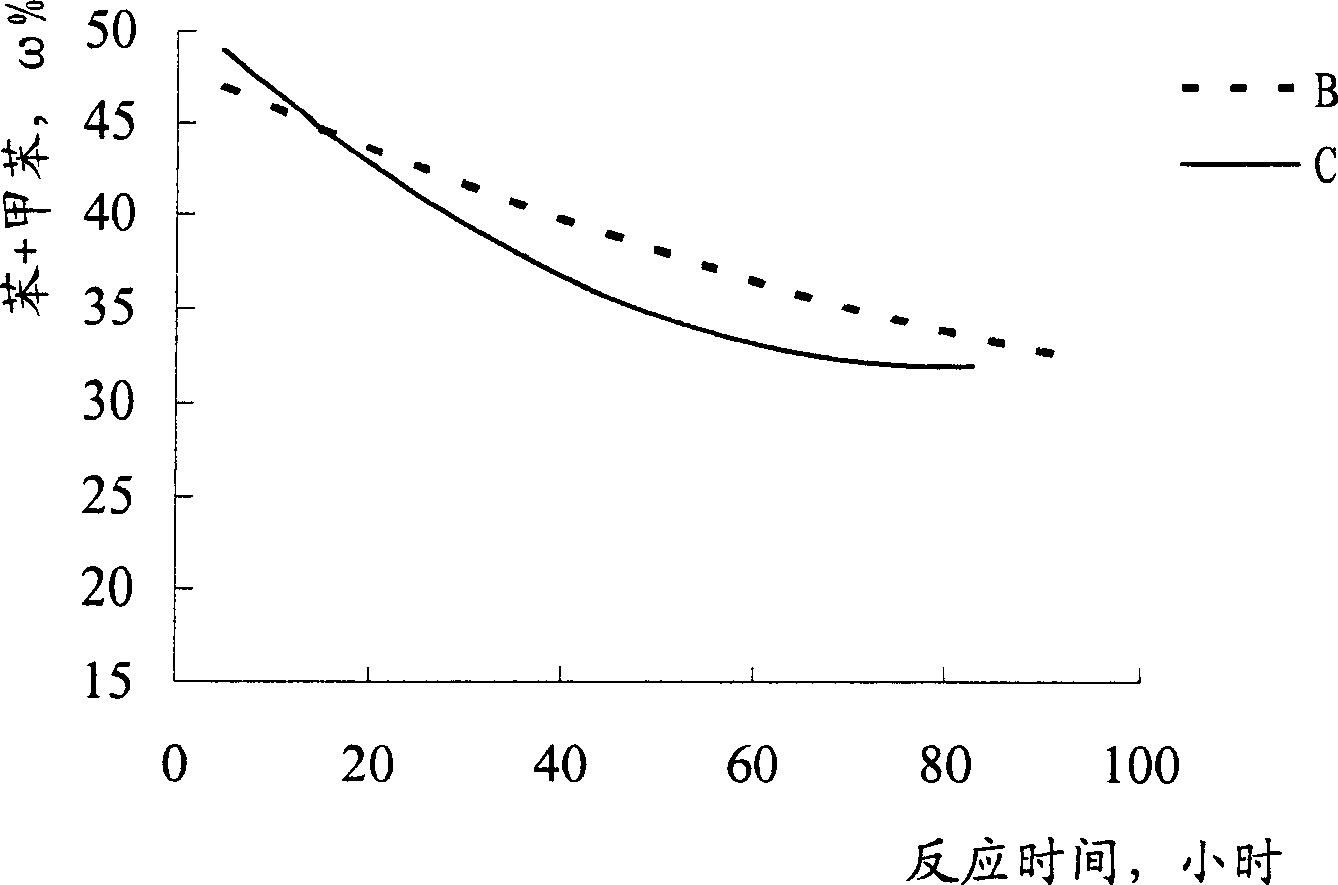
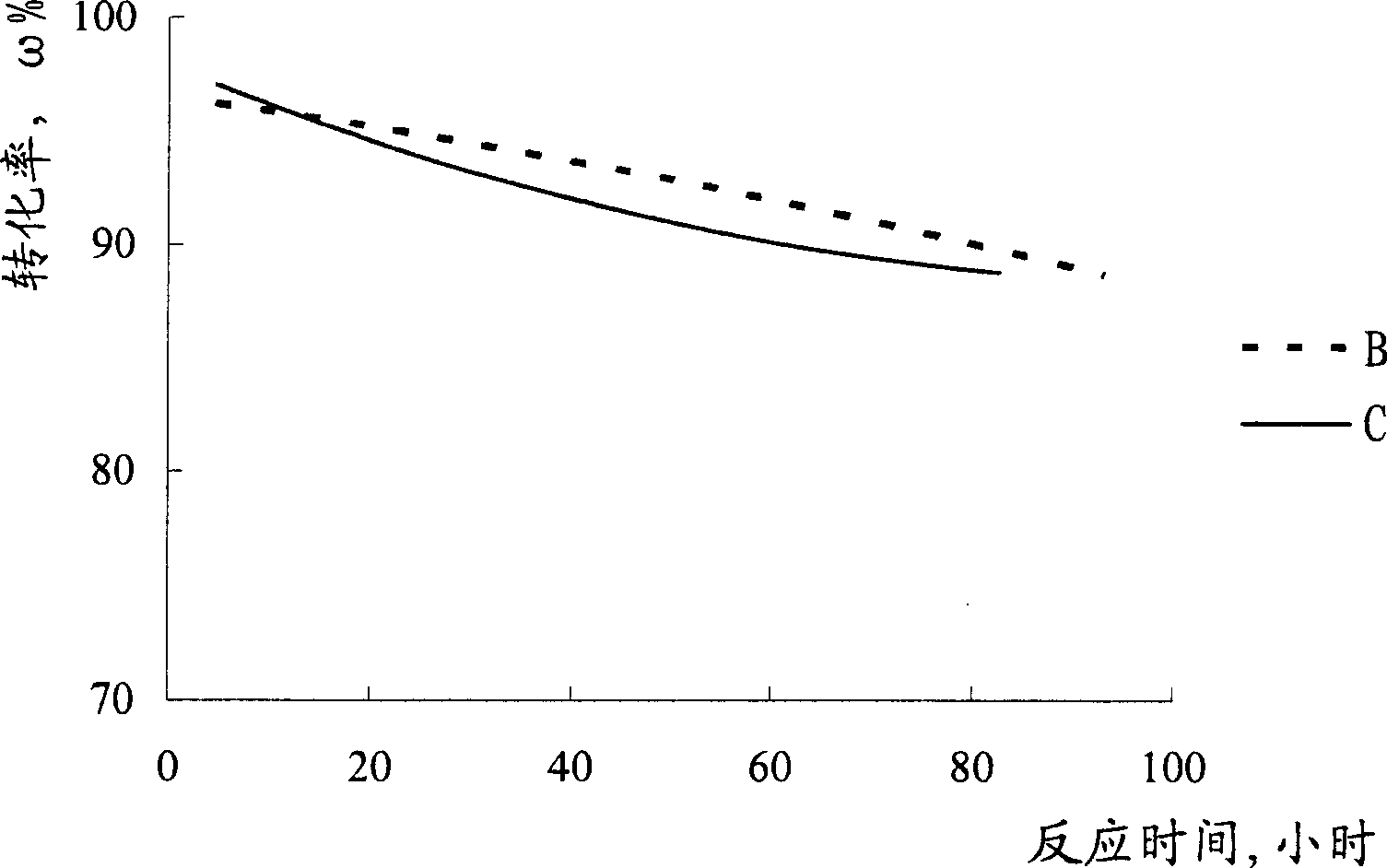
[0026] A stainless steel reactor is loaded with a bimetallic reforming catalyst, and the catalyst carrier is alumina, which contains 0.26% by mass of platinum, 0.28% by mass of rhenium, and 1.0% by mass of chlorine (both based on alumina). The reaction apparatus was purged first with nitrogen and then with hydrogen. Then, using n-heptane as a raw material, n-heptane and hydrogen are fed into the reactor, and the water content of the n-heptane is 1.0 ppm. At 500°C, 0.35MPa, n-heptane feed liquid hourly space velocity 3.0 -1 , Hydrogen / hydrocarbon volume ratio of 1000:1 under the conditions of the reaction. After the start of the reaction, phosphorus trichloride was added to the n-heptane feed every 24 hours, with each addition taking 12 hours. The addition amount of phosphorus trichloride is shown in Table 1, and the reaction result is shown in figure 1 , figure 2 .
example 2
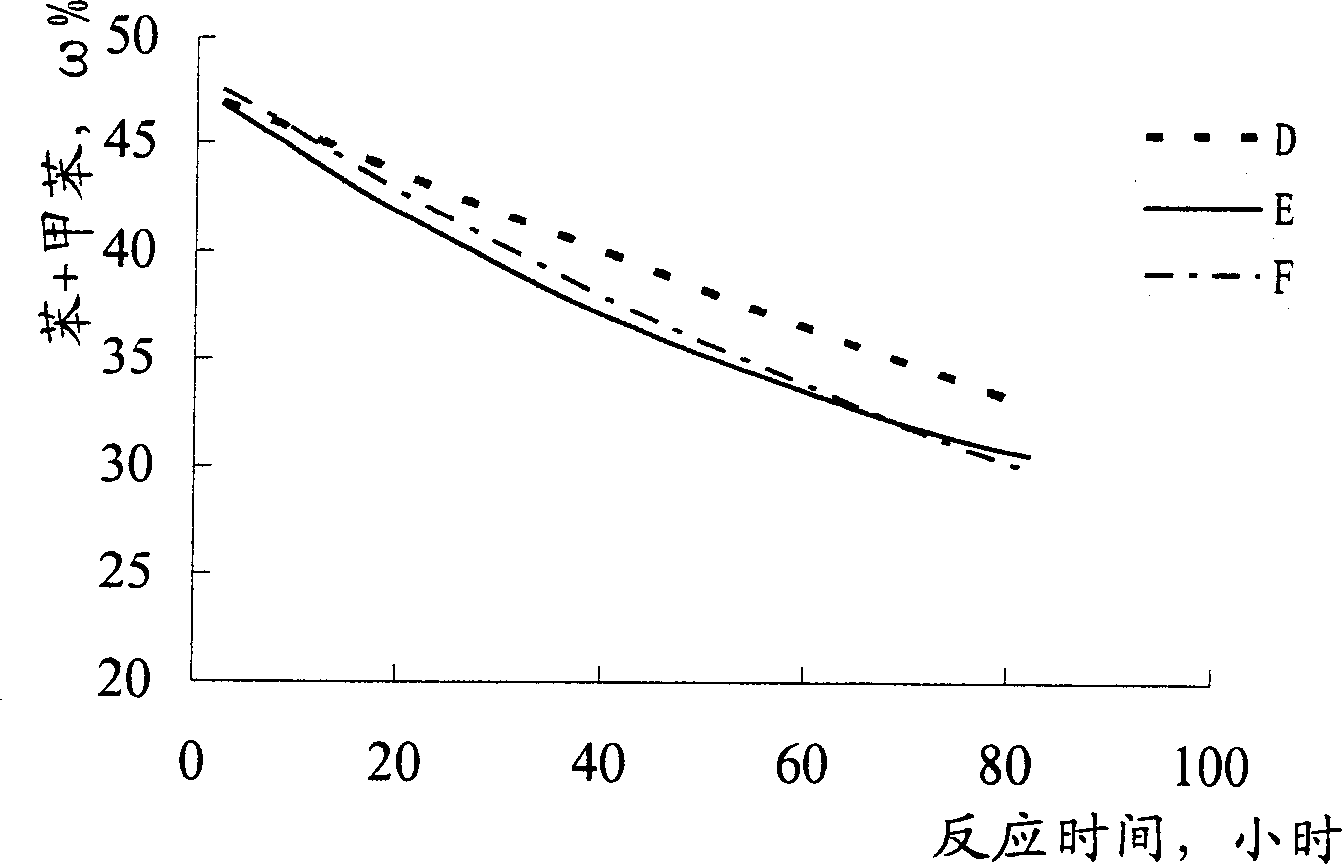
[0031] Carry out reforming reaction with n-heptane as raw material by the method for example 1, difference is to add phosphorus trichloride continuously when n-heptane feeds, and reaction result sees image 3 , Figure 4 .
example 3
[0038] Get the catalyst after the reaction of Example 2, Comparative Example 2 and Comparative Example 3, measure its carbon deposition amount, and take the catalyst carbon deposition amount without adding any substance in the raw material as a benchmark, calculate the reaction after adding different substances in the above three raw materials The amount of carbon deposition of the catalyst is reduced, such as Figure 5 shown. Depend on Figure 5 It can be seen that the reduction rate of the carbon deposition of the catalyst D obtained by the method of the present invention is close to 30%, that is to say, the carbon deposition of the catalyst has decreased by about 30%, indicating that the method of the present invention has a higher anti-coking performance.
[0039] instance number
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com