Contractibility acrylonitrile fiber capable of hypothermia staining
An acrylonitrile fiber, low-temperature dyeing technology, applied in the chemical characteristics of fibers, adding dyes in spinning solutions, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of increased loss, increased cost, increased consumption, etc., to achieve the effect of widespread use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~4
[0051] [Examples 1 to 4, Comparative Example 1]
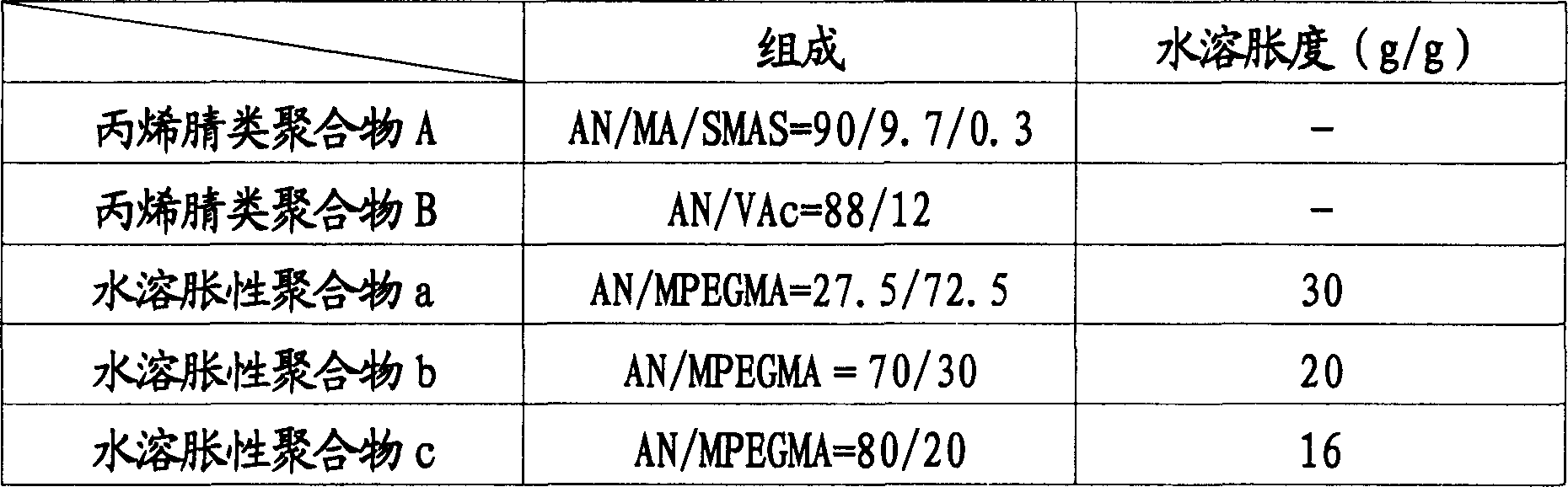
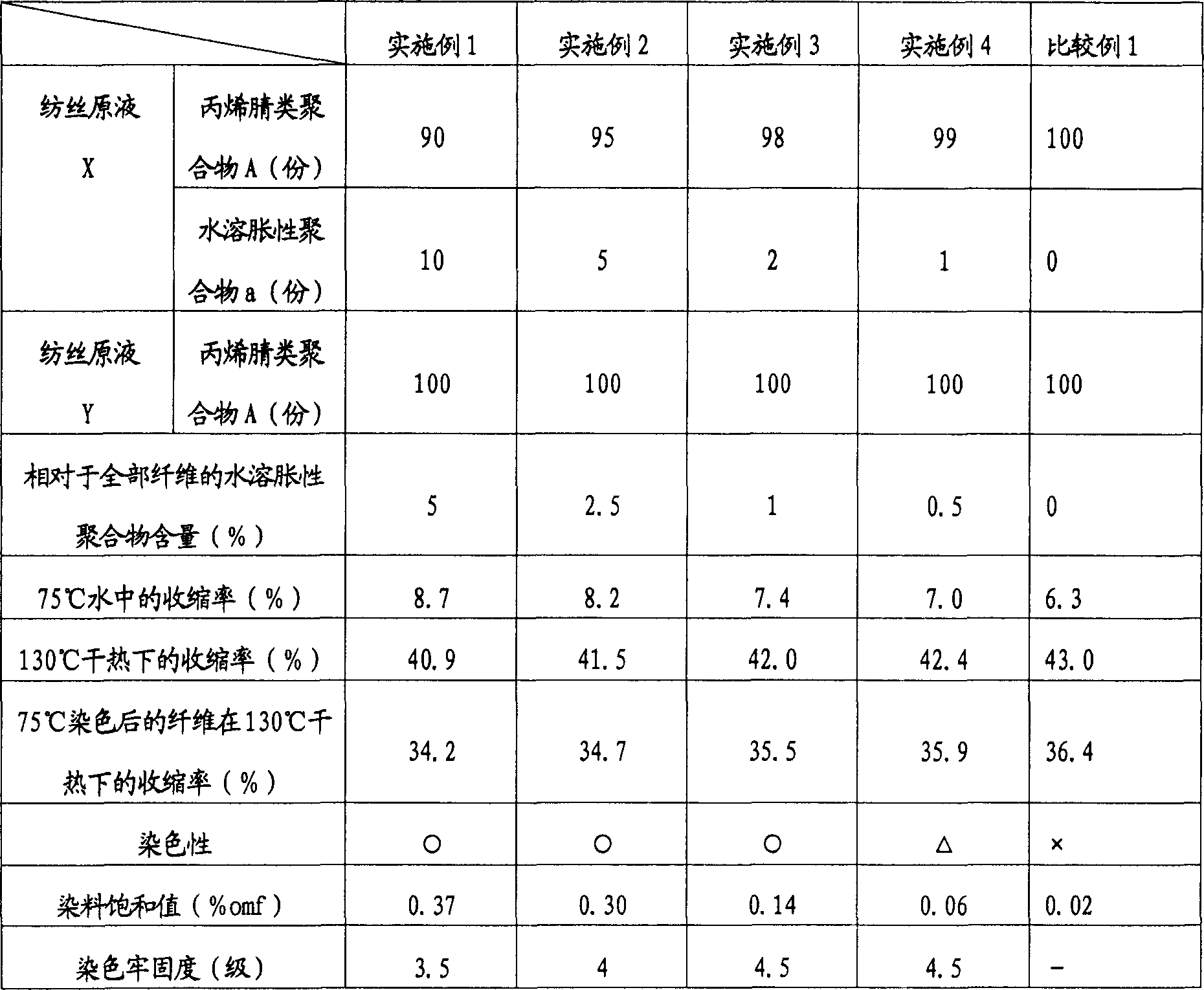
[0052] In 900 parts of a 50% sodium thiocyanate aqueous solution, the acrylonitrile-based polymer A was dissolved in the ratio shown in Table 2, and the spinning stock solution X was prepared by adding and mixing the water-swellable polymer a dispersed in water. Separately, 100 parts of acrylonitrile-based polymer A was dissolved in 900 parts of a 50% aqueous solution of sodium thiocyanate to prepare a spinning dope Y. Through the ordinary side-by-side composite fiber spinning nozzle, the X / Y ratio is 50 / 50, according to the manufacturing method of the ordinary shrinkable acrylonitrile fiber, the spinning dope X and Y are composite-spun to make the implementation Fibers of Examples 1-4. In addition, as Comparative Example 1, fibers to which no water-swellable polymer was added were produced. Table 2 lists the evaluation results of the shrinkage rate, dyeability, dye saturation value and dyeing fastness of the obtained fibers....
Embodiment 5~7、 comparative example 2
[0057] In 900 parts of a 50% sodium thiocyanate aqueous solution, the acrylonitrile-based polymer B was dissolved in the ratio shown in Table 3, and a spinning dope was prepared by adding and mixing the water-swellable polymer dispersed in water. The resulting spinning dope was spun according to the manufacturing method of common shrinkable acrylic fibers. Table 3 lists the evaluation results of the shrinkage rate, dyeability, dye saturation value and dyeing fastness of the obtained fibers.
[0058] Example 5
[0059] As shown in Table 3, in Examples 5 to 7, dyeing was possible even at 75° C., and shrinkable acrylic fibers having sufficient color fastness were obtained. Comparing these examples, it is considered that the higher the degree of water swelling of the added water-swellable polymer, the higher the dye saturation value exhibited by the fiber, and the dyeability tends to be improved. In addition, in Examples 5 to 7, the water-swellable polymer was dispers...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| shrinkage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com