Shunt circuit linearity insulating circuit apparatus
A technology of isolation circuit and photoelectric isolation circuit, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, DC isolation amplifiers, voltage/current isolation, etc., and can solve the problems of complex transformers, magnetization, and low common-mode rejection of photoelectric isolation circuits.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
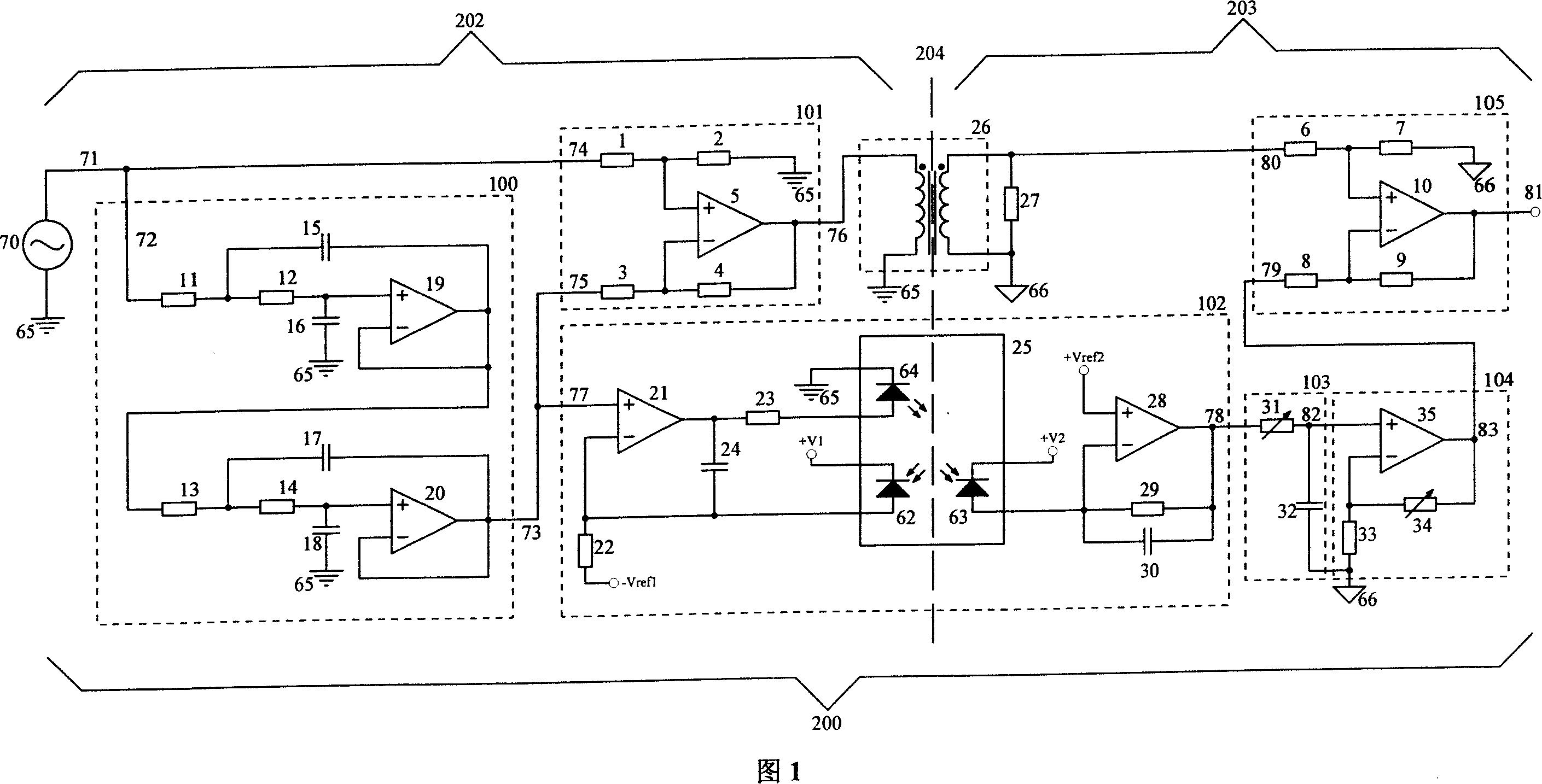
[0036] As shown in Figure 1, all components in the figure are connected by electronic components in the dotted line frame. The device of the present invention is the shunting linear isolation circuit device 200 (hereinafter referred to as the device 200) consisting of a low-pass filter 100 (hereinafter referred to as the filter 100), a subtractor 101, a transformer 26, a linear photoelectric isolation circuit 102 (hereinafter referred to as an optocoupler) Circuit 102), time constant adjustment circuit 103 (hereinafter referred to as circuit 103), low-path gain adjustment circuit 104 (hereinafter referred to as circuit 104) and signal combination circuit 105 (hereinafter referred to as combiner 105). The signal under test 70 is connected to an input 71 of the device 200 . The input 71 of the device 200 is connected to the input 72 of the filter 100 and to the positive input 74 of the subtractor 101 . The output terminal 73 of the filter 100 is not only connected to the negati...
Embodiment 2
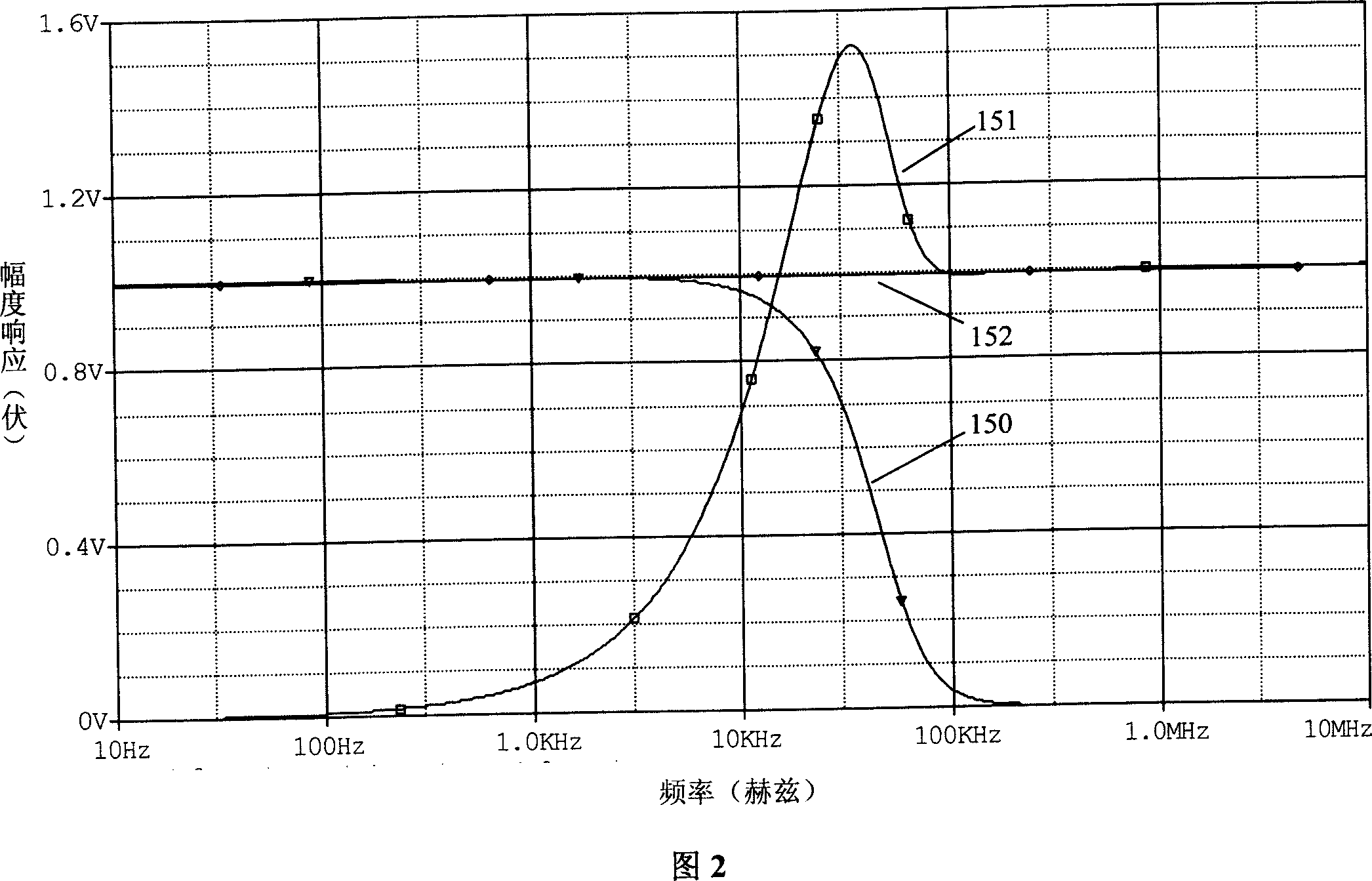
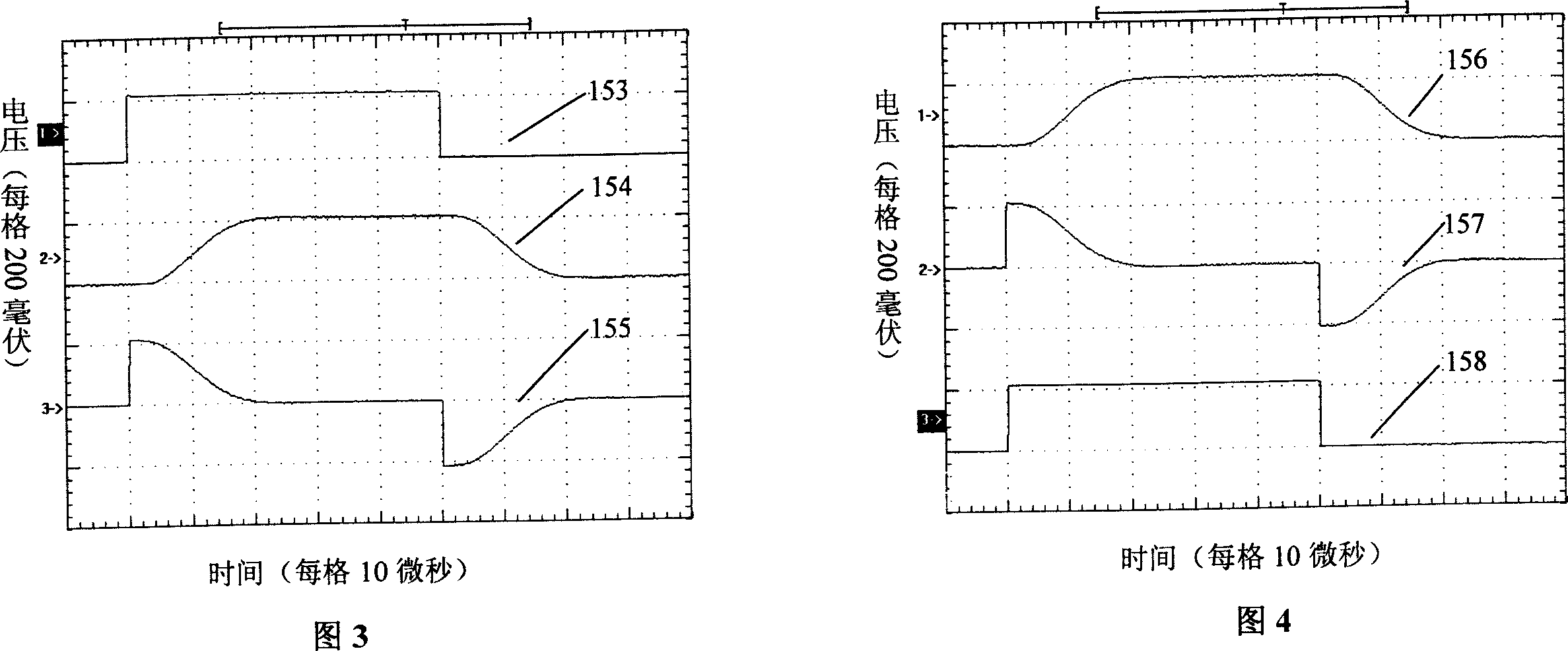
[0057] The circuit in Figure 1 has a high common-mode rejection ratio to DC and low-frequency common-mode interference, but it has a small common-mode rejection ratio to high-frequency common-mode signals. In order to further improve the high-frequency common-mode rejection ratio of the shunt linear isolation circuit device, the circuit in Figure 1 can be changed to a differential form. Figure 8 shows an example of a differential form. In Fig. 8, low-pass filter 100, subtractor 101, transformer 26, optocoupler circuit 102, time constant adjustment circuit 103, low path gain adjustment circuit 104 and signal combining circuit 105 are the same as the embodiment shown in Fig. 1 , and will not repeat them here. The difference is that the driving and receiving of the transformer are changed to differential driving and differential receiving, and the photoelectric isolation circuit adds a set of circuits exactly the same as the optocoupler circuit 102, that is, the optocoupler circ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com