Method for preserving cells, tissues or organs in hypothermia
a technology for preserving cells and tissues, applied in the field of preserving cells, tissues or organs in hypothermia, can solve the problems of not being able to meet the needs of all cell types, unable to meet the needs of thawing, and not being able to achieve the survival and maintenance of cell functional capacities, so as to improve the survival and proliferative capacity of said cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Placental blood CD34+ cells
Materials and Methods
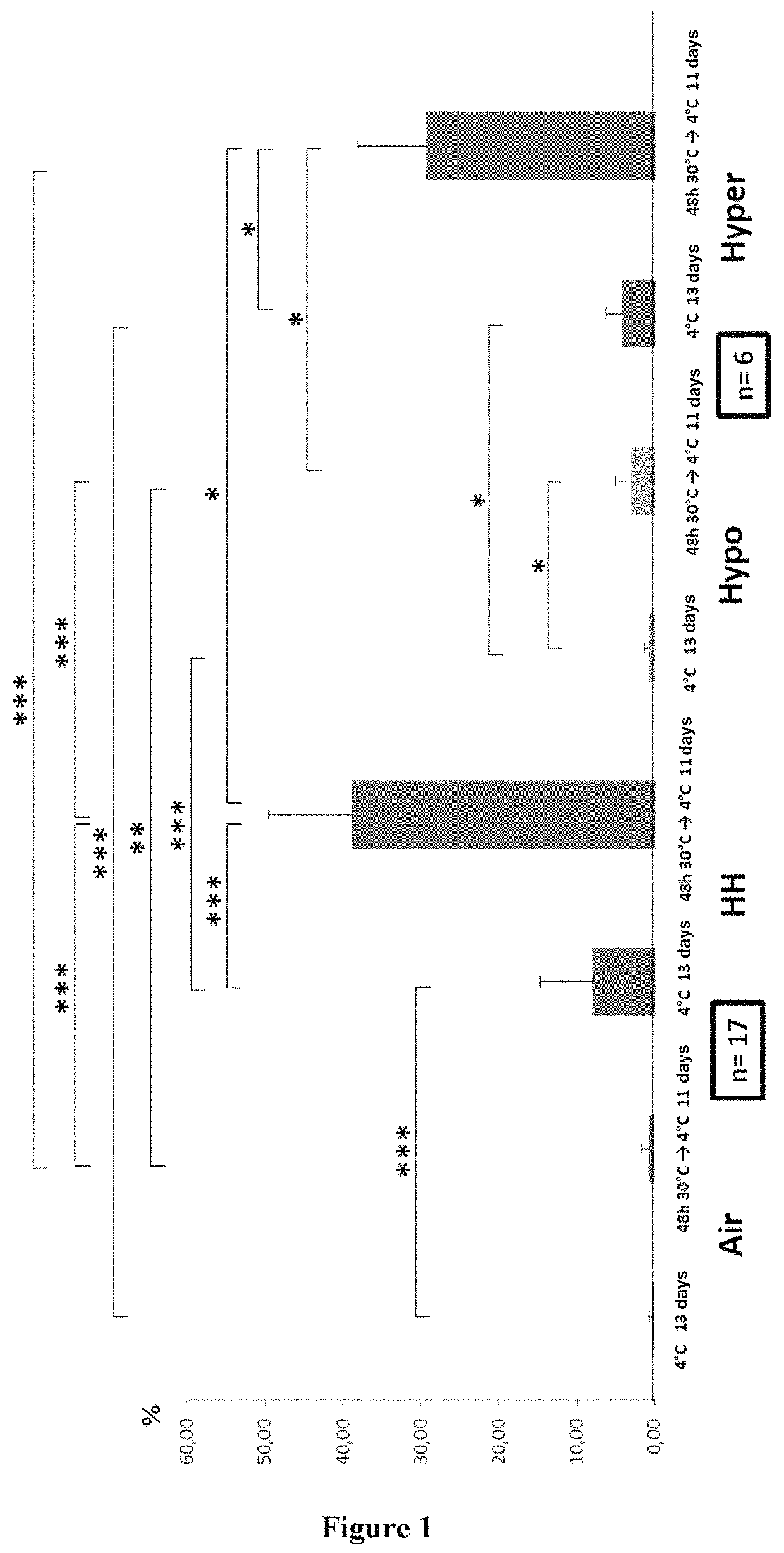
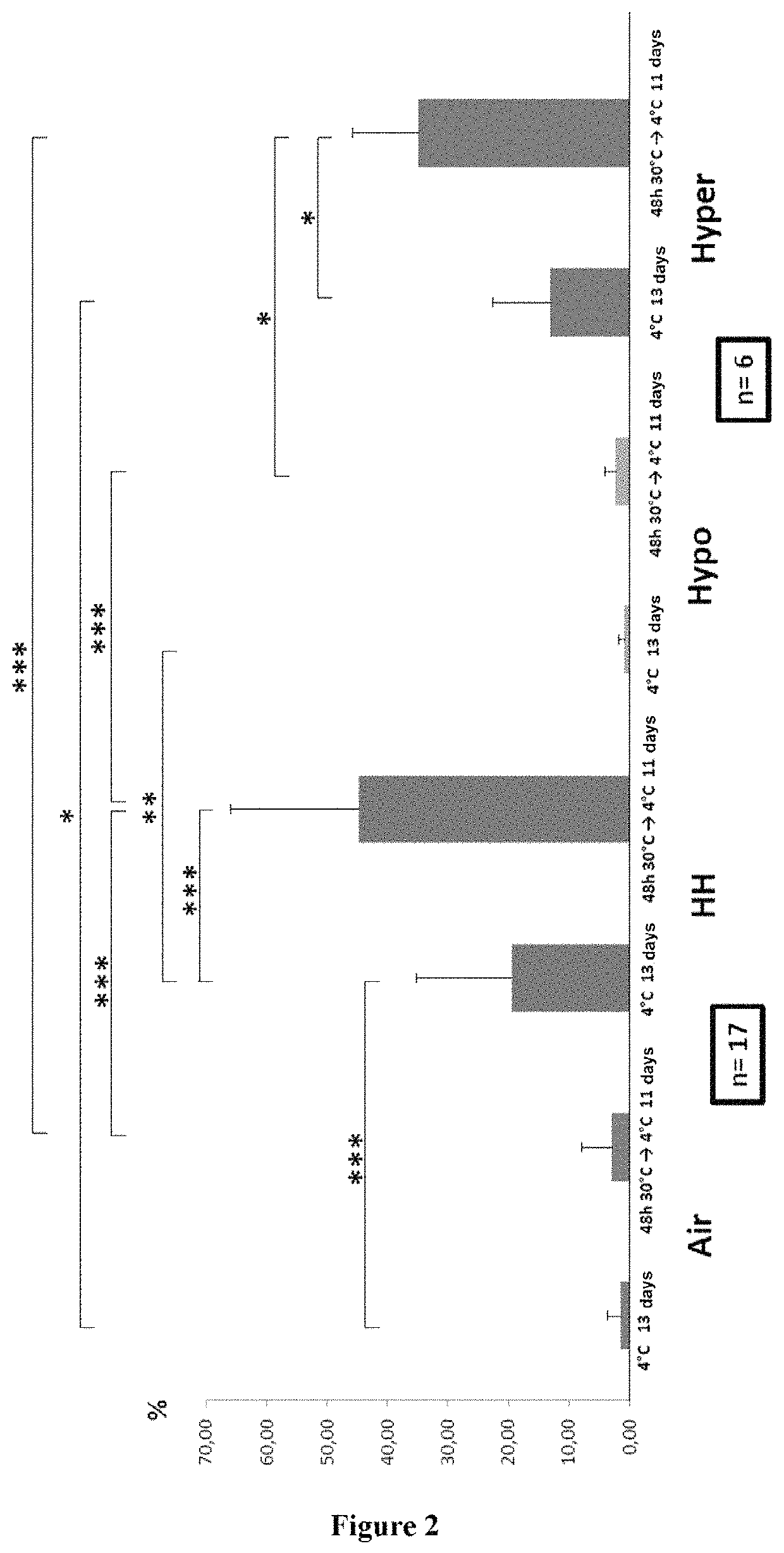
[0081]After being isolated by an immunomagnetic system, CD34+ cells were incubated overnight in culture at 37° C. in HP01 medium (Macopharma) in the presence of stem cell factor (SCF; 100 ng / mL), thrombopoietin (20 ng / mL) and IL-3 (1 ng / mL) at a concentration of about 105 cells per mL. This medium ensures the survival of CD34+ cells without stimulating their proliferation. This culture was divided into 8 gas-impermeable flasks (2 per atmospheric condition: i) air (21% O2, 0.01% CO2); ii) hypoxia / hypercapnia (HH) (9% CO2, 5% O2); iii) hypoxia (5% O2, 0.001% CO2); iv) hypercapnia (20% O2 and 20% CO2)). All the flasks are placed overnight (about 16 hours) at 37° C. then 1 hour in modified atmosphere according to the preceding conditions at 37° C. One flask per condition is placed directly at +4° C. for 13 days and the other at 30° C. for 2 days, then at +4° C. for 11 days (13 days in total). At the end of this period, the cells were heate...
example 2
Mesenchymal Cells
Materials and Methods
[0087]In this example, and for the sake of clarity, only mesenchymal cells (MCs) capable of forming adherent fibroblast-like cell colonies (CFU-F) were considered.
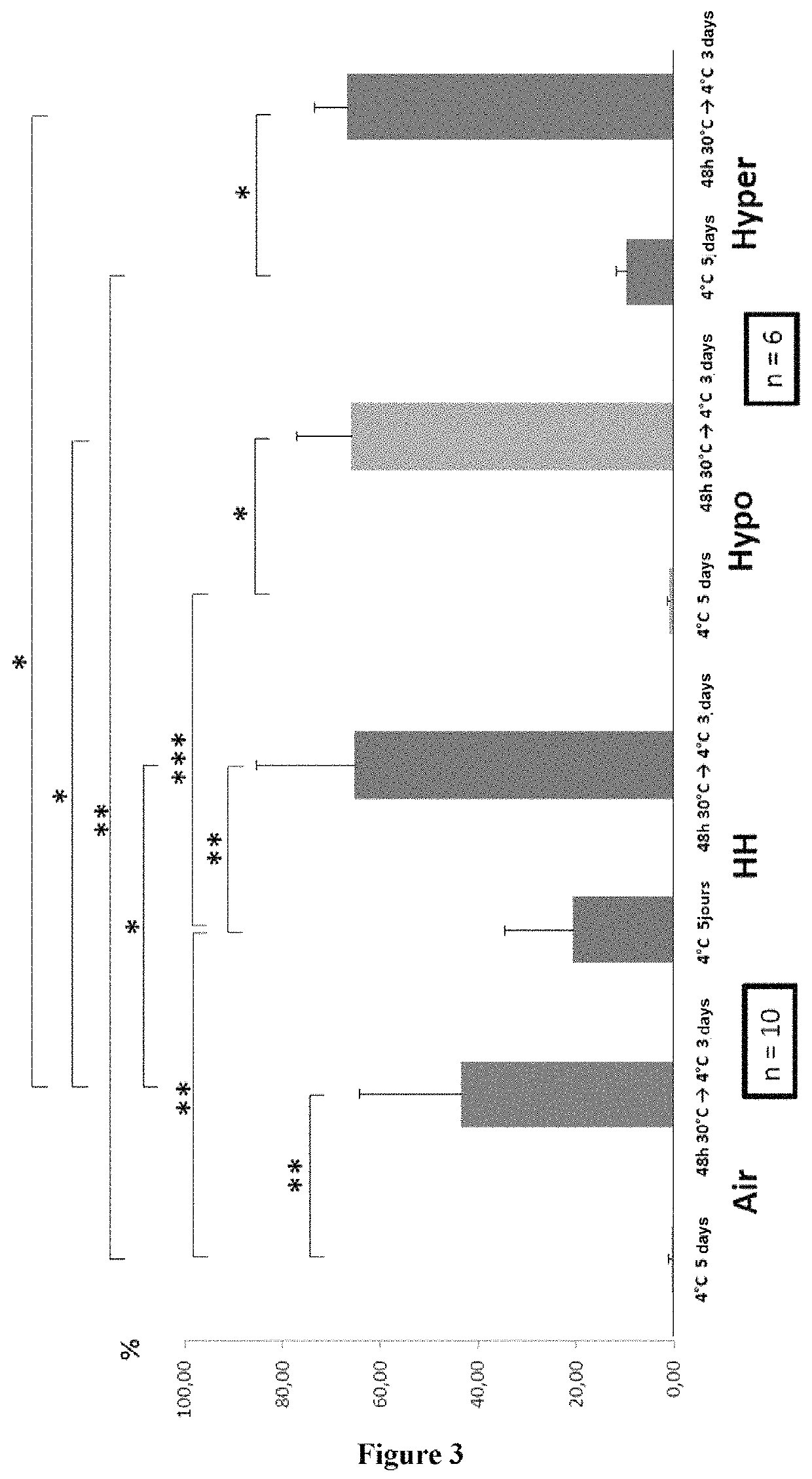
[0088]Previously frozen mesenchymal cells produced from human bone marrow (cells retained on filters used for bone marrow filtration before transplantation) were thawed, cultured (α MEM, 10% FCS, β FGF (1 ng / mL), L-glutamine (2 mM), 0.5% penicillin-streptomycin) at 37° C. and 5% CO2 in 9 flasks and amplified to confluence. The flasks are then vented at 37° C. as follows: i) air (21% O2, 0.01% CO2); ii) hypoxia / hypercapnia (HH) (9% CO2, 5% O2); iii) hypoxia (5% O2, 0.001 CO2); iv) hypercapnia (20% O2 and 20% CO2) (2 flasks per condition; the 9th flask being used for analysis of viability / apoptosis and for the clonogenic test before preservation in hypothermia). For each condition, the first flask was placed directly at +4° C. and preserved at 4° C. for 5 days and the second was maintain...
example 3
Cells of the FDCPmix Cell Line
Materials and Methods
[0092]FDCPmix cells are amplified at 37° C. and 5% CO2 in RPMI medium supplemented with 20% horse serum and 8% WEHI-conditioned medium (source of interleukin-3). The cells are then divided into 2 flasks per condition under the following conditions: i) air (21% O2, 0.01% CO2); ii) hypoxia / hypercapnia (HH) (9% CO2, 5% O2); iii) hypoxia (5% O2, 0.001 CO2); iv) hypercapnia (20% O2 and 20% CO2). The protocol followed is the same as for mesenchymal cells in Example 2.
Results
[0093]Maintenance of FDCPmix cells is poor in air and in hypoxic / hypercapnic conditions without a period in moderate hypothermia (directly at +4° C.).
[0094]On the other hand, the combination hypoxia / hypercapnia or hypercapnia alone with a period in moderate hypothermia provides very good maintenance with about 60% of the FDCPmix cells (FIG. 5).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com