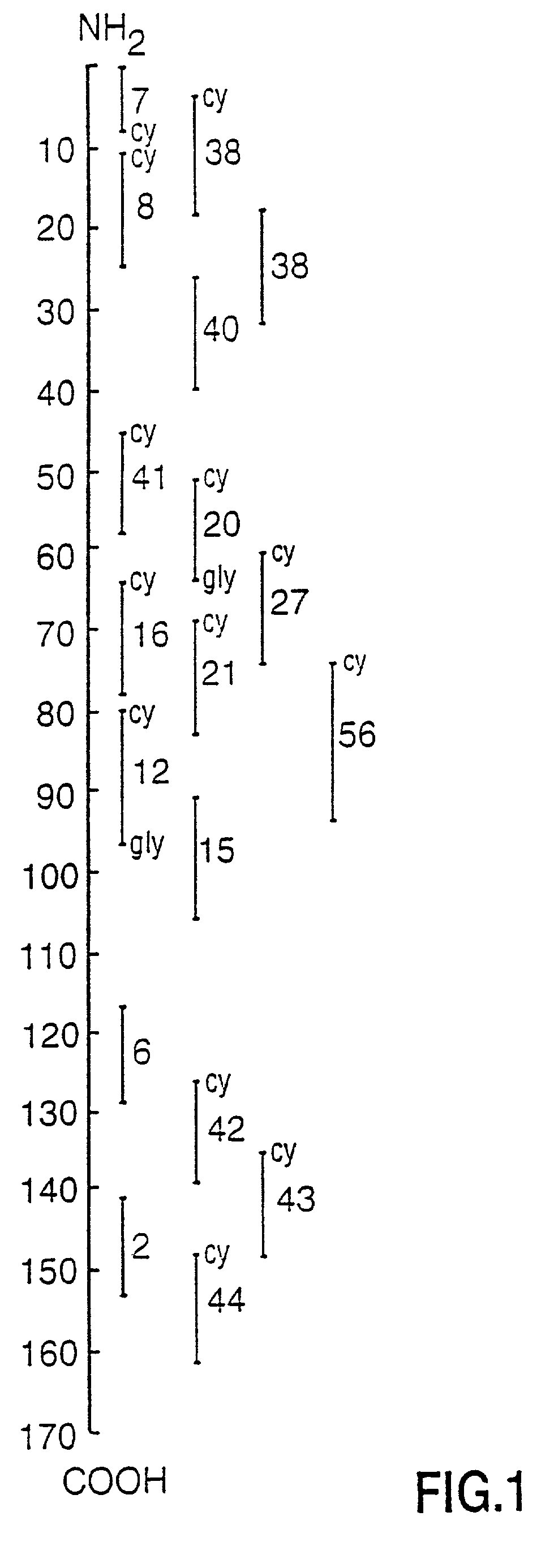
Peptide specificity of anti-myelin basic protein and the administration of myelin basic protein peptides to multiple sclerosis patients
a technology of myelin and basic protein, which is applied in the field of peptide specificity of antimyelin basic protein and the administration of myelin basic protein peptides to multiple sclerosis patients, can solve the problems of two-fold native mbp, potential danger of latent neuroviruses in the sample, and inability to treat ms by intramuscular or subcutaneous administration of heterologous mbp, etc., to achieve low levels and the effect o
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
In vivo Neutralization or Modulation of Production of Anti-Human Myelin Basic Protein
[0105] Patient Selection and Control Studies
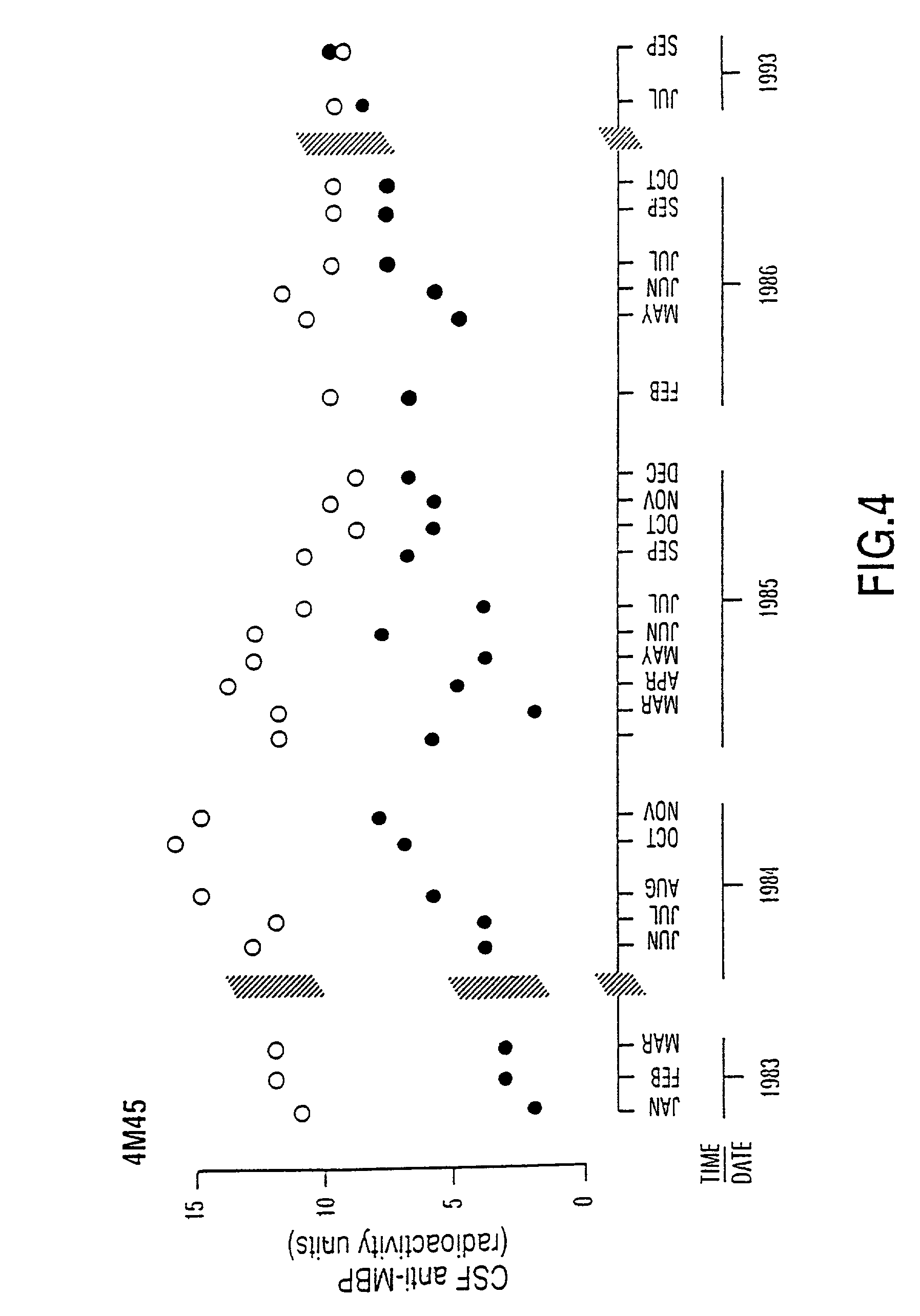
[0106] Patients who participated in this research project were seen in the Multiple Sclerosis Patient Care and Research Clinic of the University of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada. The patients have been diagnosed as having clinically definite multiple sclerosis by Schumacher criteria (1965) confirmed by magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and CSF immunochemistry profiles. In order to illustrate that in chronic progressive MS anti-MBP was persistently elevated over long periods of time, months to years, patients had repeated lumbar punctures with monitoring of F and B anti-MBP. In a patient with chronic progressive MS, it was observed that the autoantibody remained persistently elevated for periods as long as 11 years and that spontaneous decline of anti-MBP levels did not occur (FIG. 4 is an illustrative example).
[0107] In order to determine that initially ...
example 3
Appropriate Dosage of Intrathecally Administered pMBP86-95 or pMBP82-98 in Acute Relapsing Patients
[0132] MS relapses are associated with F / B anti-MBP ratios greater than 1.0 due to higher levels of free than bound antibody in CSF. Generally, over a period of 3 months, as a relapse enters into the subsequent recovery / remission phase, F anti-MBP levels gradually decline, and when biological remission is complete, CSF, F and B anti-MBP generally become undetectable in CSF.
[0133] Patients who participated in the following Examples had either relapsing-remitting or relapsing-progressive MS.
[0134] In this and the following Examples either pMBP86-95 or pMBP82-98 were used. pMBP86-95 had very low solubility in normal saline since it contained four hydrophilic and six hydrophobic residues. On the other hand, pMBP82-98 has increased solubility in normal saline, as a result of the five additional hydrophilic residues.
[0135] Two patients were studied to determine the appropriate dosage of intr...
example 4
Frequency and Duration of Administration in Patients with Monosymptomatic Relapses
[0137] In this example the frequency and duration of administration of pMBP that would maintain low or undetectable F antibody levels for a longer time period were determined. The four patients studied in this group received synthetic peptides within a week from the onset of an attack.
[0138] The first two patients had attacks of acute unilateral optic neuritis. One of these patients (FIG. 11a) received intrathecally two injections of 50 mg pMBP86-95 (it#1, it#2) four weeks apart. After each injection F anti-MBP became undetectable within 1 h. When measured 1 week after the first injection the F anti-MBP was elevated, and 4 weeks later the F antibody was significantly high. At that time the patient has a second intrathecal injection (it#2) and F anti-MBP became undetectable after 30 minutes but it was not subsequently monitored beyond 24 hours. It was concluded that this frequency was inadequate and tha...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| body weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com