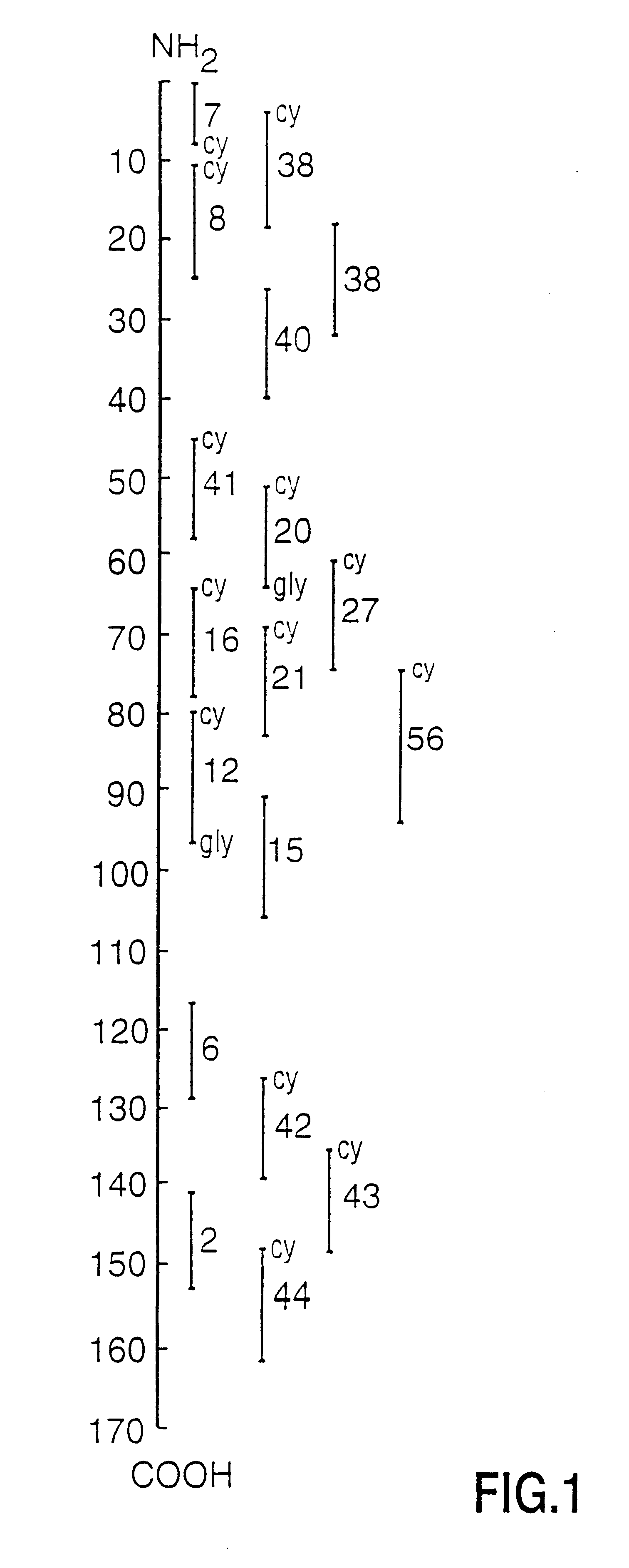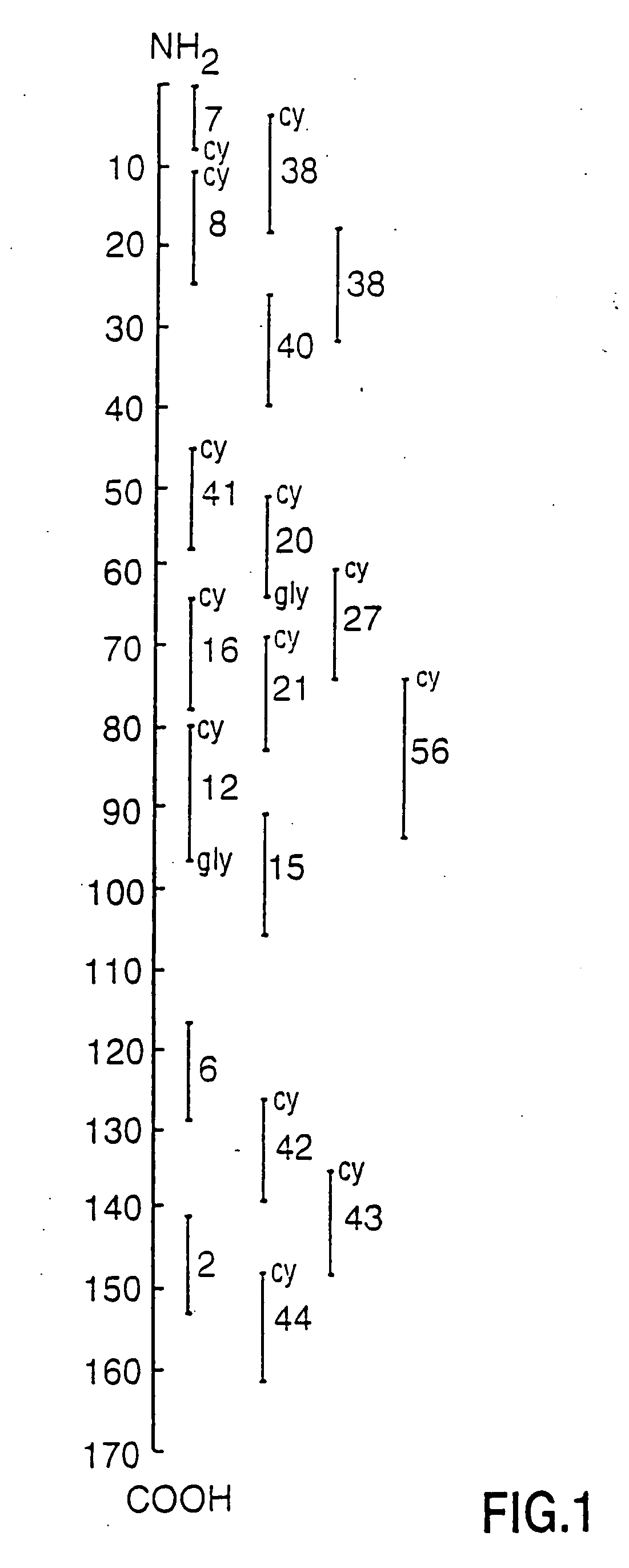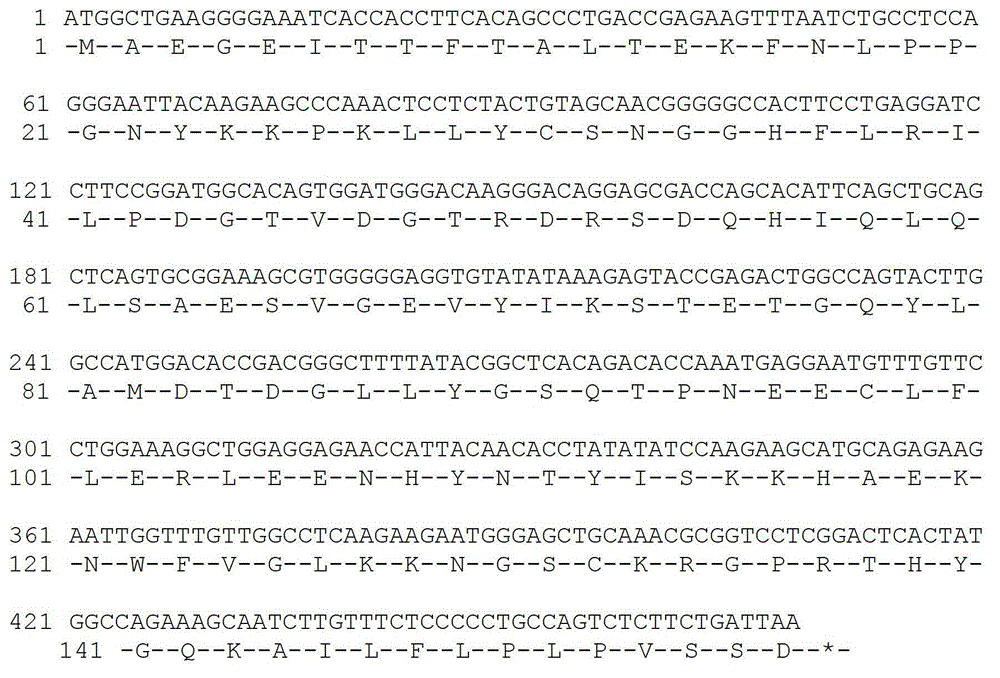Patents
Literature
78 results about "Myelin sheath structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
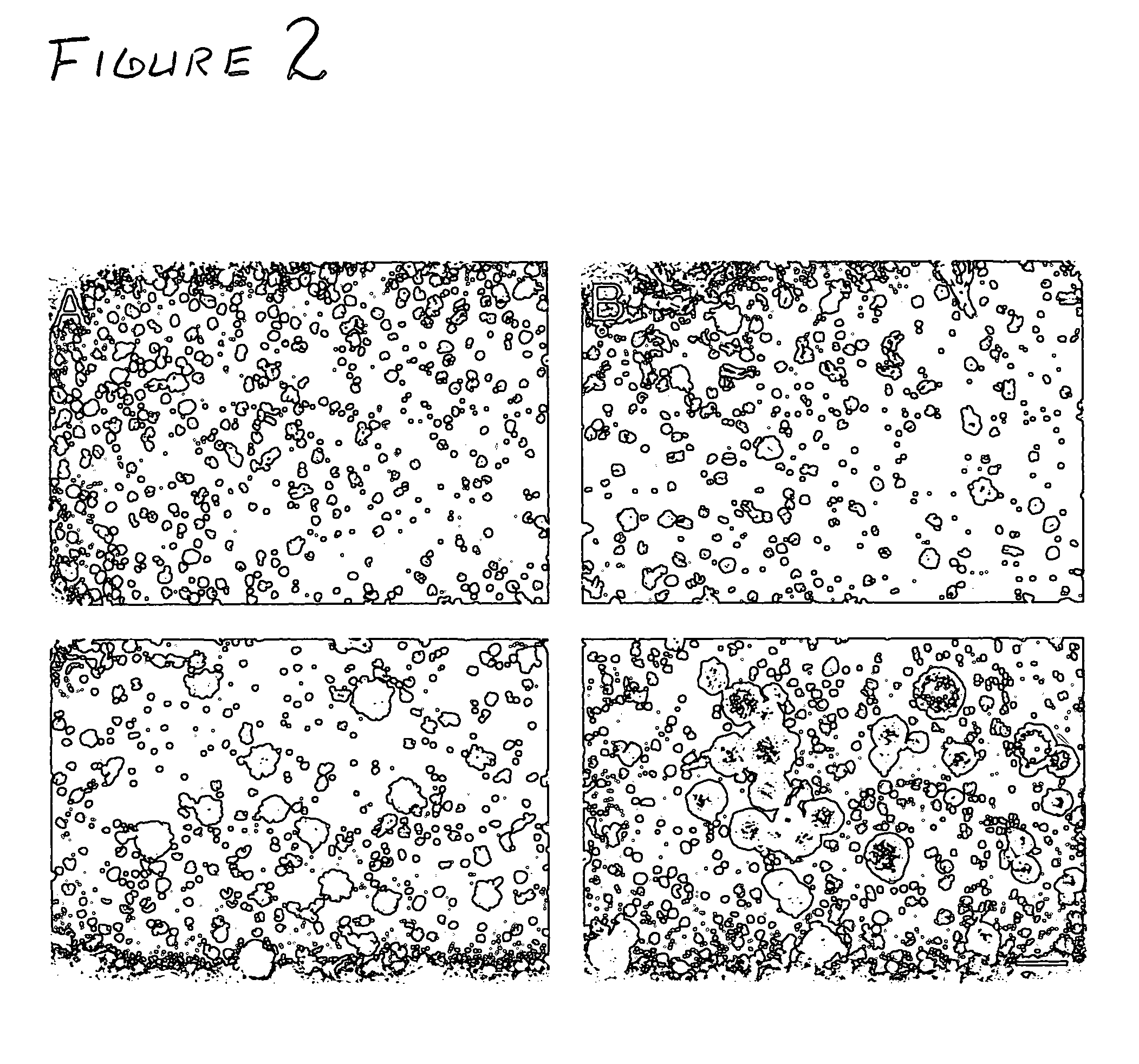
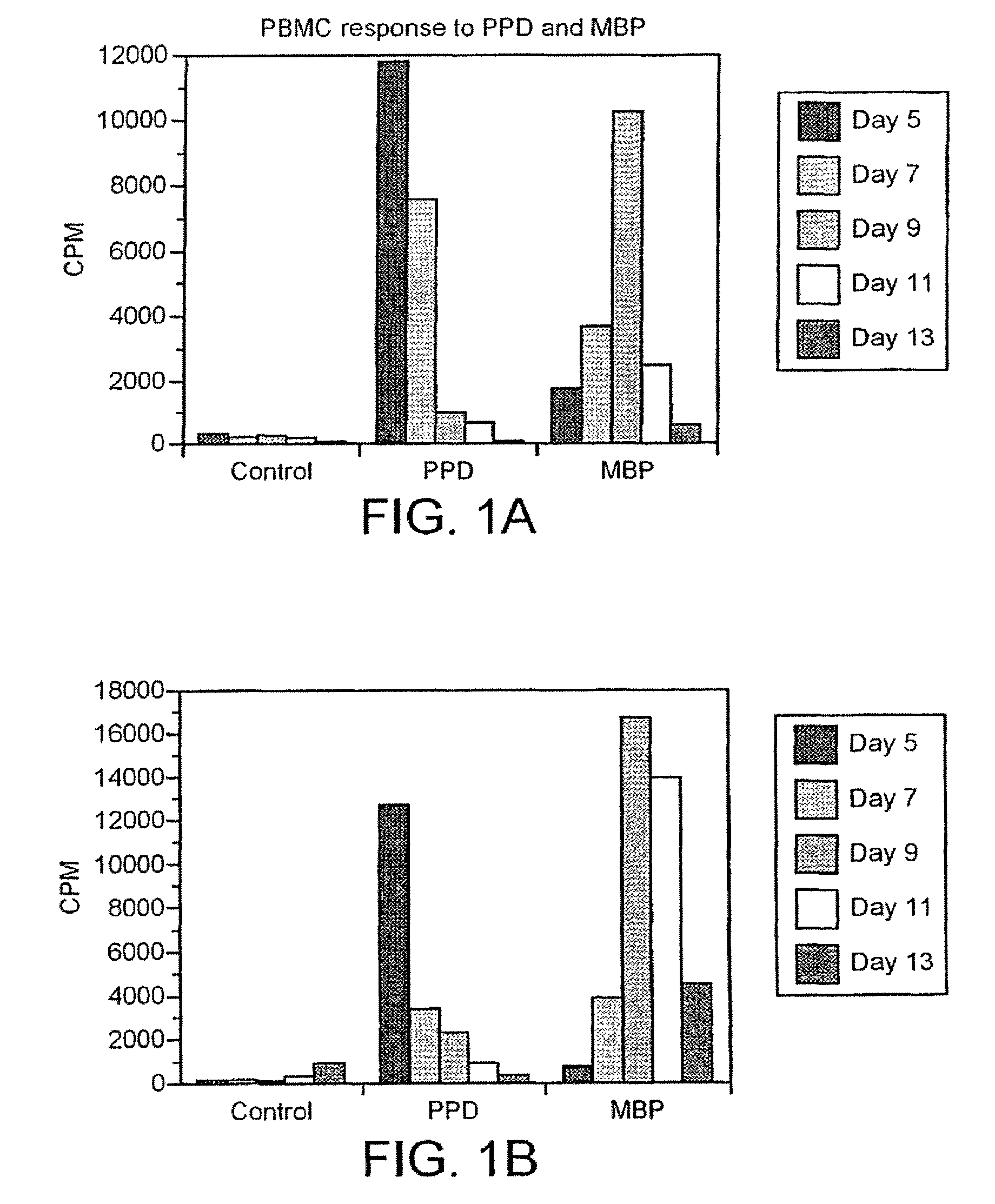
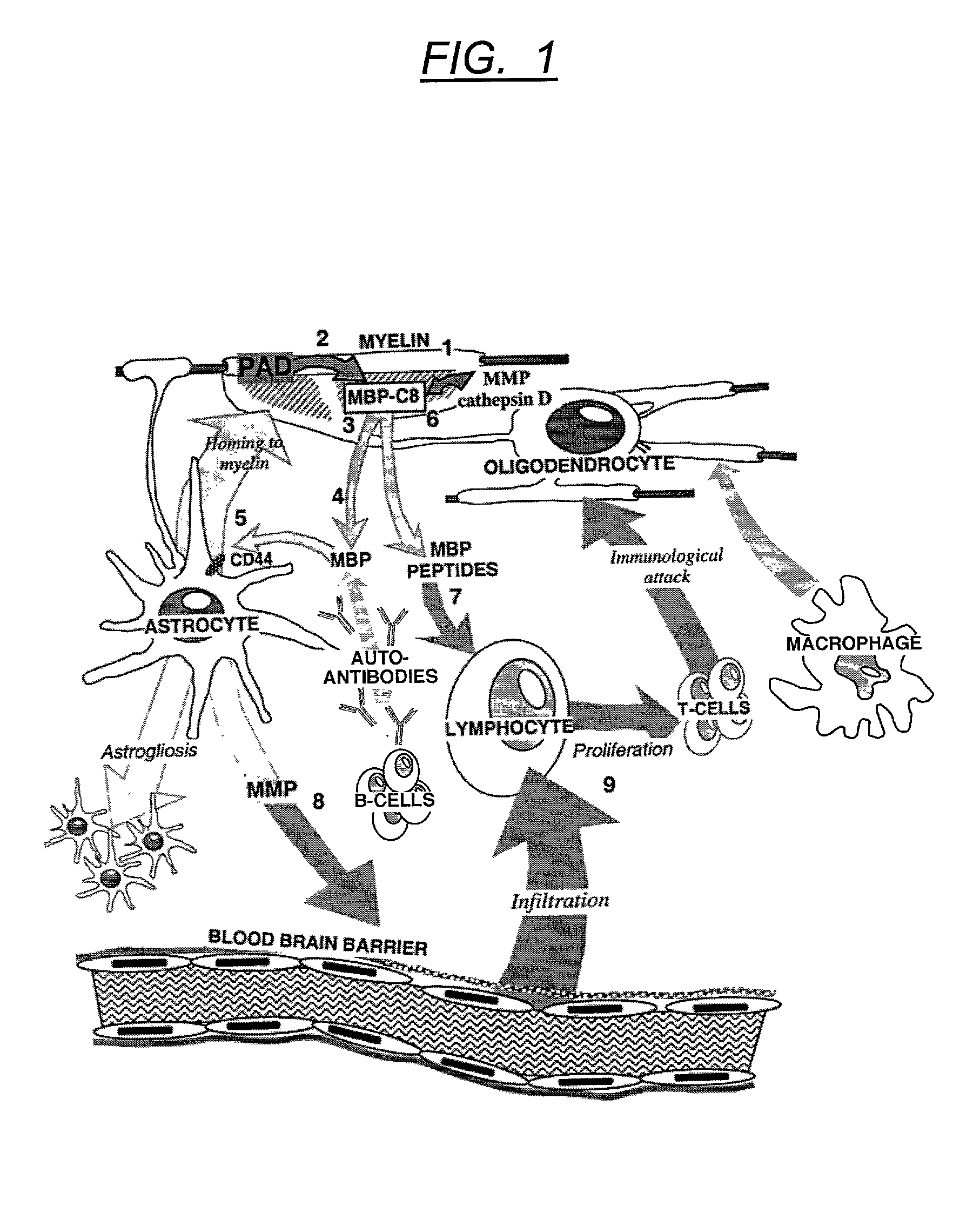
The myelin sheath is a multi-layered membrane, unique to the nervous system, that functions as an insulator to greatly increase the velocity of axonal impulse conduction. MBP maintains the correct structure of myelin, interacting with the lipids in the myelin membrane.
Peptide composition
InactiveUS8343500B2Simplify the development processReduce capacityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseMHC class I
Owner:APITOPE TECH BRISTOL
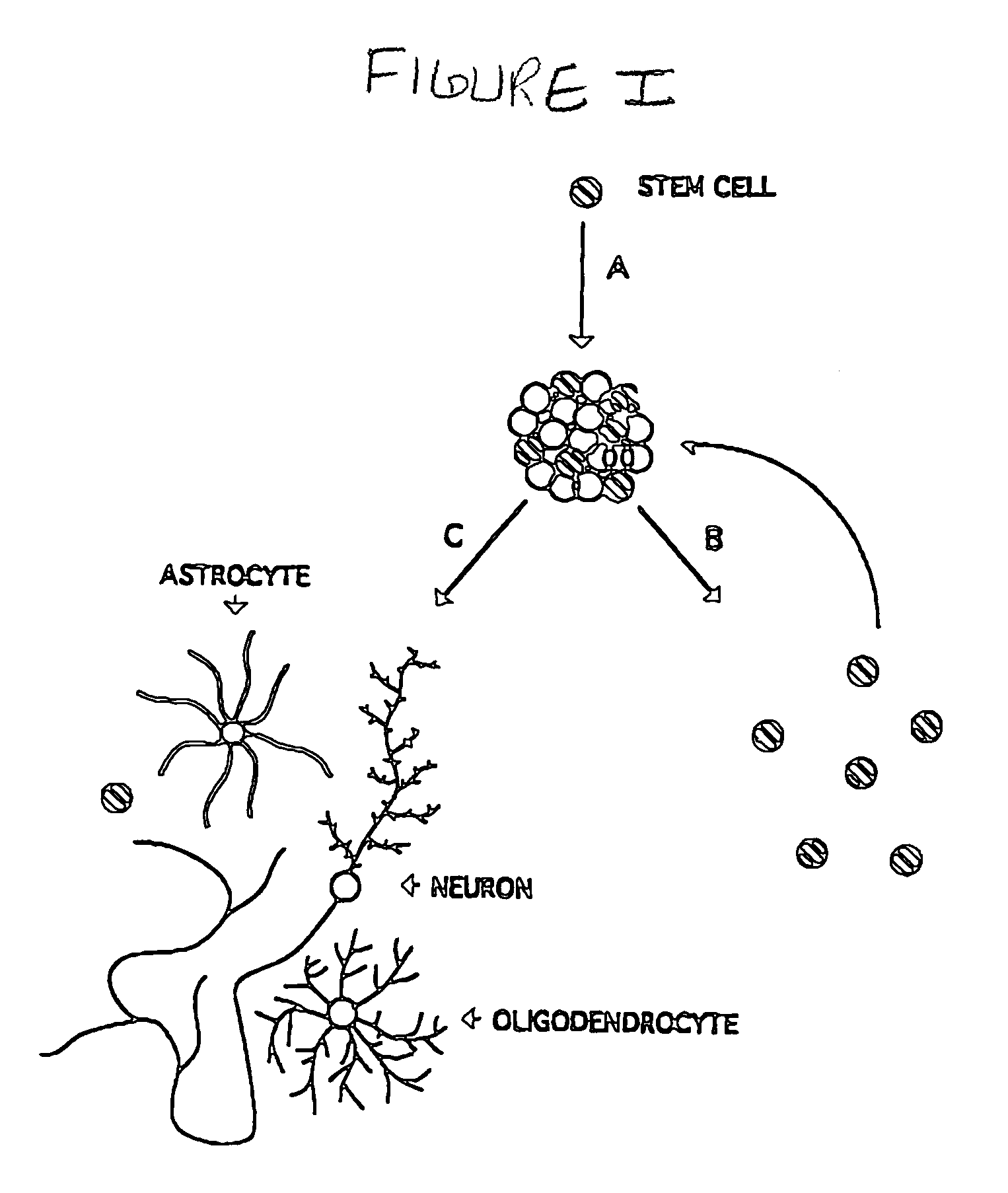
Multipotent neural stem cell compositions
ActiveUS7361505B1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsGlial fibrillary acidic proteinGlial Fibrillary Acid Protein
The invention provides in vitro cell culture compositions consisting of neurospheres and culture medium, wherein the neurospheres consist of undifferentiated cells that are nestin+, glial fibrillary acid protein (GFAP)−, neurofilament (NF)−, and myelin basic protein (MBP)− and are not nestin−.
Owner:BOCO SILICON VALLEY INC
Peptide composition
InactiveUS20080200368A1Simplify the development processReduce capacityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseMHC class I
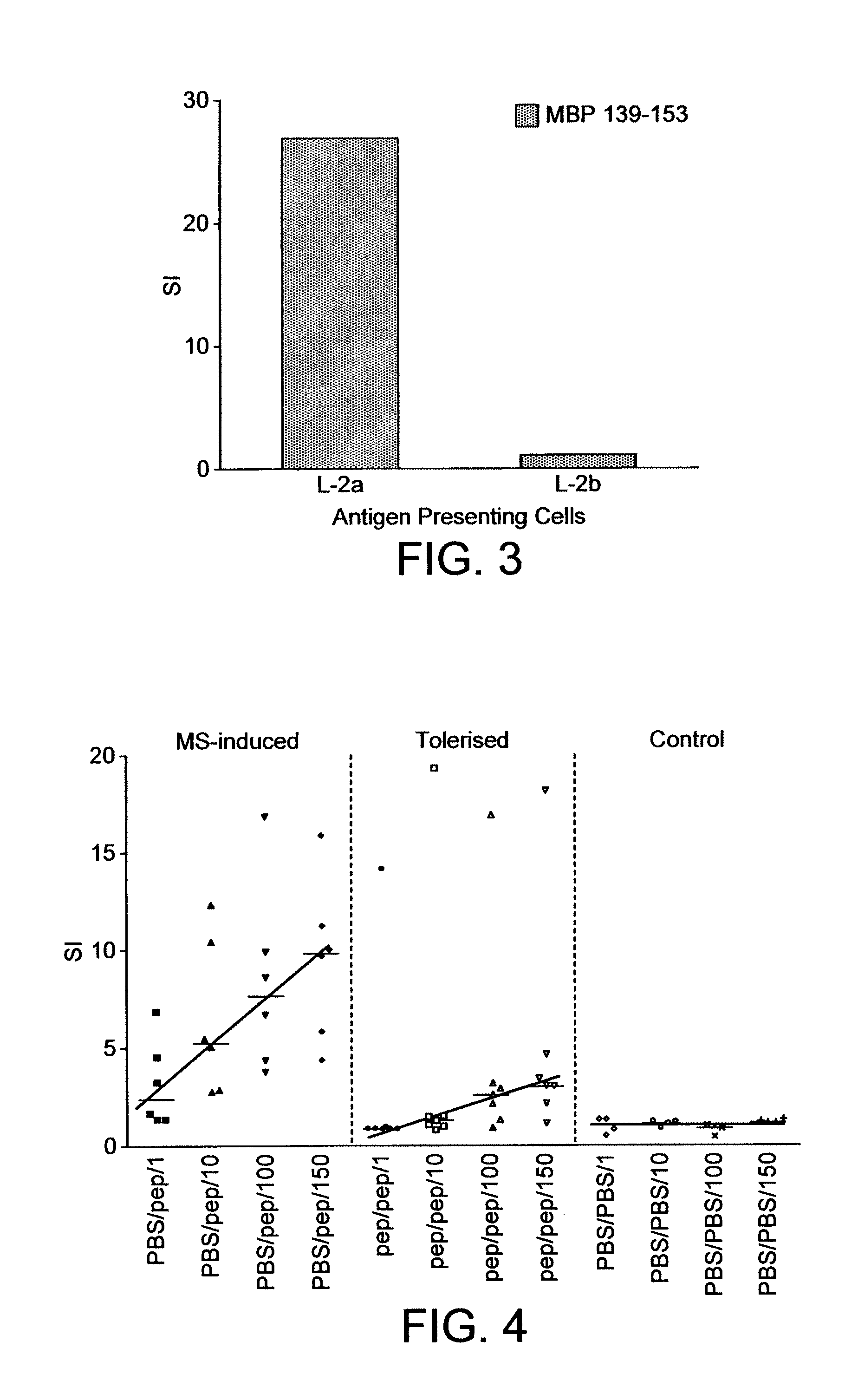
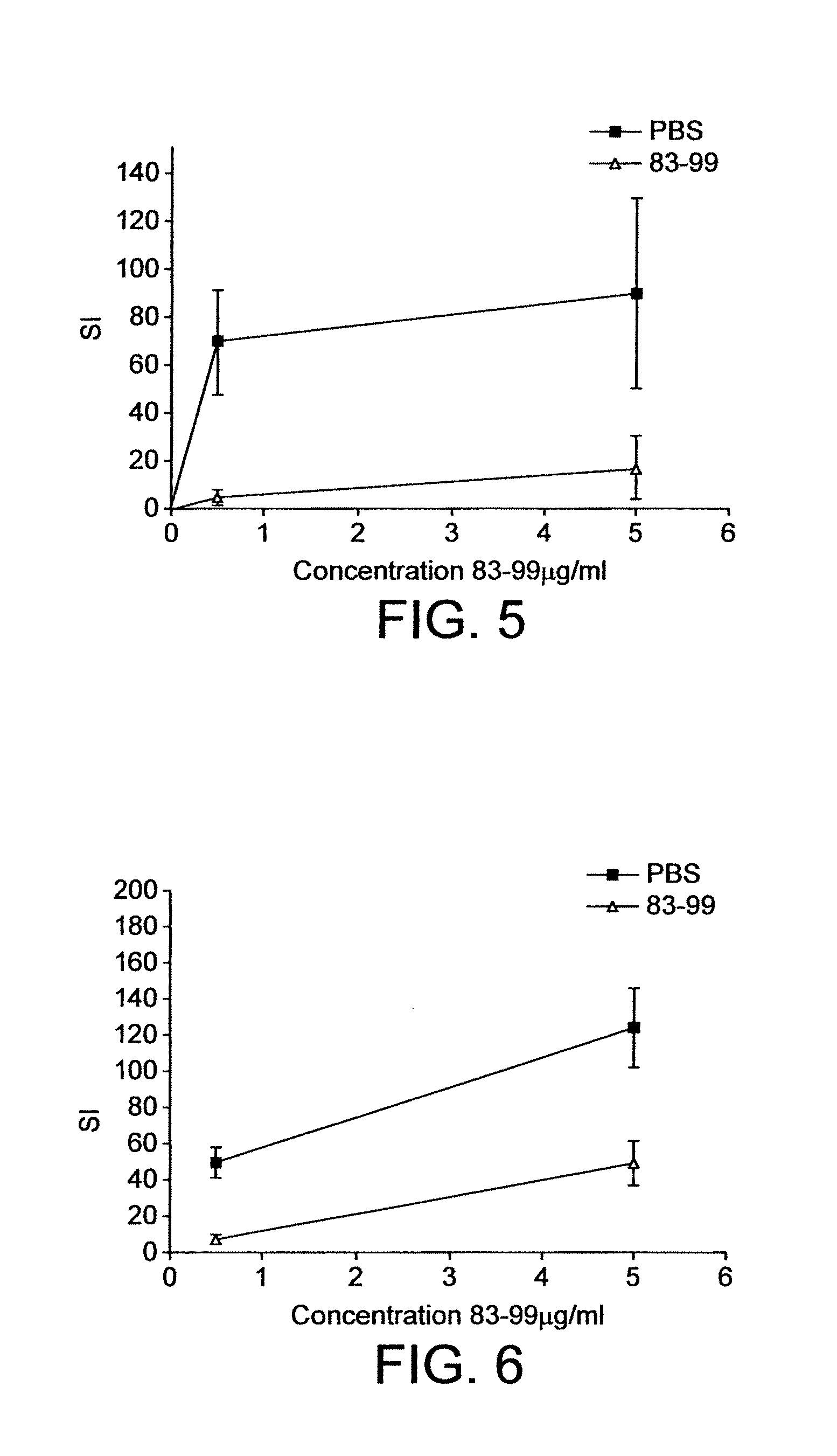
There is provided a method for selecting a tolerogenic peptide by selecting a peptide which is capable of binding to an MHC class I or II molecule without further processing. There is also provided a peptide selected by such a method and its use in a pharmaceutical composition and a method to treat and / or prevent a disease. The present invention also relates to a composition which comprises the following myelin basic protein (MBP) peptides: MBP 30-44; MBP 83-99; MBP 131-145; and MBP 140-154. The composition may be used to treat a disease, in particular multiple sclerosis and / or optical neuritis and the invention also relates to such uses and methods.
Owner:APITOPE TECH BRISTOL
Method for diagnosing multiple sclerosis and an assay therefore
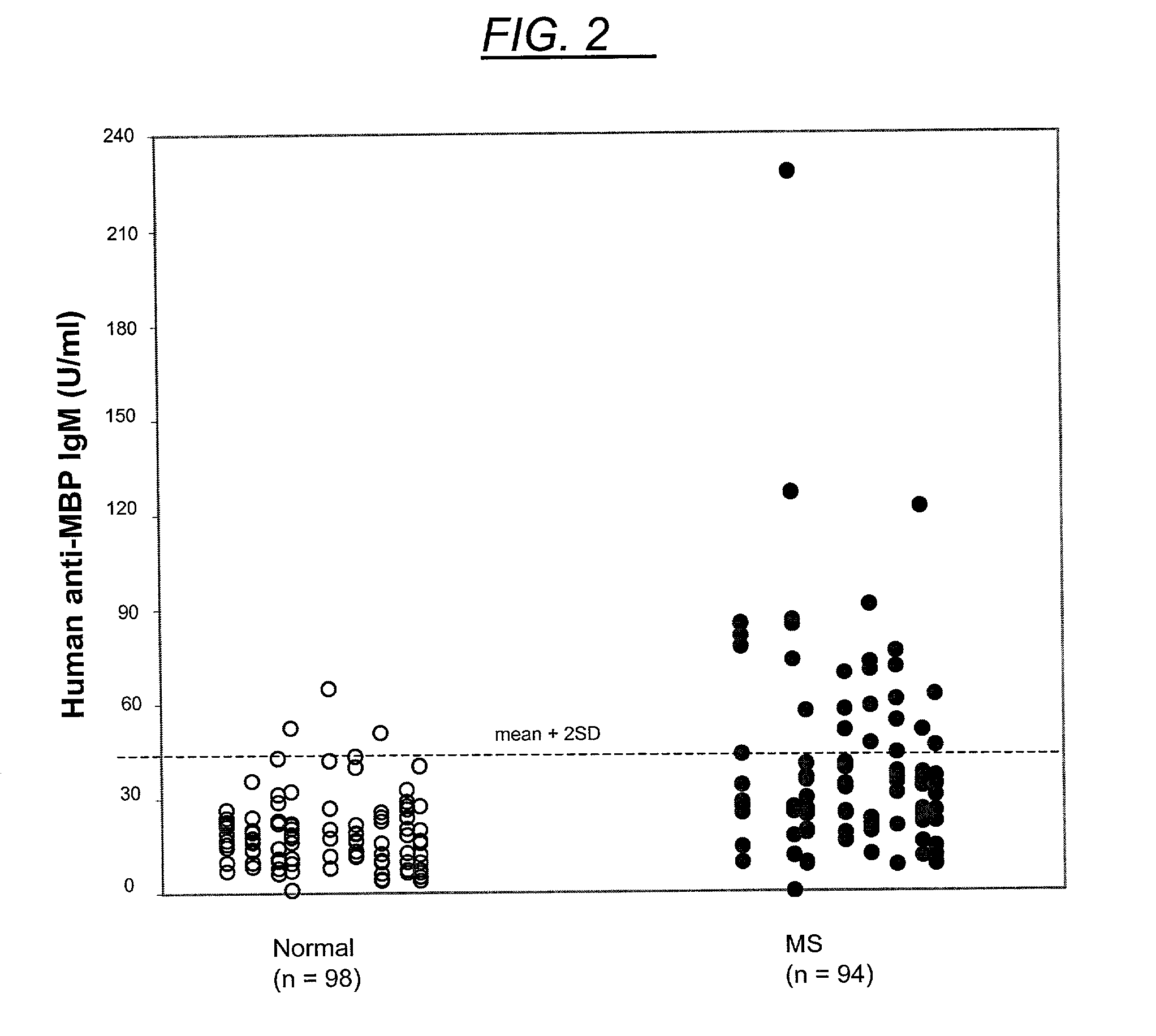
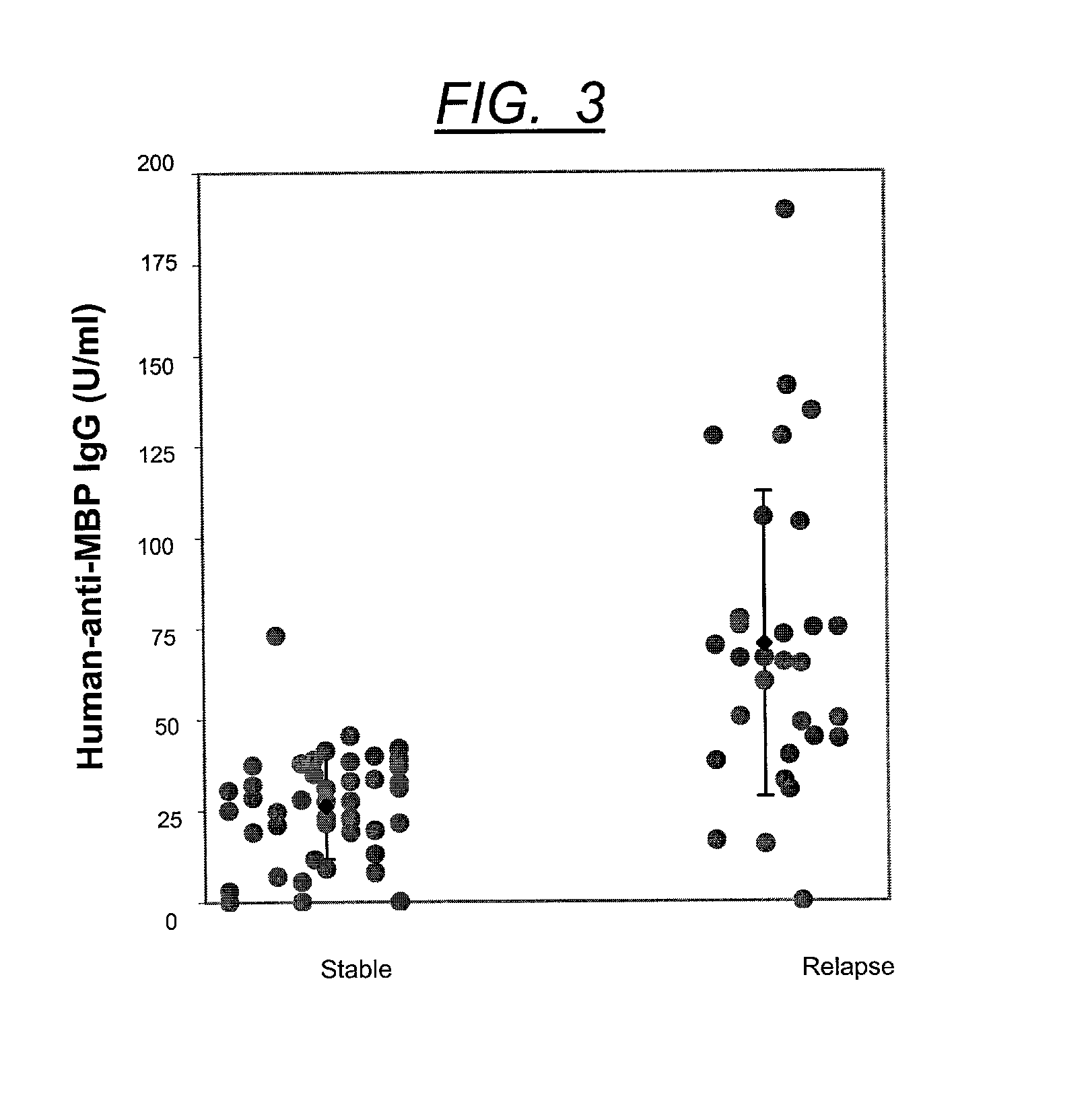
This invention is directed toward a serum / plasma assay for the diagnosis and subsequent monitoring of patients with multiple sclerosis (MS). Assay performance characteristics indicate that the assay is accurate and repeatable. Using blood from patients with clinically definite multiple sclerosis, a clinical sensitivity of 77% and a specificity of 95% has been achieved through the measurement of circulating myelin basic protein autoantibodies. The assay provides a simple, rapid, and minimally invasive tool for the diagnosis and monitoring of progression of MS.
Owner:HOSPITAL FOR SICK CHILDREN
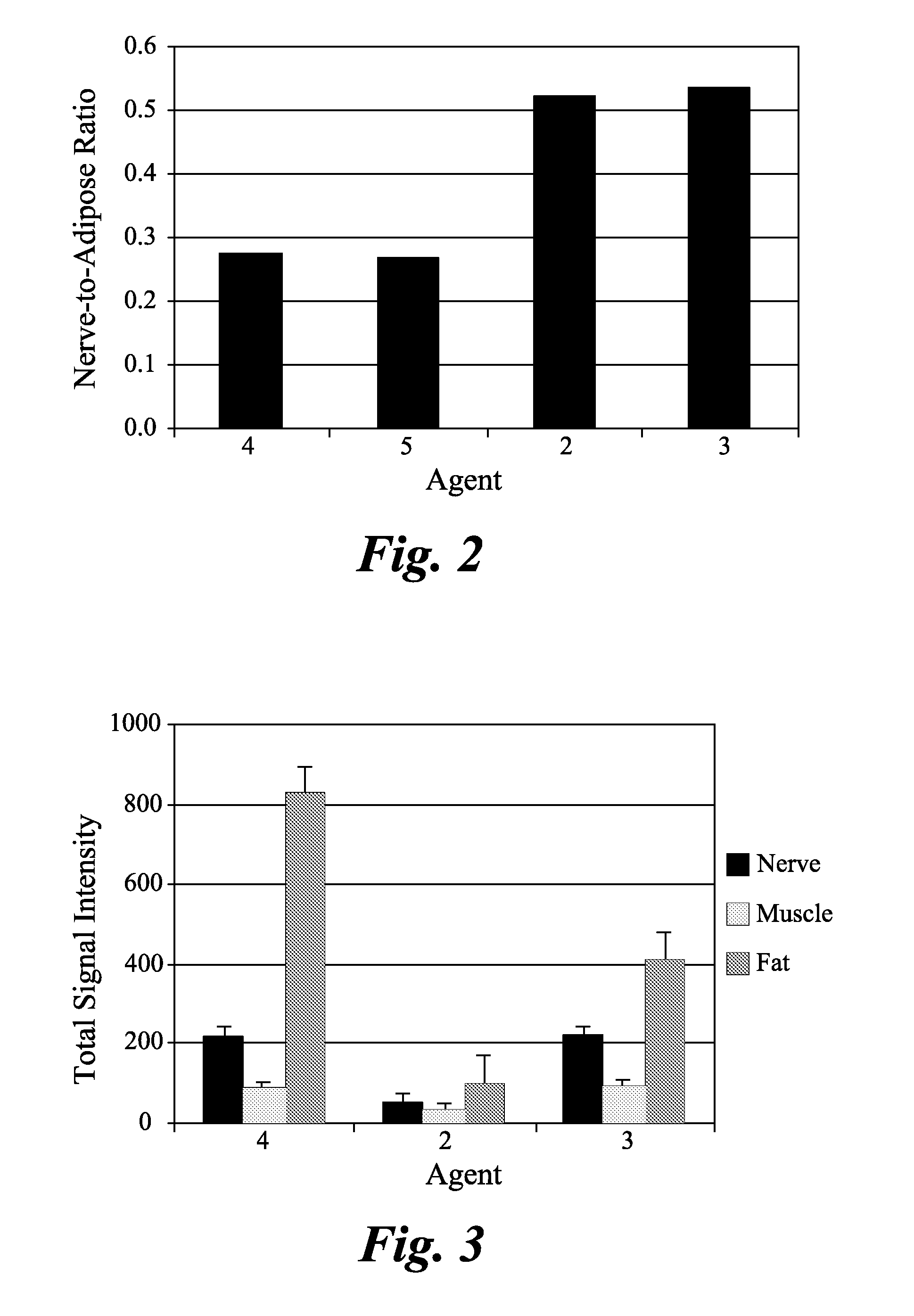
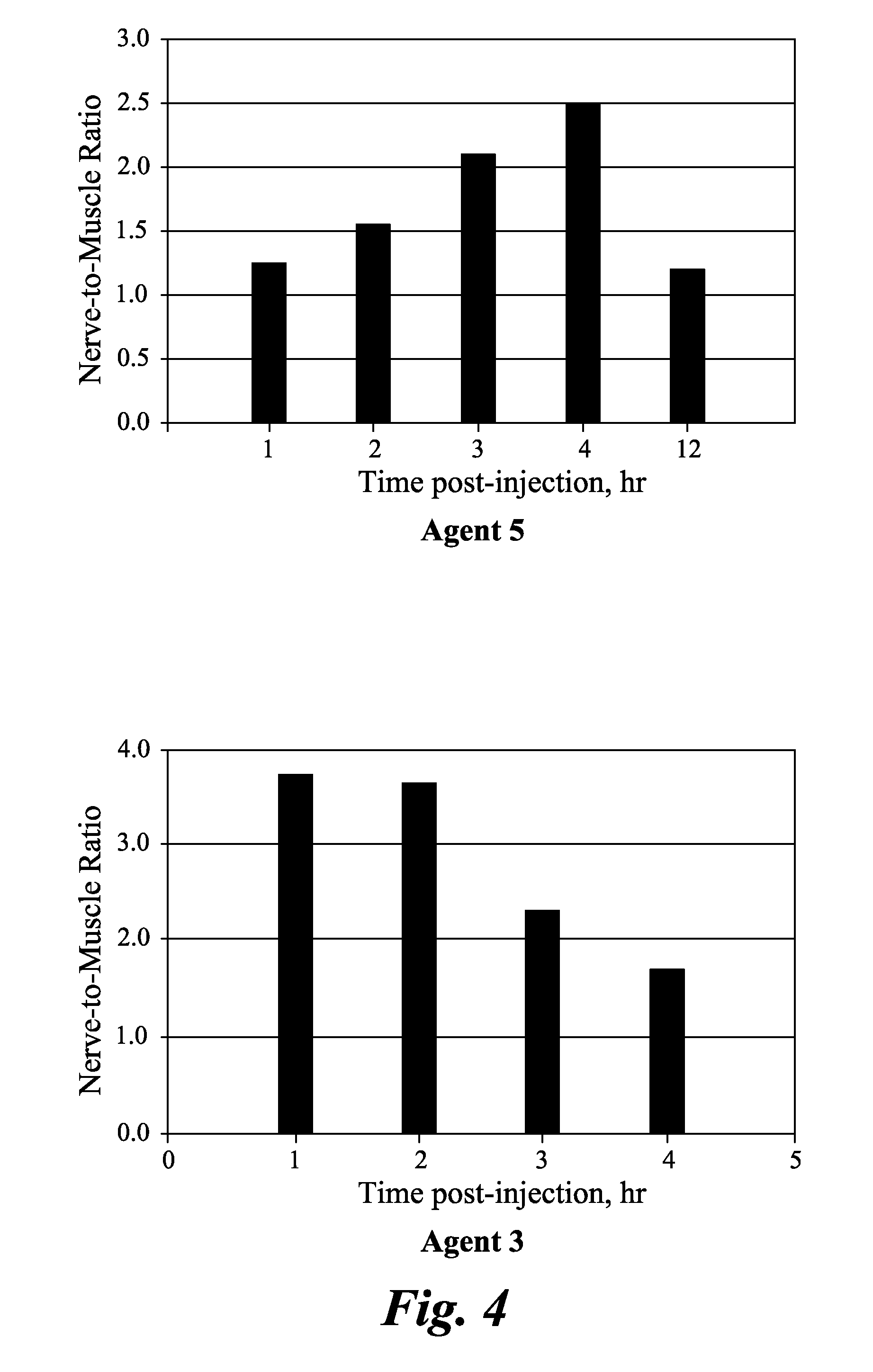
Agents and methods for the imaging of myelin basic protein
ActiveUS20110142759A1Lessen nonspecific partitioningLess and no known toxic effectOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationMedicineMyelin basic protein
The present invention relates to agents capable of binding to myelin basic protein in a subject. Also provided are methods for the detection of myelin-associated neuropathy comprising identifying a subject at risk of or diagnosed with a myelin-associated neuropathy, administering to a subject an agent that binds specifically to myelin basic protein, and determining myelination in the subject by detecting the agent present in the subject. A kit containing the agent or its derivatives for use in detecting myelin basic protein is also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
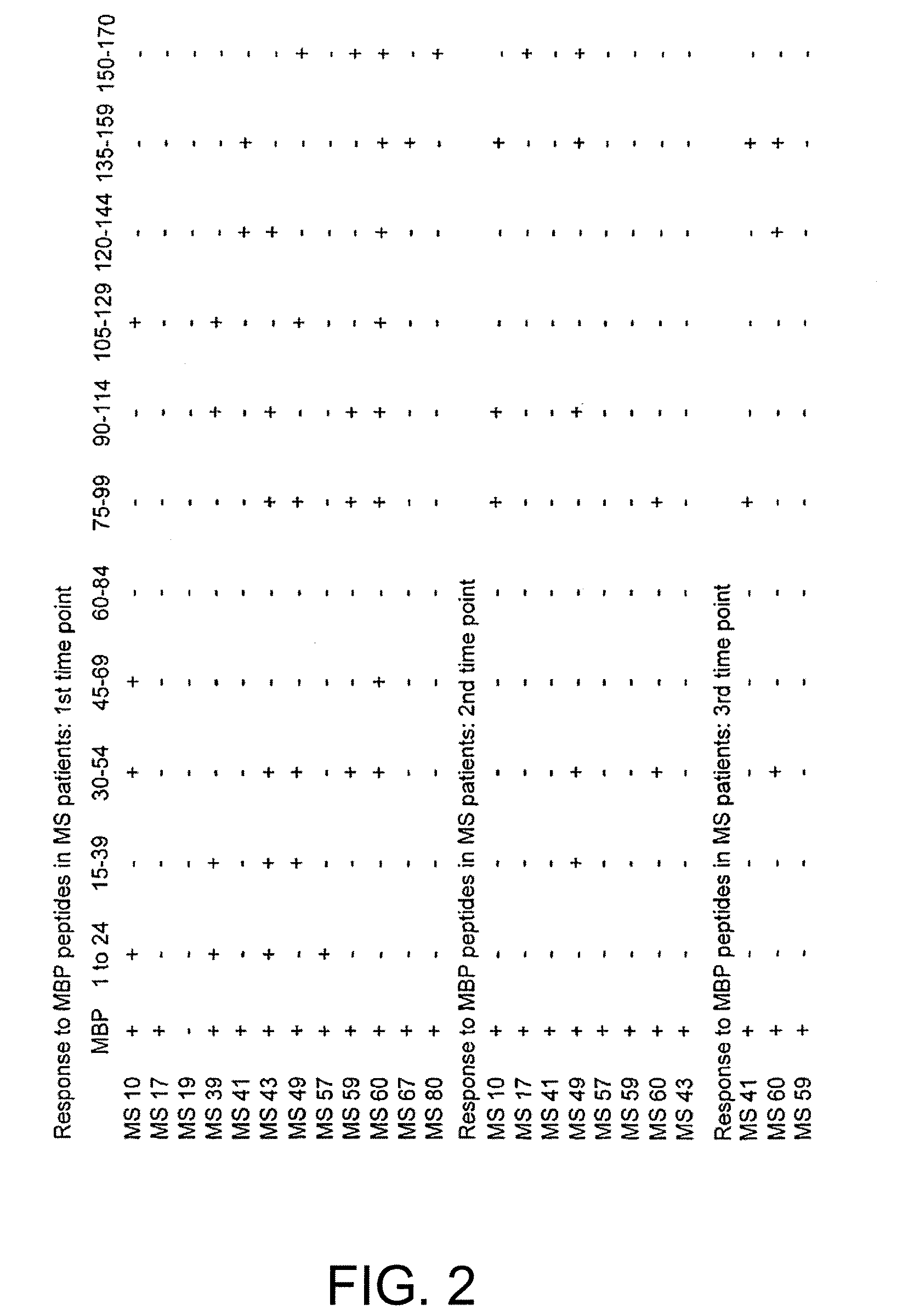
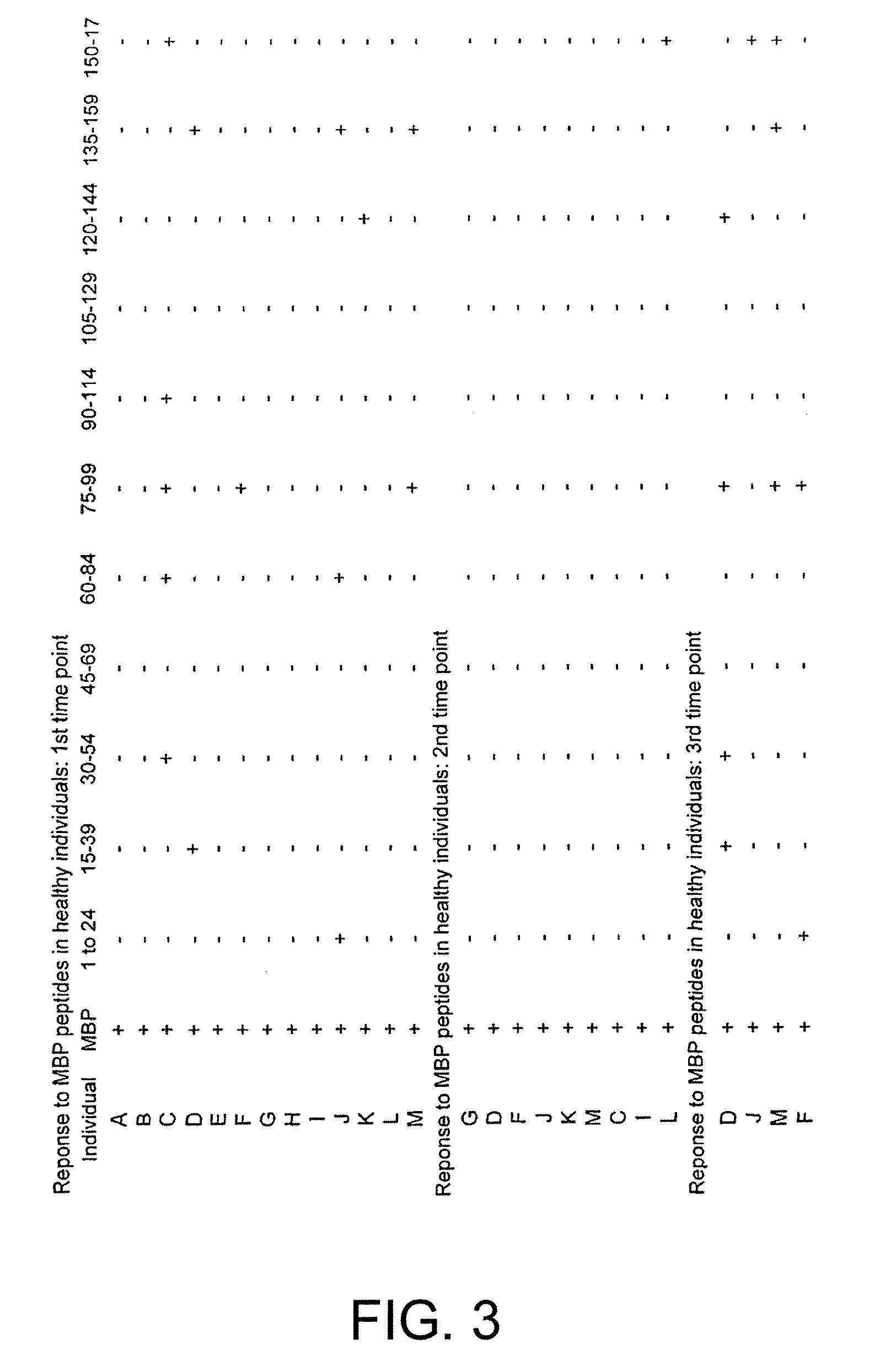
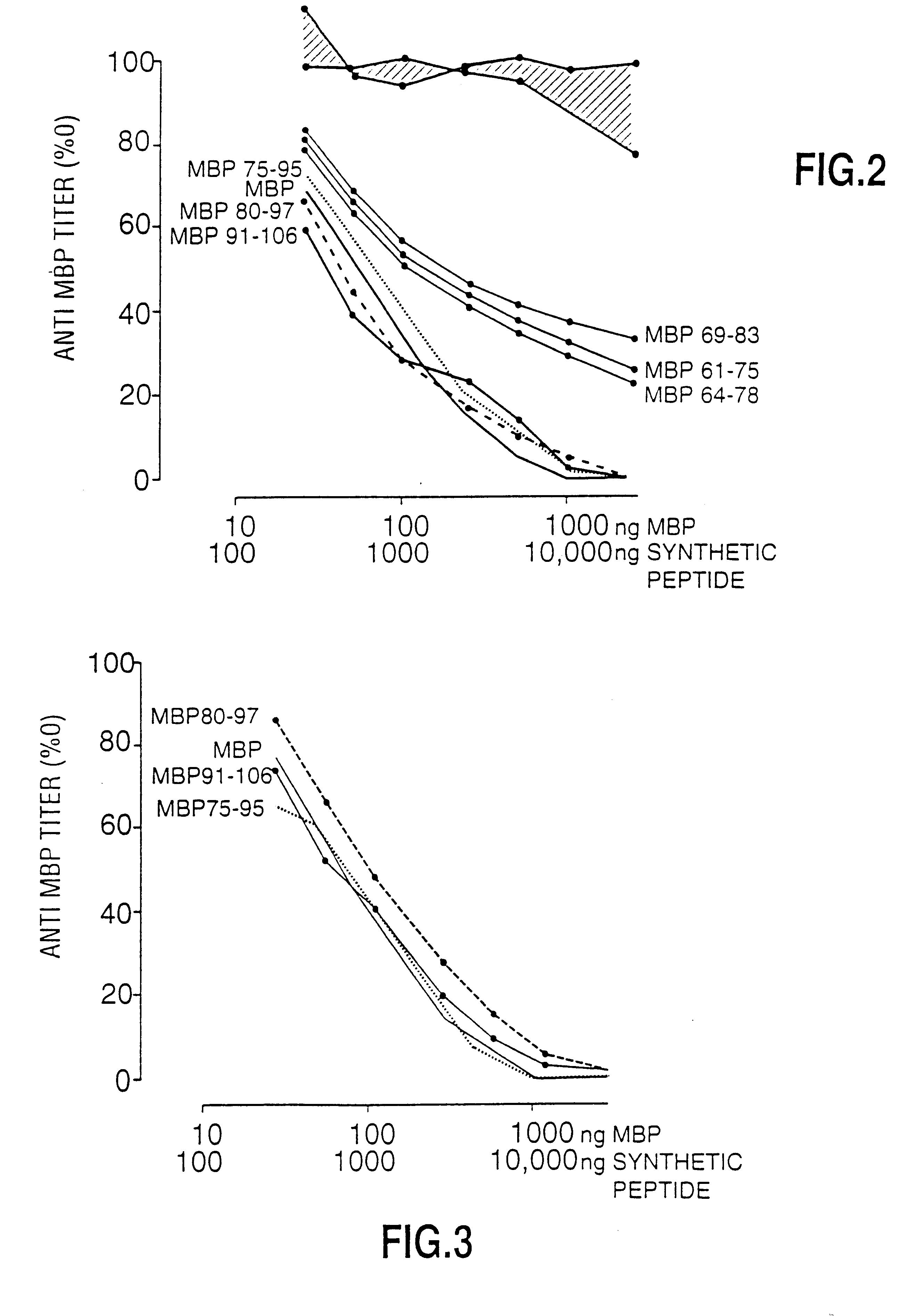
Peptide specificity of anti-myelin basic protein and the administration of myelin basic protein peptides to multiple sclerosis patients
InactiveUS6252040B1Promote tolerancePromote resultsNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsWhole bodyADAMTS Proteins
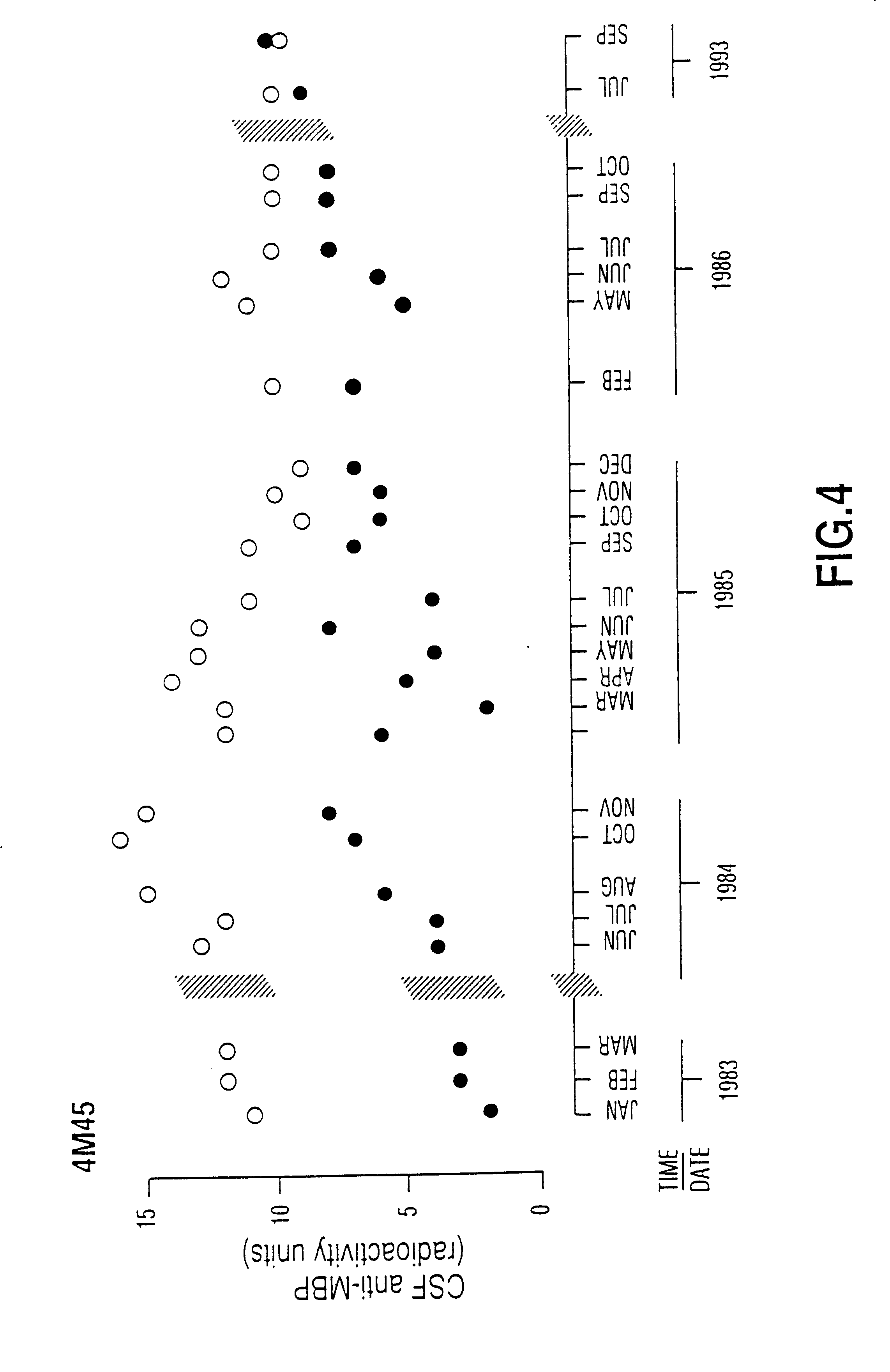
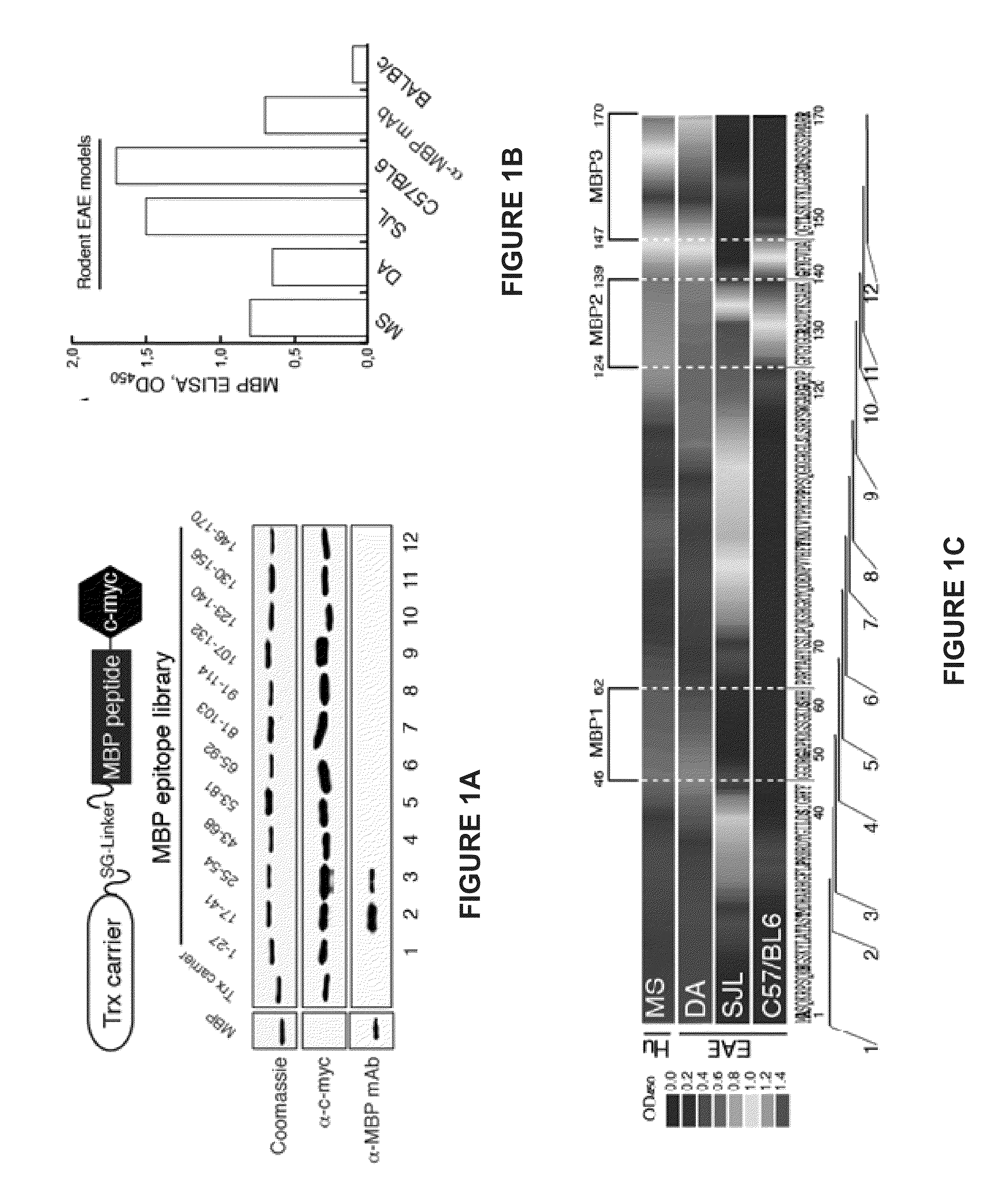
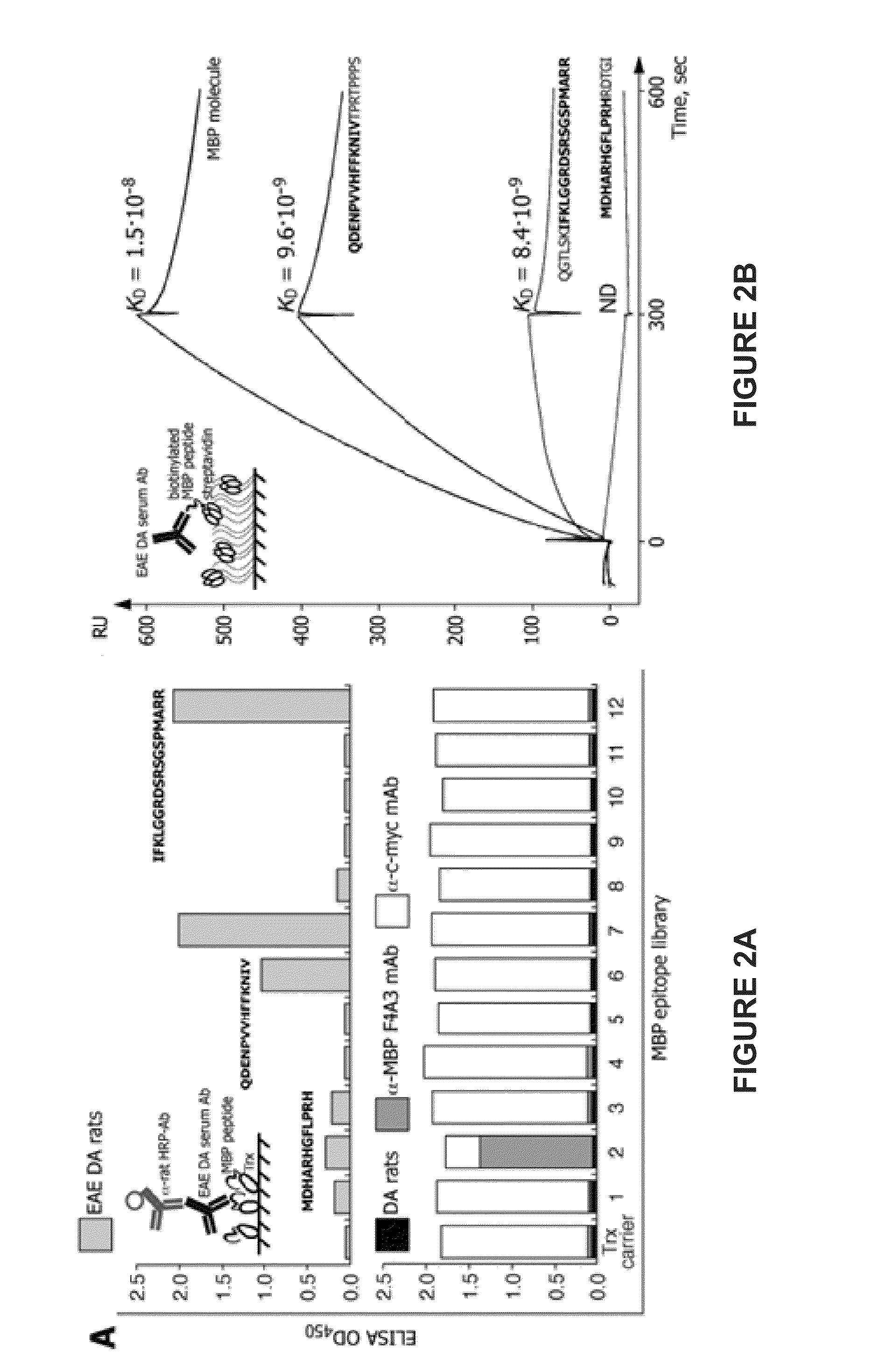
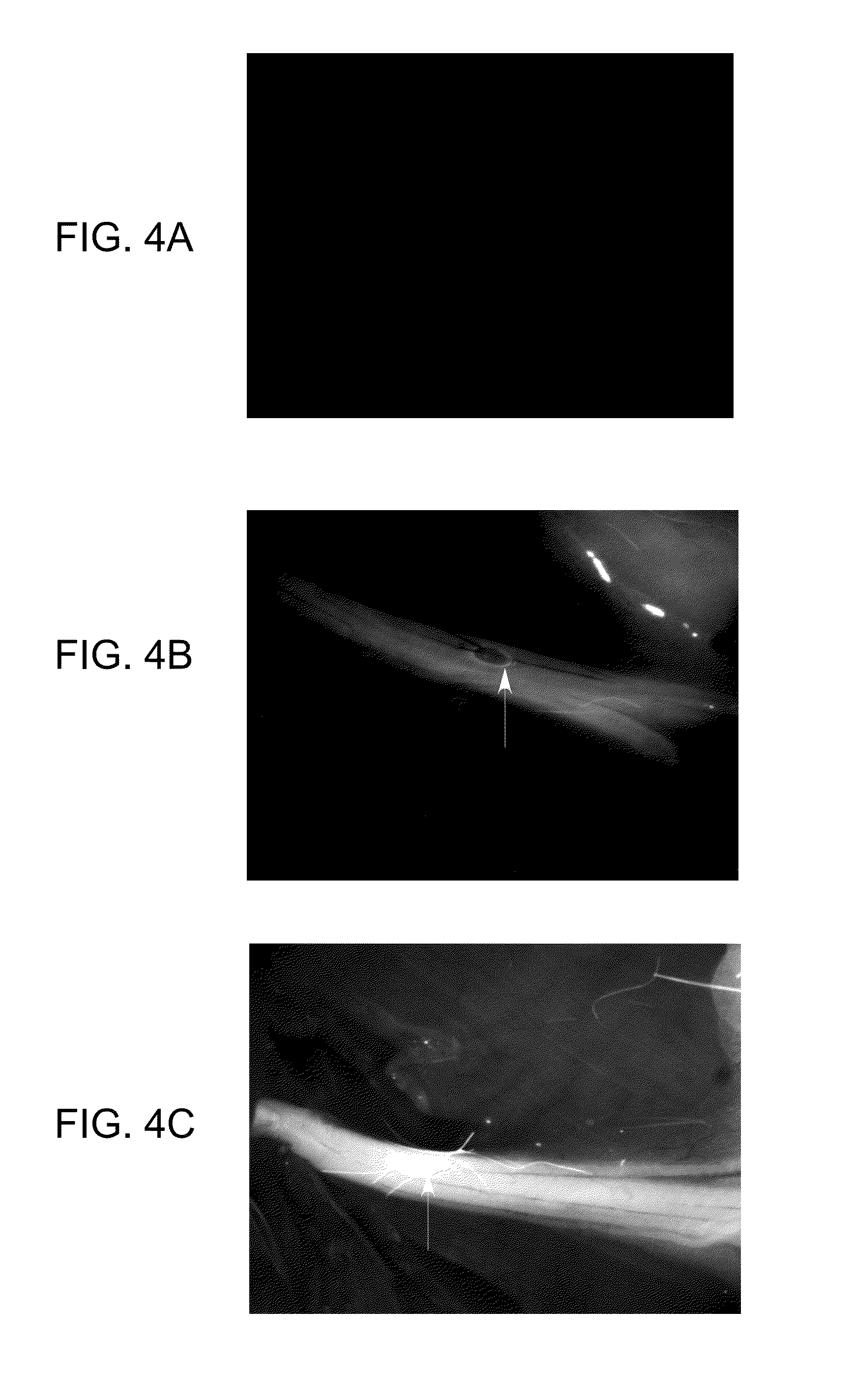
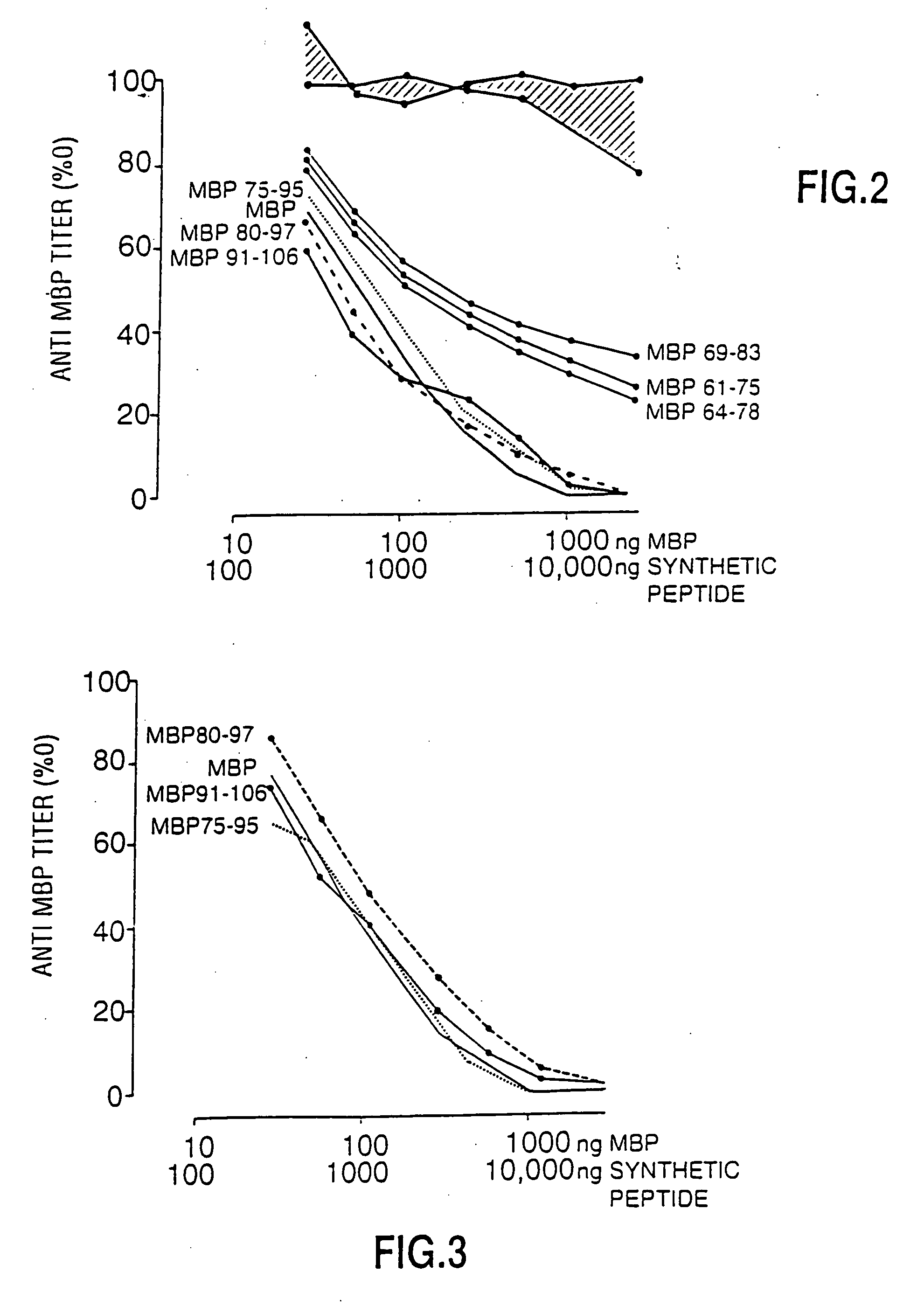
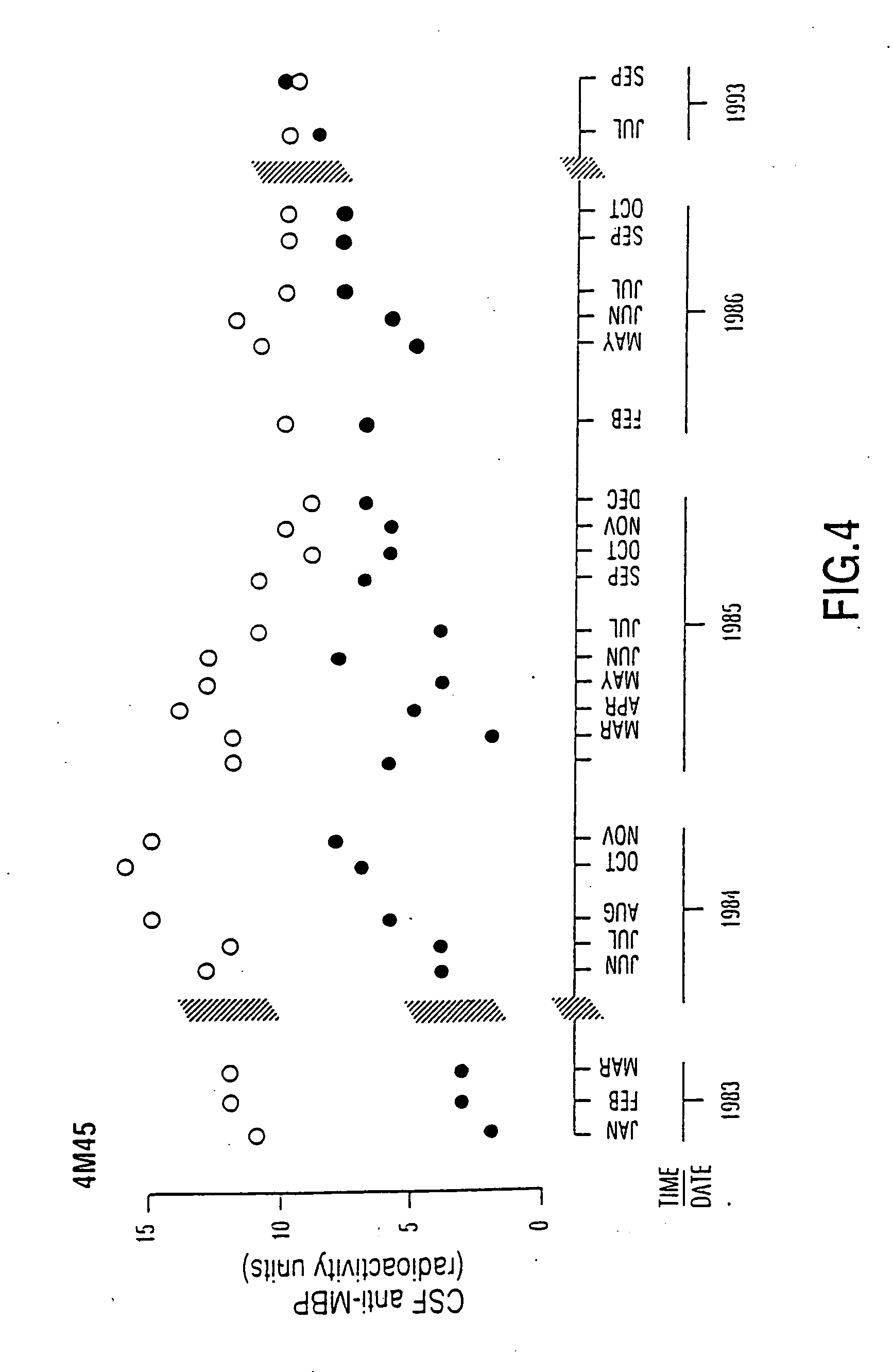
Human myelin basic protein (h-MBP) has a molecular weight of 18.5 KD and contains 170 amino acid residues. Synthetic peptides ranging in length from about 8 to 25 residues and covering the entire length of the protein have been produced. Antibodies to h-MBP (anti-MBP) were found to be neutralized by the synthetic peptides, in vitro, which span the h-MBP from about amino acid residue 61 to about amino acid residue 106. The peptides, which cover both the amino (about residues 1 to 63) and carboxy (about residues 117 to 162) terminals of h-MBP did not neutralize purified anti-MBP. Intrathecal administratin of peptide MBP(75-95), MBP(86-95), or MBP(82-98) produced complete binding-neutralization of free (F) anti-MBP with no change in bound (B) levels. A control peptide MBP35-58 had no effect on F or B anti-MBP levels. Intravenous administration of MBP(75-95), MBP(86-95), or MBP(82-98) resulted in significant decline of F and B CSF anti-MBP levels. Administration of MBP synthetic peptides to MS patients either intrathecally or intravenously did not have any adverse neurological effects and systemic complications did not occur. The MBP epitope for MS anti-MBP has been localized to an area between amino acid 86 and amino acid 95.
Owner:ALBERTA THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV
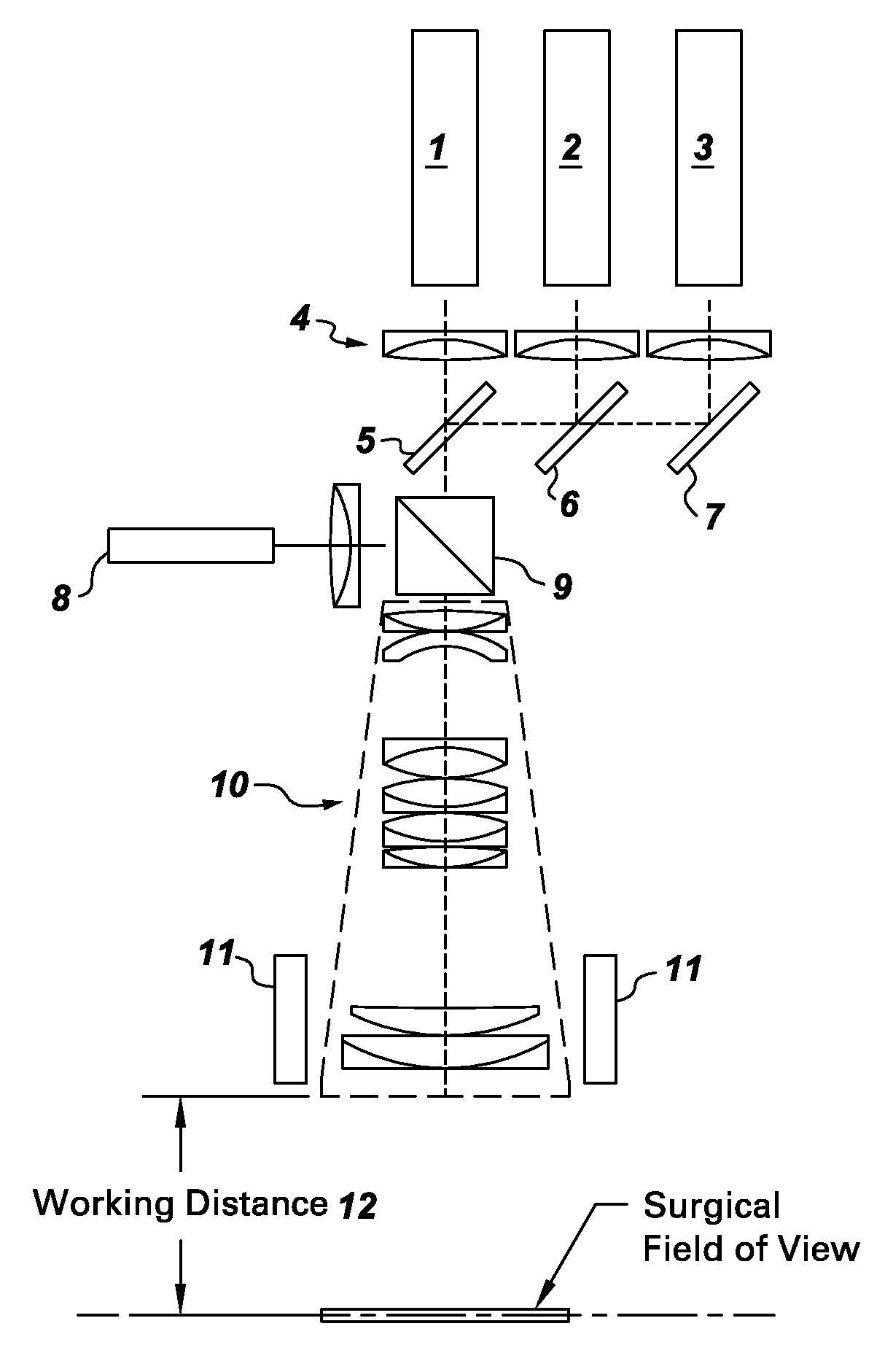
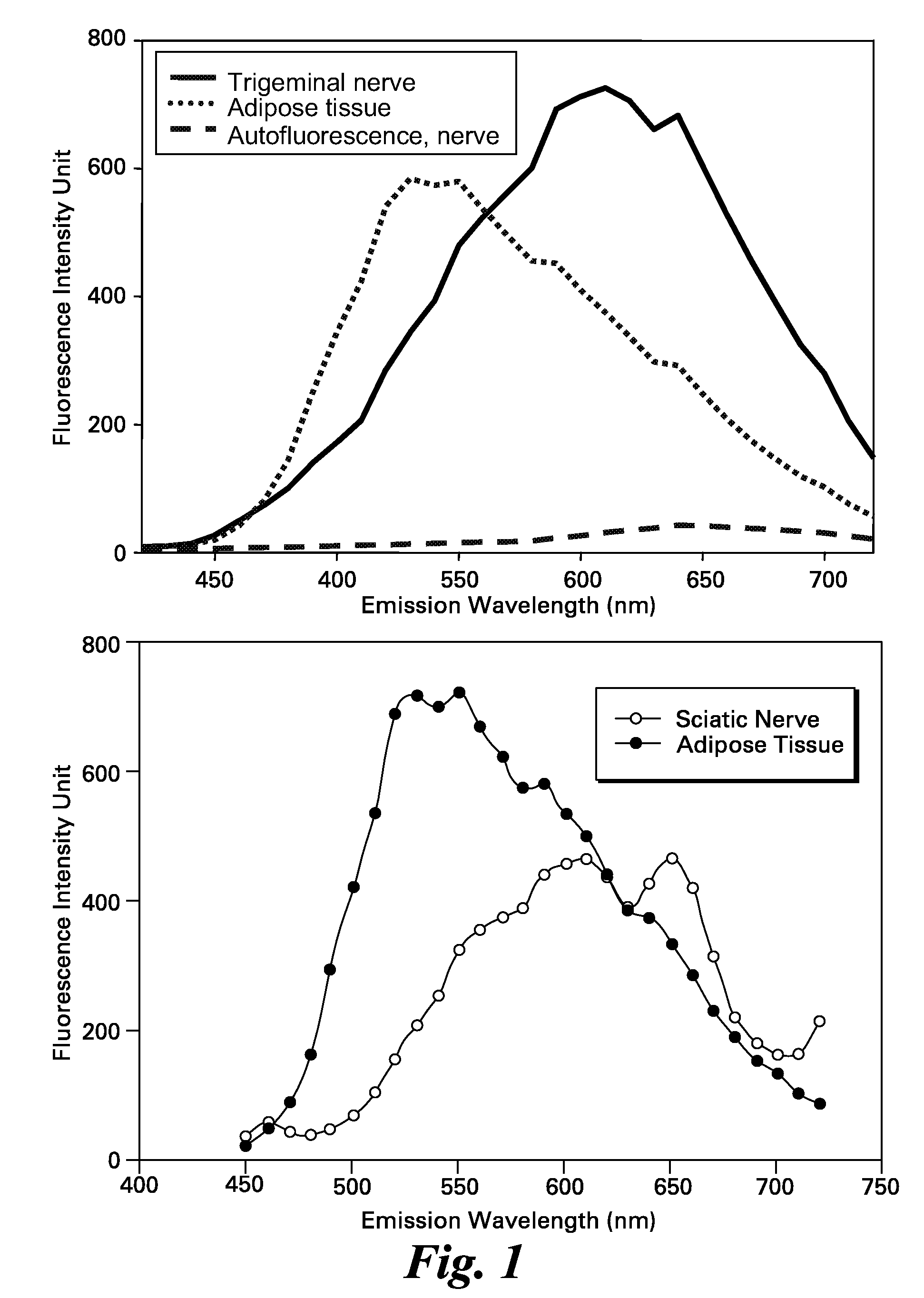
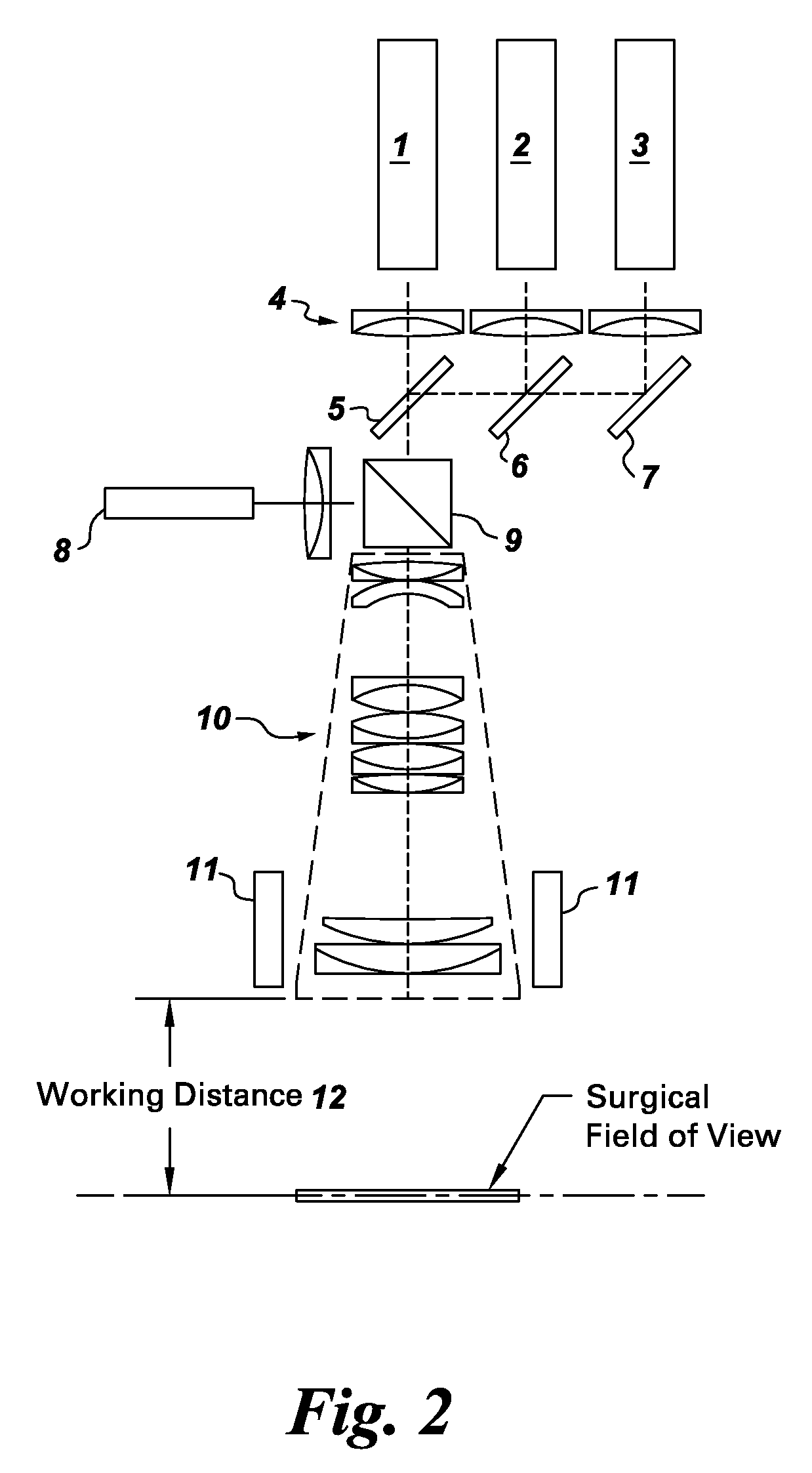
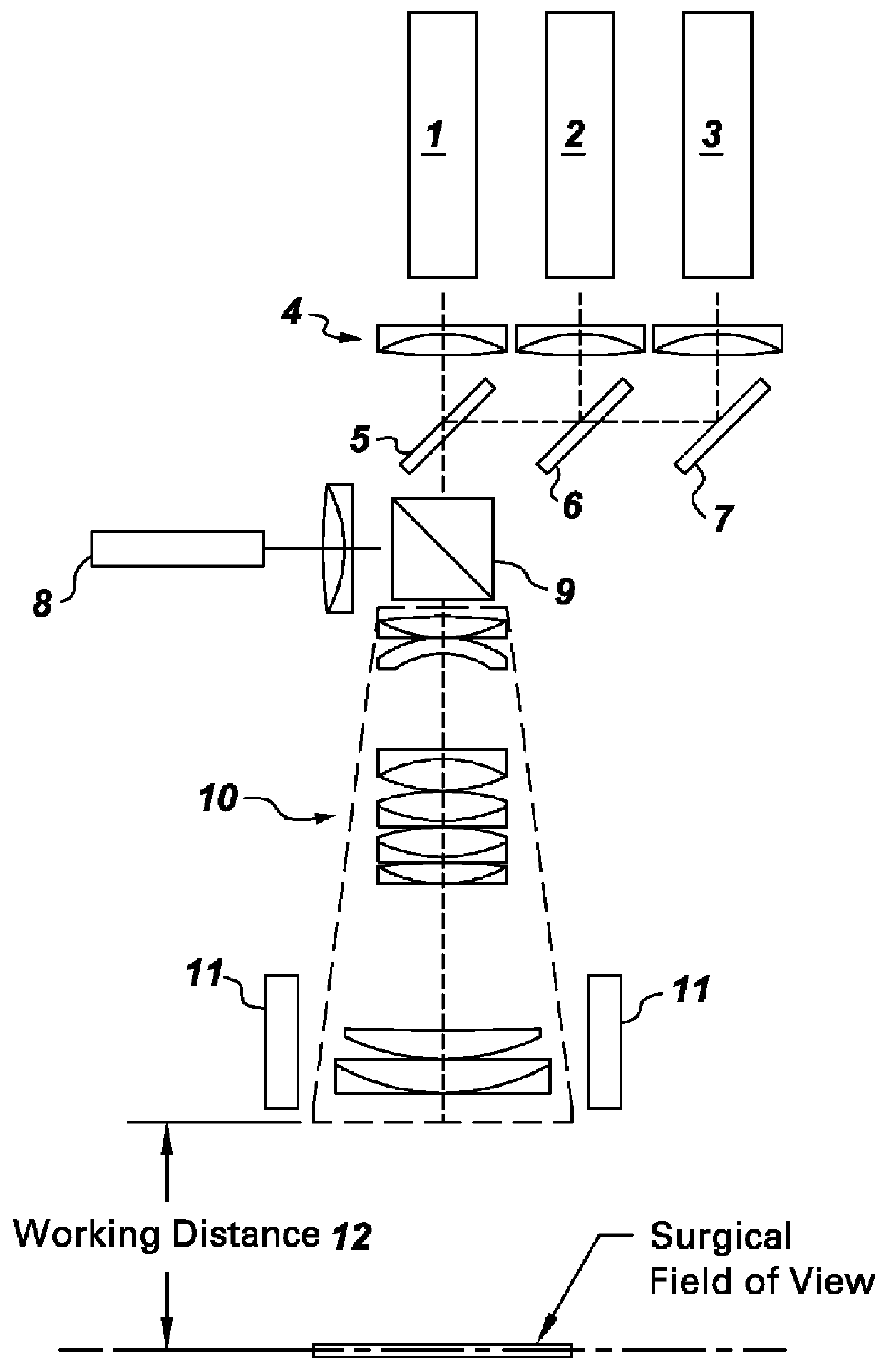
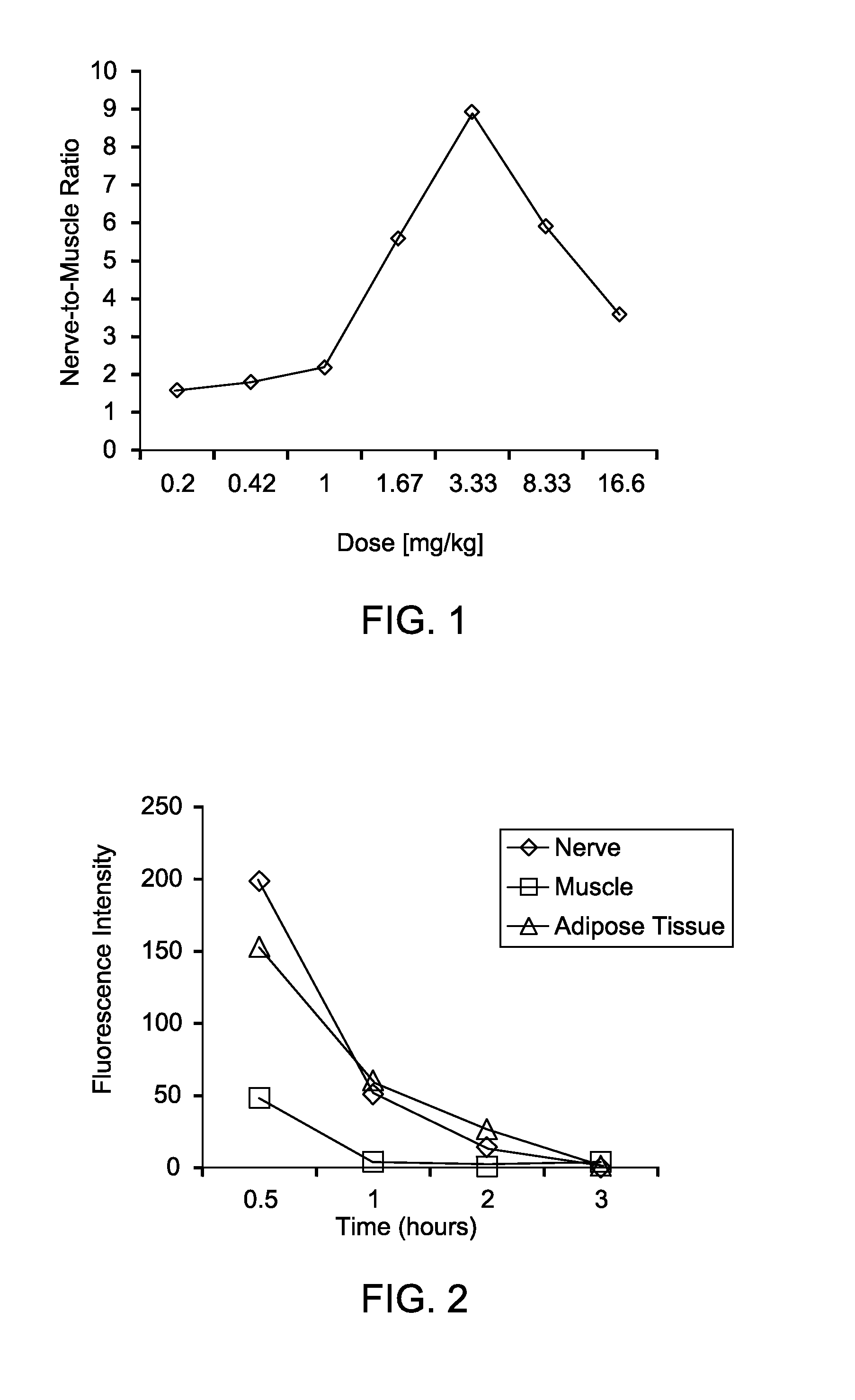
Systems for intraoperative nerve imaging
ActiveUS20100312122A1High collection powerMicroscopesIn-vivo testing preparationsMini invasive surgeryFluorescence
Disclosed are systems for intraoperative nerve imaging using compact high collection power imaging devices for fluorescence and white light imaging of myelin basic protein (MBP) nerve imaging agents during open and minimally invasive surgery.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for detecting radiolysis behavior of 30% TBP (Tri-Butyl-Phosphate)-kerosene
ActiveCN102778522AShort irradiation timeComponent separationColor/spectral properties measurementsFuel reprocessingPhosphate
The invention discloses a method for detecting radiolysis behavior of 30% TBP (Tri-Butyl-Phosphate)-kerosene, belonging to the technical field of post-treatment of spent fuel. The method comprises the following steps of: using a radiolysis source to carry out radiolysis on an extraction system in a Purex procedure; subsequently detecting the radiolysis products, i.e. DBP (Dibutyl Phthalate), MBP (Myelin Basic Protein) and carbonyl compounds. The method is characterized in that the radiolysis source is 238Pu. With the adoption of the method, the influence of alpha radiolysis on the TBP-kerosene system can be obtained.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
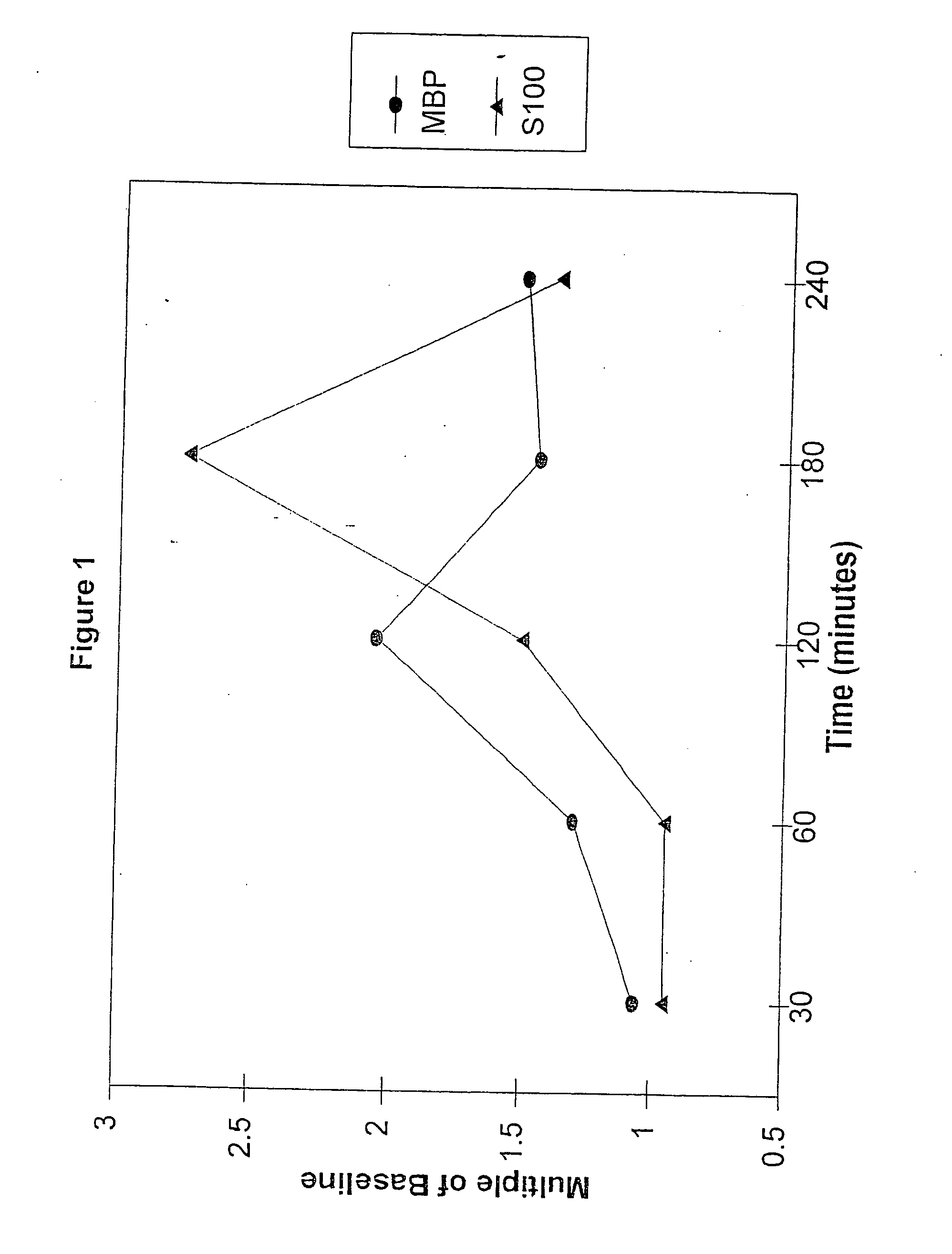
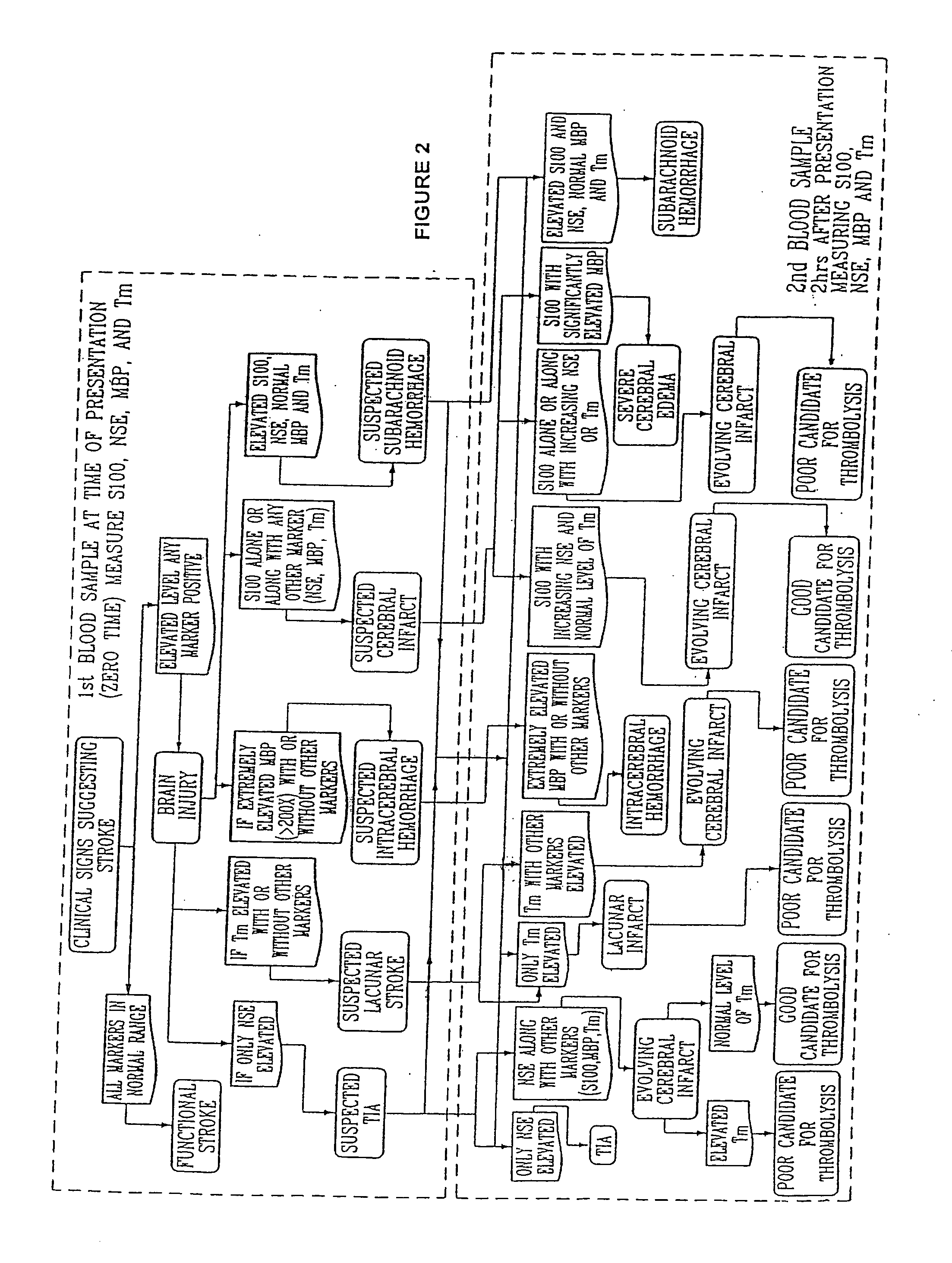
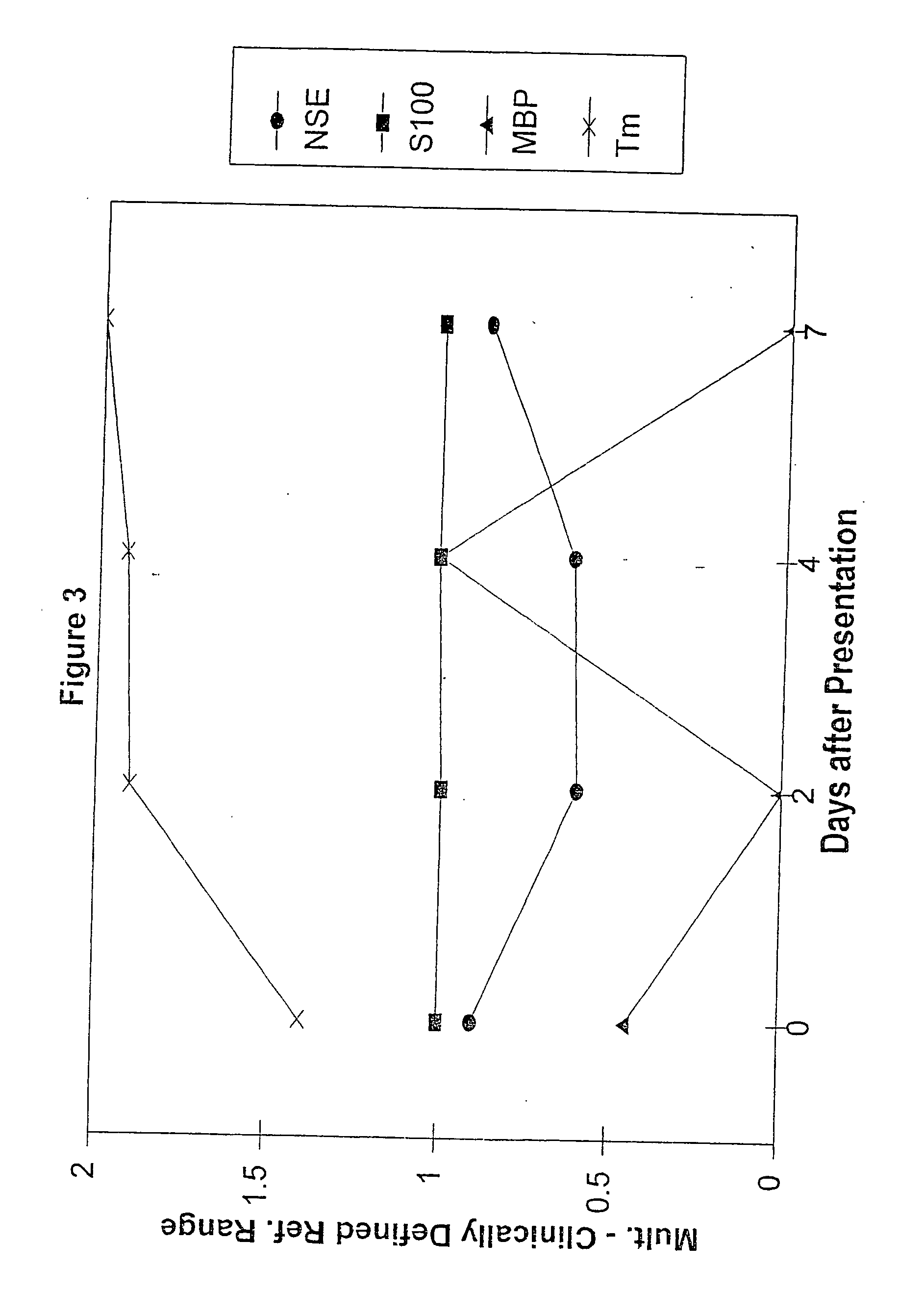
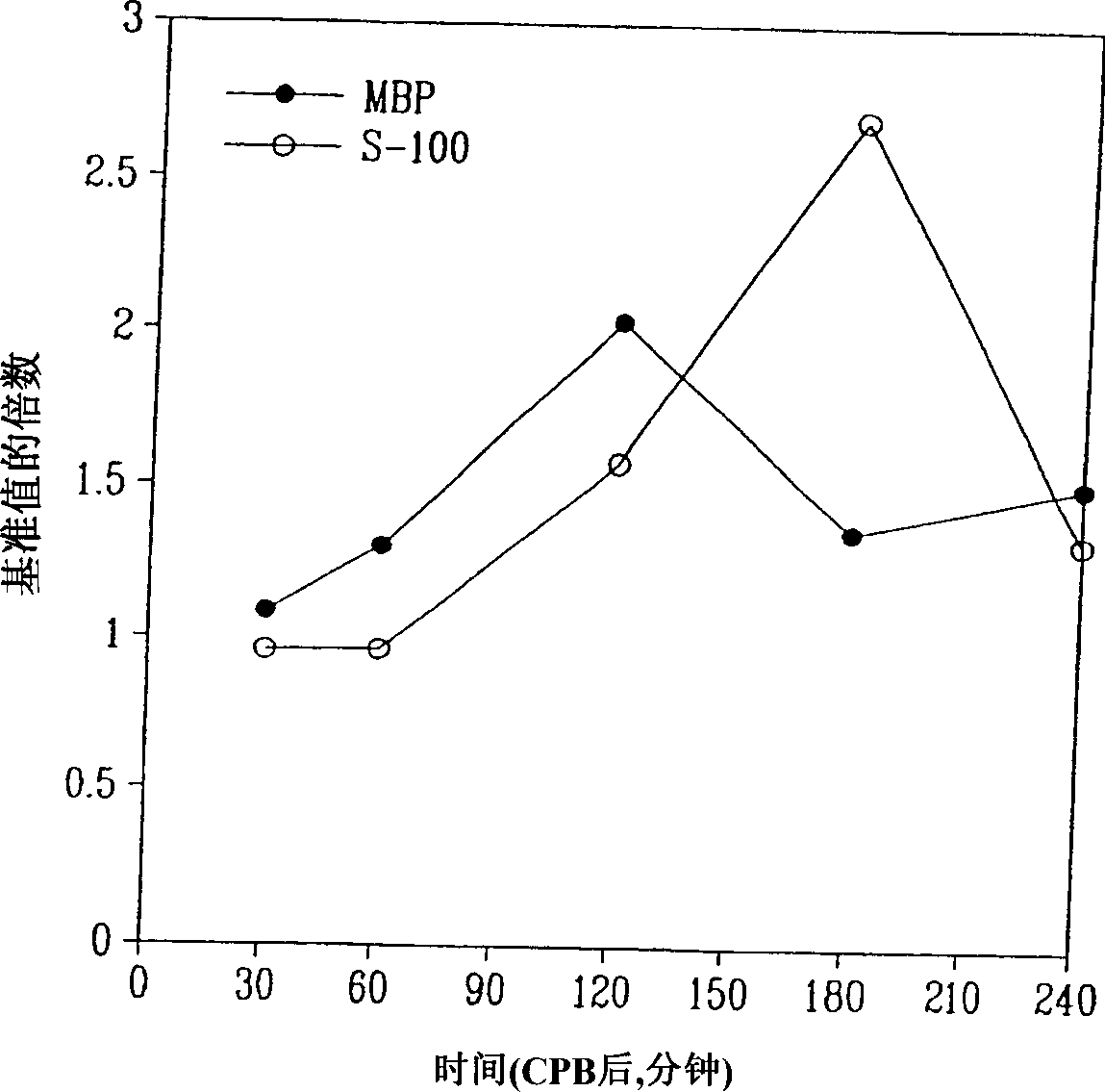
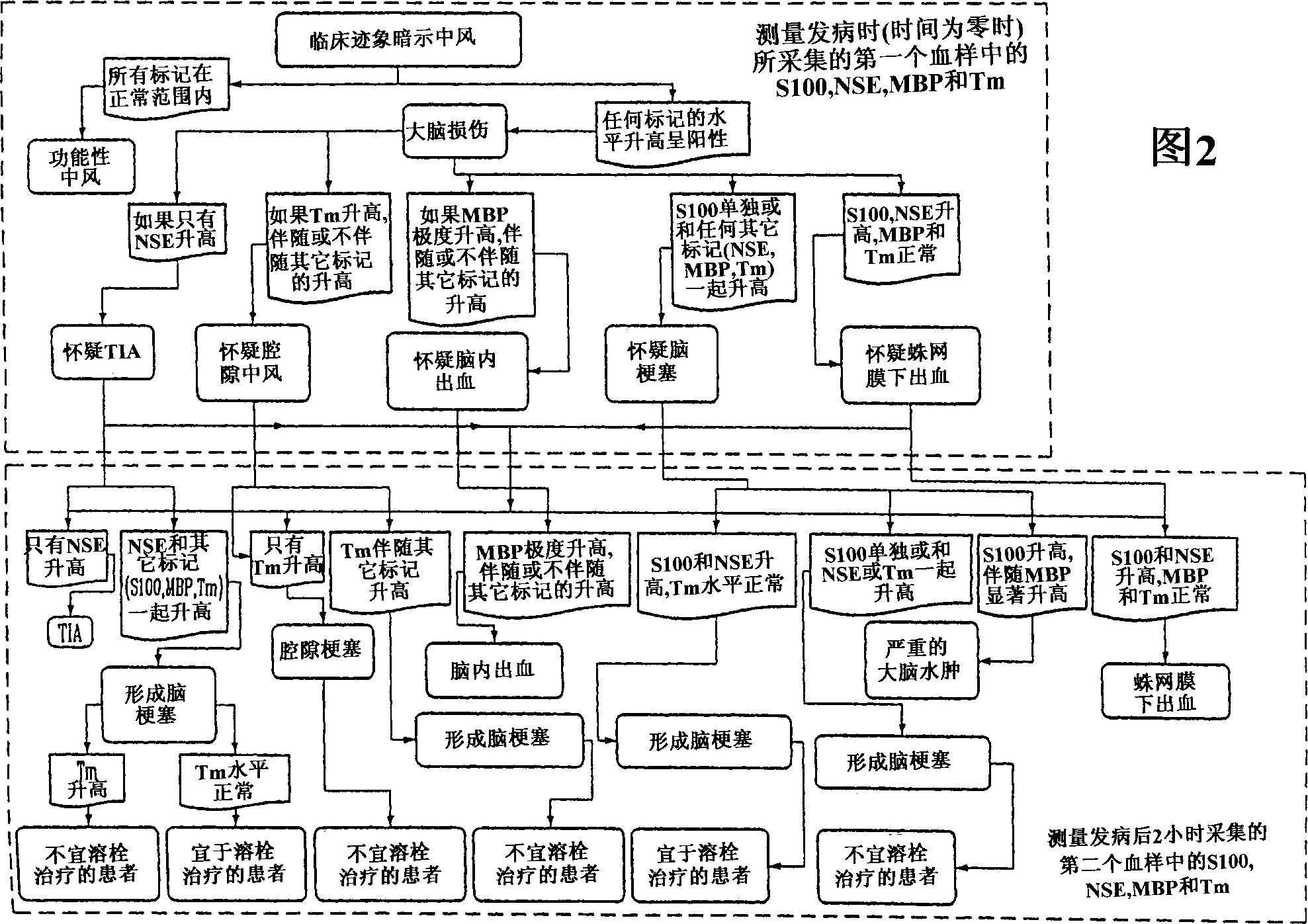
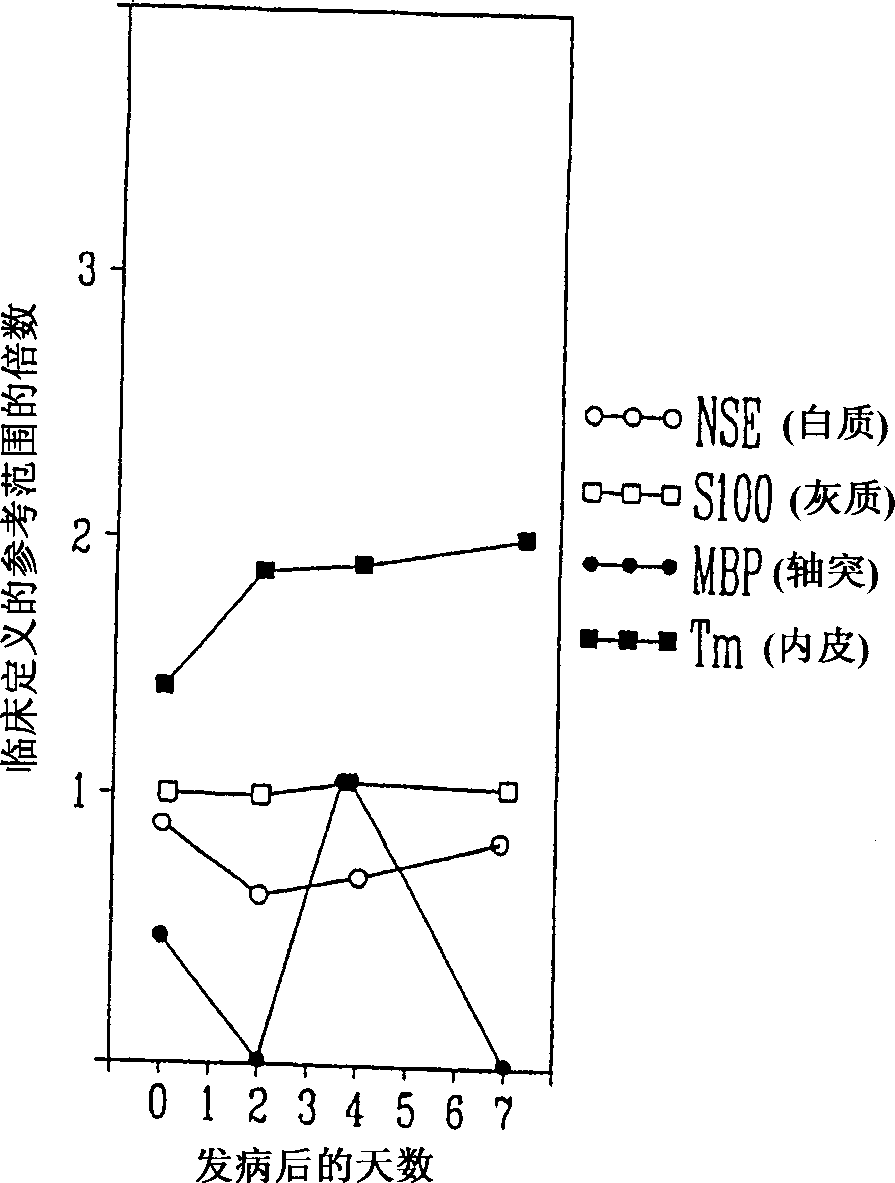
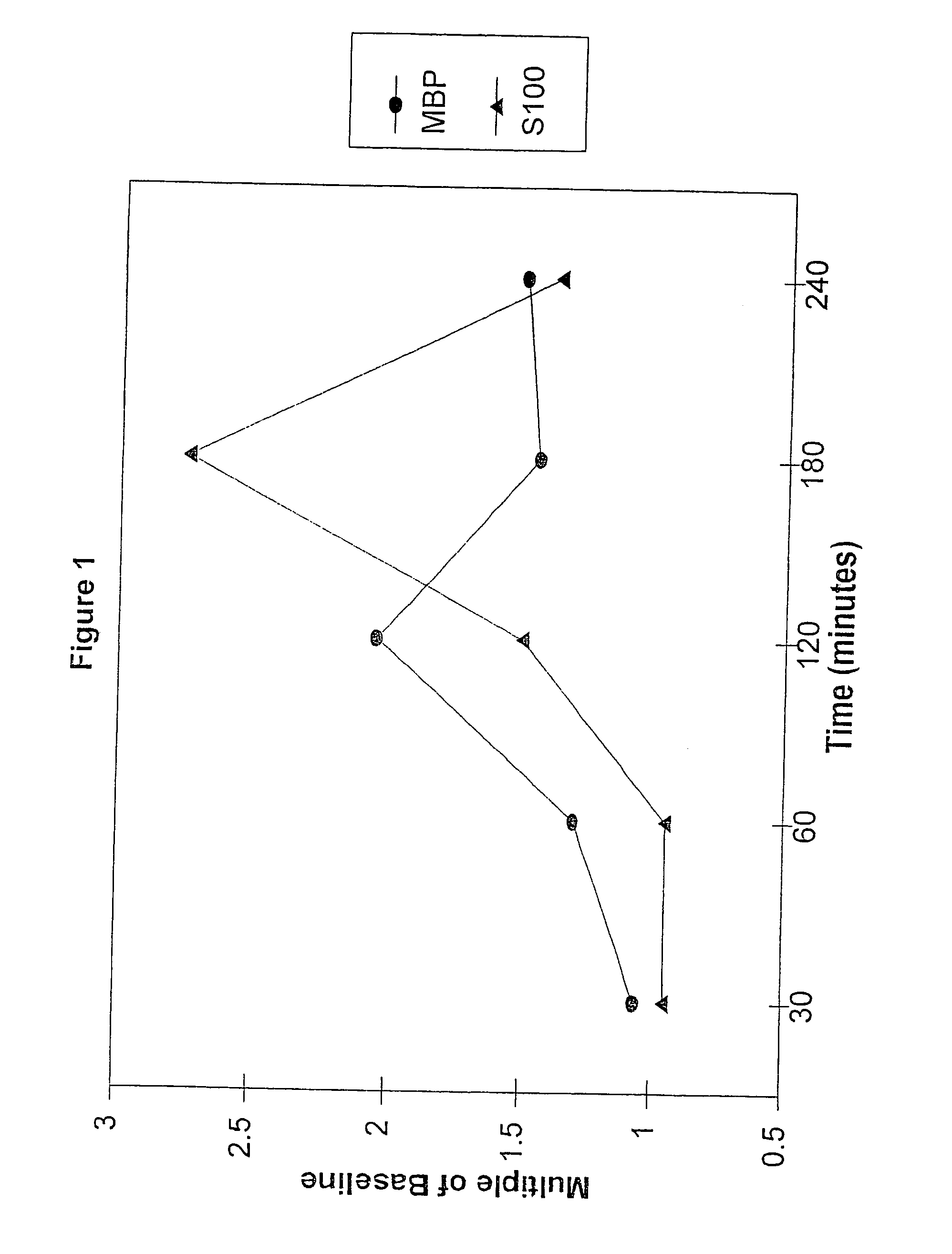
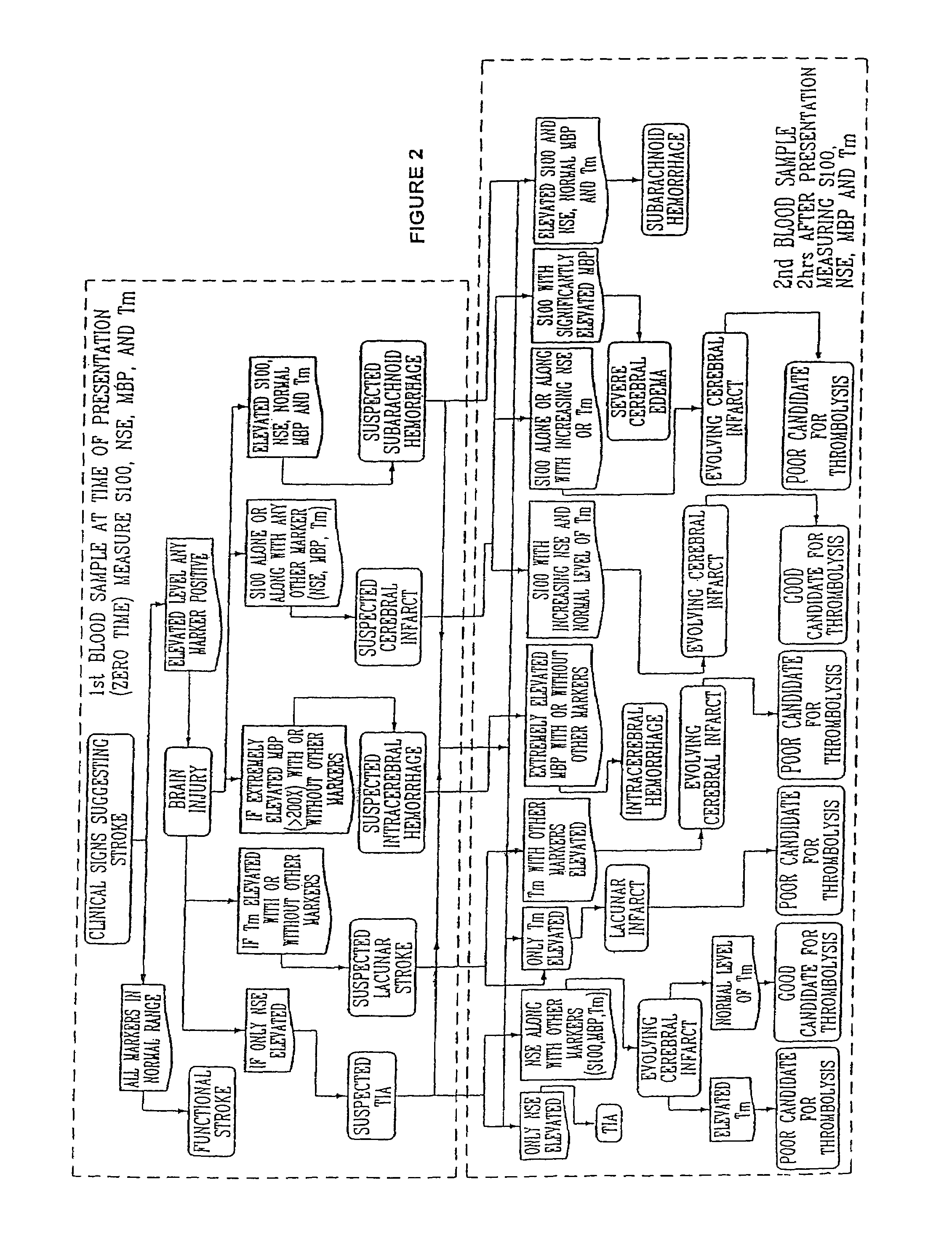
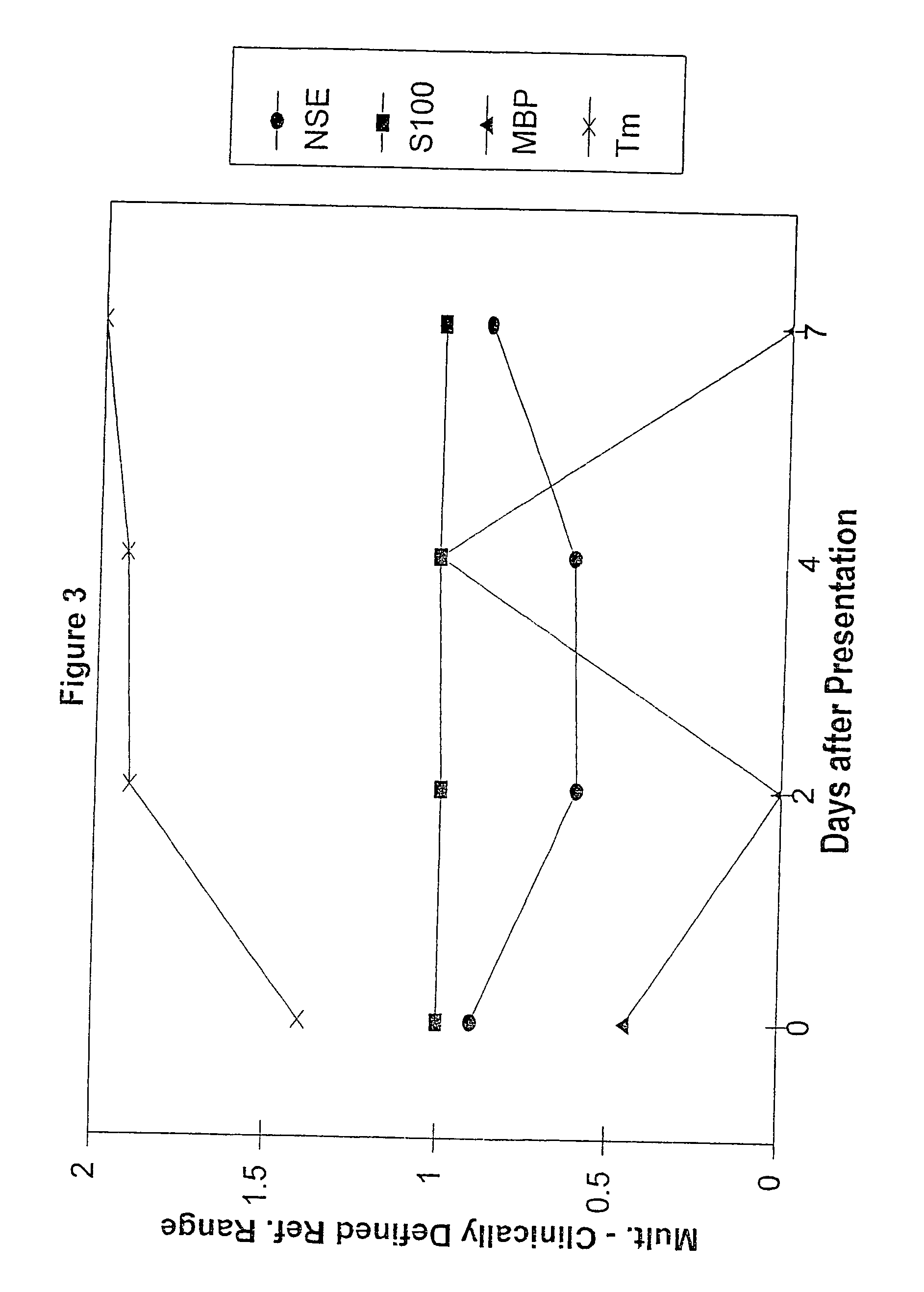
Method for diagnosing and distinguishing stroke and diagnostic devices for use therein
InactiveUS20050136496A1Improve patient selectionMicrobiological testing/measurementSnake antigen ingredientsThrombusS100 protein
A method for determining whether a subject has had a stroke and, if so, the type of stroke which includes analyzing the subject's body fluid for at least four selected markers of stroke, namely, myelin basic protein, S100 protein, neuronal specific enolase and a brain endothelial membrane protein such as thrombomodulin or a similar molecule. The data obtained from the analyses provide information as to the type of stroke, the onset of occurrence and the extent of brain damage and allow a physician to determine quickly the type of treatment required by the subject.
Owner:SKYE PHARMATECH
Transgenically produced non-secreted proteins
InactiveUS20060179493A1Reduce amountEliminate needPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticMammalGlutamate decarboxylase
The invention provides a method of making and secreting a non-secreted protein. The method includes expressing the protein from a nucleic acid construct which includes: (a) a mammary epithelial specific promoter; (b) a milk protein specific signal sequence which can direct the secretion of a protein; (c) optionally, a sequence which encodes a sufficient portion of the amino terminal coding region of a secreted protein to allow secretion in the milk of a transgenic mammal, of the non-secreted protein; and (d) a sequence which encodes a non-secreted protein, wherein elements (a), (b), optionally (c), and (d) are preferably operatively linked in the order recited. Both glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and myelin basic protein (MBP), which are cytoplasmic proteins, have been produced by the methods of the present invention. The invention also provides methods for treating diabetes and multiple sclerosis using proteins produced by the methods of the present invention.
Owner:GTC BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Systems for intraoperative nerve imaging
Disclosed are systems for intraoperative nerve imaging using compact high collection power imaging devices for fluorescence and white light imaging of myelin basic protein (MBP) nerve imaging agents during open and minimally invasive surgery.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for diagnosing and distinguishing stroke
InactiveCN1339108AConfirm progressIncreased risk of bleedingMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymologyS100 proteinRisk stroke
A method for determining whether a subject has had a stroke and, if so, the type of stroke which includes analyzing the subject's body fluid for at least four selected markers of stroke, namely myelin basic protein, S100 protein, neuronal specific enolase and a brain endothelial membrane protein such as thrombomodulin or a similar molecule. The data obtained from the analyses provide information as to the type of stroke, the onset of occurrence and the extent of brain damage and allow a physician to determine quickly the type of treatment required by the subject.
Owner:SYN X PHARMA
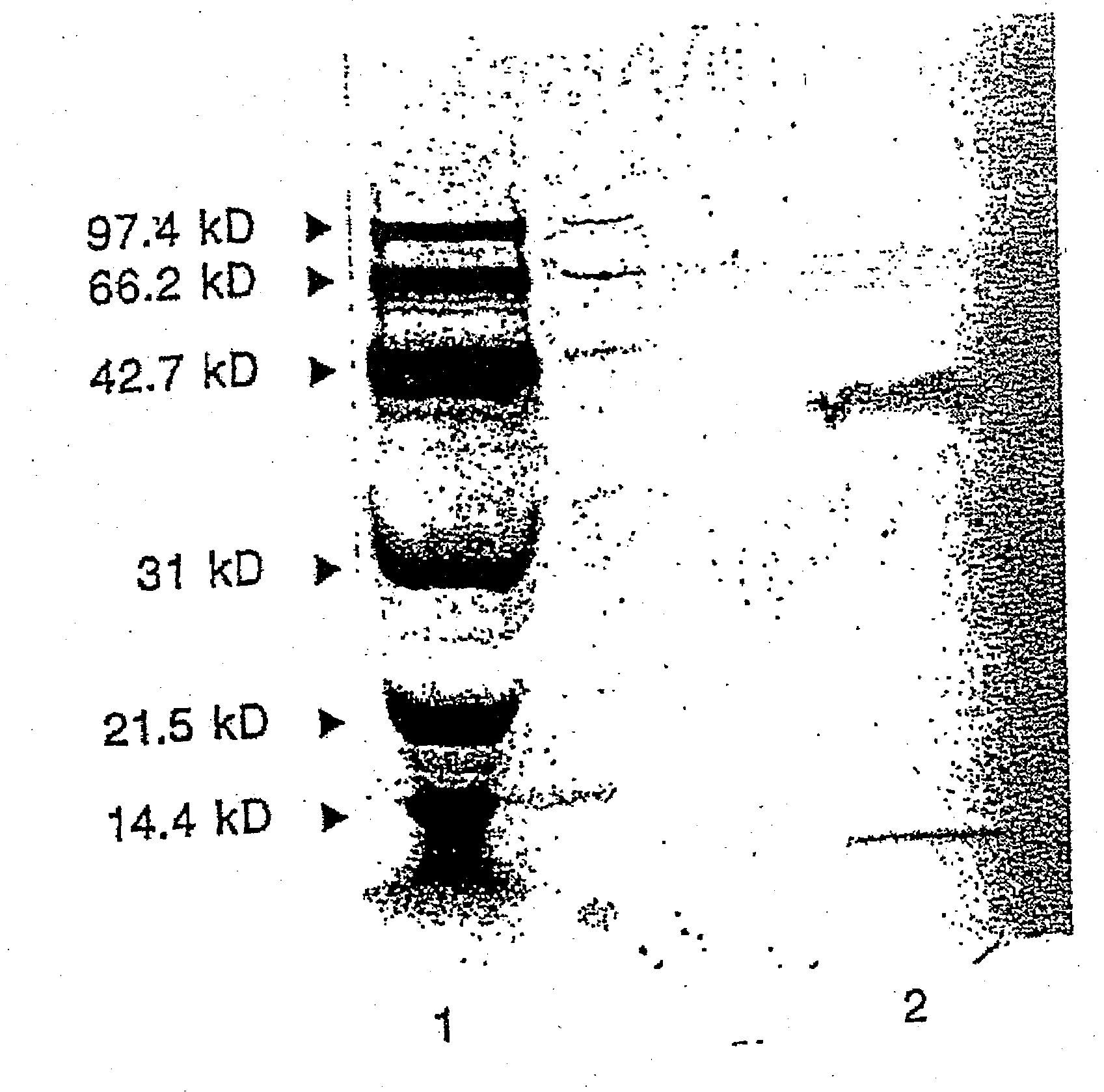
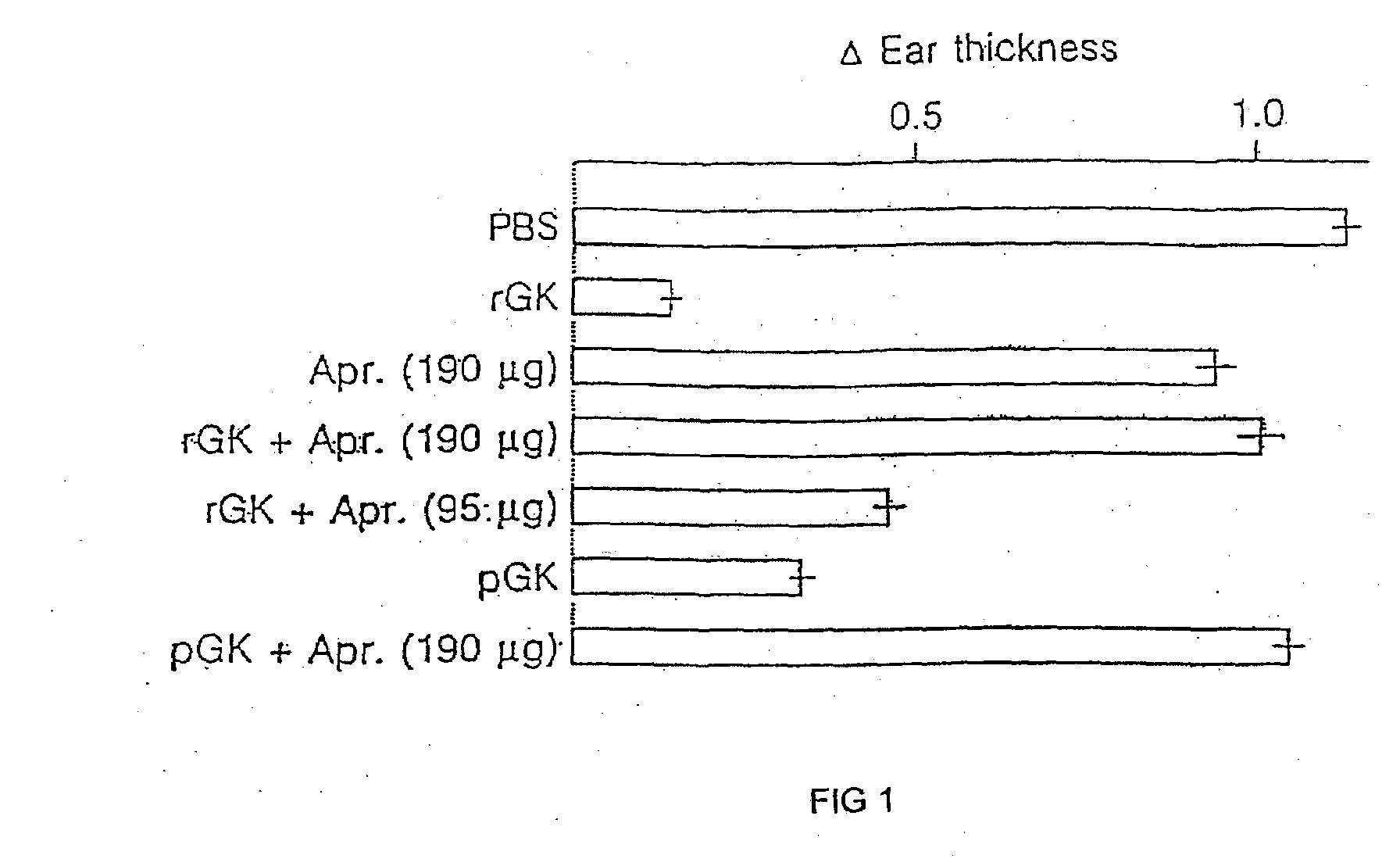
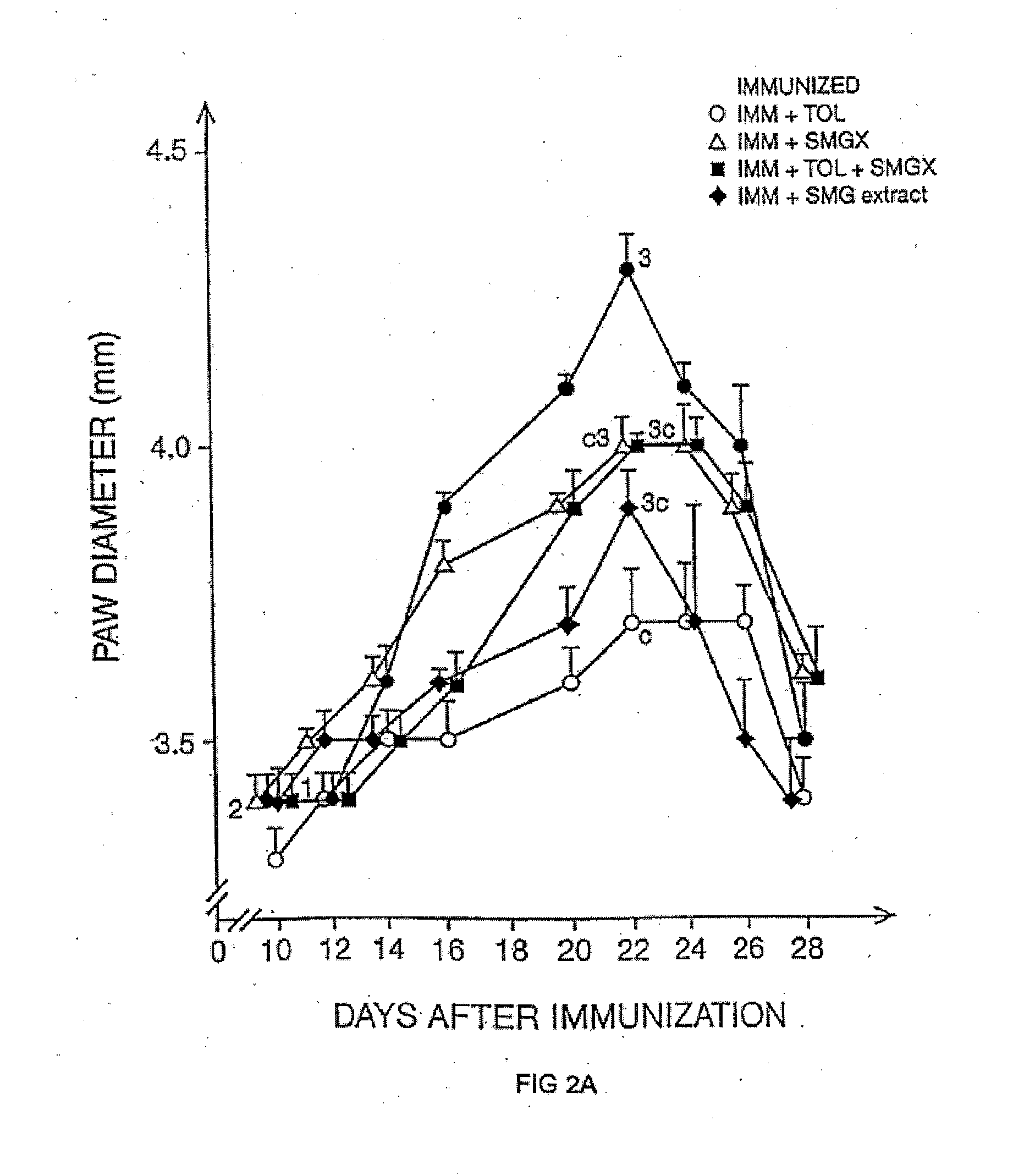
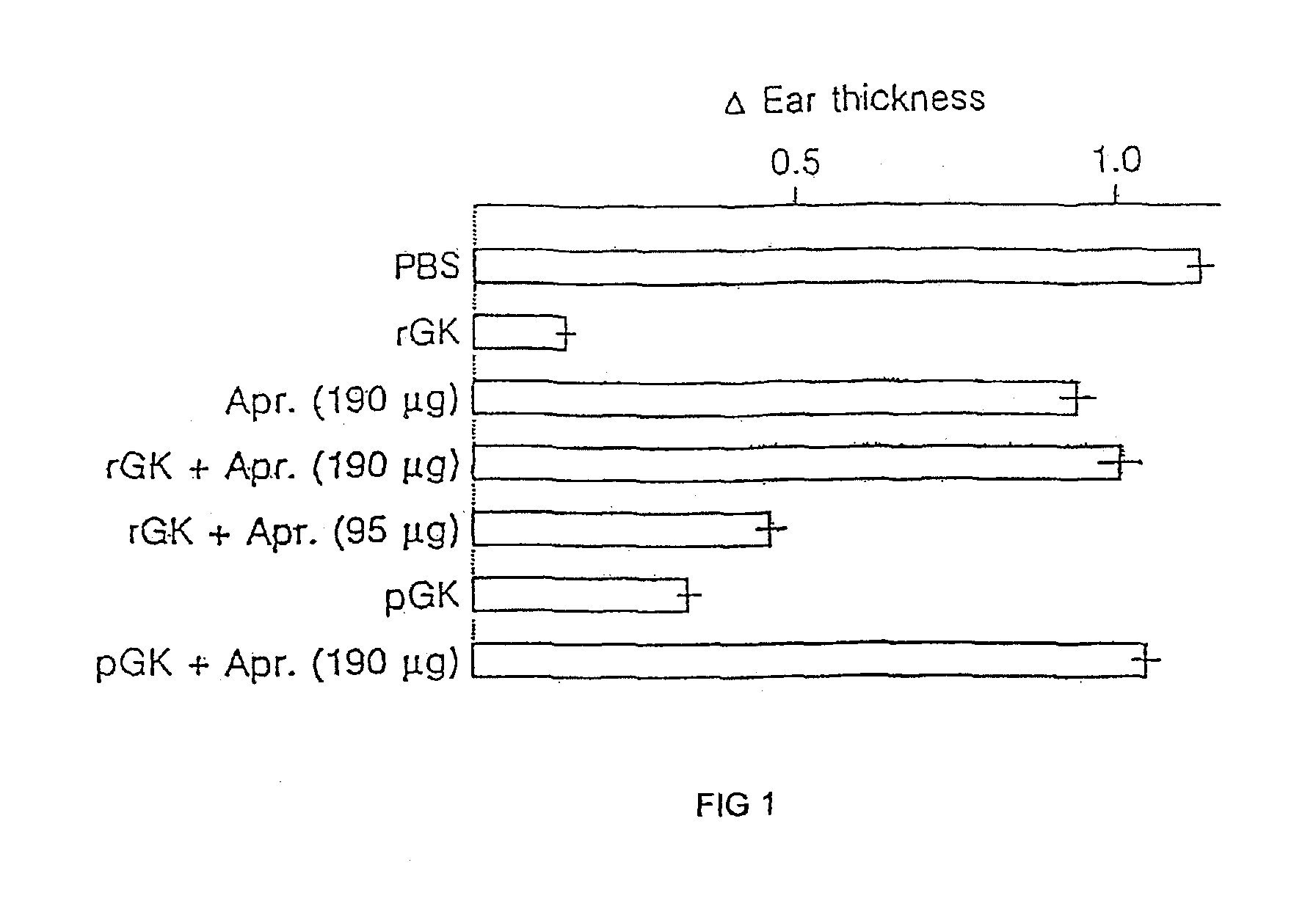
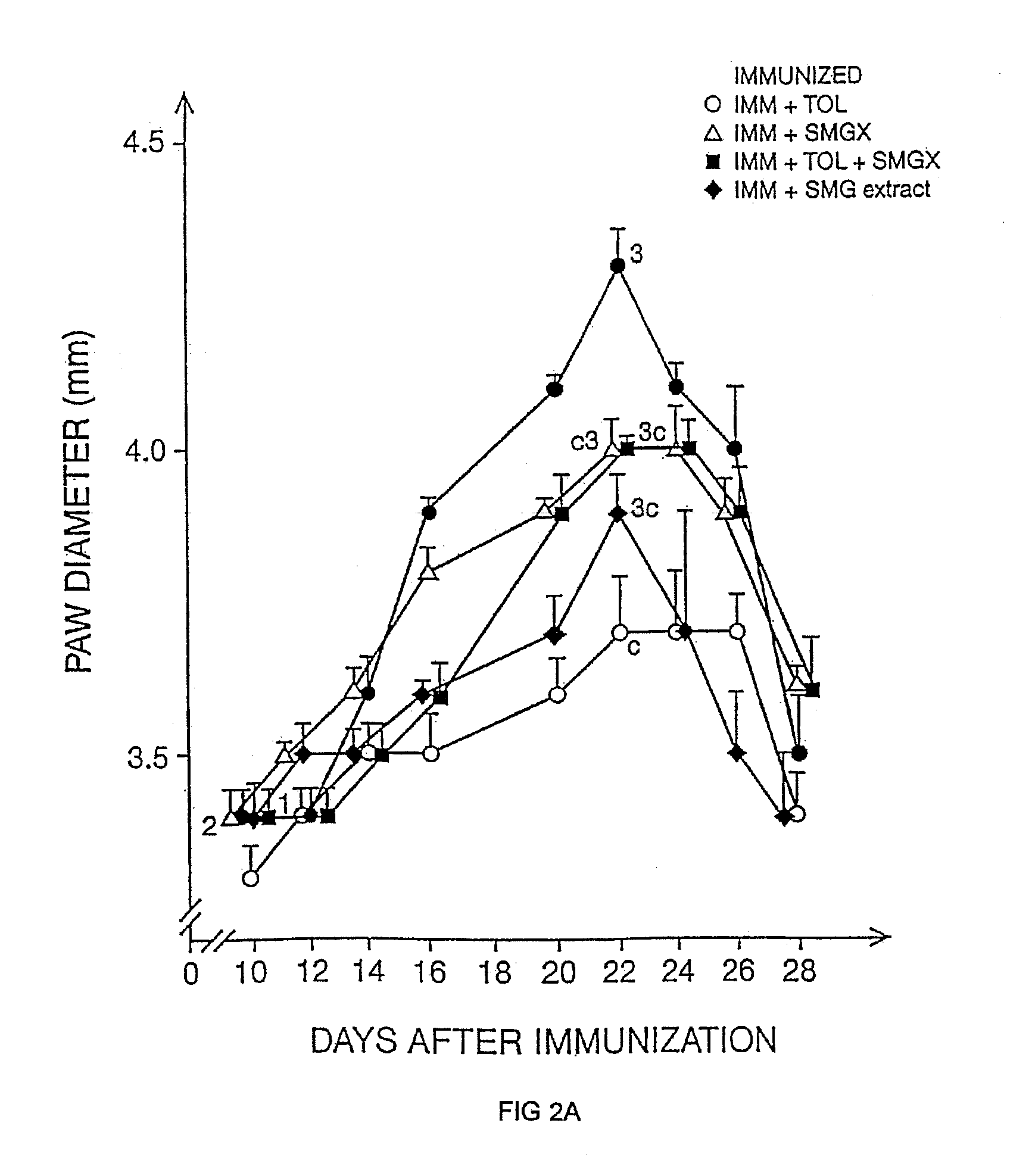
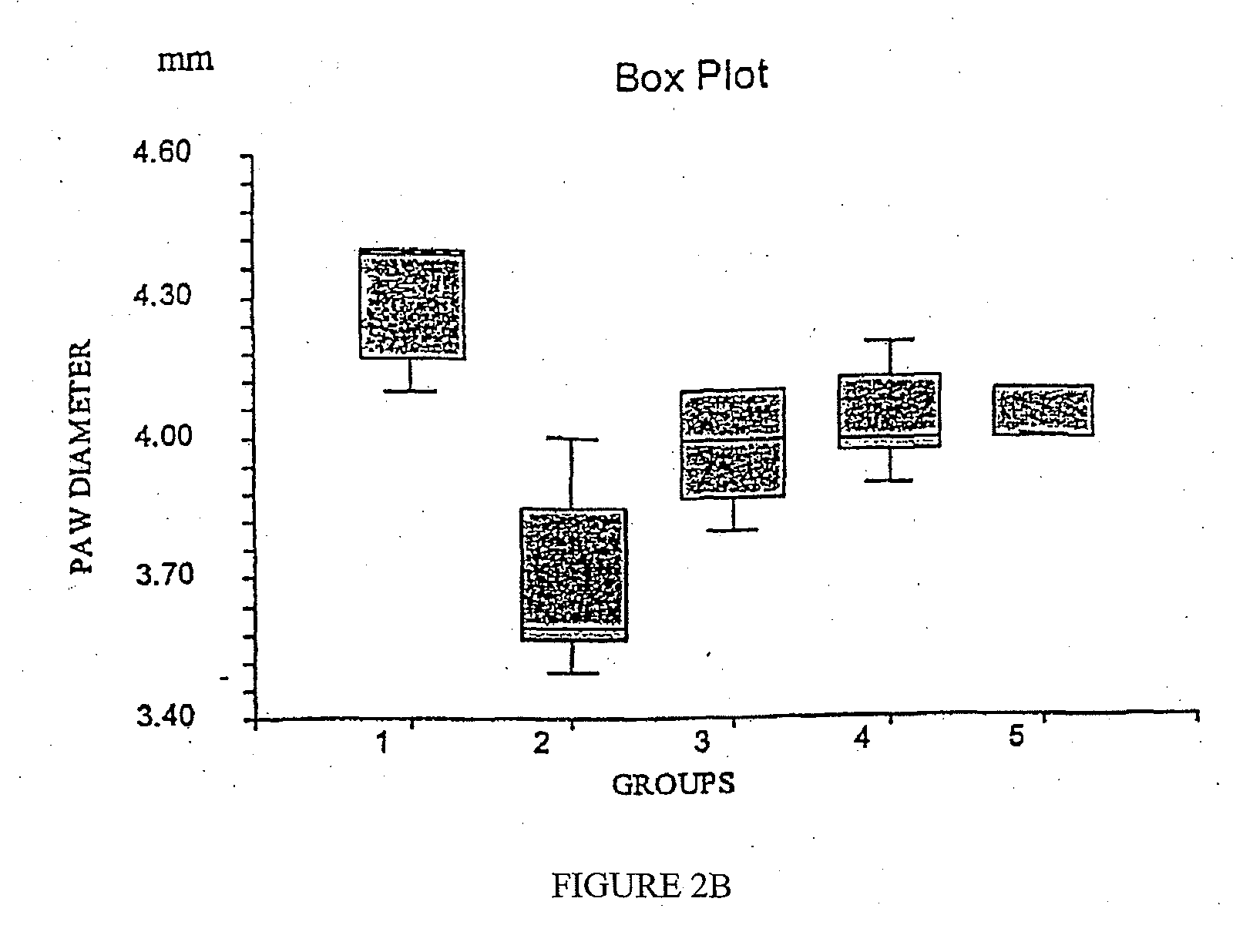
Therapeutic uses of glandular kallikrein
InactiveUS20090162342A1Lower immune responsePeptide/protein ingredientsImmunological disordersAutoimmune responsesGlandular Kallikrein
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising glandular kallikrein in combination with myelin basic protein or copaxone for use in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. The present invention further relates to a method of suppressing autoimmune responses in a patient afflicted with or suffering at least one clinical sign of multiple sclerosis, comprising administering to said patient a therapeutically effective amount of glandular kallikrein in combination with a therapeutically effective amount of myelin basic protein or copaxone.
Owner:DIAMEDICA INC
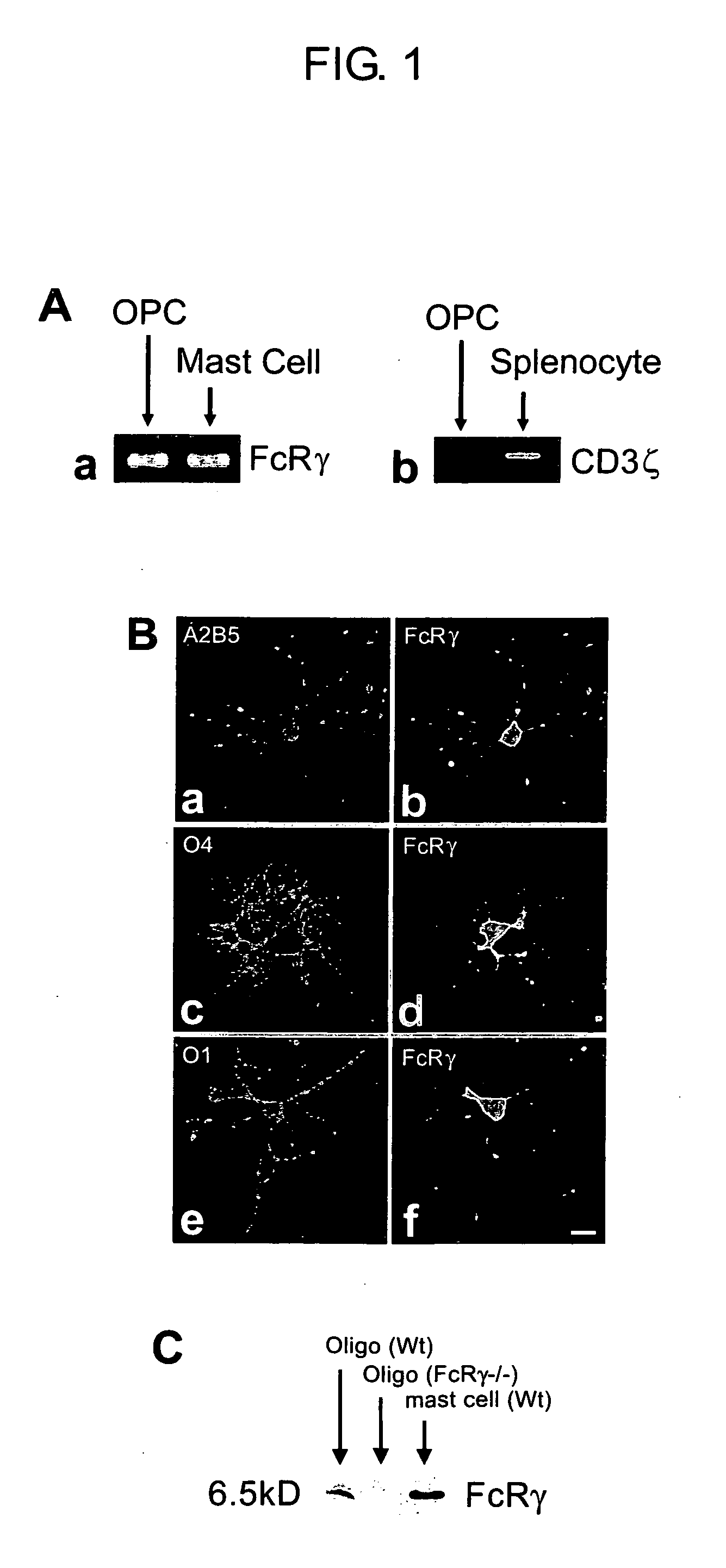
Medicinal compositions containing fc receptor gamma-chain activator
InactiveUS20050175998A1Clarifying mechanismIncrease enzyme activityNervous disorderAntipyreticFc(alpha) receptorFc receptor
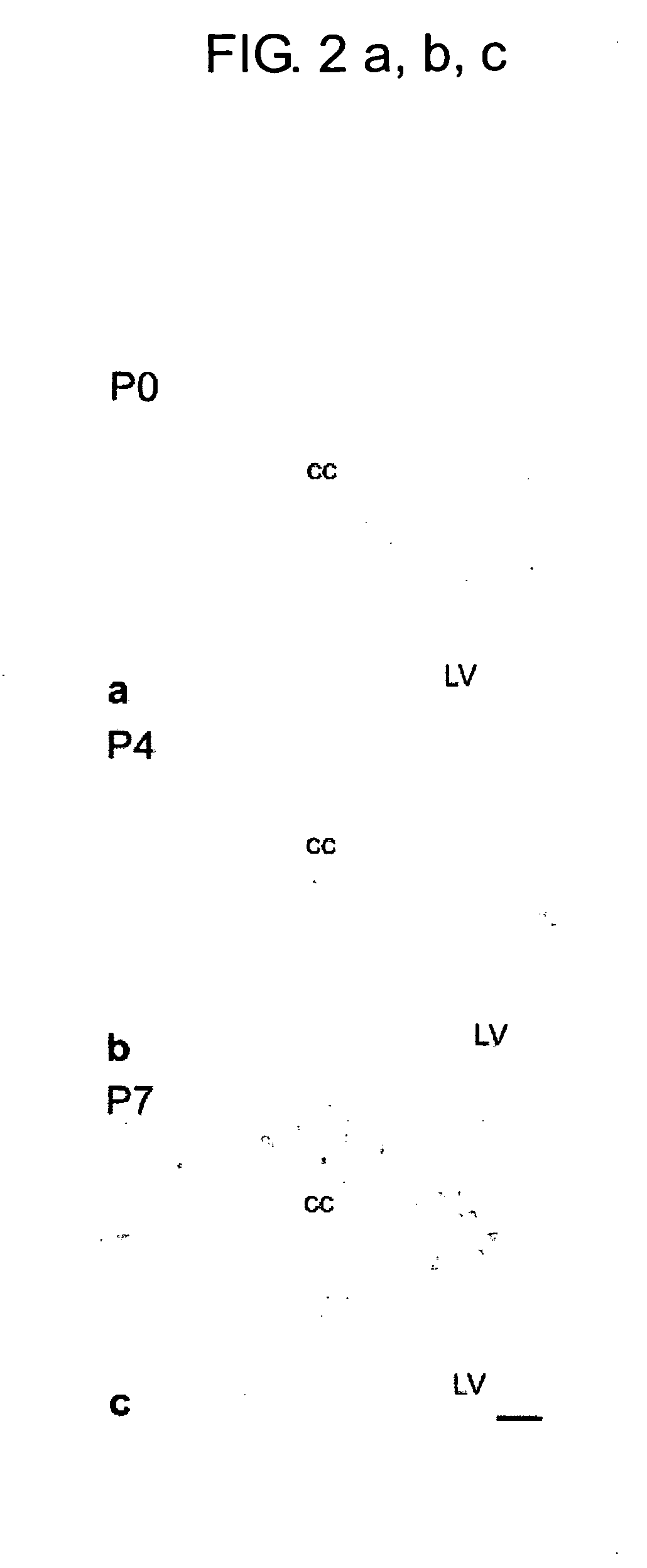
The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising, as an active ingredient, a substance capable of activating the γ chain of Fc receptors (FcRγ) (provided that the substance is not an immunoglobulin for intravenous injection), and agents for stimulating myelinogenesis. The invention also provides agents for stimulating the differentiation of oligodendroglial precursor cells, agents for activating Fyn tyrosine kinase, and agents for stimulating the expression of myelin basic protein, all comprising a substance capable of activating FcRγ as an active ingredient. Further, the invention provides a method of detecting myelinogenetic oligodenroglias or precursor cells thereof which comprises using the expression of FcRγ in oligodendroglias or precursor cells thereof as an indicator.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
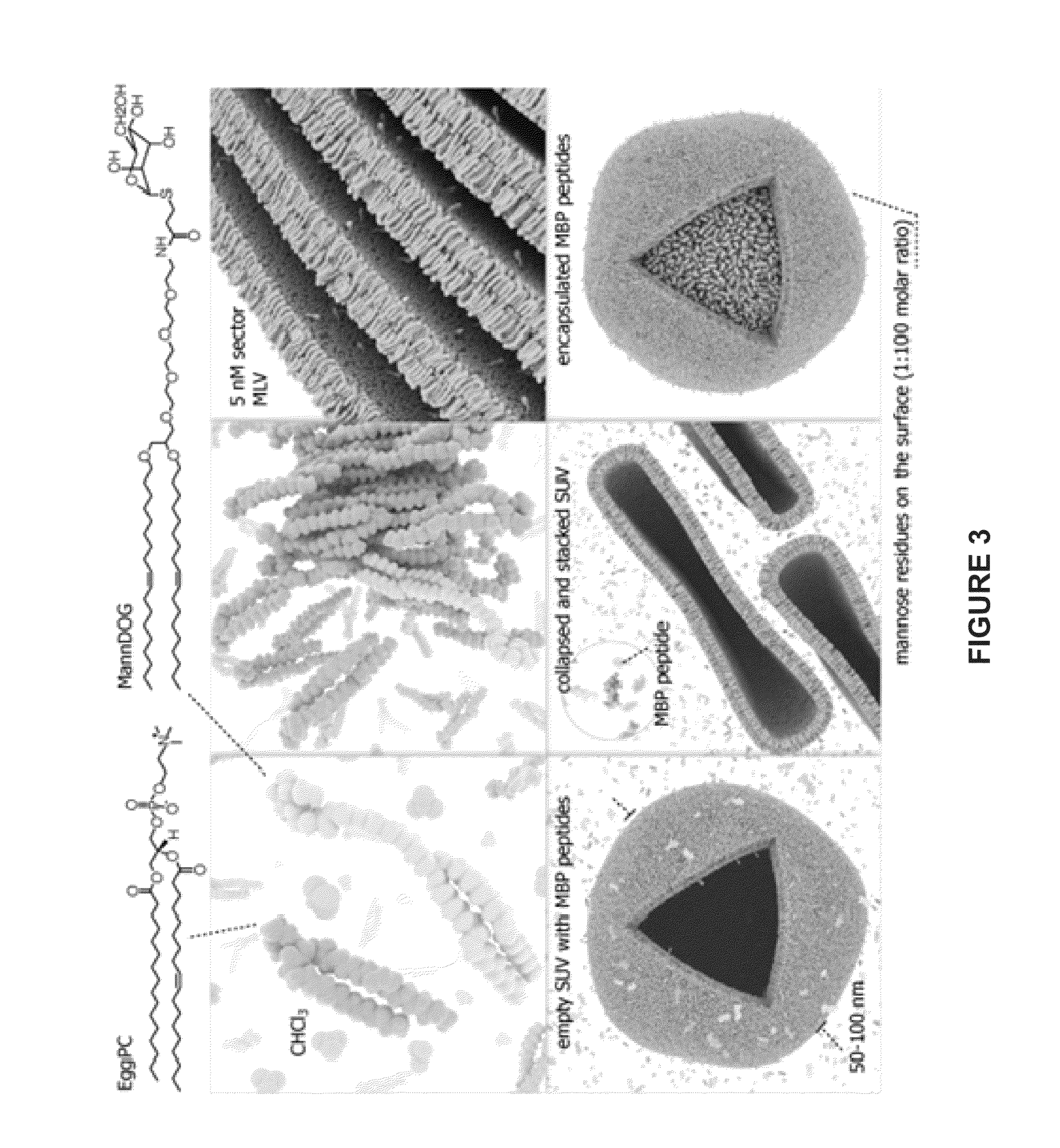
Liposomes containing oligopeptide fragments of myelin basic protein, a pharmaceutical composition and a method for treatment of multiple sclerosis
InactiveUS20130058994A1Reduce paralysisReduce deliveryNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineOligopeptide
The present invention provides compositions and methods for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Among others, the invention provides compositions of immunodominant peptides of myelin basic protein encapsulated in mannosylated liposomes. In a specific embodiment, the compositions comprise mylein basic protein (MBP) peptides MBP(46-62), MBP(124-139), and MBP(147-170).
Owner:LIPOXEN TECHNOLOGIES LTD
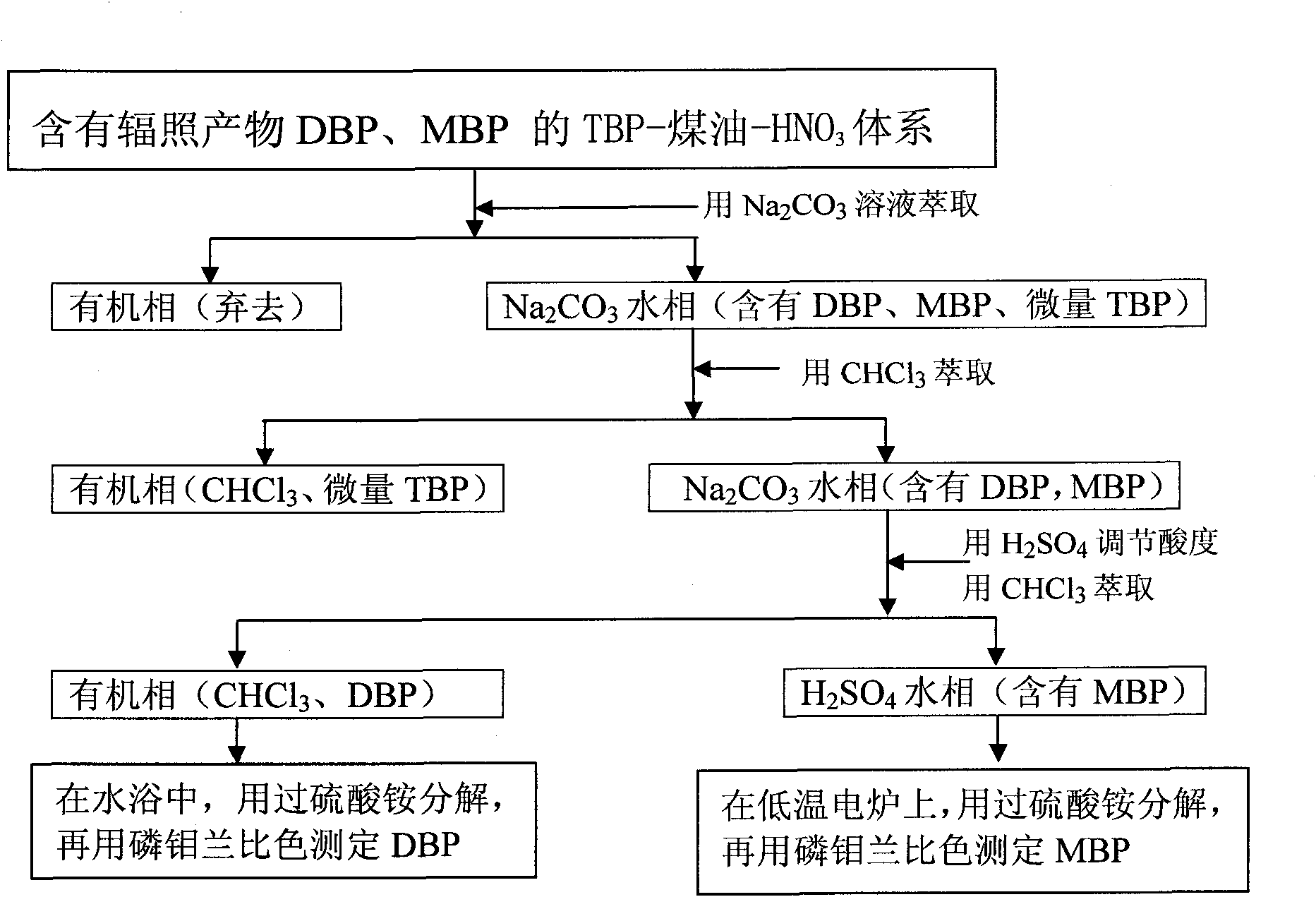
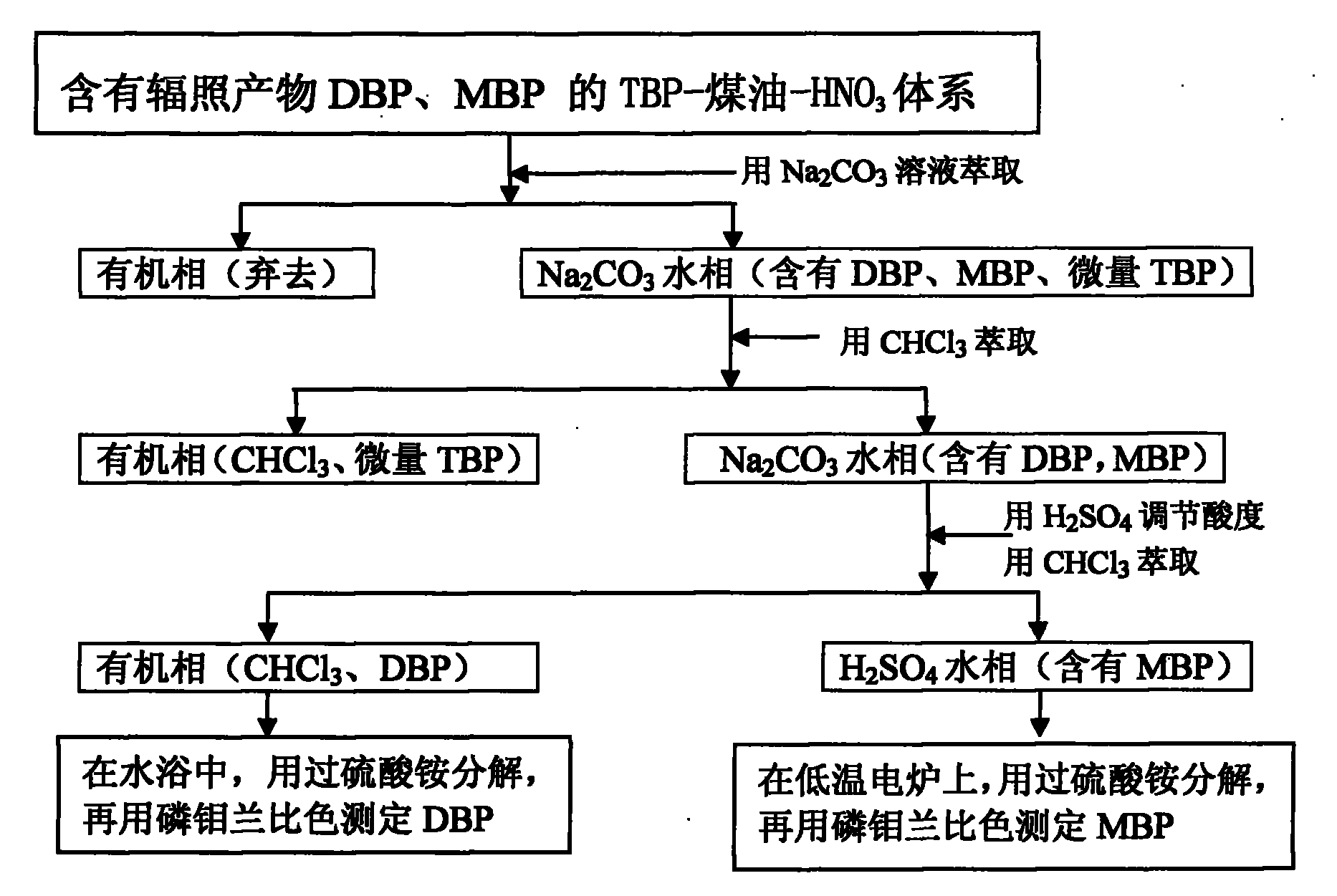
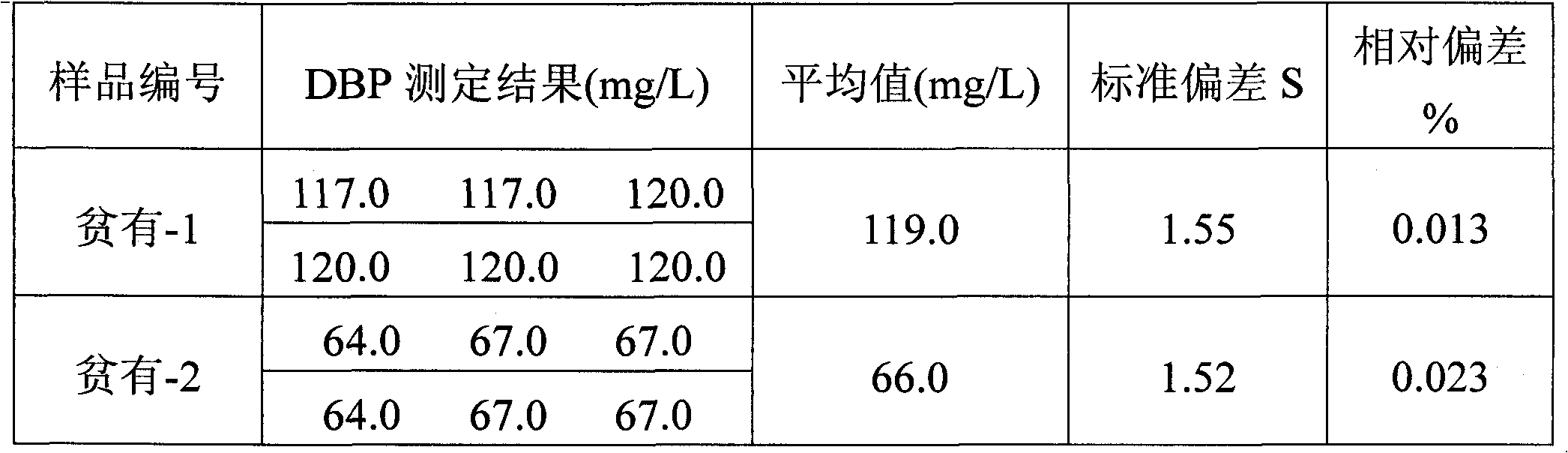
Separation and detection method of irradiation product DBP (Double-Base Propellant) and/or MBP (Myelin Basic Protein) in TBP (Ttri-Butyl phosphate)-kerosene-HNO3 system
InactiveCN101830924AHigh sensitivityShort analysis periodMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPhosphateKerosene
The invention relates a separation and detection method of an irradiation product DBP (Double-Base Propellant) and / or MBP (Myelin Basic Protein) in a TBP (Tri-Butyl Phosphate)-kerosene-HNO3 system, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: firstly, extracting the TBP-kerosene-HNO3 system containing the irradiation product DBP and MBP with a Na2CO3 solution and separating to obtain an organic phase containing a TBP-kerosene-HNO3 system and a Na2CO3 aqueous phase containing DBP, MBP and micro TBP; and secondly, extracting the obtained Na2CO3 aqueous phase containing DBP, MBP and micro TBP with CHCl3 and separating to obtain a CHCl3 organic phase containing micro TBP and a Na2CO3 aqueous phase containing DBP and MBP. The separation and detection method is simple and convenient, does not need expensive instruments and has a short analysis period.
Owner:中核二七二铀业有限责任公司
Method for preparing pre-staining luminescent protein marker
InactiveCN107298719AAdd binding sitesOptical signal enhancementAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsG-proteinsBinding siteX-ray
The invention provides a method for preparing a pre-staining luminescent protein marker. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a protein A gene, a protein G gene, an MBP (Myelin Basic Protein) gene and a heavy chain constant region gene (CH gene) of a mouse and rabbit derived antibody, and cutting and combining the genes according to sizes of different proteins in a pre-staining luminescent protein marker; expressing the proteins, purifying, and mixing proteins of different molecule weights according to a certain ratio so as to obtain a luminescent protein marker; mixing the prepared luminescent protein marker with the pre-staining luminescent protein marker according to different ratios. The pre-staining luminescent protein marker prepared by using the method is capable of recognizing primary antibodies or secondary antibodies of different sources, binding sites of proteins are increased, light signals are intensified, not only are general positions of proteins indicated in the electrophoresis process and after membrane transfer, but also precise positions of the proteins can be indicated on X-ray films, no extra pre-staining marker channels are needed, no extra antibodies are needed, and the luminescent proteins can be combined with IgG or anti-rabbit and anti-mouse secondary antibodies derived from species such as human beings, rats, mice and rabbits.
Owner:南京赛诺博生物科技有限责任公司
Imaging of myelin basic protein
InactiveUS20100310456A1In-vivo radioactive preparationsDiagnostic recording/measuringMedicineMyelin basic protein
The present invention relates to methods for myelin basic protein detection comprises identifying a subject at risk of or diagnosed with a myelin-associated neuropathy, parenterally administering to the subject the agent, and determining myelination in the subject by detecting binding to myelin basic protein. Methods for the detection of myelin and a quantitative measurement of its local concentration in a sample using an agent with specific binding to myelin basic protein are also provided as is a kit containing the agent or its derivatives for use in detecting myelin basic protein
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods of detecting myelin basic protein
ActiveUS9040019B2In-vivo radioactive preparationsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsTissue sampleMyelin basic protein
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Peptide specificity of anti-myelin basic protein and the administration of myelin basic protein peptides to multiple sclerosis patients
Human myelin basic protein (h-MBP) has a molecular weight of 18.5 KD and contains 170 amino acid residues. Synthetic peptides ranging in length from about 8 to 25 residues and covering the entire length of the protein have been produced. Antibodies to h-MBP (anti-MBP) were found to be neutralized by the synthetic peptides, in vitro, which span the h-MBP from about amino acid residue 61 to about amino acid residue 106. The peptides, which cover both the amino (about residues 1 to 63) and carboxy (about residues 117 to 162) terminals of h-MBP did not neutralize purified anti-MBP. Intrathecal administratin of peptide MBP(75-95), MBP(86-95), or MBP(82-98) produced complete binding-neutralization of free (F) anti-MBP with no change in bound (B) levels. A control peptide MBP35-58 had no effect on F or B anti-MBP levels. Intravenous administration of MBP(75-95), MBP(86-95), or MBP(82-98) resulted in significant decline of F and B CSF anti-MBP levels. Administration of MBP synthetic peptides to MS patients either intrathecally or intravenously did not have any adverse neurological effects and systemic complications did not occur. The MBP epitope for MS anti-MBP has been localized to an area between amino acid 86 and amino acid 95.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Imaging of myelin basic protein
The present invention relates to methods for myelin basic protein detection comprises identifying a subject at risk of or diagnosed with a myelin-associated neuropathy, parenterally administering to the subject the agent, and determining myelination in the subject by detecting binding to myelin basic protein. Methods for the detection of myelin and a quantitative measurement of its local concentration in a sample using an agent with specific binding to myelin basic protein are also provided as is a kit containing the agent or its derivatives for use in detecting myelin basic protein
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Myelin basic protein peptide composition
The present invention relates to a composition which comprises the following myelin basic protein peptides: MBP 30-44, MBP 83-99, MBP 131-145, and MBP 140-154. The composition may be used to treat a disease, in particular multiple sclerosis and / or optical neuritis and the invention also relates to such uses and methods.
Owner:WORG PHARM (ZHEJIANG) CO LTD
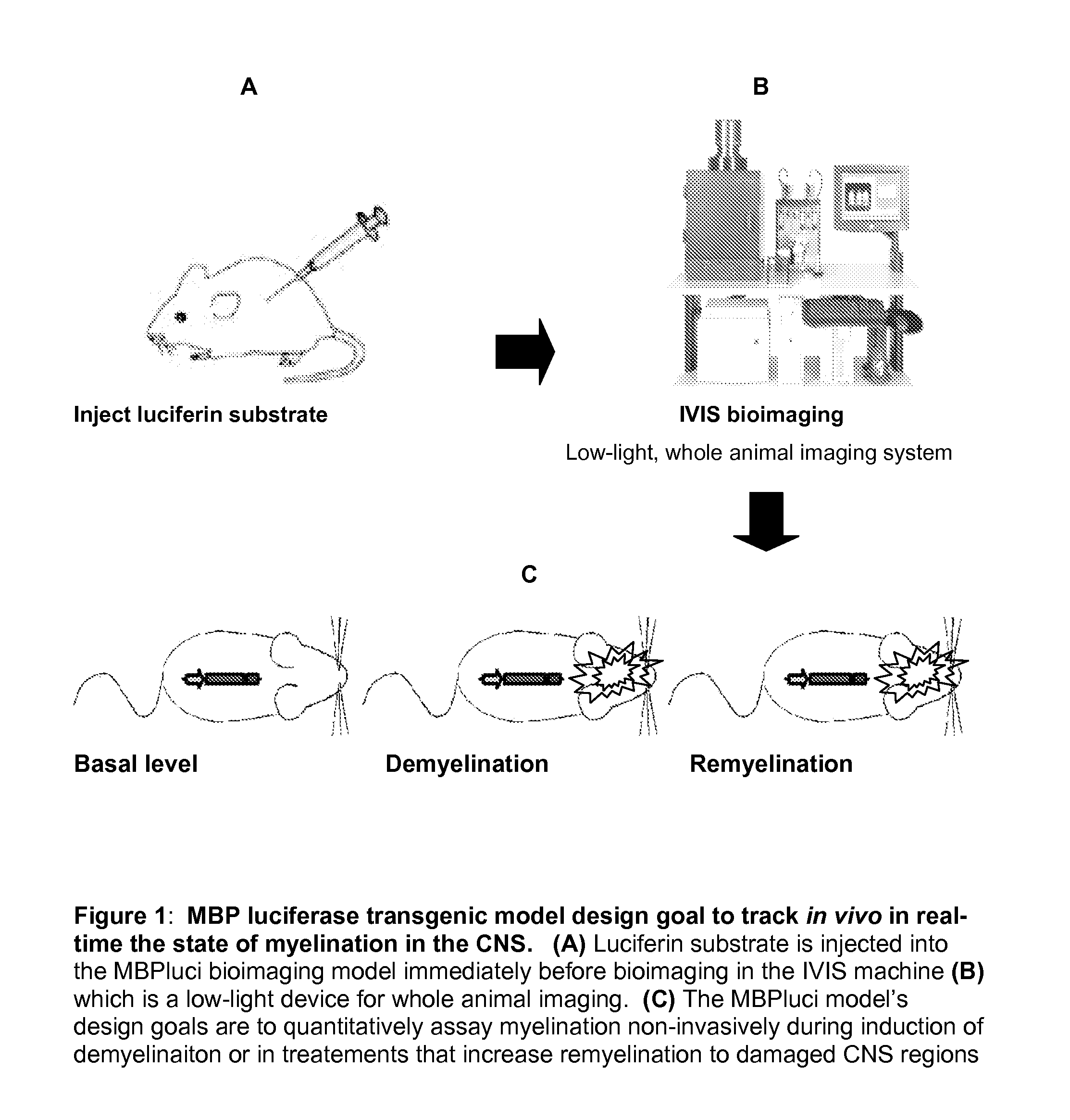
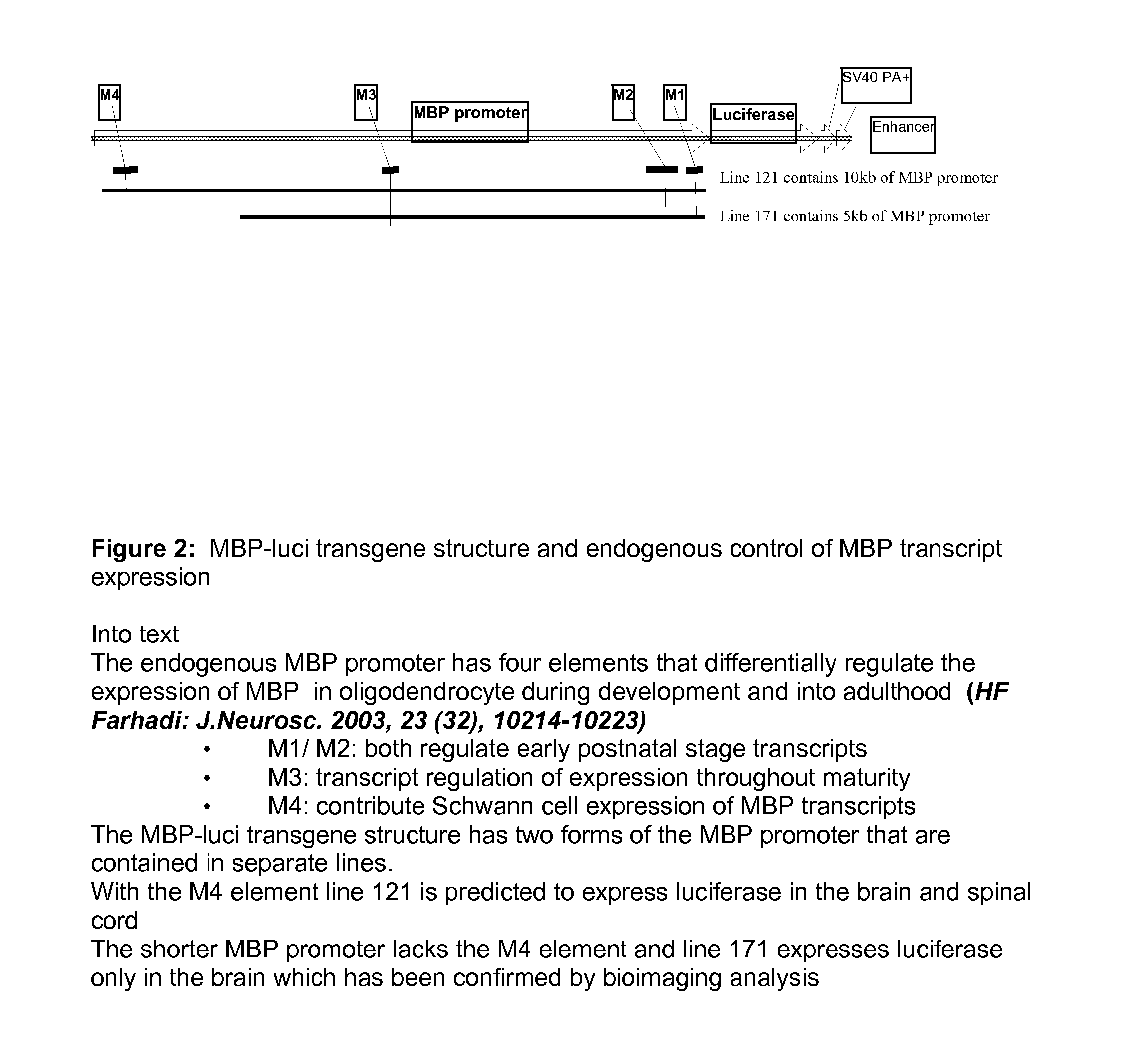
Animal Model Expressing Luciferase under Control of the Myelin Basic Protein Promoter (MBP-luci) and Use of the Model for Bioluminescence In Vivo Imaging
InactiveUS20130117868A1Avoid sacrificeContinuous trackingGenetic engineeringMaterial analysisRemyelinationIn vivo
A Myelin Basic Protein-luciferase bioimaging noninvasive model to visualize and quantify demyelination and remyelination events in the CNS at transcriptional level in vivo is provided. Luciferase-expressing transgenic animals were generated with myelin basic protein (MBP) promoter coupled to firefly luciferase reporter. The MBP-luci bioimaging model provides a means to monitor myelination status and the efficacy of a remyelination modulating test compound. An advantage of bioimaging is that a subject in a longitudinal study can serve as its own control. The same subject can be tracked over a demyelination and remyelination process continuously over a period of at least 10 weeks. This model enables normalization of individual animal imaging response and provides quality data with considerably reduced variance. In addition, because cohorts of animals need not be sacrificed at different time points, reduction in the number necessary for a compound efficacy study is possible.
Owner:SANOFI SA
Agents and methods for the imaging of myelin basic protein
The present invention relates to agents capable of binding to myelin basic protein in a subject. Also provided are methods for the detection of myelin-associated neuropathy comprising identifying a subject at risk of or diagnosed with a myelin-associated neuropathy, administering to a subject an agent that binds specifically to myelin basic protein, and determining myelination in the subject by detecting the agent present in the subject. A kit containing the agent or its derivatives for use in detecting myelin basic protein is also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Preparation method of FGF1 (fibroblast growth factor 1) full-length protein by utilizing escherichia coli
InactiveCN102978212AImprove solubilityHigh purityFibroblast growth factorFermentationSolubilityEscherichia coli
The invention relates to recombinant human acidic fibroblast growth factor (FGF1), in particular relates to a preparation method of FGF1 full-length protein by utilizing escherichia coli, which comprises the following steps of amplifying by utilizing a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method to obtain a human FGF1 full-length gene PCR product; and digesting the PCR product by using incision enzyme. According to the preparation method, the full-length gene of the human acidic fibroblast growth factor is cloned to a pMAL-p5X expression carrier; the recombinant plasmid expresses the FGF1 full-length protein containing MBP (myelin basic protein) fusion label at high efficiency in the escherichia coli, wherein the protein in soluble expression; and the protein with MBP infusion label is purified by utilizing an MBP affinity column, and a complete FGF1 protein without the fusion label is prepared by utilizing TEV (tobacco etch virus) enzyme binding site and using TEV digested and purified infusion protein. The FGF1 full-length protein has high solubility and higher purity.
Owner:赵谦
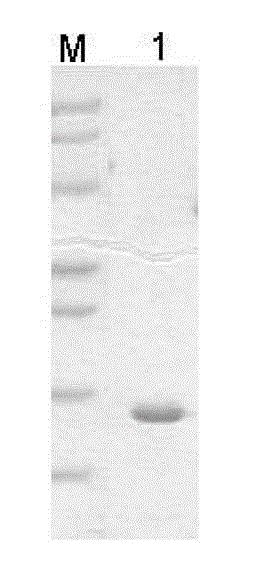
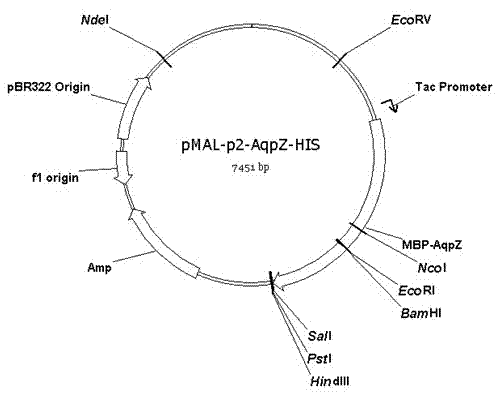
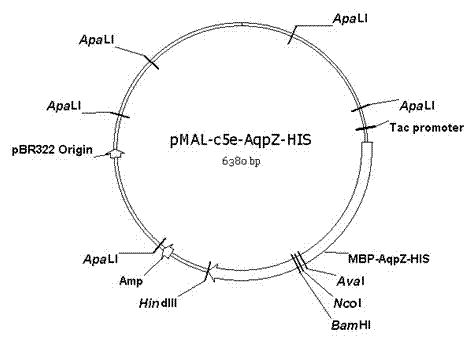
Method for embedded membrane expression and aquaporins (AqpZ) purification in escherichia coli
InactiveCN102643849AEfficient expressionAvoid toxicityMicroorganism based processesPeptide preparation methodsEscherichia coliInclusion bodies
The invention discloses a method for embedded membrane expression and aquaporins (AqpZ) purification in escherichia coli. According to the method, firstly, AqpZ- histidine (HIS) of the escherichia coli is amplified, then, recombination expression vectors and inducible expression engineering bacterial strains are constructed, fusion protein myelin basic protein (MBP)-AqpZ-HIS thalli are obtained through ultrasonic crushing, and finally, the AqpZ is obtained through purification. The method has the advantages that the efficient expression of maltose-binding protein-AqpZ-poly histidine binary tag fusion protein is realized in the escherichia coli, and the problems of insoluble inclusion body forming and host cell toxicity caused by the traditional overexpression AqpZ are solved; and in addition, high-purity AqpZ can be obtained only through two turns of simple affinity chromatography separation on the AqpZ expressed by the method, the operation is simple, and the method can be applied to industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for diagnosing and distinguishing stroke and diagnostic devices for use therein
InactiveUS7655424B2Improve patient selectionMicrobiological testing/measurementSnake antigen ingredientsS100 proteinRisk stroke
A method for determining whether a subject has had a stroke and, if so, the type of stroke which includes analyzing the subject's body fluid for at least four selected markers of stroke, namely, myelin basic protein, S100 protein, neuronal specific enolase and a brain endothelial membrane protein such as thrombomodulin or a similar molecule. The data obtained from the analyses provide information as to the type of stroke, the onset of occurrence and the extent of brain damage and allow a physician to determine quickly the type of treatment required by the subject.
Owner:SKYE PHARMATECH
Methods of detecting myelin basic protein
ActiveUS20140154178A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsMyelin body formationTissue sample
A method and a kit for detecting myelin basic protein are provided. The method comprises administering an agent, which binds to myelin basic protein (MBP), to a subject at risk of or diagnosed with a myelin-associated neuropathy, and determining myelination by detecting the agent resided in the subject. The amount of the agent present in the subject is indicative of a myelin-associated neuropathy. A method of quantifying an amount of MBP present in a tissue sample is also provided, wherein the method comprises contacting the tissue sample with the same agent, detecting the agent present in the tissue sample; and quantifying an amount of the agent present in the tissue sample.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Diagnostic method
ActiveUS20110124010A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisAlpha-synucleinMyelin basic protein
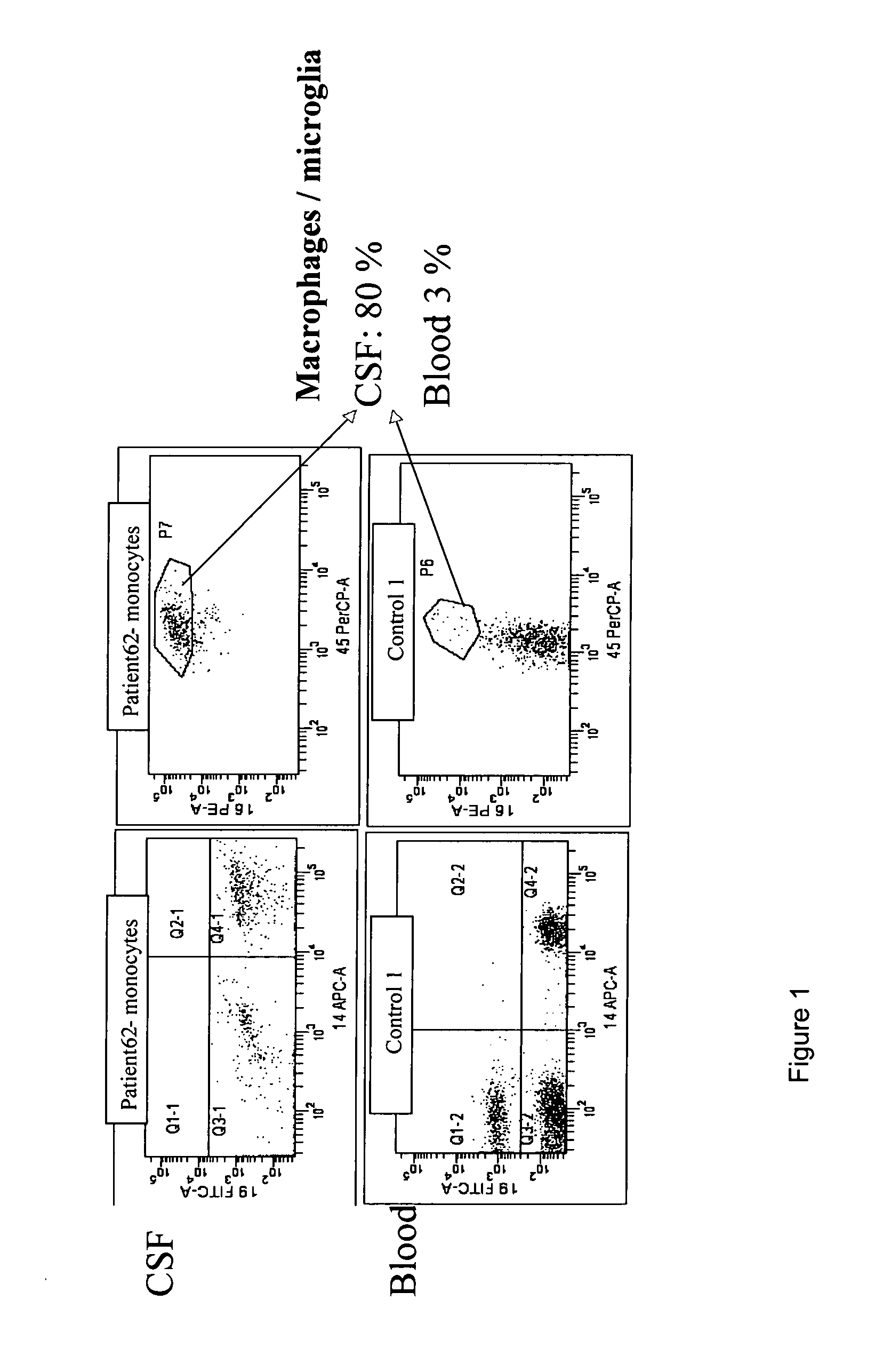
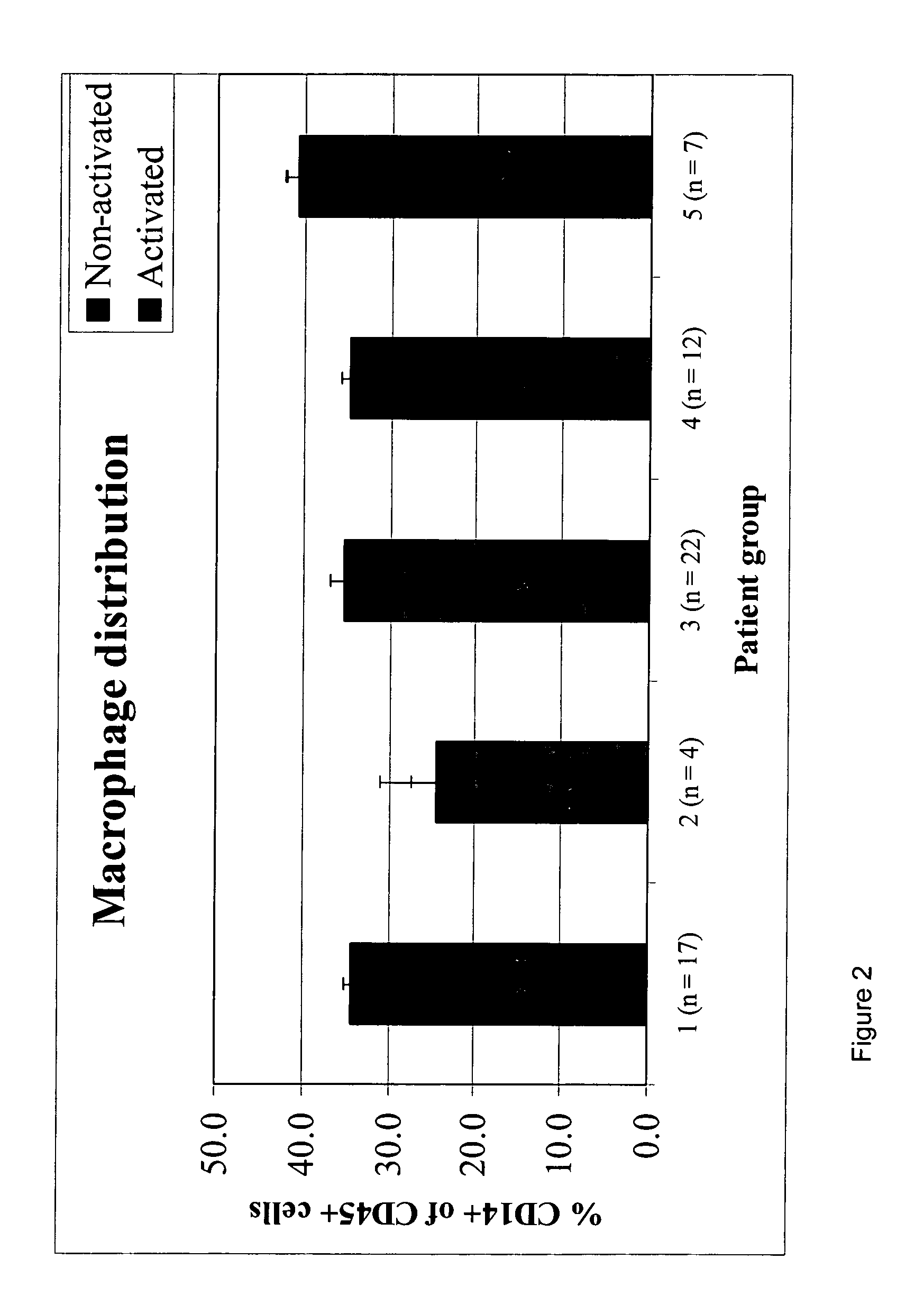
A method of detecting the presence, or monitoring the severity of a condition characterised by the presence of fragments of a marker protein in the brain of a patient. The method comprises: (i) providing a sample comprising macrophages obtained from the patient; and (ii) detecting the presence of the marker protein or fragments thereof in the macrophages. The presence of abnormal levels of the marker protein and / or fragments thereof in the macrophages is indicative of the presence of the condition in the patient. The condition and the marker proteins can be: Alzheimer's Disease and the Abeta peptide, Parkinson's Disease and ubiquitin, Multiple Sclerosis and myelin basic protein, FrontoTemporal Dementia and tau, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and tau, Parkinson's disease, Lewy Body dementia or Alzheimer's Disease and alpha-synuclein.
Owner:INVEN2
Therapeutic uses of glandular kallikrein
InactiveUS20130224230A1Lower immune responsePeptide/protein ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsAutoimmune responsesGlandular Kallikrein
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising glandular kallikrein in combination with myelin basic protein or copaxone for use in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. The present invention further relates to a method of suppressing autoimmune responses in a patient afflicted with or suffering at least one clinical sign of multiple sclerosis, comprising administering to said patient a therapeutically effective amount of glandular kallikrein in combination with a therapeutically effective amount of myelin basic protein or copaxone.
Owner:DIAMEDICA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com