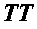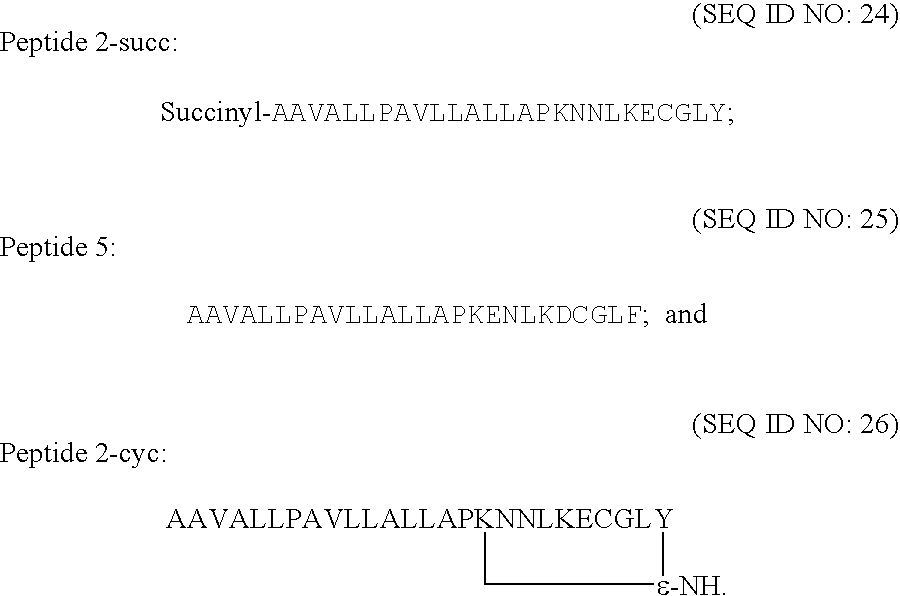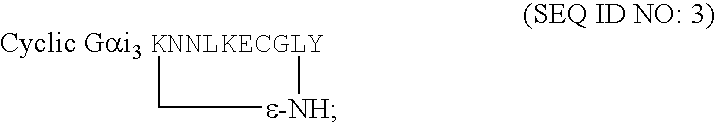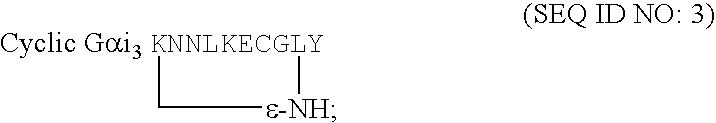Patents
Literature
59results about "G-proteins" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
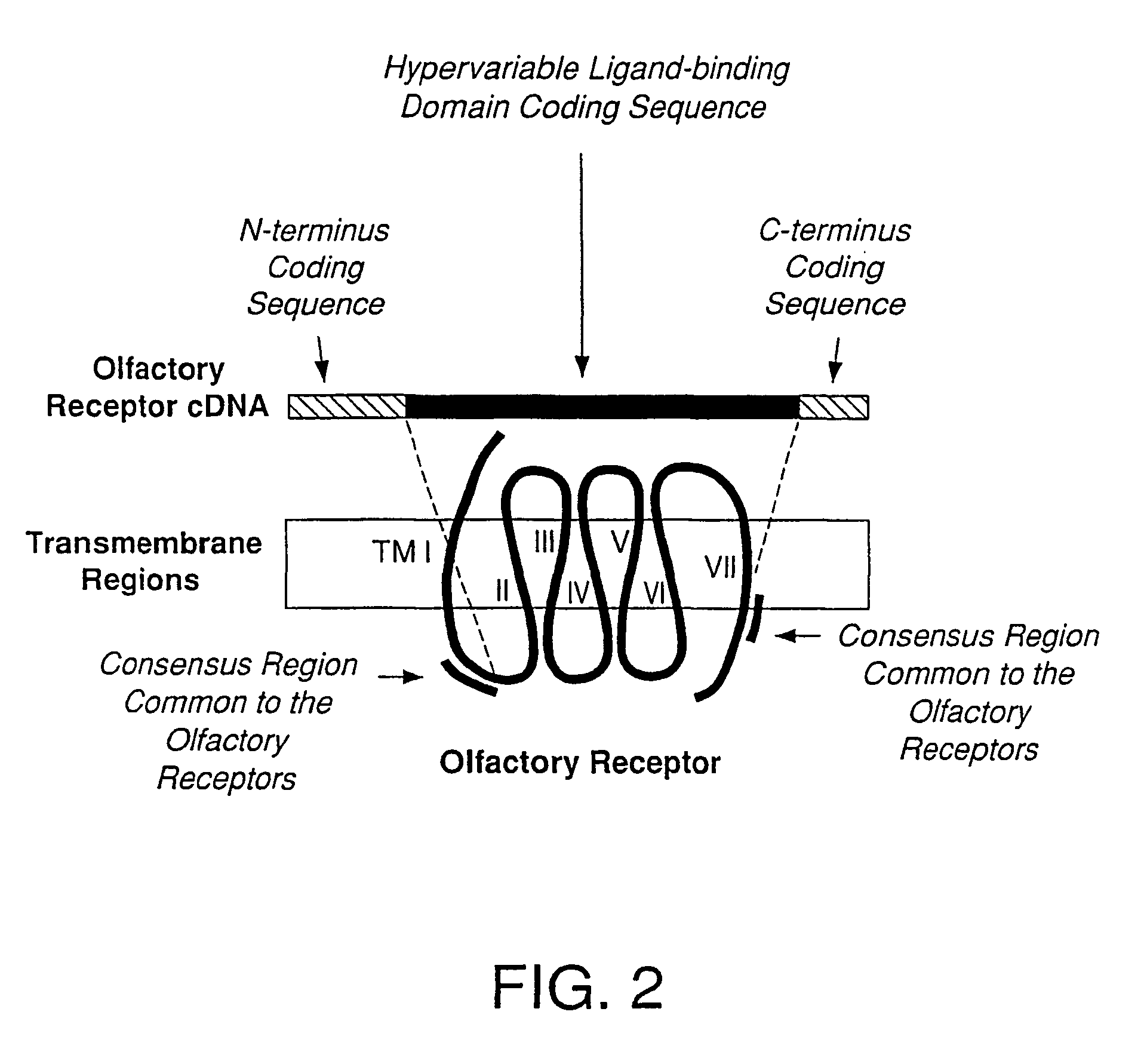
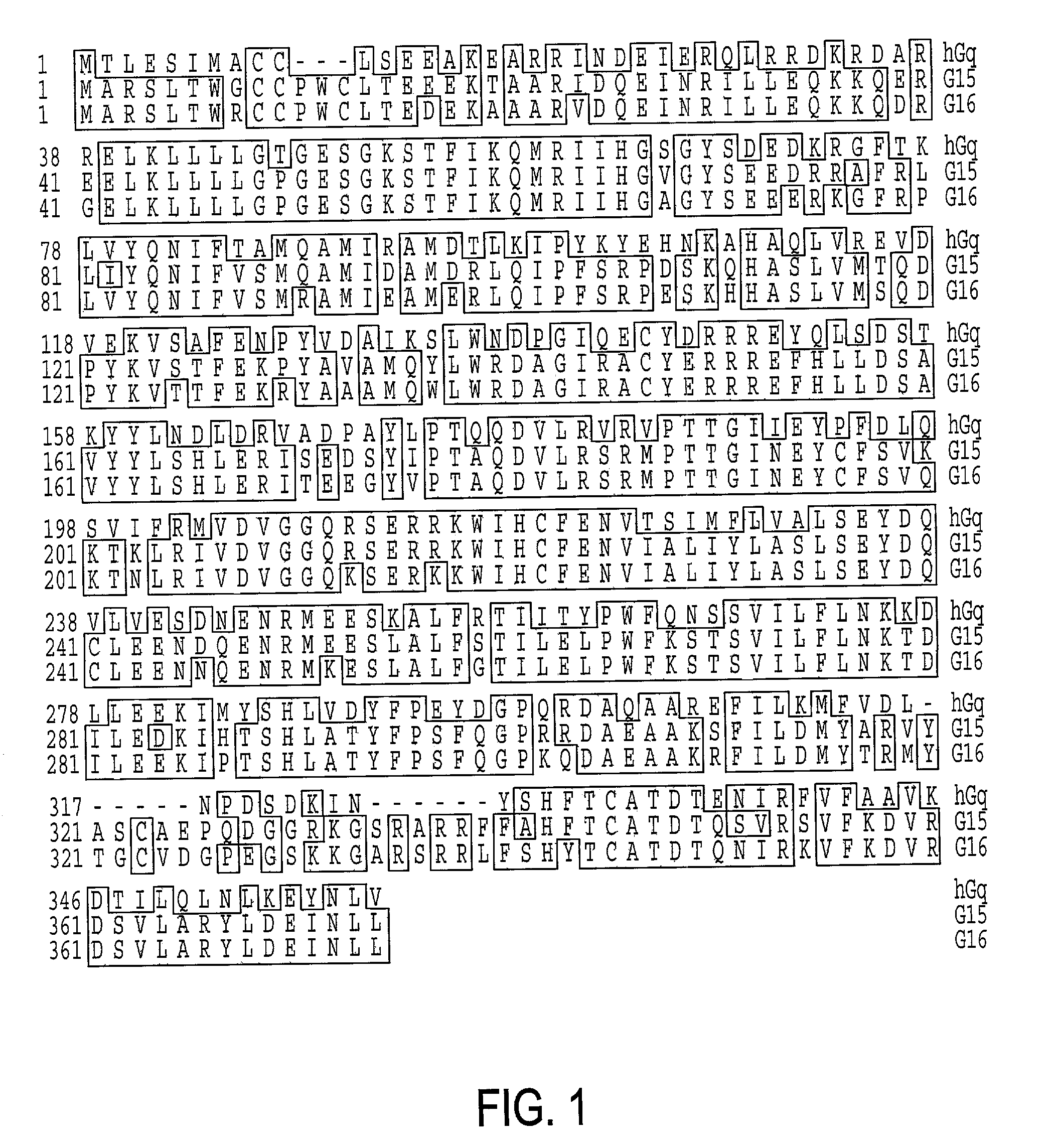
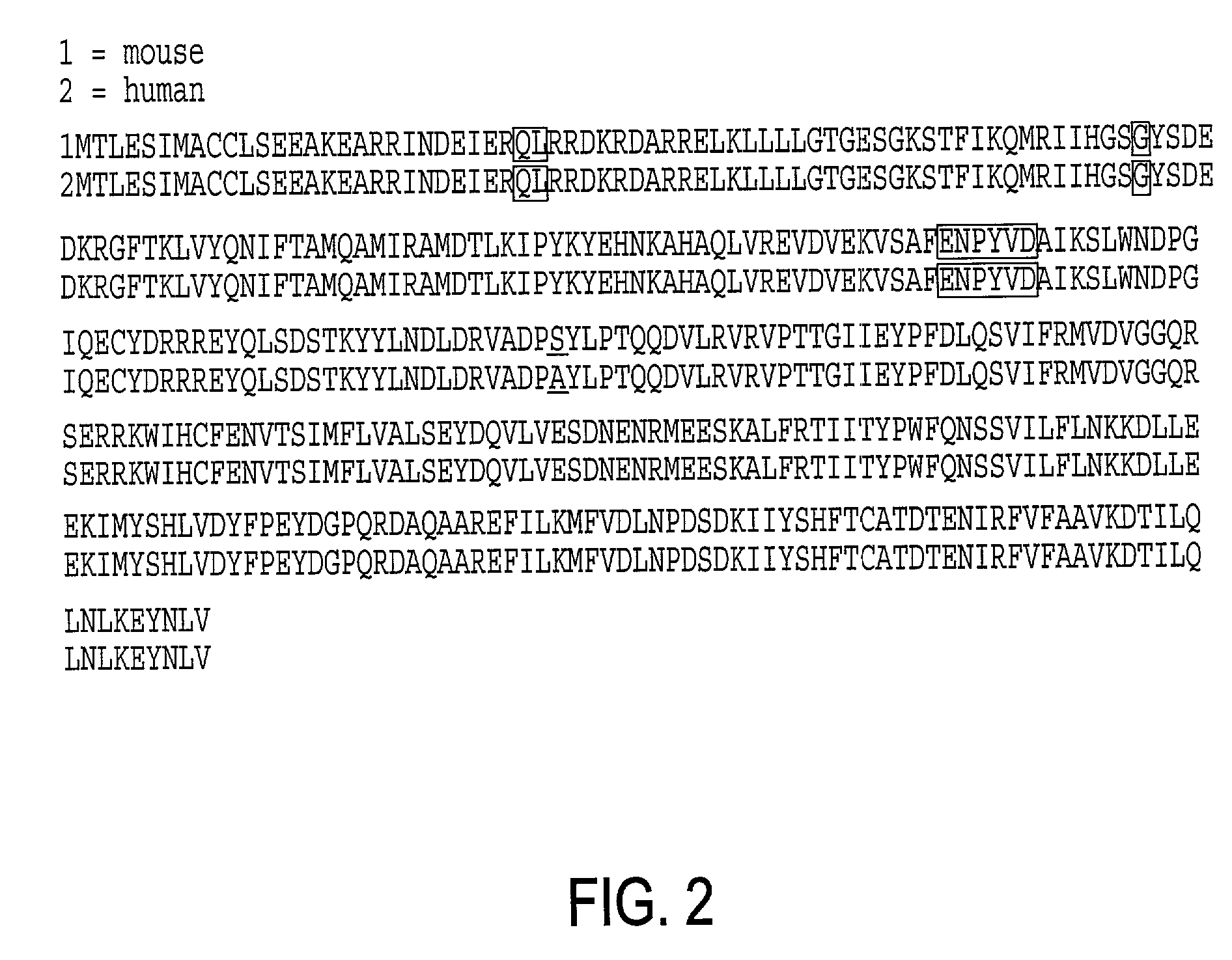
Gaq protein variants and their use in the analysis and discovery of agonists and antagonists of chemosensory receptors
ActiveUS20020143151A1Improved functional couplingAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTissue cultureSensory cellFluorescence
The invention provides a series of Galphaq protein variants that functionally couple to sensory cell receptors such as taste GPCRs (TRs) and olfactory GPCRs (ORs) in an overly promiscuous manner. According to the invention, the functional coupling can be determined, for example, by measuring changes in intracellular IP3, or calcium. In a particular embodiment, the Galphaq protein variants can be expressed in mammalian cell lines or Xenopus oocytes, and then evaluated using calcium fluorescence imaging and electrophysiological recording.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Galphaq protein variants and their use in the analysis and discovery of agonists and antagonists of chemosensory receptors
Owner:SENOMYX INC
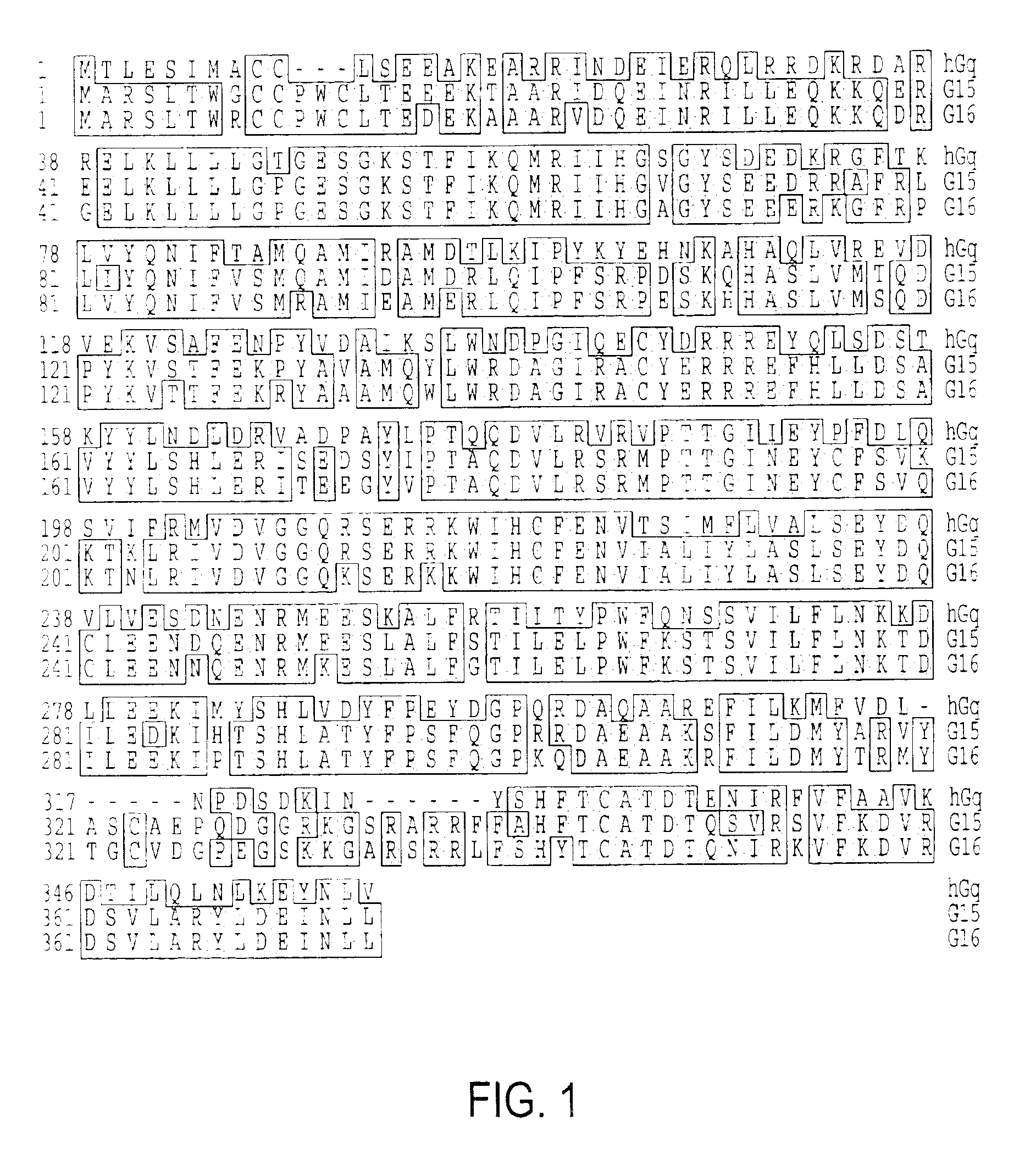
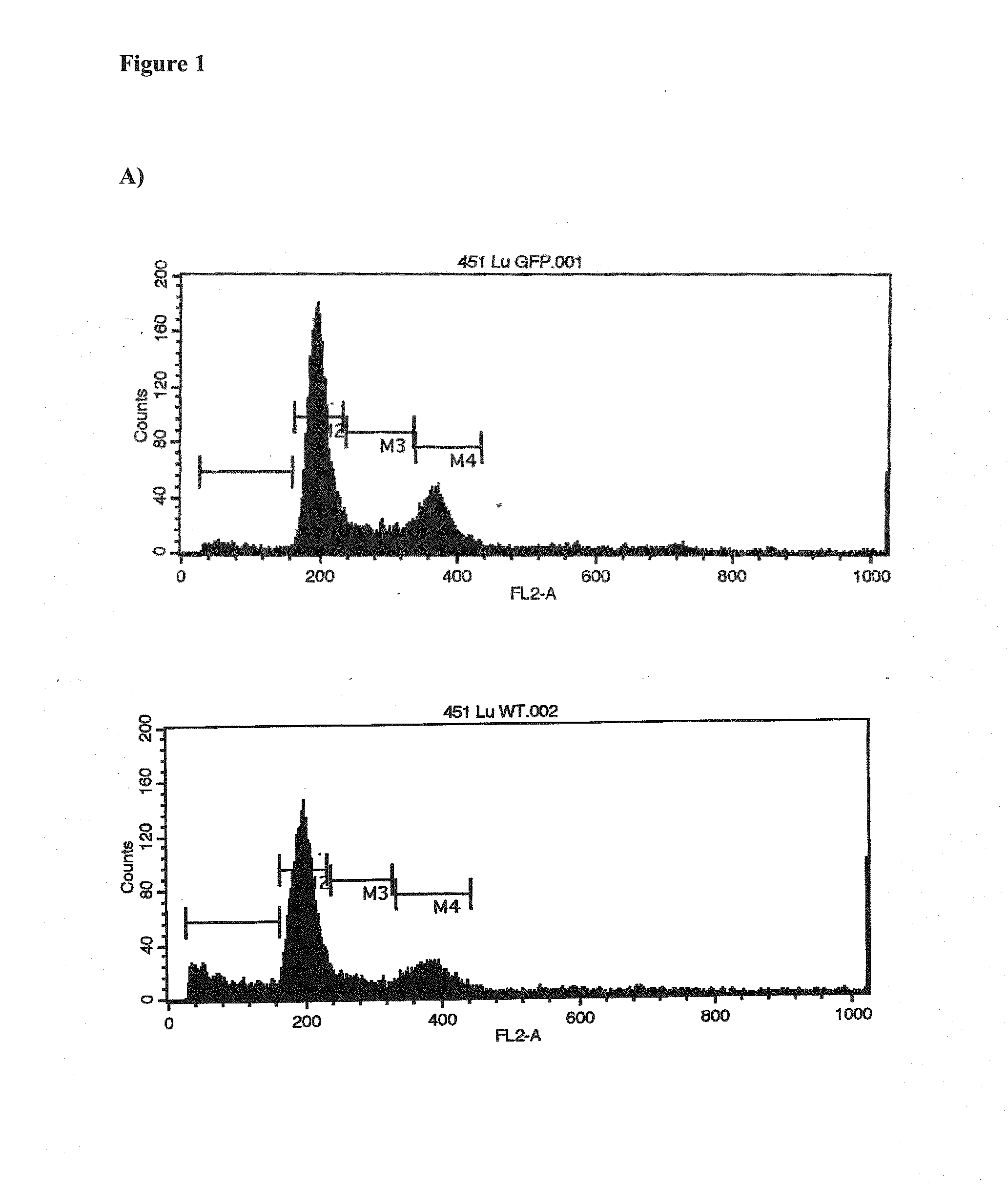
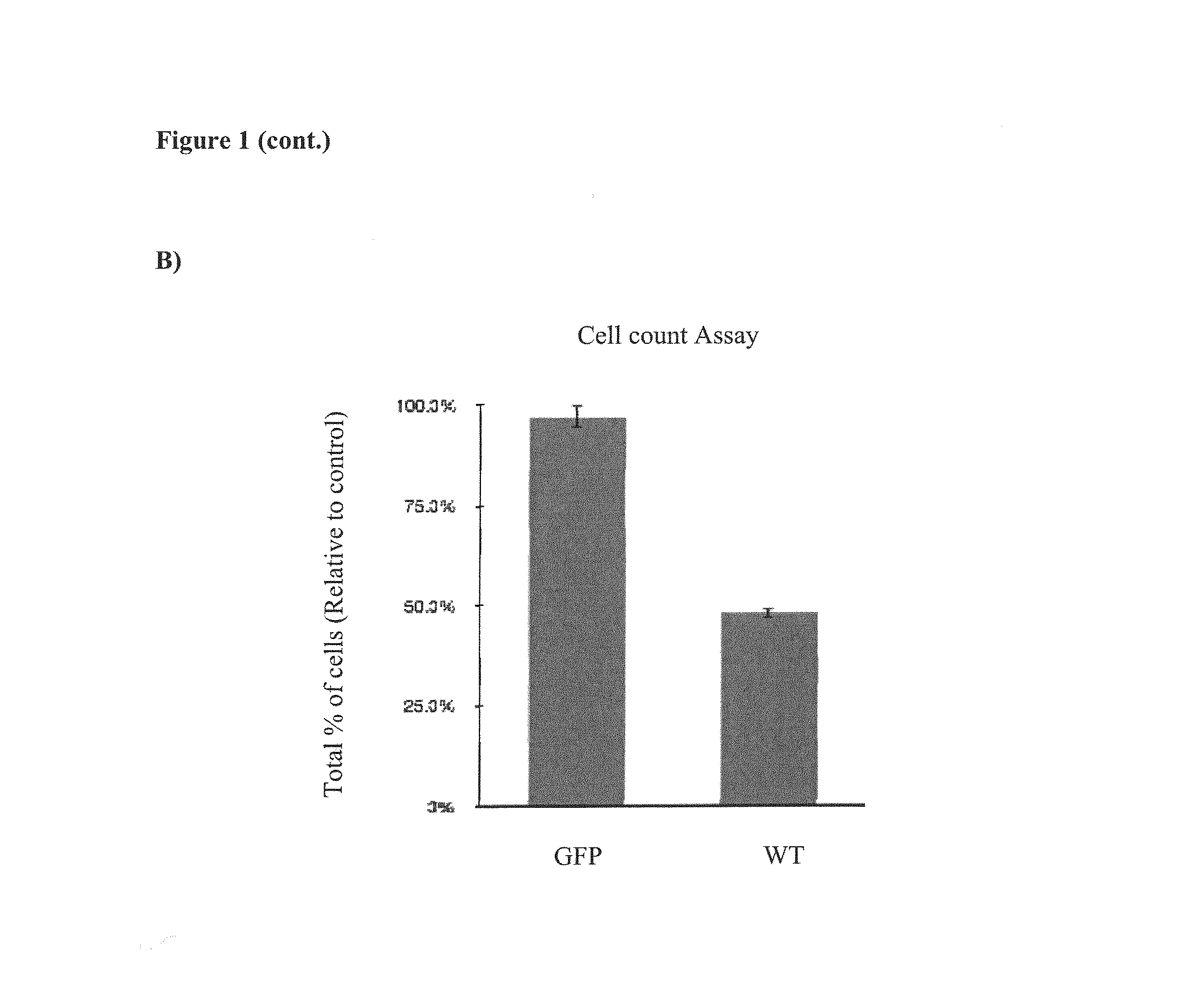
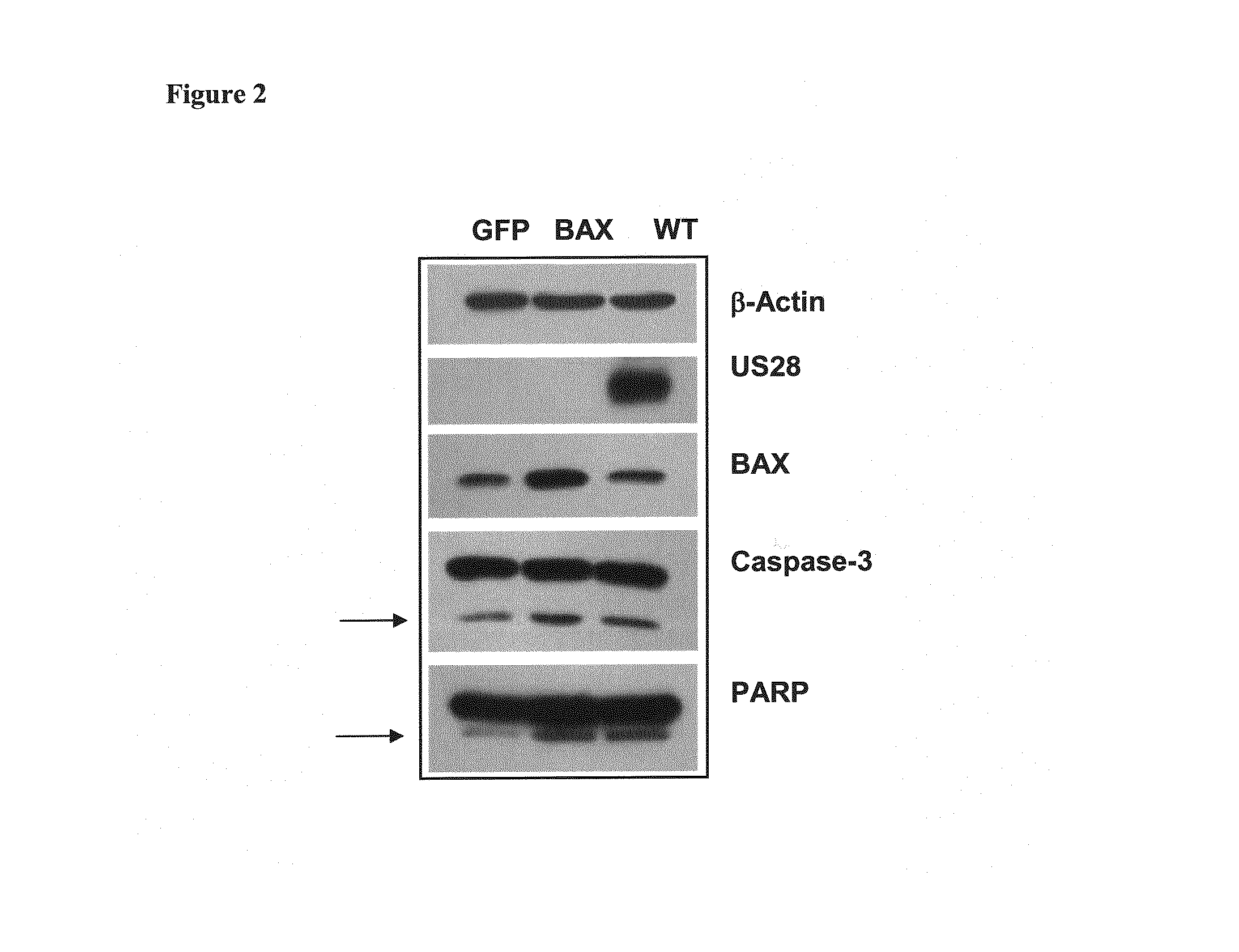
Cancer gene therapy using nucleic acids encoding us28 and g-protein
InactiveUS20140024702A1Reduce deliveryOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCancer genesTherapeutic treatment
The invention relates to the gene therapeutic treatment of cancer using co-expressed nucleic acids encoding US28 and a G-protein. e.g. GNA-13, or functional fragments thereof, or using nucleic acids encoding fusion polypeptides of US28 and a G-protein or functional fragments thereof. The pharmaceutical compositions according to the invention are used in the treatment of cancer patients to induce apoptosis in tumor cells.
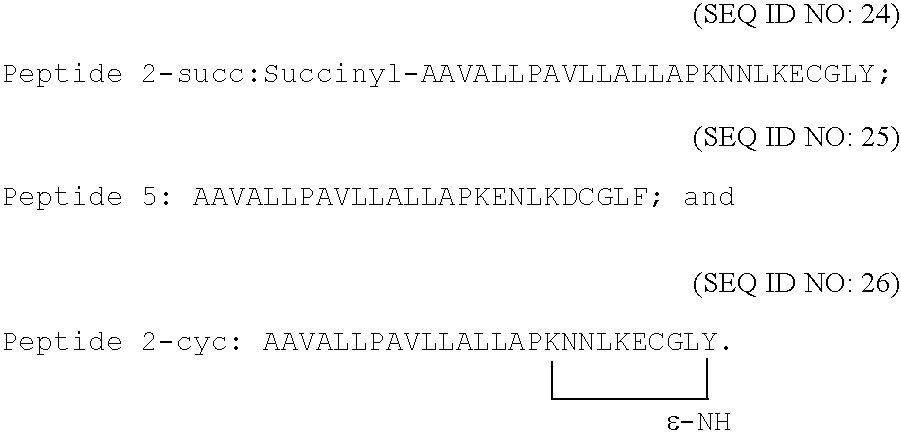
Owner:MEDIZINISCHE UNIV GRAZ
Transgenic animal
A transgenic rat containing in its genome a nucleotide sequence encoding a Ga subunit protein, which Ga protein subunit is uncoupled from regulation by Regulators of G-Protein Signaling (RGS) proteins, which Gx subunit protein is eventually the dominant-negative G188S mutant of Gax9, which nucleotide sequence is operatively associated with a neuron-specific expression control sequence, wherein the transgenic rat expresses the GA subunit protein in neural cells resulting in extended D-protein coupled receptor signaling mediated by the Ga subunit protein.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Biosensor for defecting chemical agents
InactiveUS7223550B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsYeastDrug product
A biosensor for the identification of olfactants, including chemical and biological agents, prefumery, explosives and pharmaceuticals. The biosensors comprise robust eukaryotic cells, such as yeast, into which at least one exogenous olfactory signaling pathway has been genetically integrated to detect molecules of interest.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
Materials and methods relating to g-protein coupled receptor oligomers
ActiveUS20070099263A1Alter potencyImprove bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsOligomerG protein-coupled receptor
The invention provides materials and methods relating to G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) oligomers. Complexes of two or more GPCRs associated with G-proteins are provided. Also provided are fusion proteins comprising a GPCR and a G-protein, nucleic acids, expression vectors and host cells. Methods of producing the complexes and fusion proteins of the invention are also provided.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF GLASGOW
Agents for prophylaxis or treatment of neurological related diseases and conditions
InactiveUS20080306007A1Reduce the binding forceNervous disorderHydrolasesCell vesiclePhosphorylation
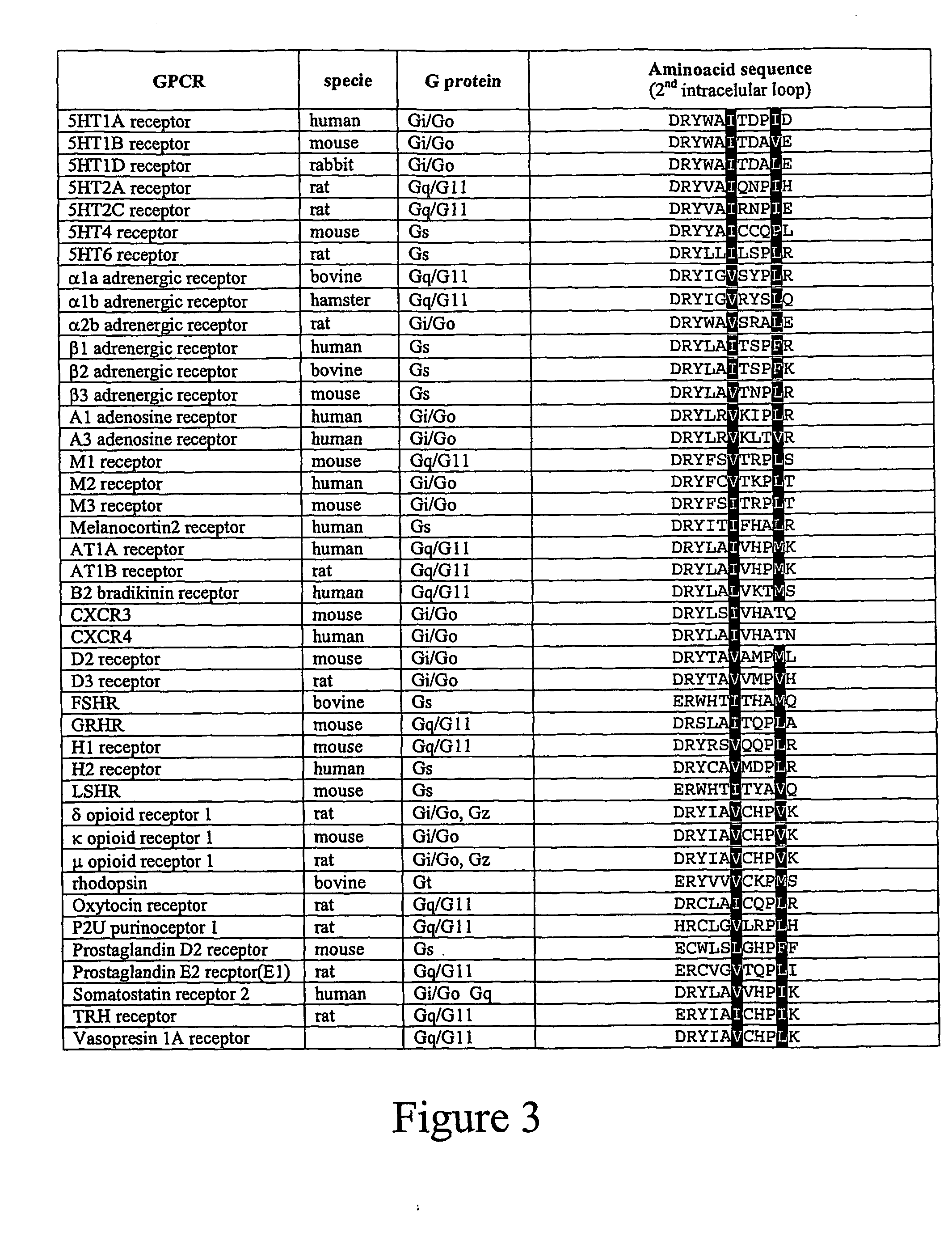
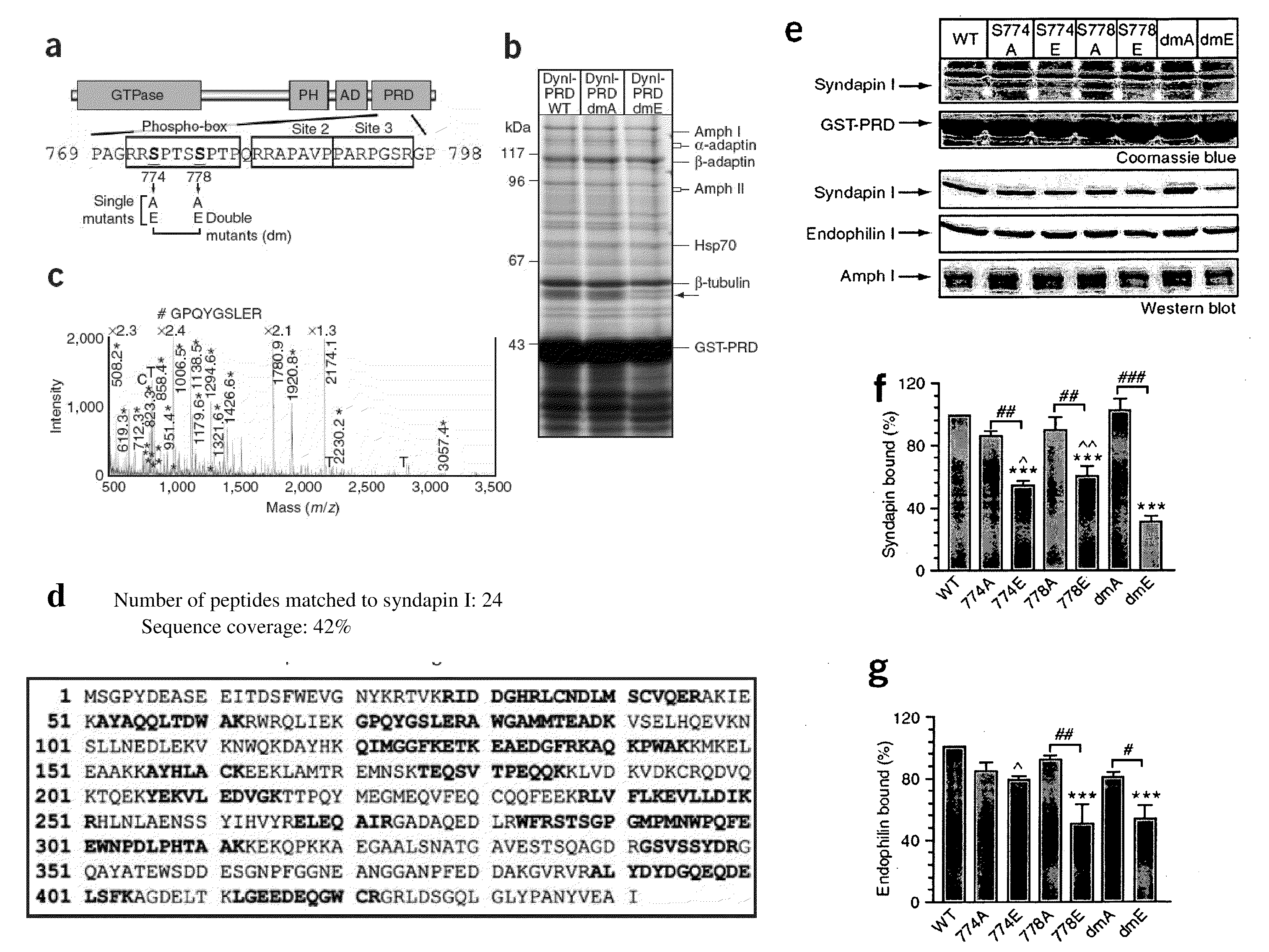
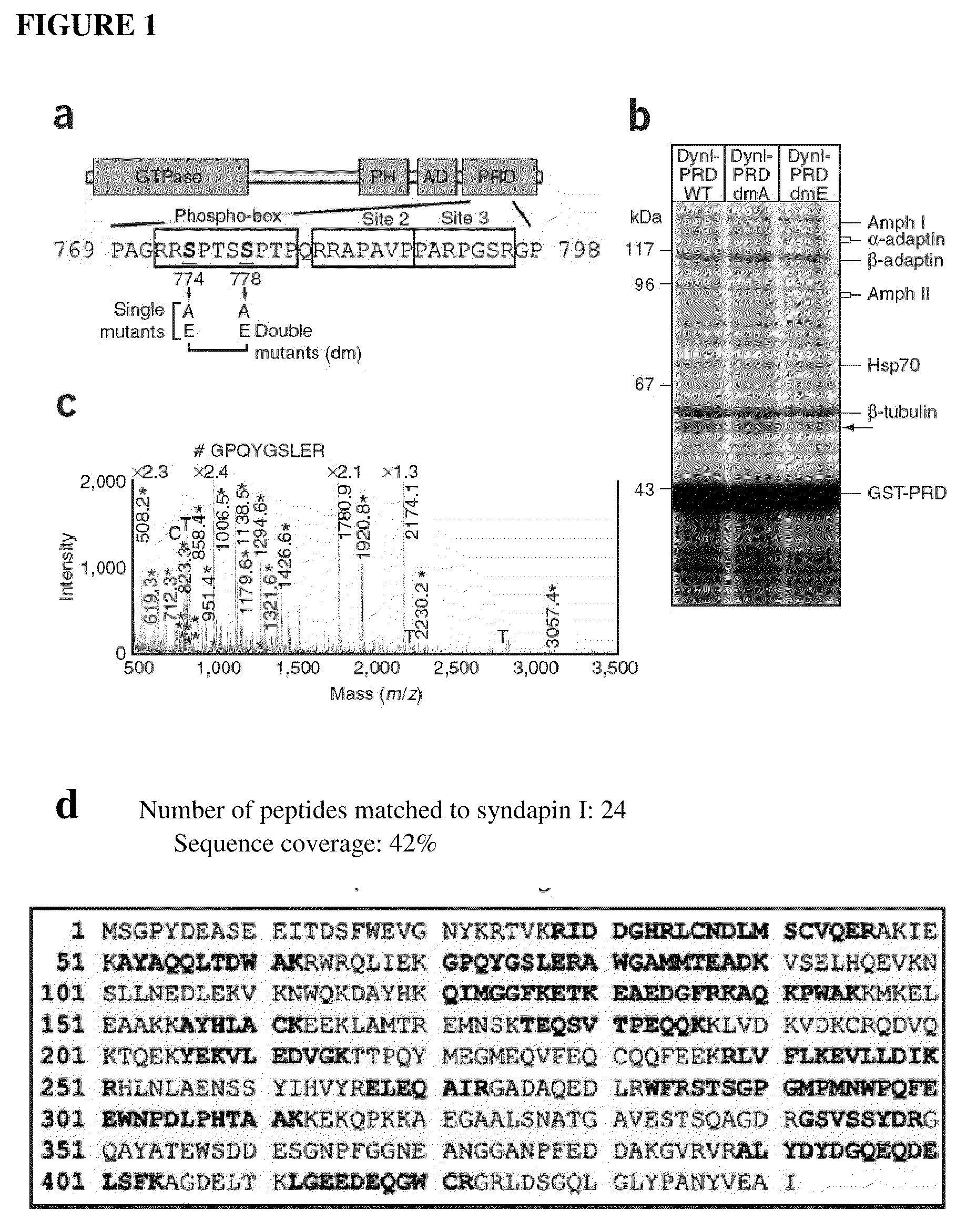
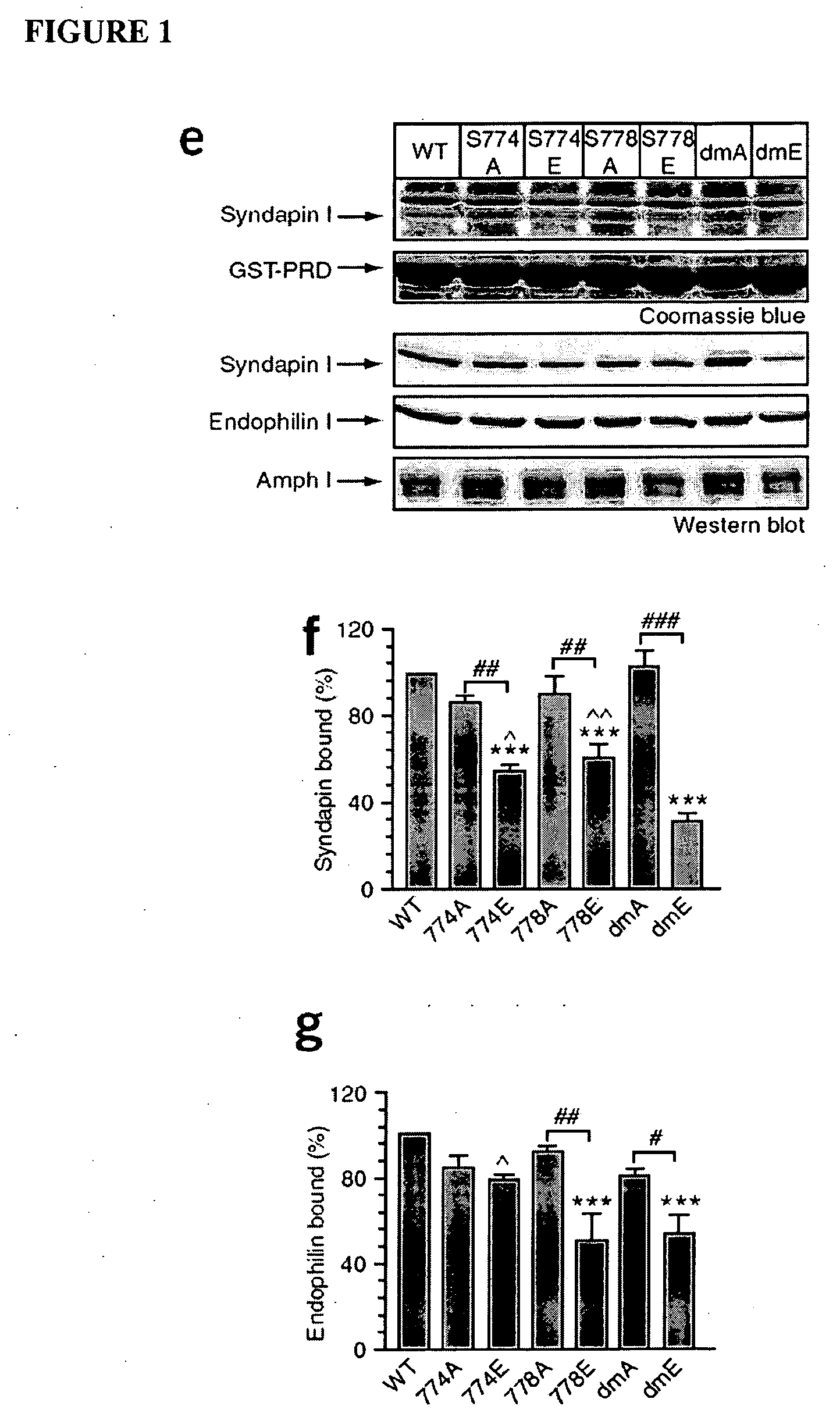
Inhibitors of syndapin I binding to dynamin I (DynI) are provided. Examples include mimetics of a region of DynI including the serine residues S774 and S778 or phosphorylatable amino acids in homologous positions. Typically, the mimetics exclude or do not imitate at least one phosphorylation site provided by the serine residues or phosphorylatable amino acids. Peptide fragment inhibitors comprising or consisting of this region of DynI are also described. The inhibitors have application in the prophylaxis or treatment of neurological diseases or conditions. The inhibitors can also be used to inhibit neuronal cell vesicle trafficking and synaptic signal transmission.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL RES INST +2
Galphaq protein variants and their use in the analysis and discovery of agonists and antagonists of chemosensory receptors
ActiveUS7041457B2Increase promiscuityHigh activityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTissue cultureSensory cellFluorescence
The invention provides a series of Galphaq protein variants that functionally couple to sensory cell receptors such as taste GPCRs (TRs) and olfactory GPCRs (ORs) in an overly promiscuous manner. According to the invention, the functional coupling can be determined, for example, by measuring changes in intracellular IP3, or calcium. In a particular embodiment, the Galphaq protein variants can be expressed in mammalian cell lines or Xenopus oocytes, and then evaluated using calcium fluorescence imaging and electrophysiological recording.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
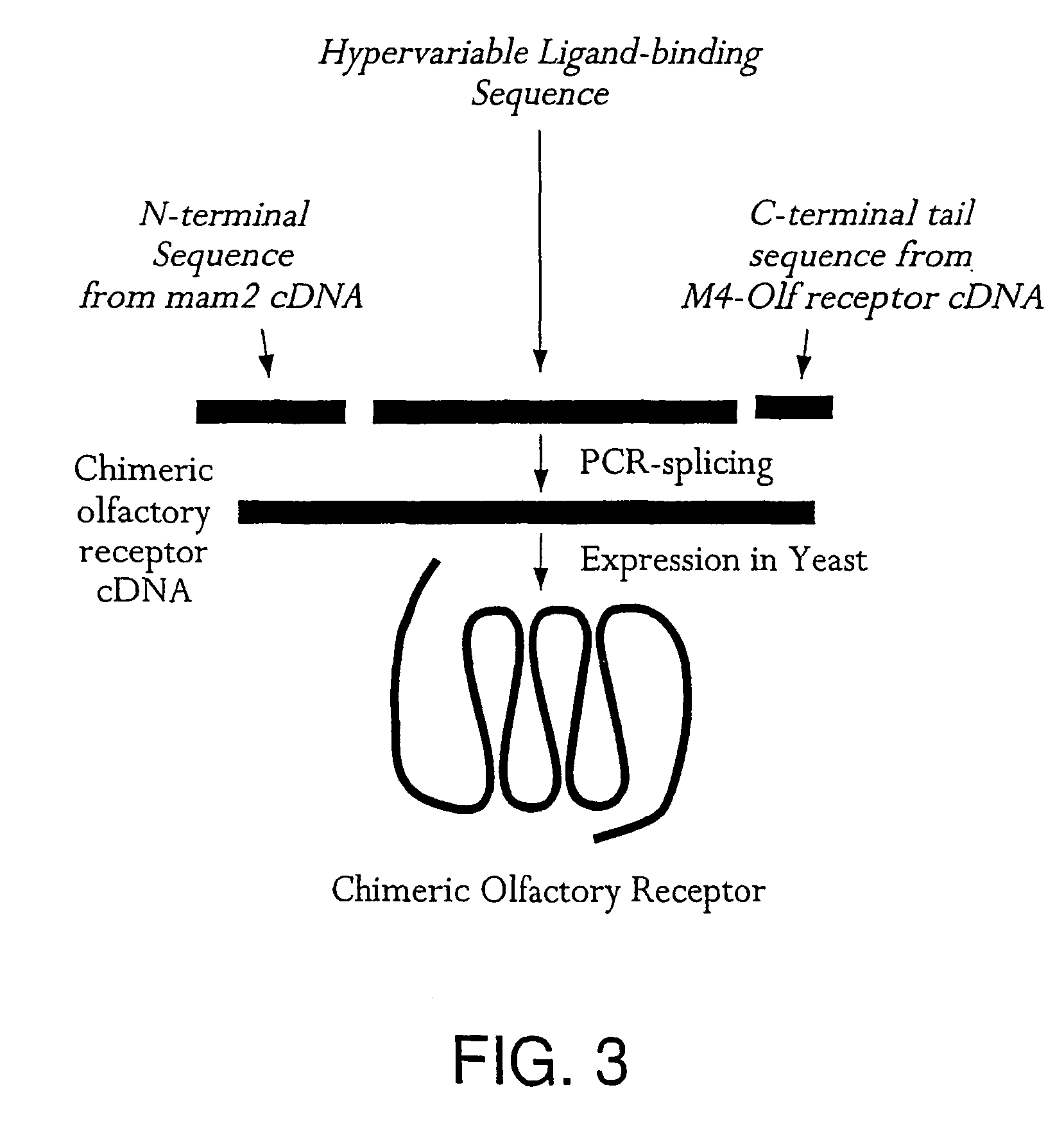
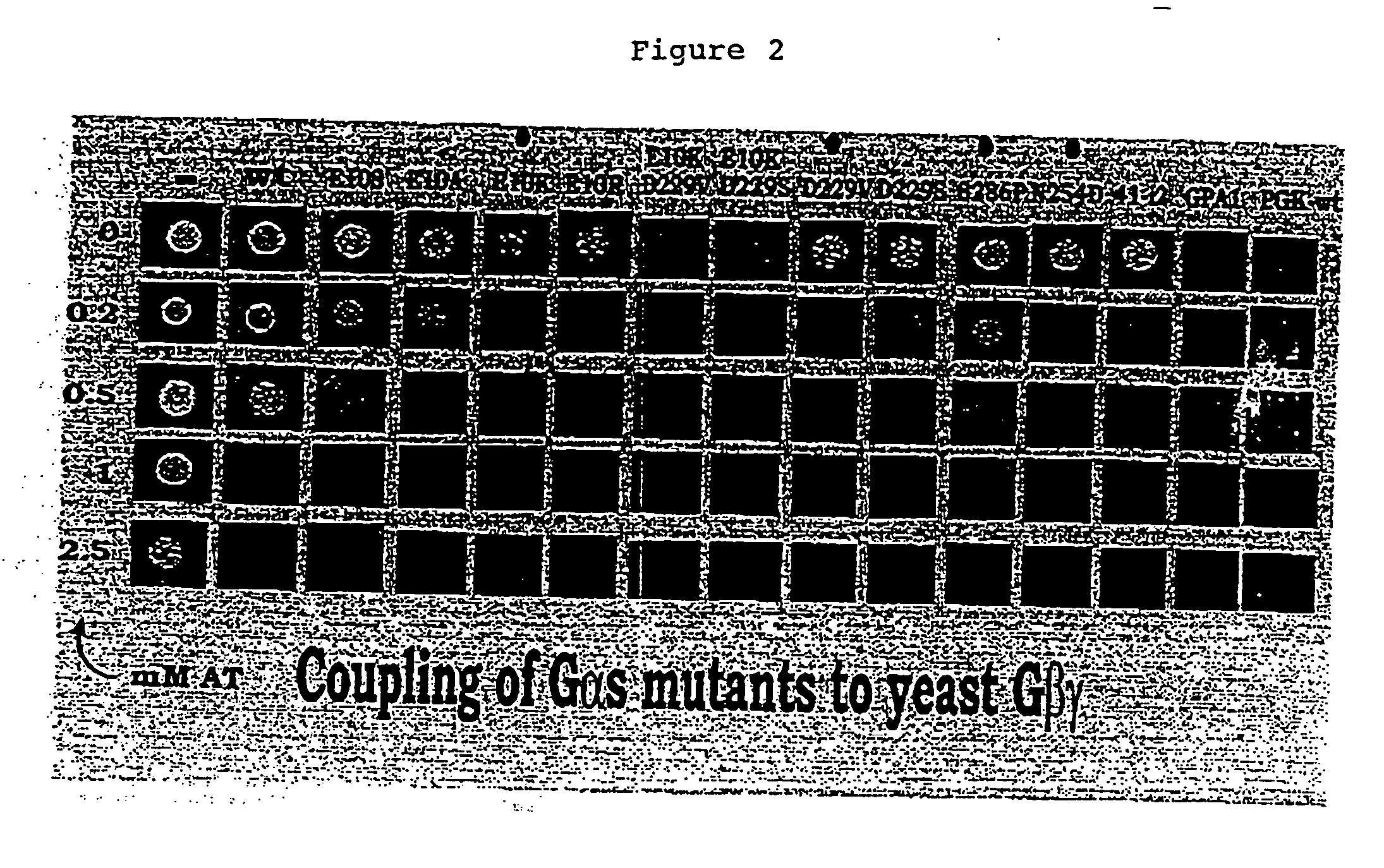
Yeast cells expressing modified G proteins and methods of use therefor
InactiveUS20050202403A1High expressionEnhanced couplingCompound screeningFungiHeterologousG protein-coupled receptor
The present invention pertains to novel yeast cells which are useful for the expression of heterologous G protein coupled receptors. The yeast cells of the present invention can be used in screening assays which can be used to screen for modulators of G protein coupled receptors. Specifically, the invention provides novel yeast cells which express a heterologous G protein coupled receptor and mutant and / or chimeric G protein subunit molecules which serve to functionally integrate the heterologous into the pheromone signaling pathway of the yeast cell. The invention also provides for the expression of heterologous G protein coupled receptors which are functionally integrated into the yeast cell membrane using a yeast a factor leader sequence. Drug discovery assays using the subject yeast cells are also provided.
Owner:CADUS TECH
Solid phase isolation of proteins, nucleic acids and other macromolecules
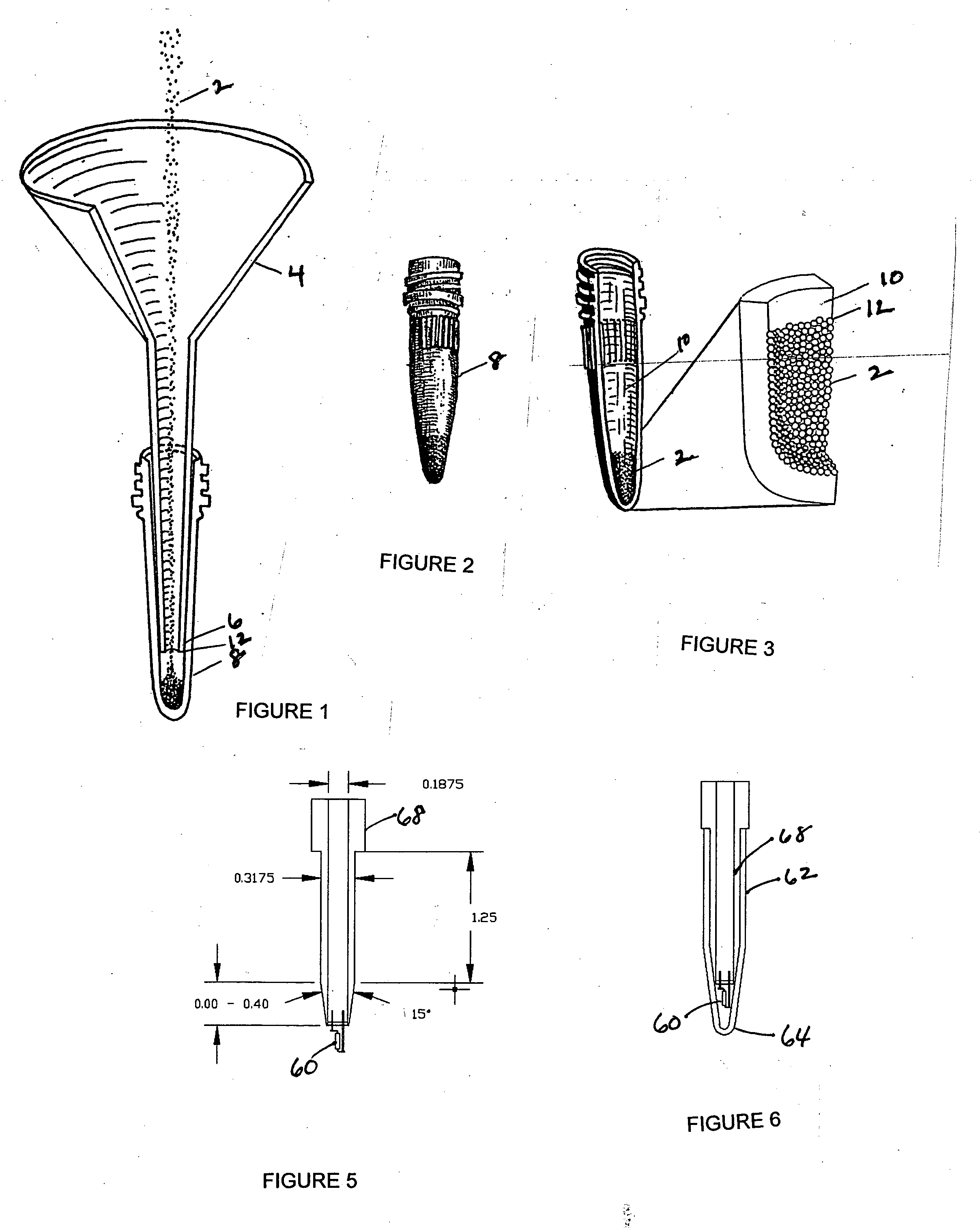
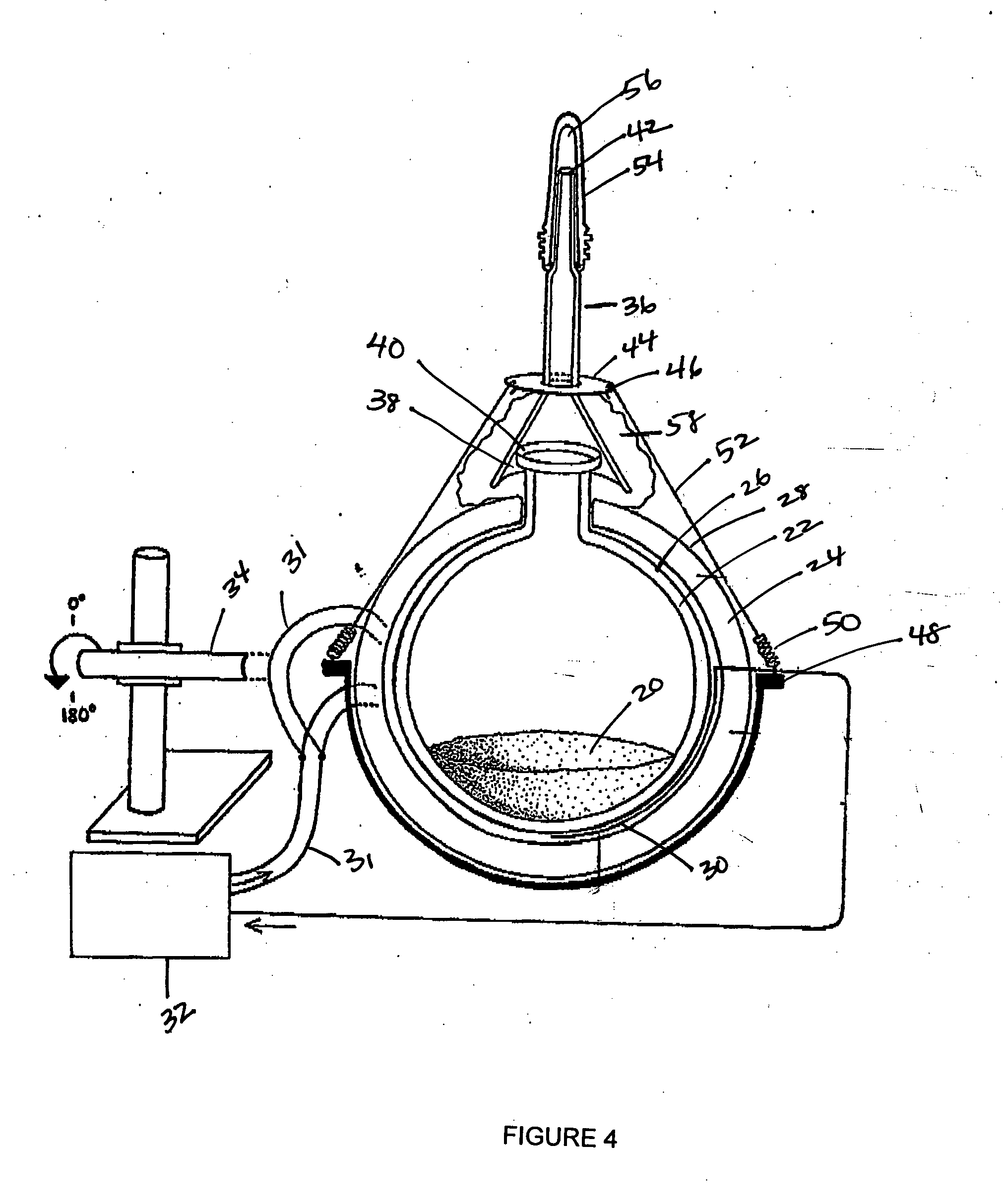
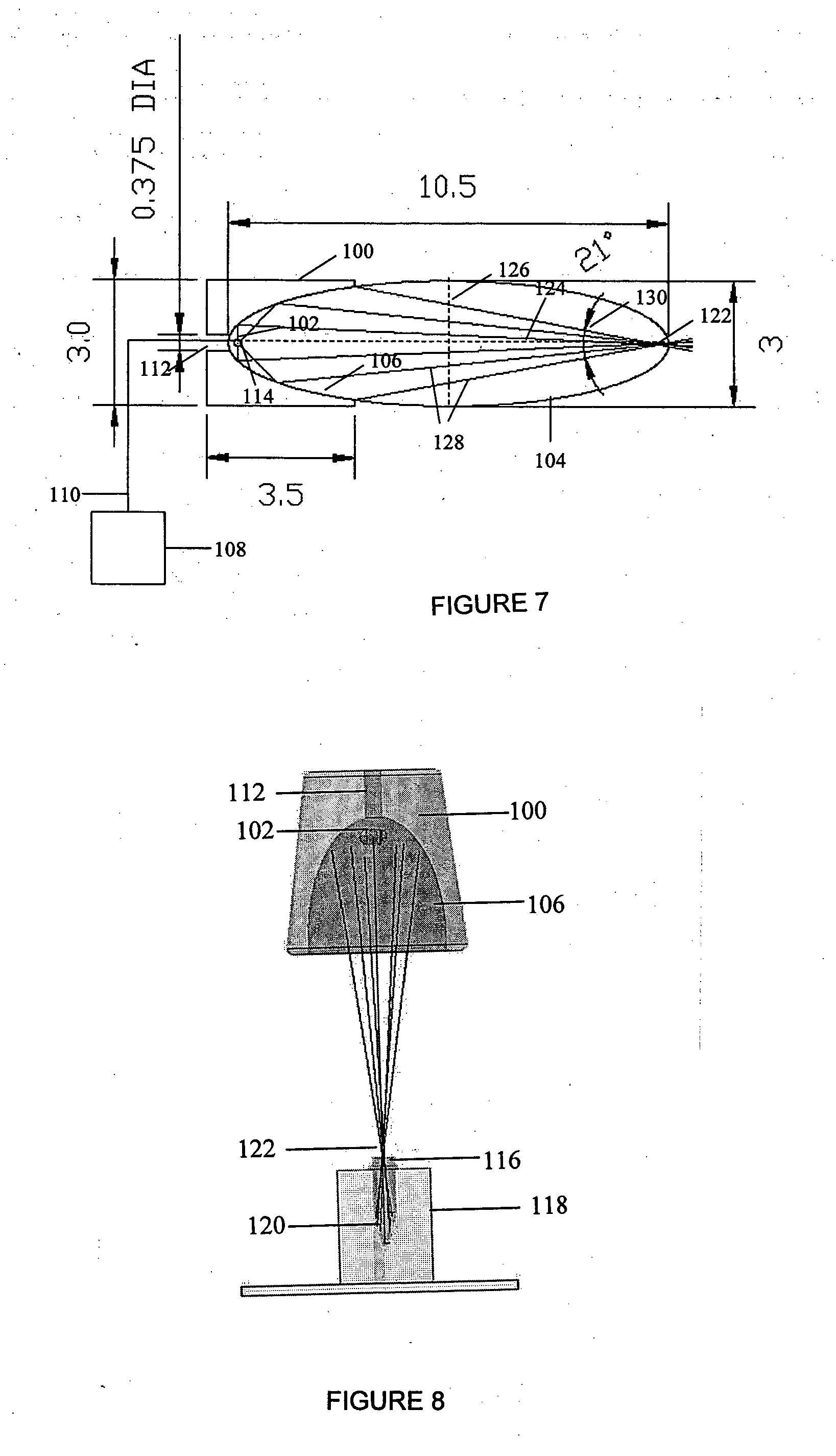
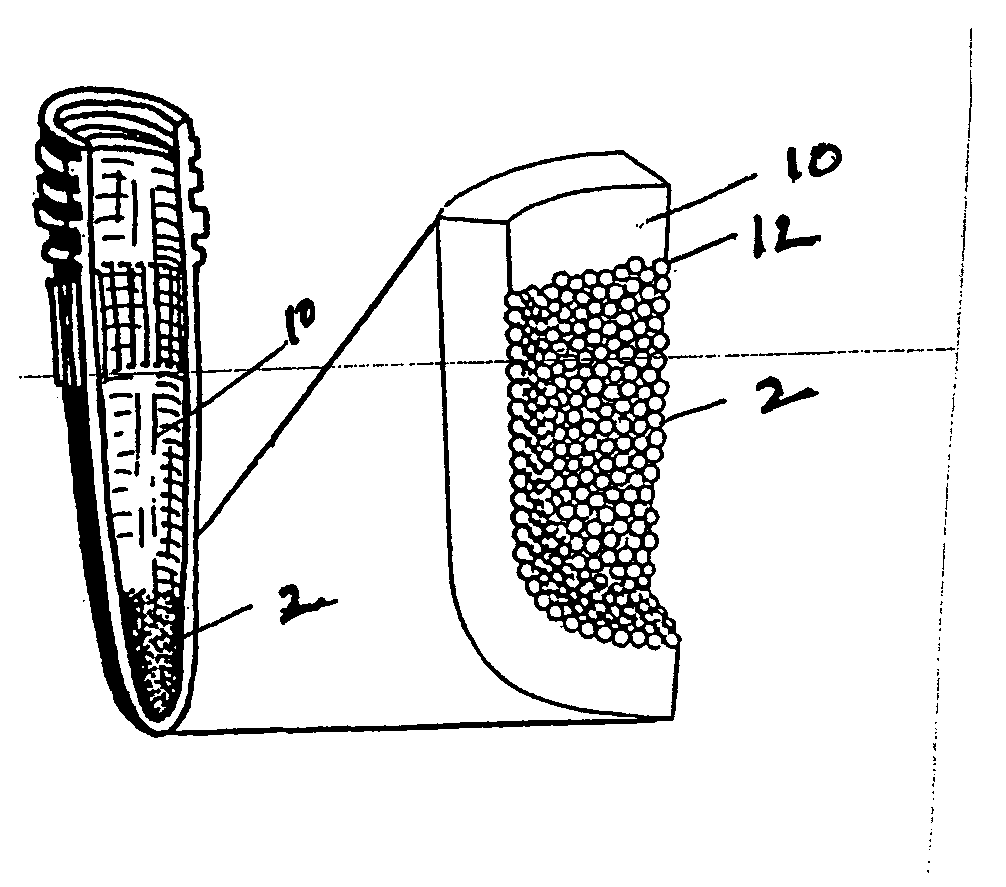
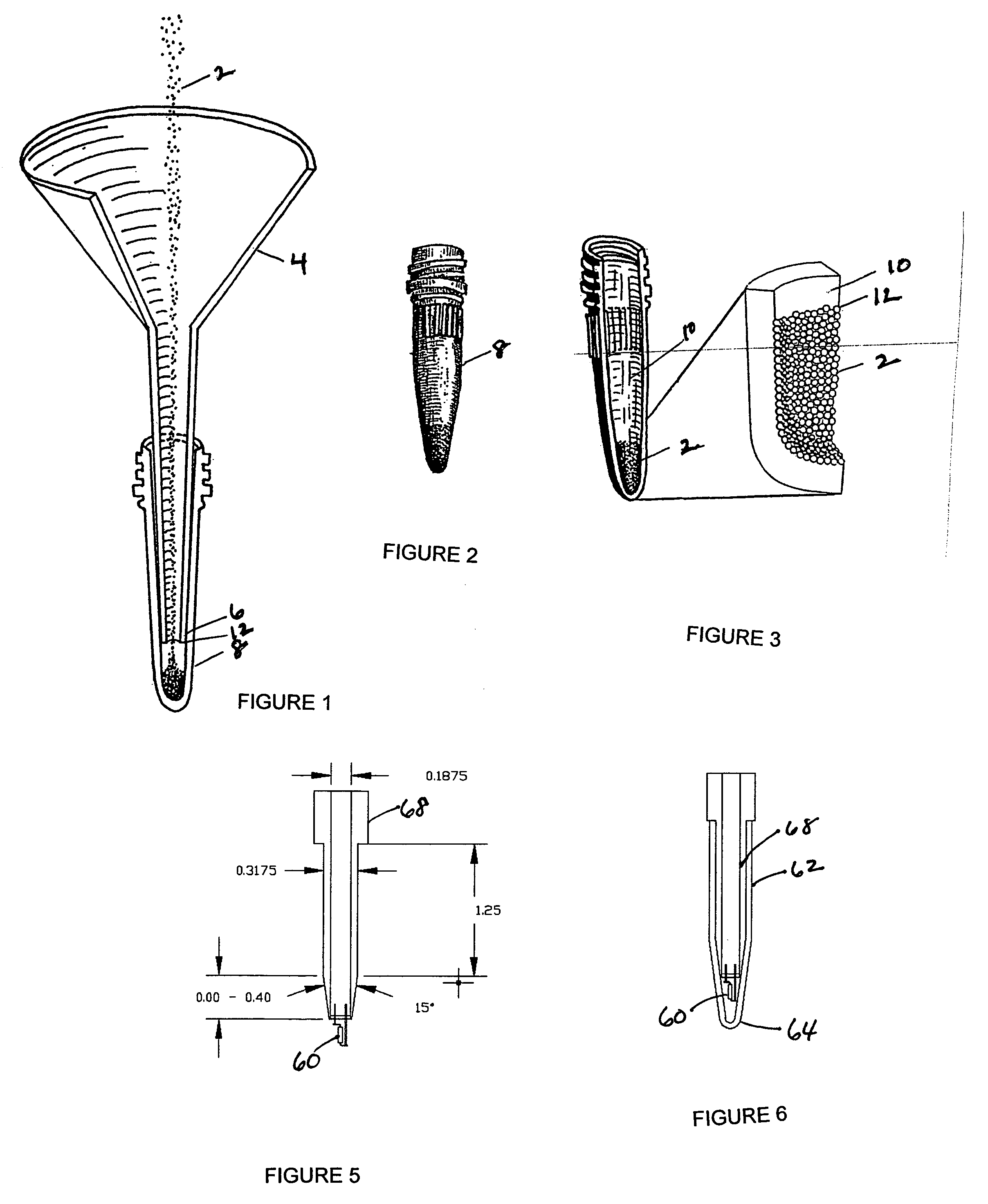
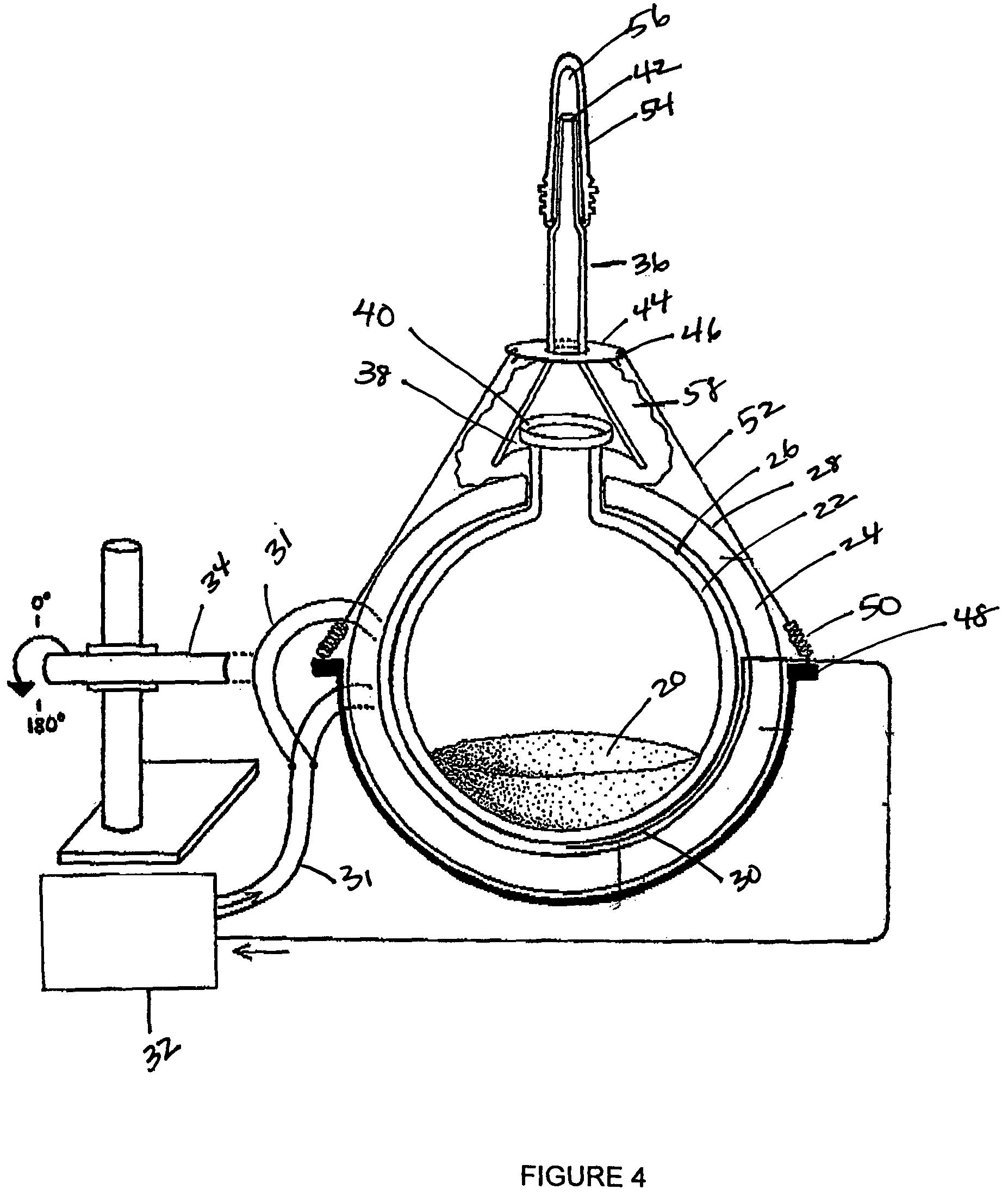
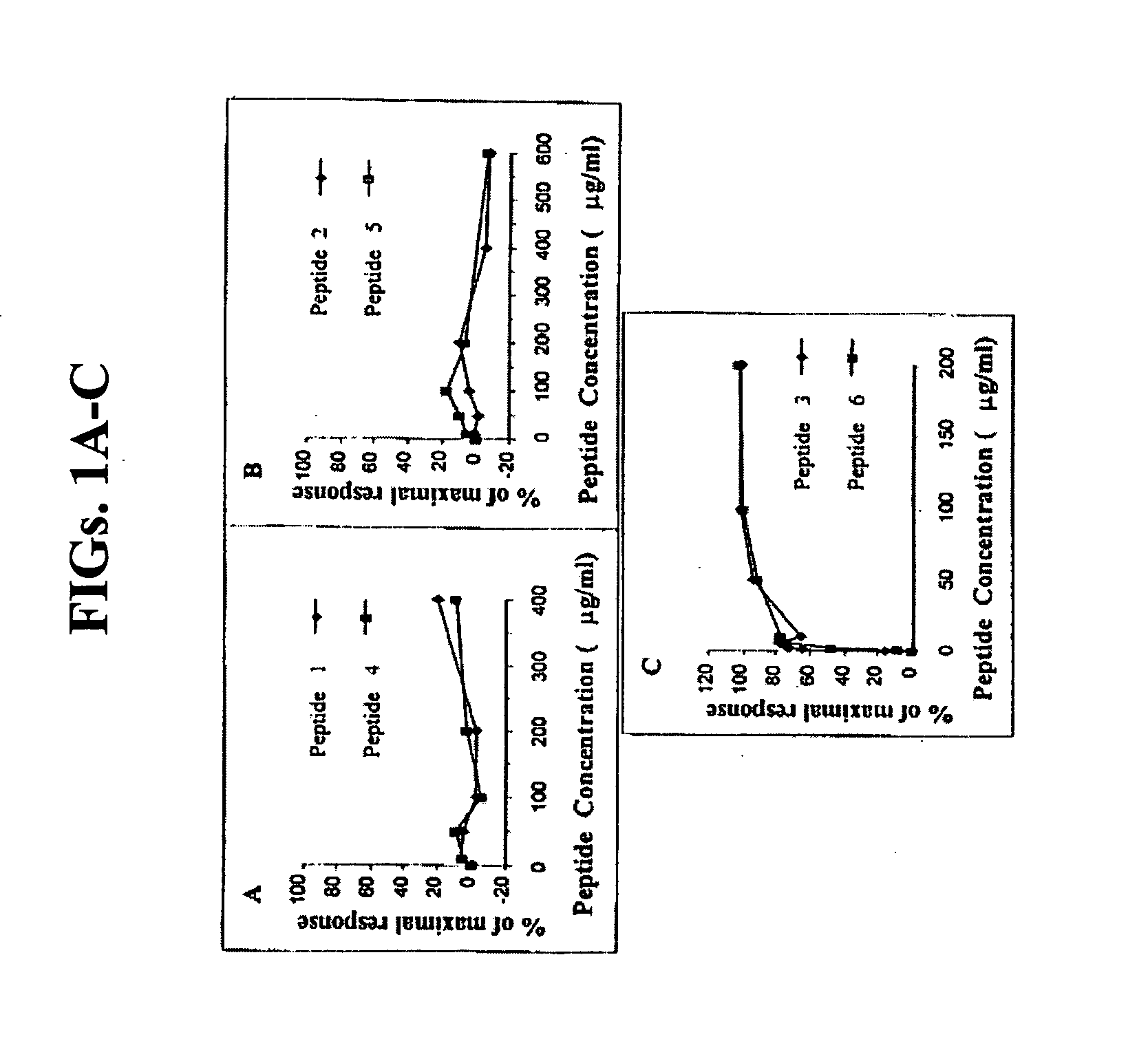
InactiveUS20050164408A1Rapid fashionPeptide preparation methodsG-proteinsCrystallographyGuanine Nucleotide Binding Protein
The invention is a method for the isolation of molecules of interest using tubes in which at least a portion of the inner walls of the tube are coated with microbeads that are coated with a capture reagent to bind the molecule of interest. The microbeads may be glass or polymer beads. The invention is a method and apparatus for preparation of the tubes for use in the method of the invention. The invention is a method for determining ratios of guanine nucleotides bound to guanine-nucleotide binding proteins.
Owner:CA RGT UNIV OF
Method for preparing pre-staining luminescent protein marker
InactiveCN107298719AAdd binding sitesOptical signal enhancementAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsG-proteinsBinding siteX-ray
The invention provides a method for preparing a pre-staining luminescent protein marker. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a protein A gene, a protein G gene, an MBP (Myelin Basic Protein) gene and a heavy chain constant region gene (CH gene) of a mouse and rabbit derived antibody, and cutting and combining the genes according to sizes of different proteins in a pre-staining luminescent protein marker; expressing the proteins, purifying, and mixing proteins of different molecule weights according to a certain ratio so as to obtain a luminescent protein marker; mixing the prepared luminescent protein marker with the pre-staining luminescent protein marker according to different ratios. The pre-staining luminescent protein marker prepared by using the method is capable of recognizing primary antibodies or secondary antibodies of different sources, binding sites of proteins are increased, light signals are intensified, not only are general positions of proteins indicated in the electrophoresis process and after membrane transfer, but also precise positions of the proteins can be indicated on X-ray films, no extra pre-staining marker channels are needed, no extra antibodies are needed, and the luminescent proteins can be combined with IgG or anti-rabbit and anti-mouse secondary antibodies derived from species such as human beings, rats, mice and rabbits.
Owner:南京赛诺博生物科技有限责任公司
Atlastin
The present invention relates to methods and compositions of a novel gene and the peptide encoded by the gene. Mutations in the gene, named atlastin, are factors in the disease Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia and related disorders. The present invention will be used for the in the research, diagnosis and treatment of these disabling diseases.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
Galphaq protein variants and their use in the analysis and discovery of agonists and antagonists of chemosensory receptors
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Transgenic animal
Owner:WYETH LLC
Yeast cells expressing modified G proteins and methods of use therefor
InactiveUS7361498B2High expressionEnhanced couplingCompound screeningFungiHeterologousG protein-coupled receptor
The present invention pertains to novel yeast cells which are useful for the expression of heterologous G protein coupled receptors. The yeast cells of the present invention can be used in screening assays which can be used to screen for modulators of G protein coupled receptors. Specifically, the invention provides novel yeast cells which express a heterologous G protein coupled receptor and mutant and / or chimeric G protein subunit molecules which serve to functionally integrate the heterologous into the pheromone signaling pathway of the yeast cell. The invention also provides for the expression of heterologous G protein coupled receptors which are functionally integrated into the yeast cell membrane using a yeast α factor leader sequence. Drug discovery assays using the subject yeast cells are also provided.
Owner:CADUS TECH
Anti-allergic complex molecules
InactiveUS7112568B2Reducing degranulationPreventing late phase inflammatory responsesSenses disorderNervous disorderProtein kinase activationMedicine
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Solid phase isolation of proteins, nucleic acids and other macromolecules
InactiveUS7981694B2Rapid fashionPeptide preparation methodsG-proteinsCrystallographyGuanine Nucleotide Binding Protein
Owner:CA RGT UNIV OF
Anti-allergic complex molecules
InactiveUS20070009544A1Reducing degranulationPreventing late phase inflammatory responsesImmunoglobulinsCyclic peptide ingredientsProtein kinase activationMedicine
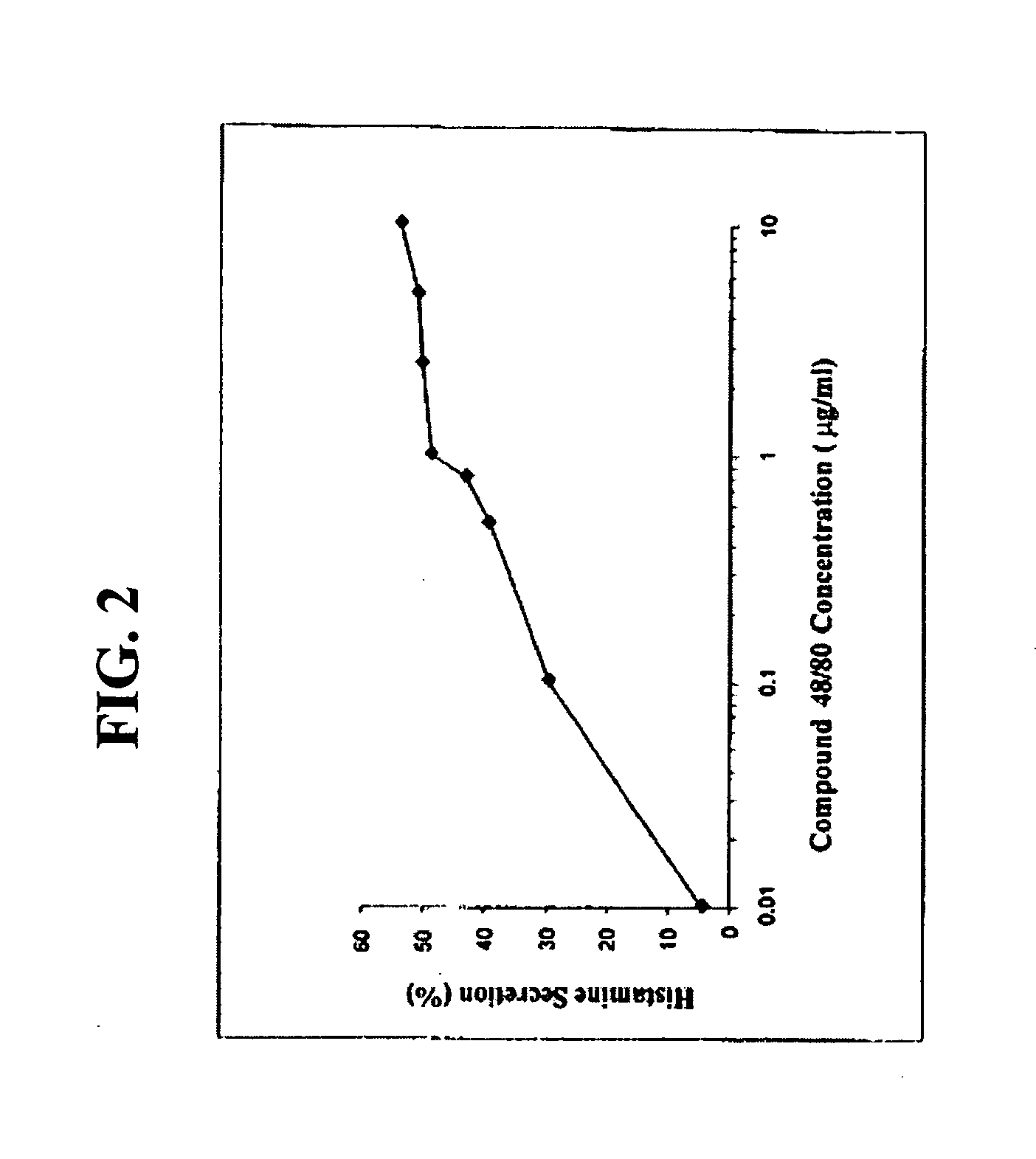
The present invention discloses novel therapeutic complex molecules, and in particular, peptidic or peptidomimetic molecules, comprising a first part which is competent for cell penetration and a second part which is able to reduce or abolish mast cell degranulation, in particular to reduce or abolish allergy mediators, including histamine secretion from mast cells and protein kinase activation, wherein the first part is connected to the second part via a linker or a direct bond that creates a conformational constraint by forming a bend or turn.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
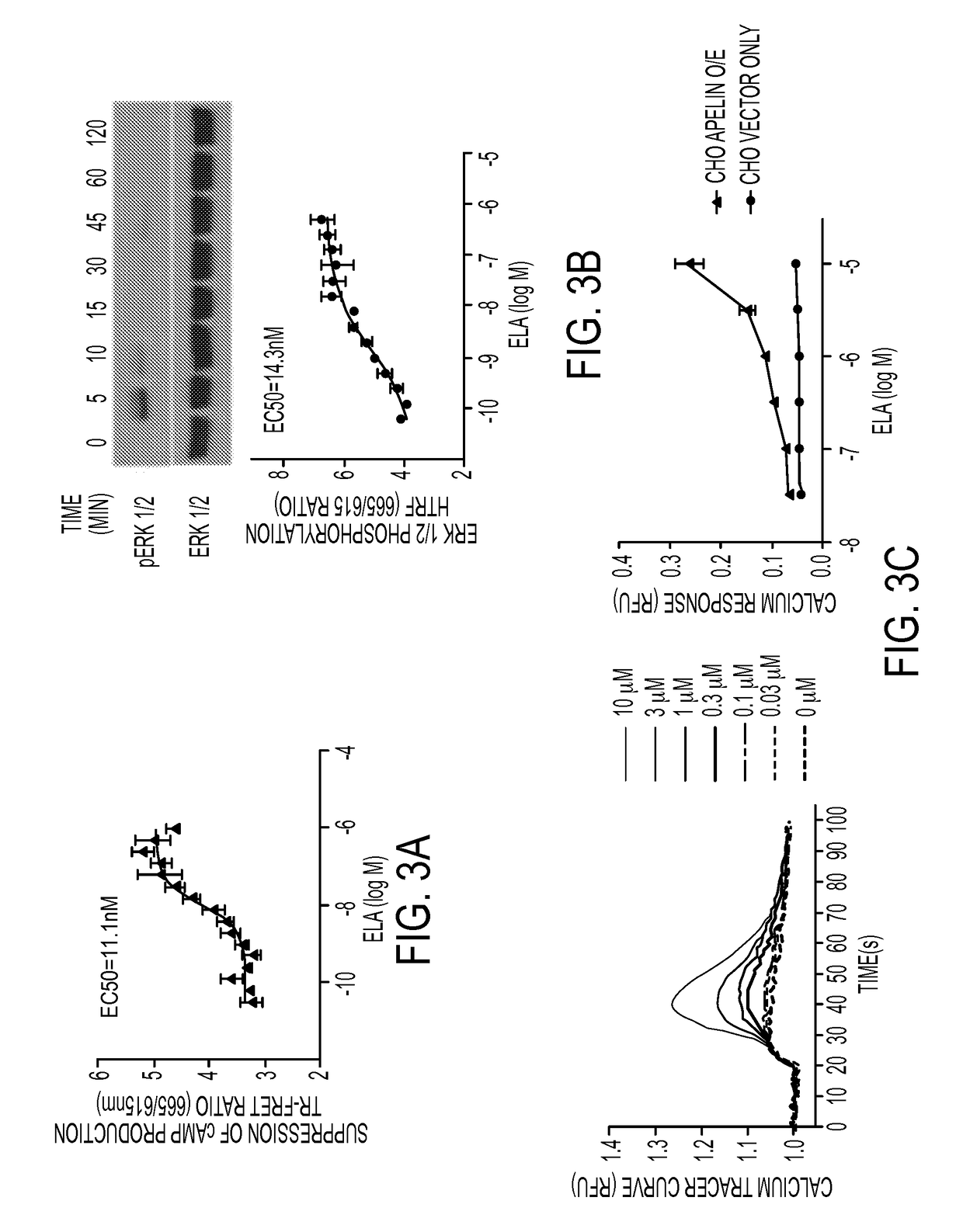
Methods for treating cardiovascular dysfunction and improving fluid homeostasis with a peptide hormone
ActiveUS20170224779A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifHormone peptidesCvd riskHeart disease
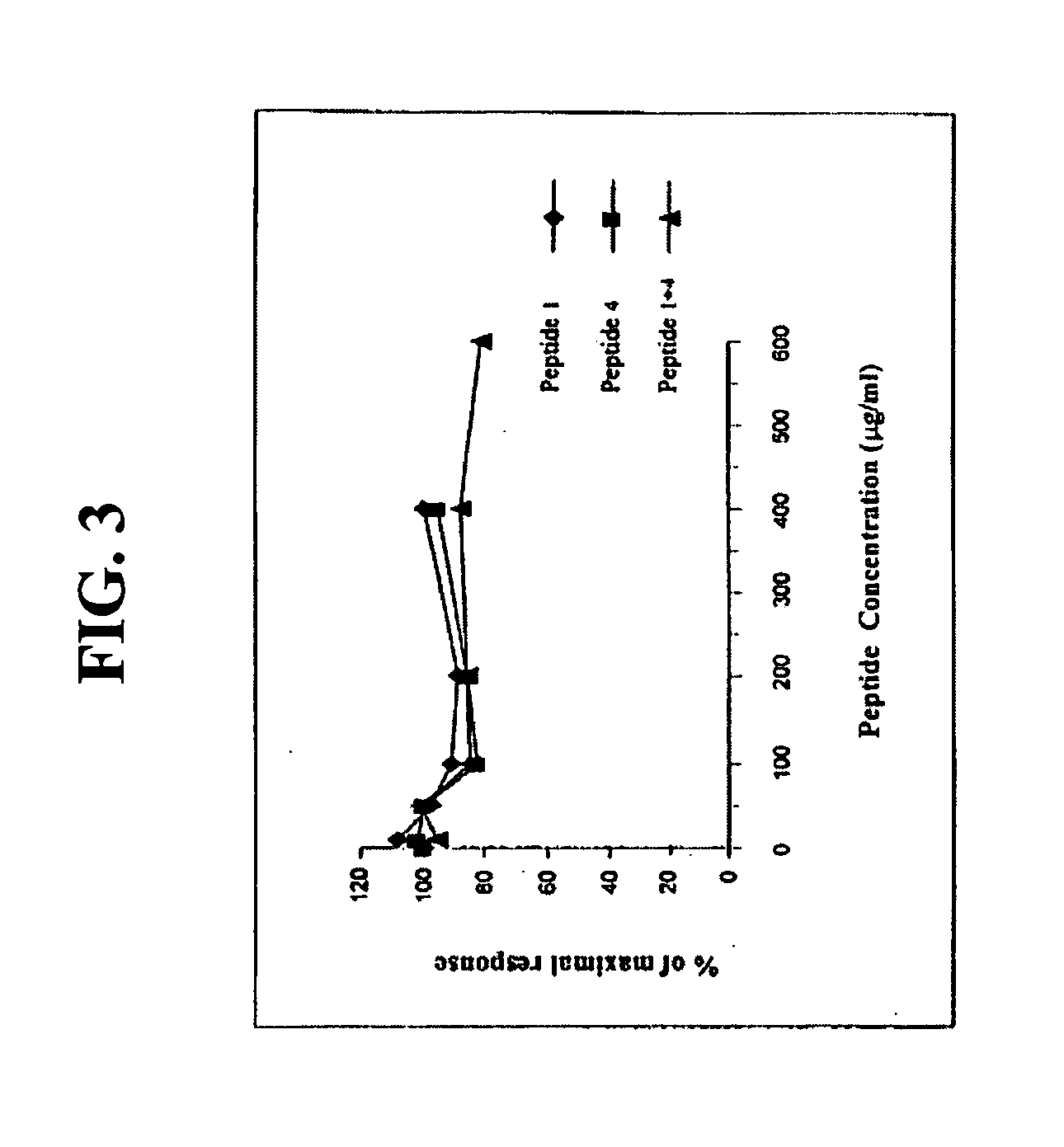
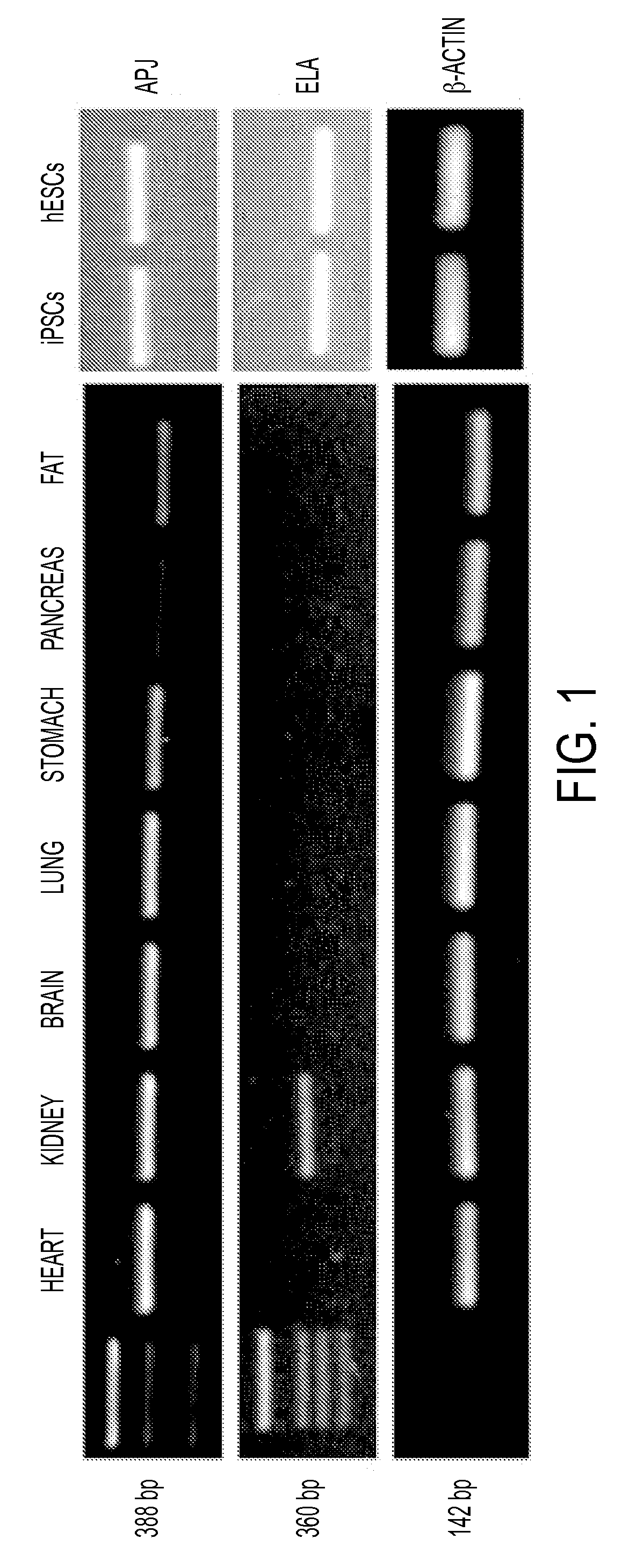
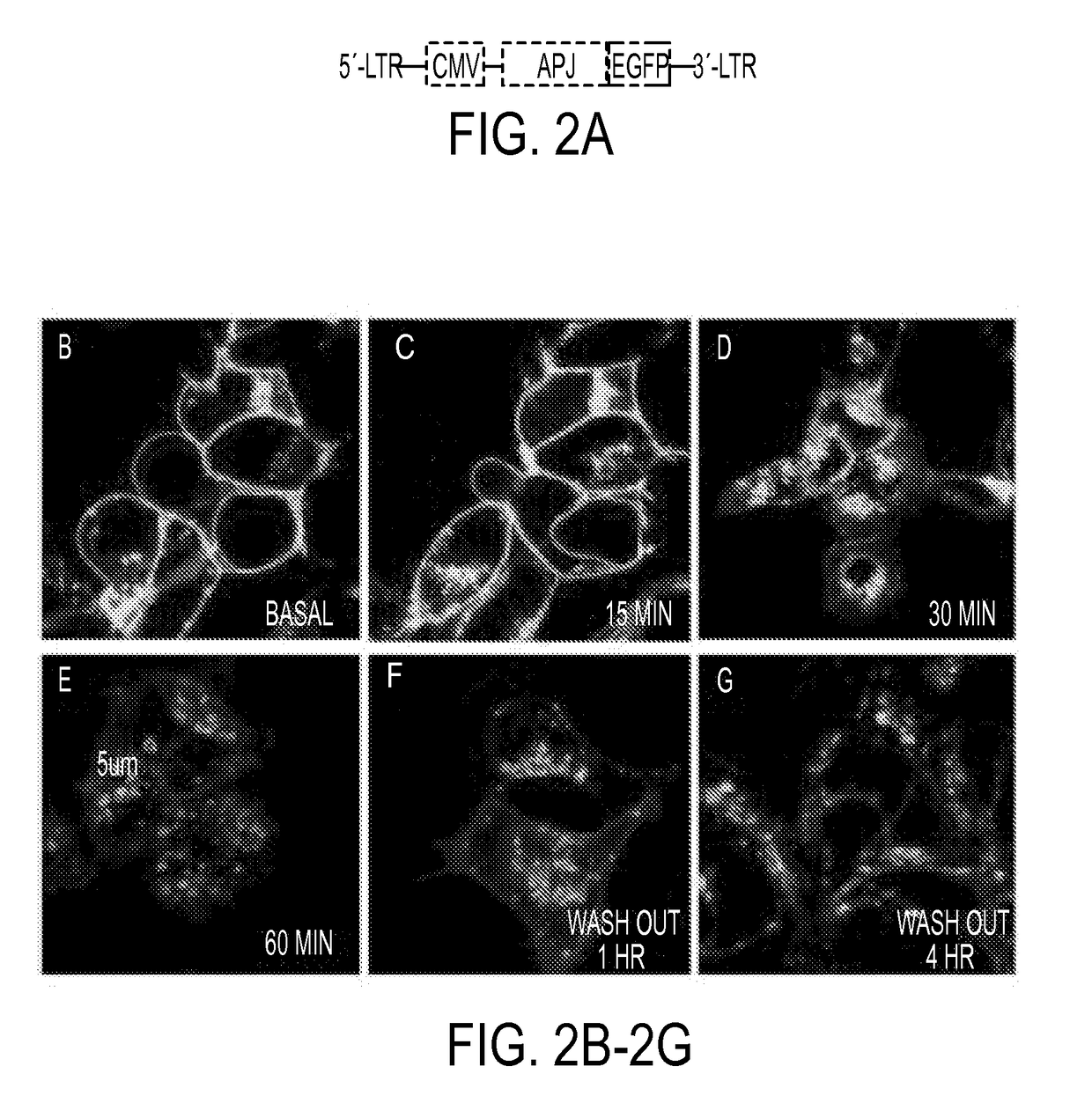
The present invention generally to methods of treating subjects suffering from a cardiac condition or having a risk factor for developing a cardiac condition by administering an ELA peptide or fusion protein to a subject in need. The invention relates to fusion proteins of Fc-ELA-32 and Fc-ELA-21 that exhibit improved properties for use as therapeutic agents, e.g. in the treatment of cardiac conditions. In addition, the present invention relates to polynucleotides encoding such fusion proteins, and vectors and host cells comprising such polynucleotides. The invention further relates to methods for producing the fusion proteins of the invention, and to methods of using them in the treatment of disease.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
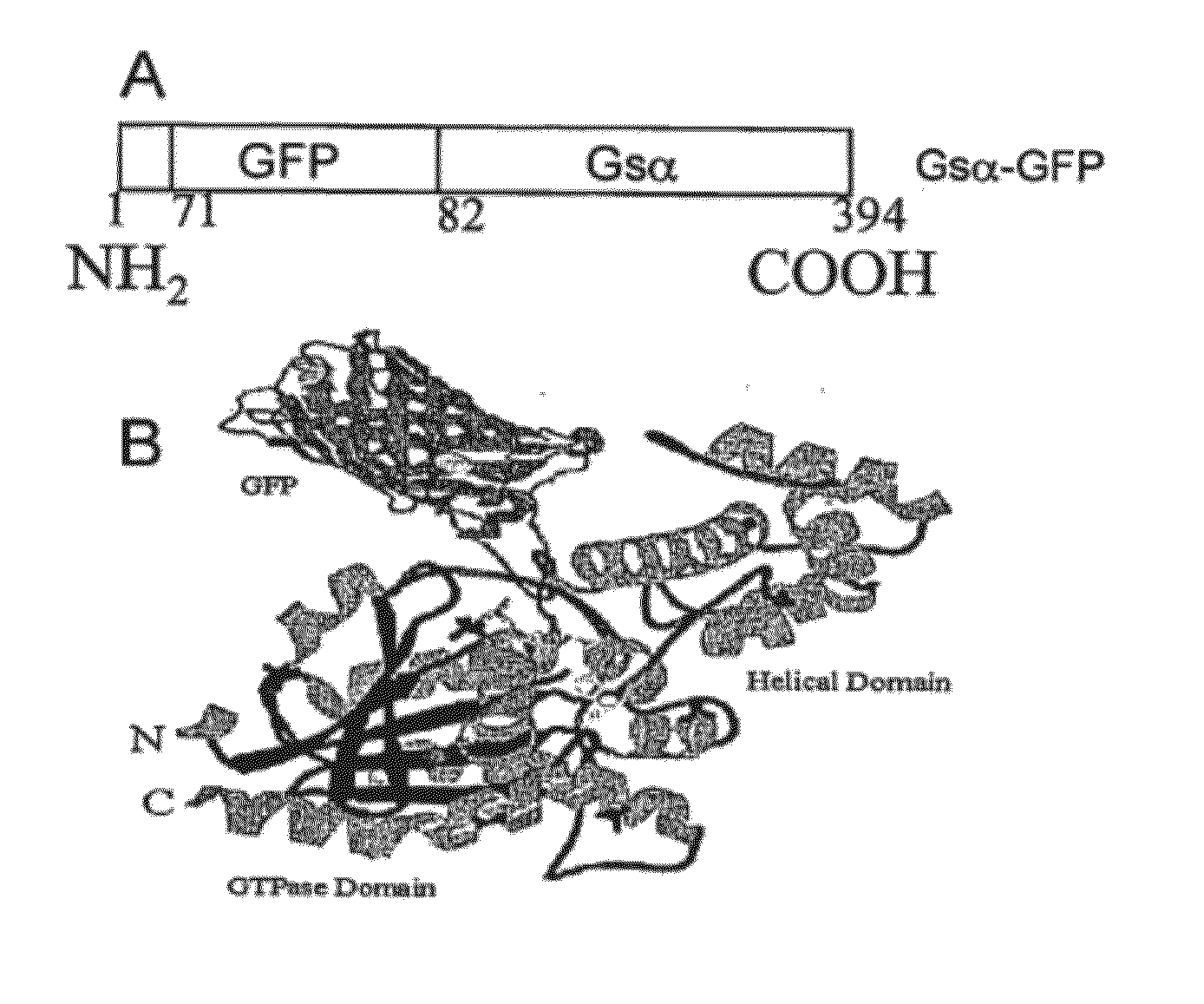
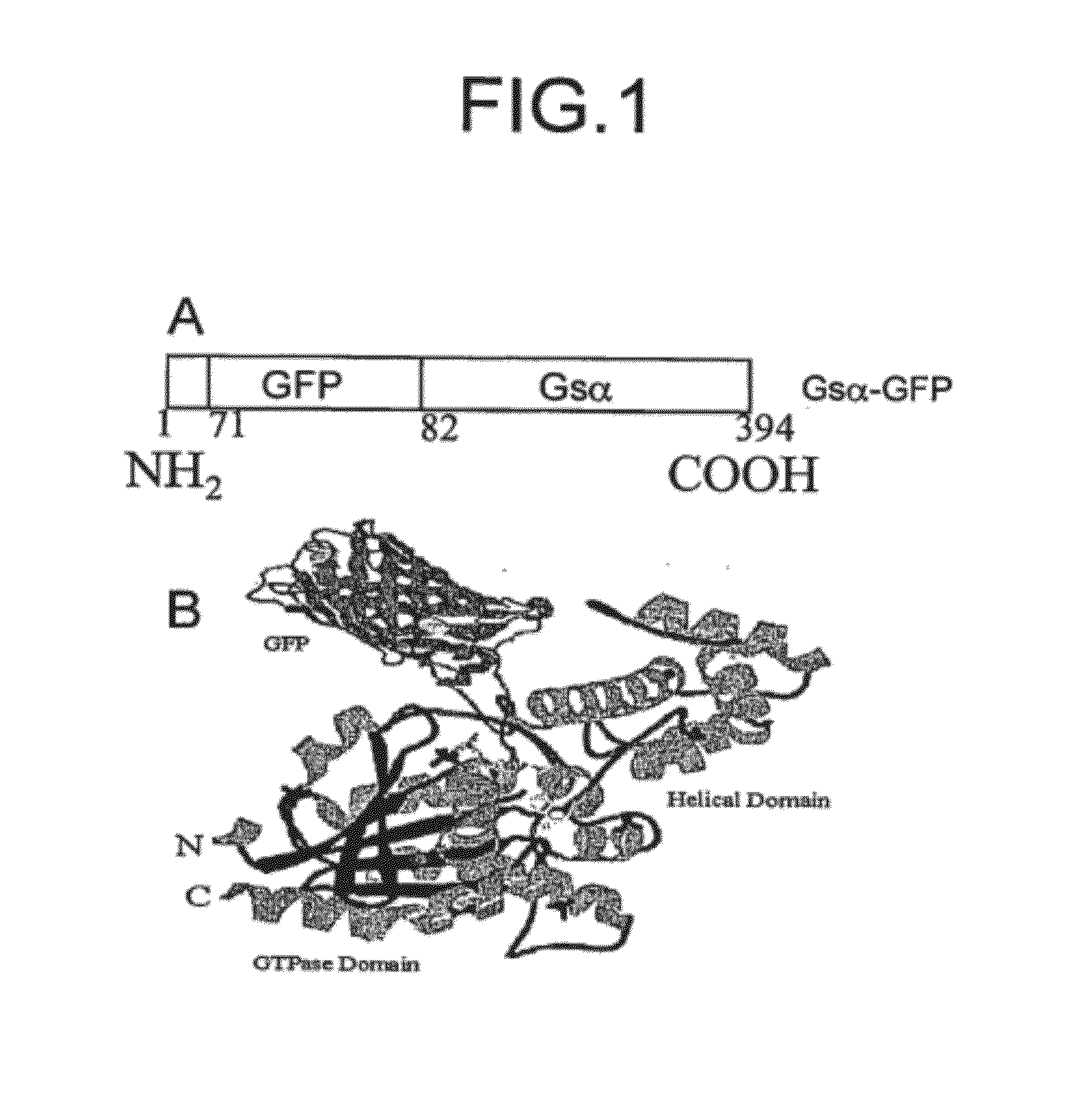
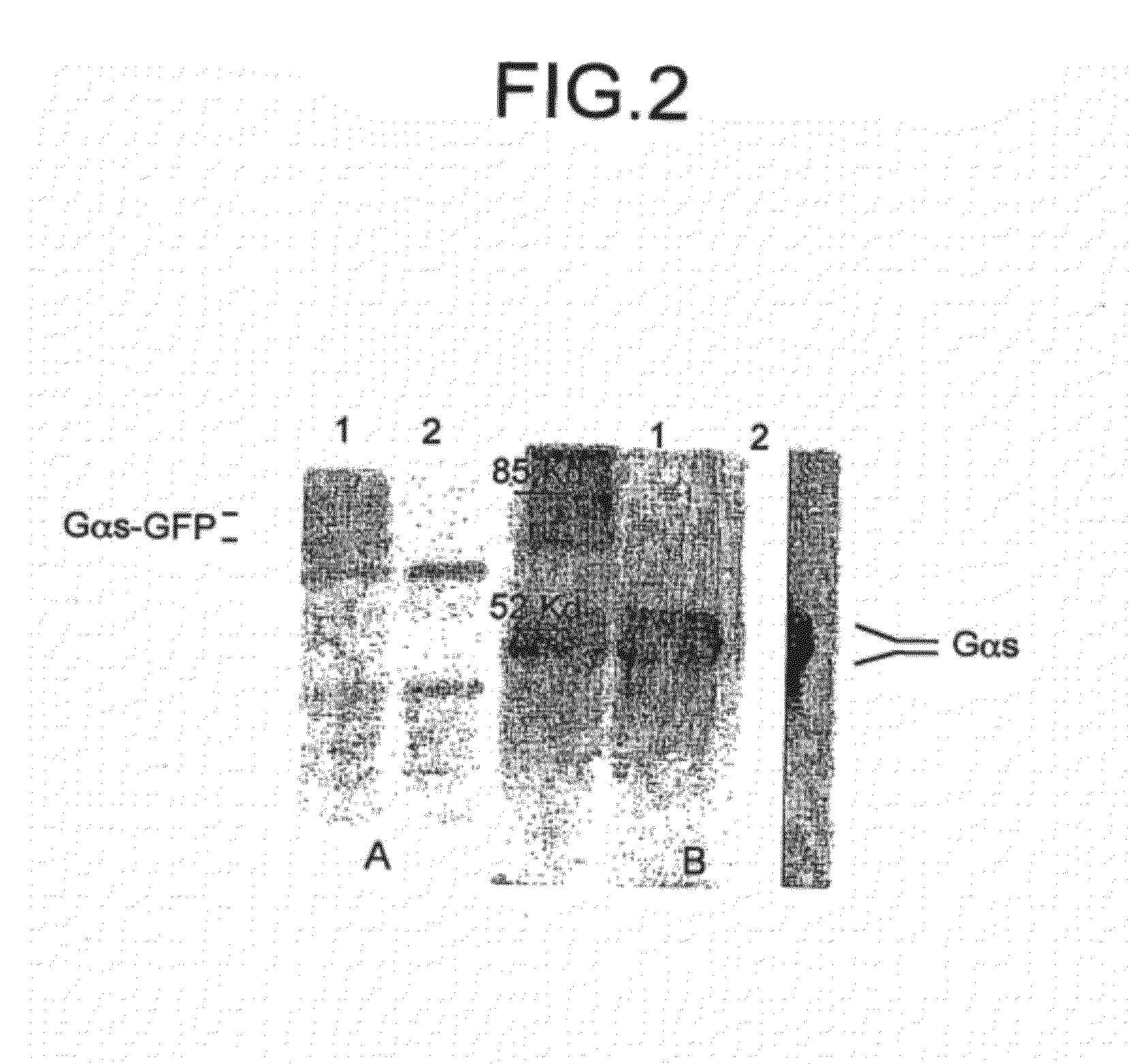
Gfp fusion proteins and their use
InactiveUS20120142015A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBiological activationAmino acid
The present invention provides fusion proteins including a green fluorescent protein inserted into the internal amino acid sequence of a Gαs protein and further provides method of using the fusion protein construct to follow activation of a G-protein receptor by a candidate drug.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Yeast cells expressing modified g proteins and methods of use therefor
InactiveUS20080268475A1High expressionEnhanced couplingPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCompound screeningHeterologousG protein-coupled receptor
The present invention pertains to novel yeast cells which are useful for the expression of heterologous G protein coupled receptors. The yeast cells of the present invention can be used in screening assays which can be used to screen for modulators of G protein coupled receptors. Specifically, the invention provides novel yeast cells which express a heterologous G protein coupled receptor and mutant and / or chimeric G protein subunit molecules which serve to functionally integrate the heterologous into the pheromone signaling pathway of the yeast cell. The invention also provides for the expression of heterologous G protein coupled receptors which are functionally integrated into the yeast cell membrane using a yeast α factor leader sequence. Drug discovery assays using the subject yeast cells are also provided.
Owner:CADUS TECH
A lentiviral vector efficiently mediating Galpha gene overexpression, a lentivirus and constructing methods of the lentiviral vector and the lentivirus
InactiveCN106244628AHigh transfection efficiencyPromote stable expressionG-proteinsFermentationProteolipid protein 2Lentivirus
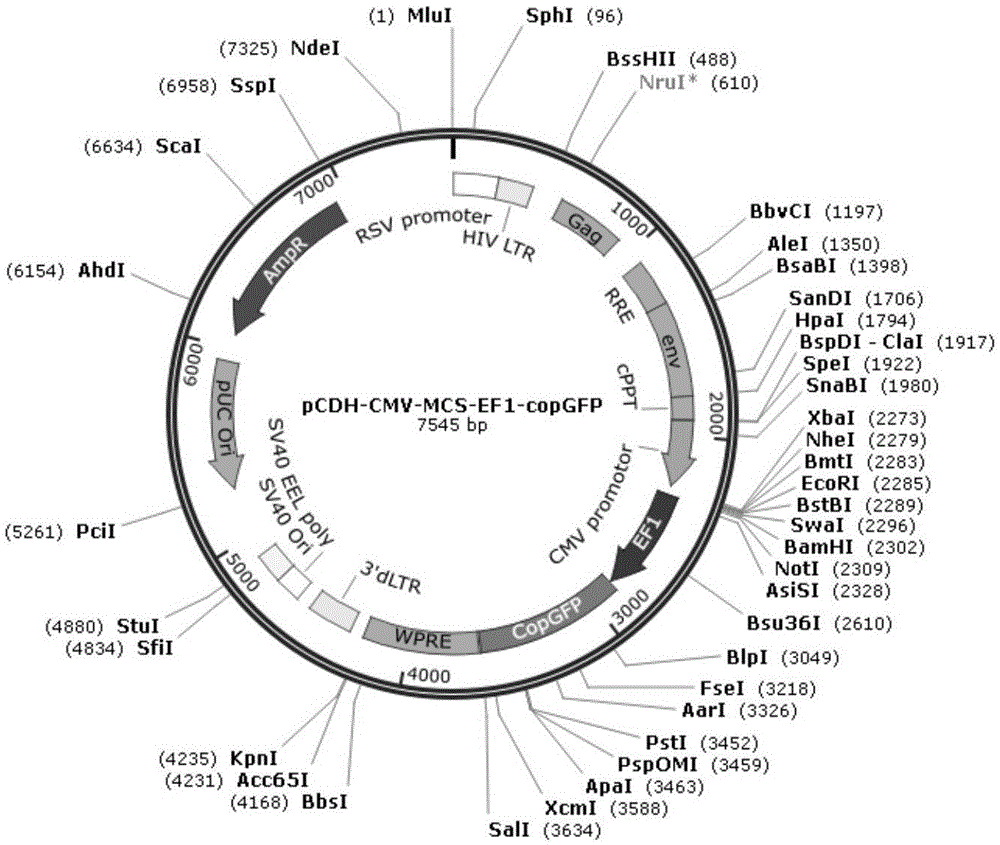
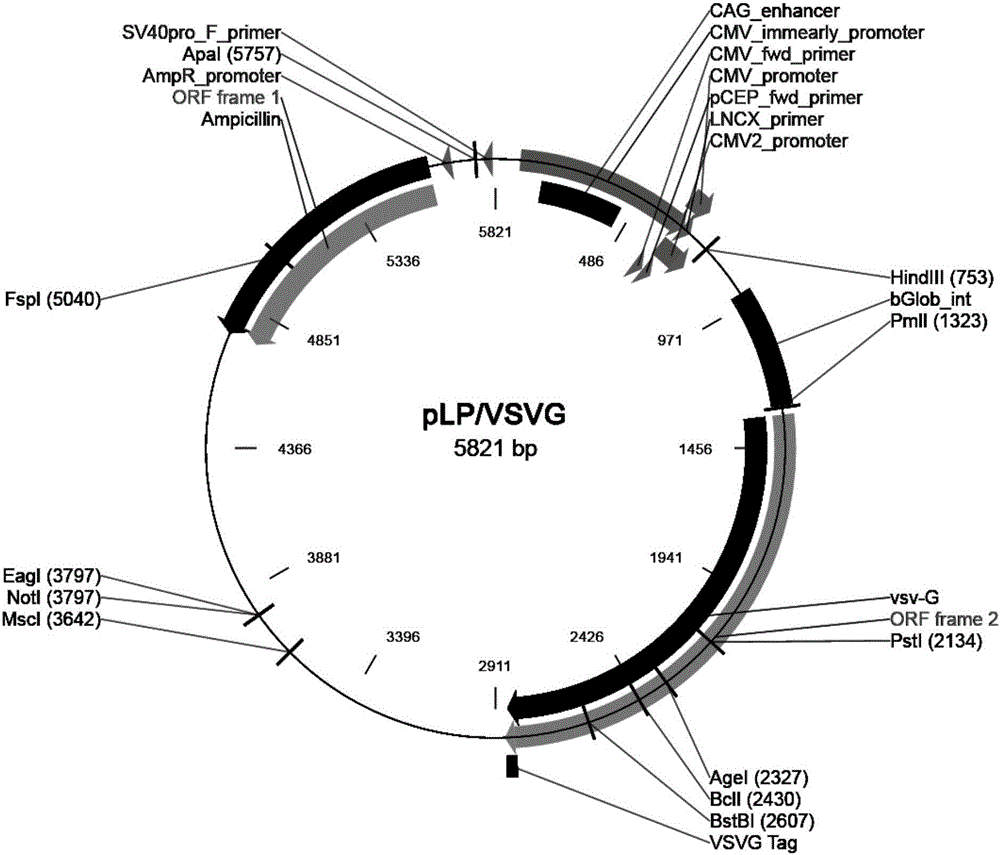
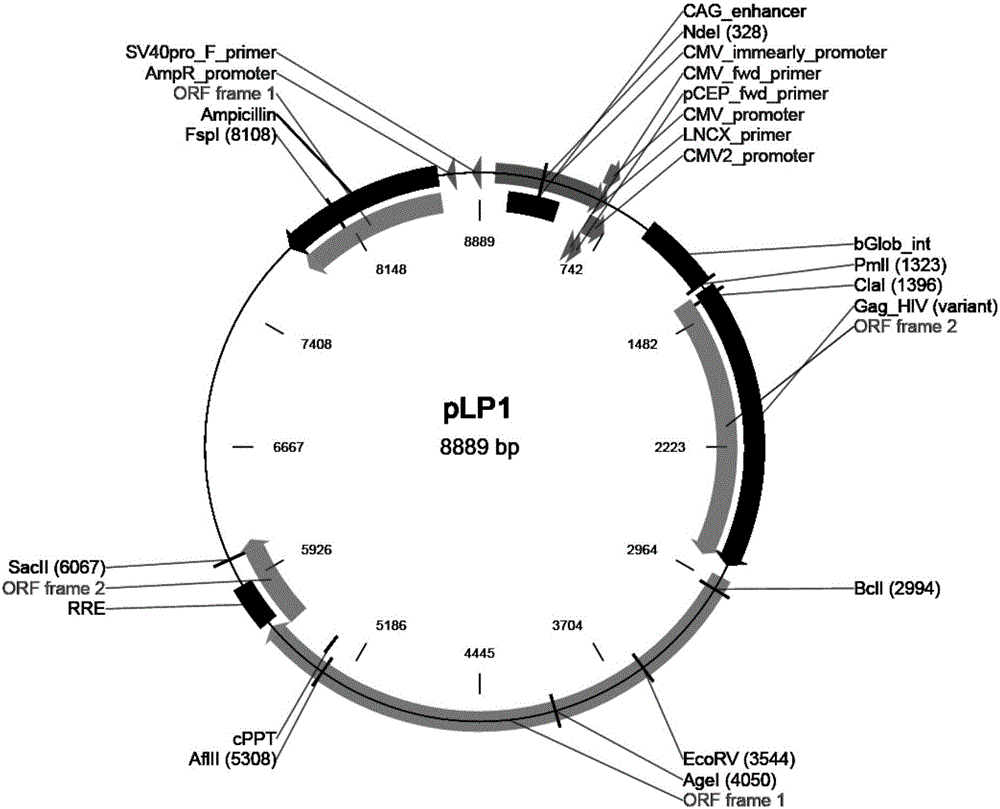
The invention relates to a lentiviral vector efficiently mediating Galpha gene overexpression, a lentivirus and constructing methods of the lentiviral vector and the lentivirus, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. Through a gene recombination technique, construction is performed based on a pCDH-CMV-MCS-EF1-copGFP lentiviral expression vector, and a Galpha gene is combined to obtain the Galpha-gene-overexpression lentiviral vector that is pCDH-CMV-MCS-EF1-copGFP-Galpha. Lentiviral packaging plasmids which are pLP / VSVG, pLP1 and pLP2 are adopted to package the Galpha-gene-overexpression lentiviral vector that is the pCDH-CMV-MCS-EF1-copGFP-Galpha, and a Galpha lentivirus is obtained through transfecting an HEK293 cell. The Galpha-gene-overexpression lentiviral vector is high in host cell transfection efficiency and capable of specifically, continuously and efficiently promoting stable expression of the Galpha gene in host cells.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
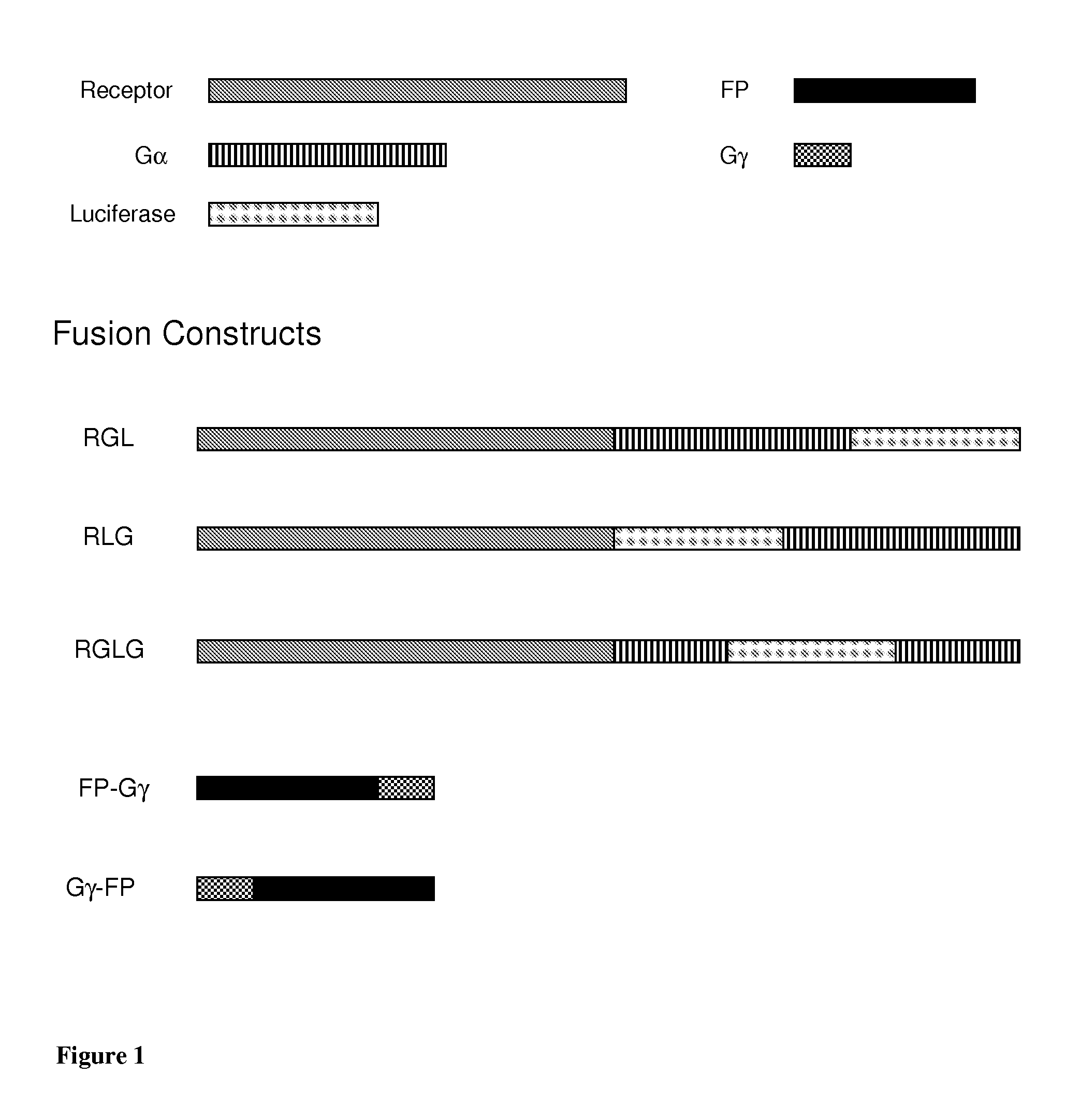
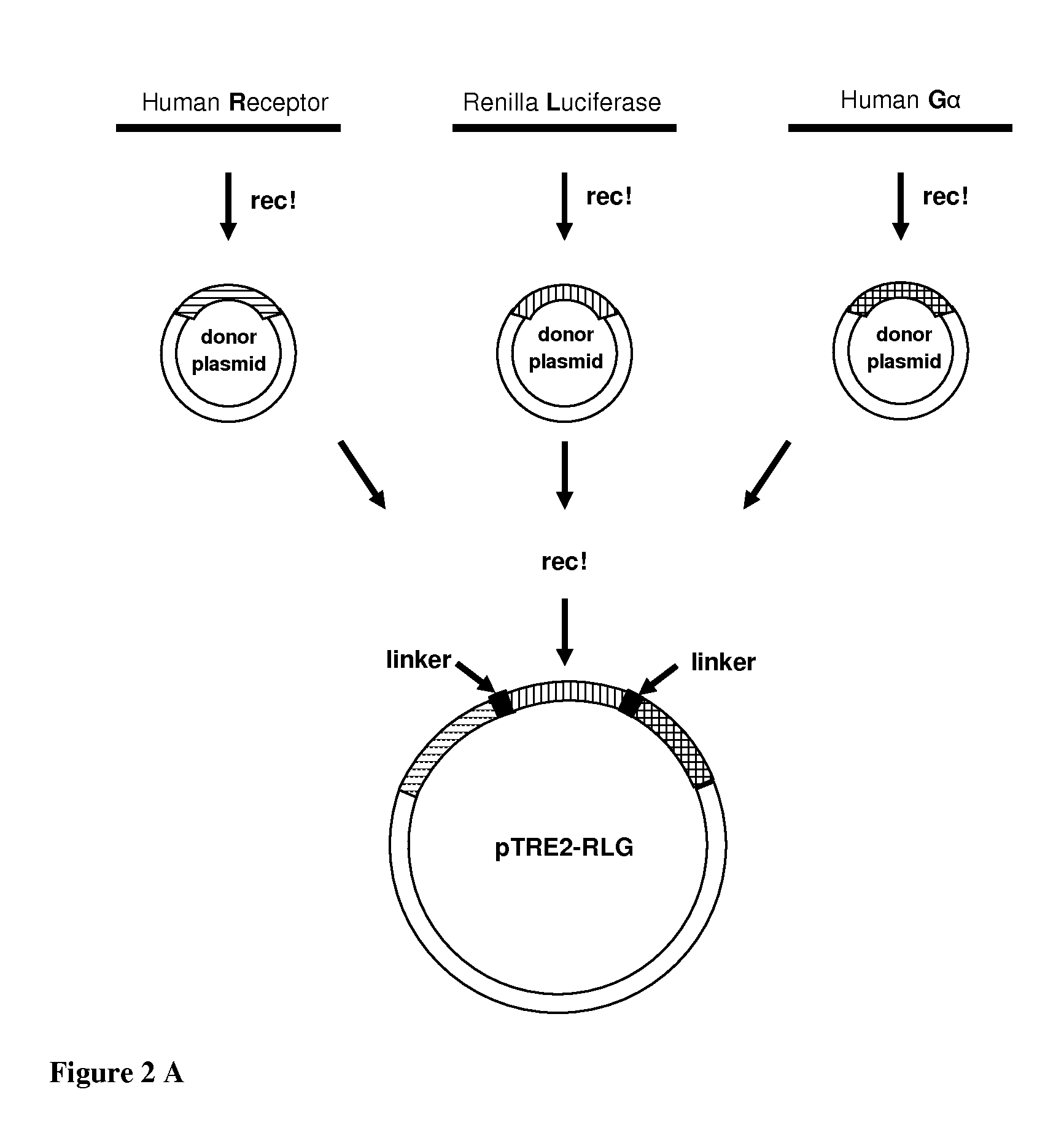
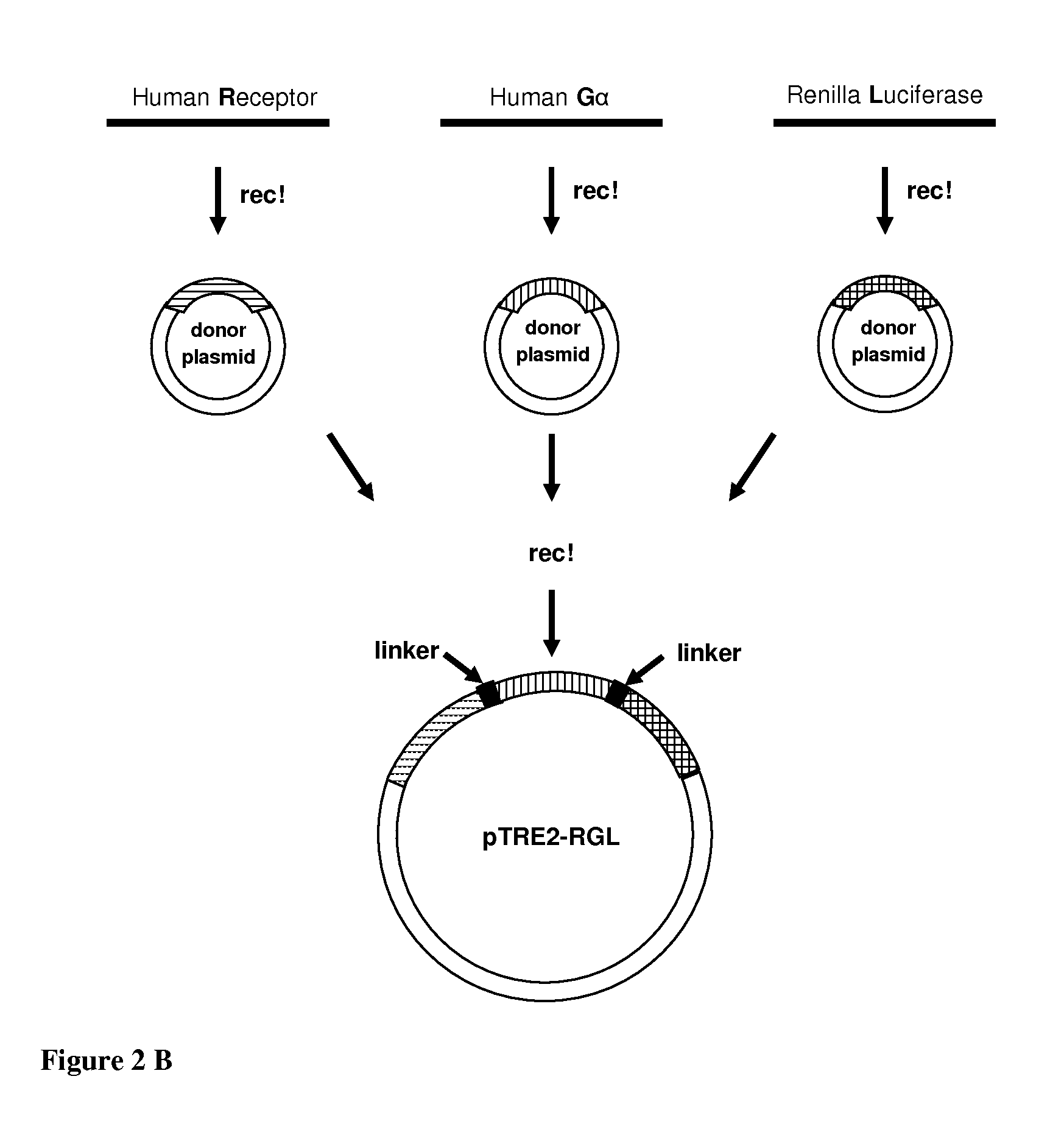
Chimeric Polypeptides Useful in Proximal and Dynamic High-Throughput Screening Methods
InactiveUS20130035256A1Eliminate artifactsCompound screeningApoptosis detectionScreening proceduresLow affinity
The present invention provides a method of high-throughput screening (HTS) of active agents of a cell-surface G-Protein coupled receptor (GPCR) or another target receptor of interest. The method uses a non-invasive, sensitive reporting system that is proximal to the target of interest, combined with a dynamic, automated screening procedure so as to detect orthosteric ligands, such as agonists and antagonists, but is also suitable to detect allosteric or low affinity active agents of a GPCR and possibly other disease-related receptors.
Owner:ADDEX PHARM SA
Chimeric vsv-g proteins as nucleic acid transfer vehicles
ActiveUS20150306248A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseFusion with RNA-binding domainGene deliveryPlasmid dna
The design and generation of a number of chimeric VSV-G (or VSV-G variants) proteins are used as transfer vehicles to enhance delivery of nucleic acids like plasmid DNA, single and double stranded DNA and RNA, and antisense oligonucleotides into human and animal cells. These chimeric VSV-G protein-nucleic acid transfer vehicles have widespread applications to deliver nucleic acids for exon skipping and gene delivery for gene replacement in human and animals.
Owner:OPAL IP LTD
Coding sequence of Gnb2 gene and application of coding sequence of Gnb2 gene in constructing mouse model
InactiveCN110904114ALow densityReduce the numberStable introduction of DNAG-proteinsStainingDendrite
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, provides a coding sequence of a Gnb2 gene and application of the coding sequence of the Gnb2 gene in constructing a mouse model. After the coding sequence of the Gnb2 gene is knocked out, development of neuron dendritic spines is influenced to cause reduction of the density of the dendritic spines. The density of cone neurondendritic spines is analyzed by a Golgi staining method; and the result shows that after the Gnb2 gene is knocked out, the number of dendritic spines on the bottom dendrite and the top dendrite is obviously reduced and the density of the dendritic spines in unit length is obviously reduced. The result indicates that after the coding sequence of the Gnb2 gene is knocked out, the density of the conoid neuron dendritic spines is influenced, so that the conoid neuron dendritic spines are obviously reduced and the thus the density of the dendritic spines is obviously reduced. Therefore, the codingsequence of a Gnb2 gene has the great significance in the research and analysis of dendritic spine development and function regulation.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Galpha gene overexpression lentiviral vector and lentivirus and construction method thereof
InactiveCN106191119AHigh transfection efficiencyPromote stable expressionG-proteinsFermentationHEK 293 cellsLentivirus
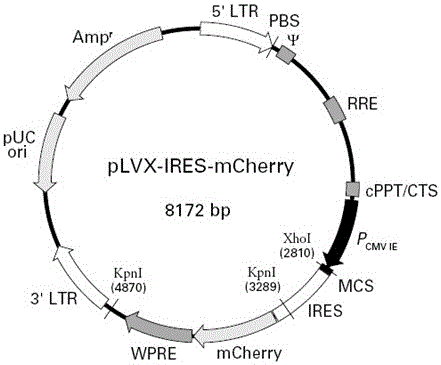
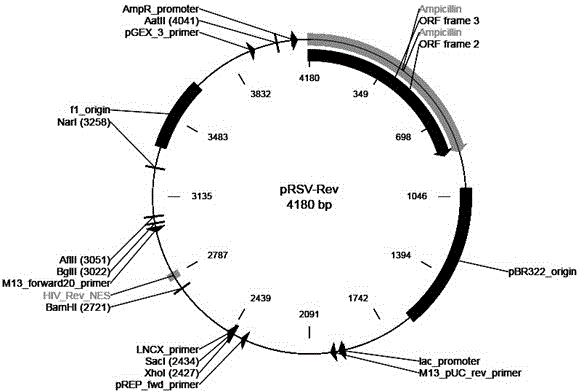
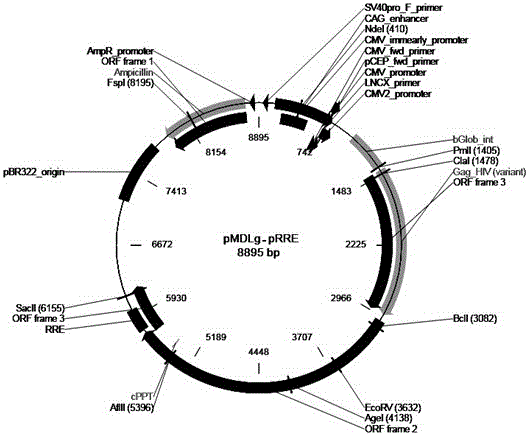
The invention relates to a Galpha gene overexpression lentiviral vector and lentivirus and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. Construction is conducted by taking a pLVX-IRES-mCherry lentiviral expression vector as a basis through a gene recombination technology, a Galpha gene is integrated on the vector, and the Galpha gene overexpression lentiviral vector pLVX-IRES-mCherry-Galpha is obtained. The Galpha gene overexpression lentiviral vector pLVX-IRES-mCherry-Galpha is packaged through lentiviral packaging plasmids including pRSV-Rev, pMDLg-pRRE and pMD2.G, HEK 293 cell transfection is conducted, and the Galpha lentivirus is obtained. The Galpha gene overexpression lentiviral vector constructed through the method is high in host cell transfection efficiency and can specifically, continuously and efficiently promote stable expression of the Galpha gene in host cells.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
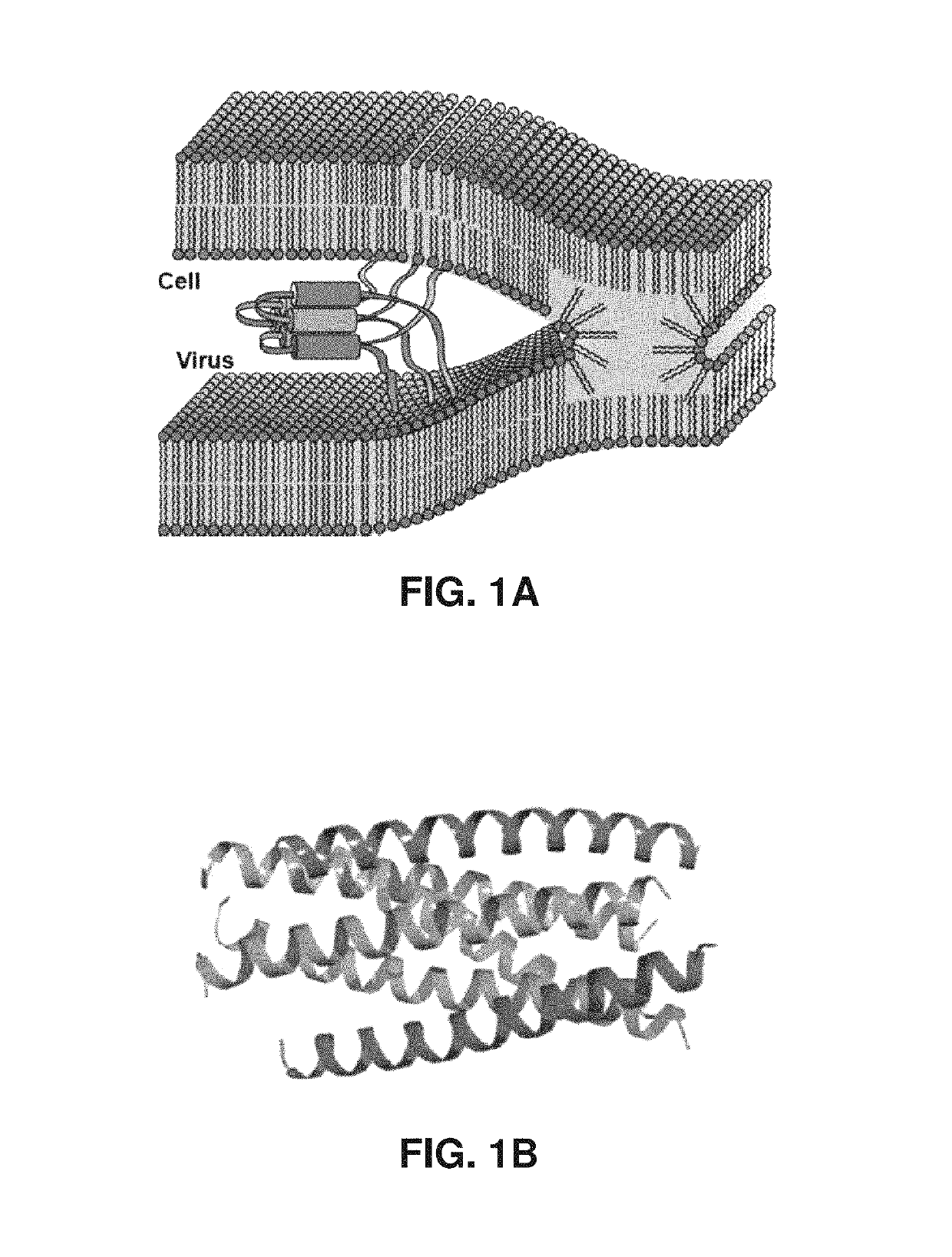
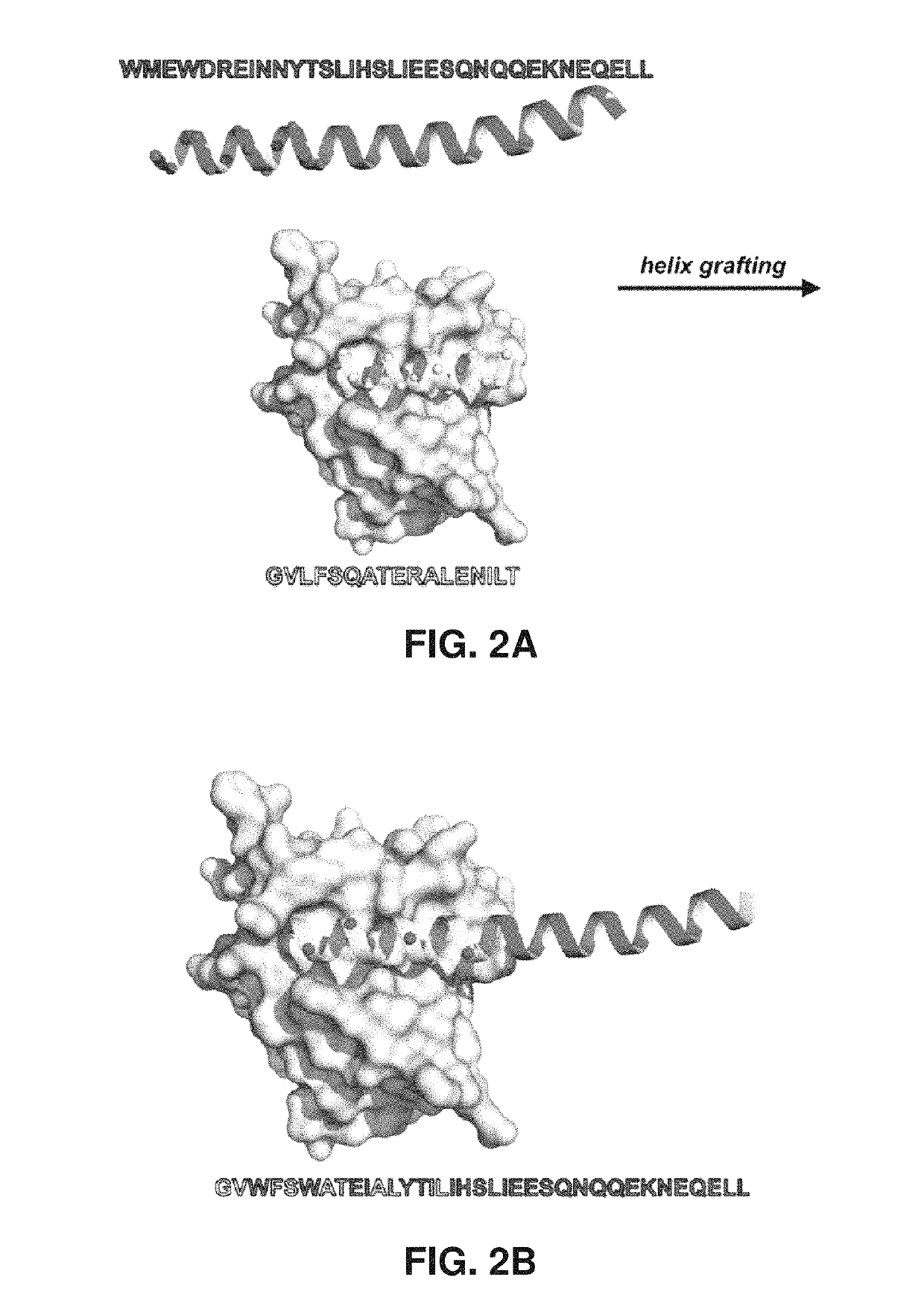
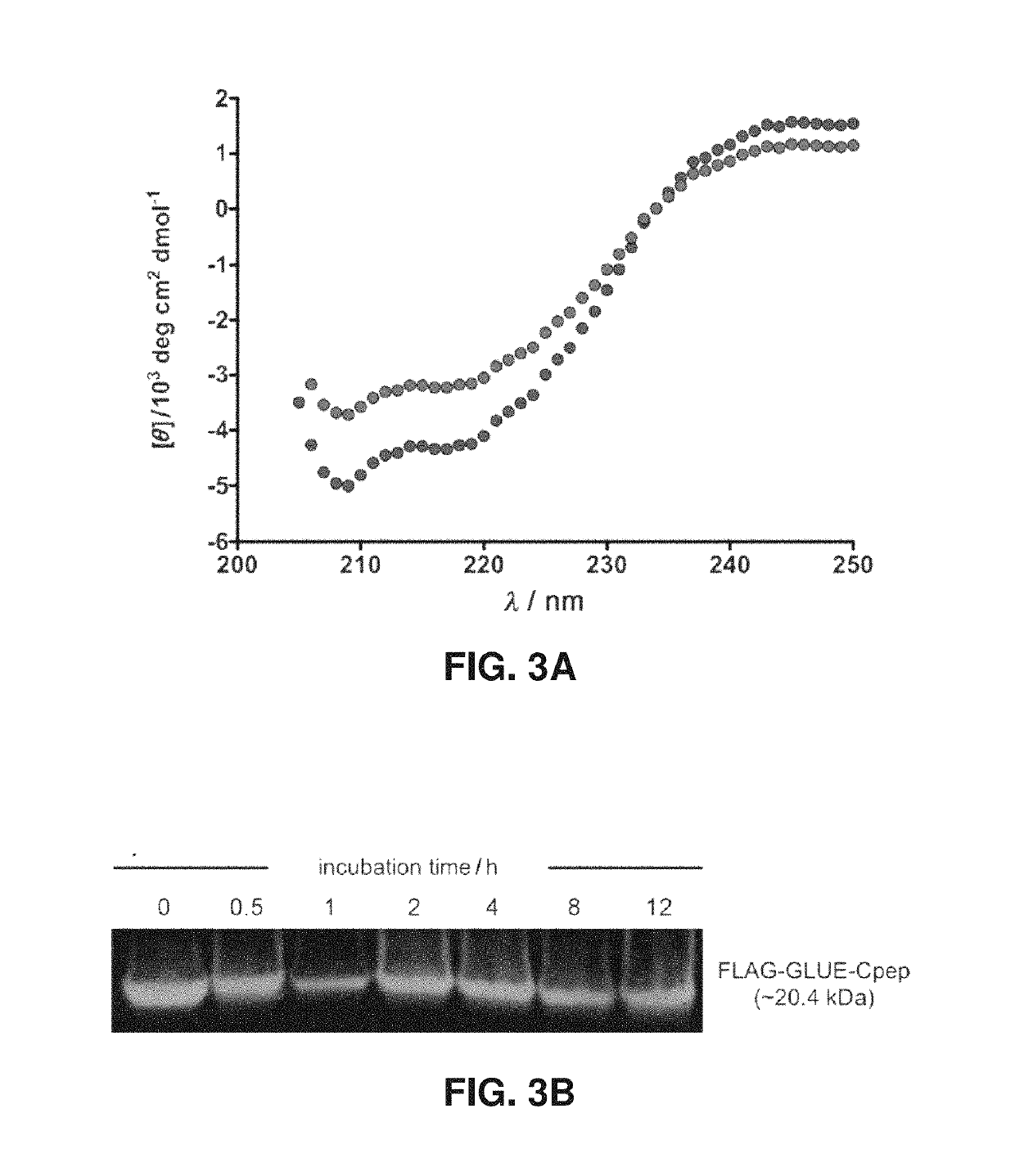
Helix-grafted proteins as inhibitors of disease-relevant protein-protein interactions
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
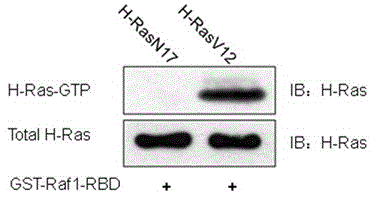
Method and kit for detecting Ras activity of small molecular G protein by utilizing GST pull-down and Western-Blot
InactiveCN105467128AEasy to operateImprove standardizationNucleic acid vectorG-proteinsWestern blotOrganism
The present invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, and discloses a method and kit for detecting Ras activity of a small molecular G protein by utilizing GST pull-down and Western-Blot. The kit comprises: a conventional GST pull-down experimental components, a GST-Raf1-RBD fusion protein in specific binding with Ras-GTP, and an antibody for specific recognition of three Ras subtypes (H-ras, K-ras and N-ras). In the detection of Ras activity, the method and kit for detecting Ras activity of a small molecular G protein have the advantages of rapidness, accuracy and simpleness, and is conducive to clinical and research application.
Owner:TAISHAN MEDICAL UNIV
Anti-allergic complex molecules
InactiveUS20060100141A1Effect is exertedReducing degranulationSenses disorderNervous disorderProtein kinase activationMedicine
The present invention discloses novel anti-allergic complex molecules, and in particular, peptidic or peptidomimetic molecules, that includes a first part which is competent for cell penetration and a second part which is able to reduce or abolish mast cell degranulation, in particular to reduce or abolish allergy mediators, including histamine secretion from mast cells and protein kinase activation, wherein the first part is connected to the second part via a linker or a direct bond that creates a conformational constraint by forming a bend or turn.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Atlastin
The present invention relates to methods and compositions of a novel gene and the peptide encoded by the gene. Mutations in the gene, named atlastin, are factors in the disease Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia and related disorders. The present invention will be used for the in the research, diagnosis and treatment of these disabling diseases.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com