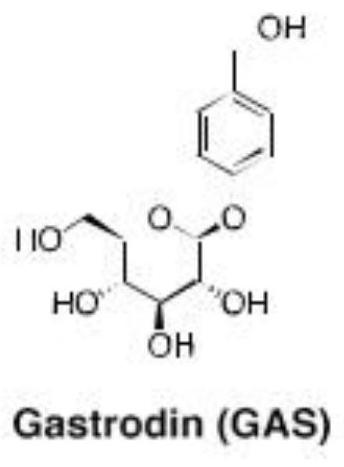
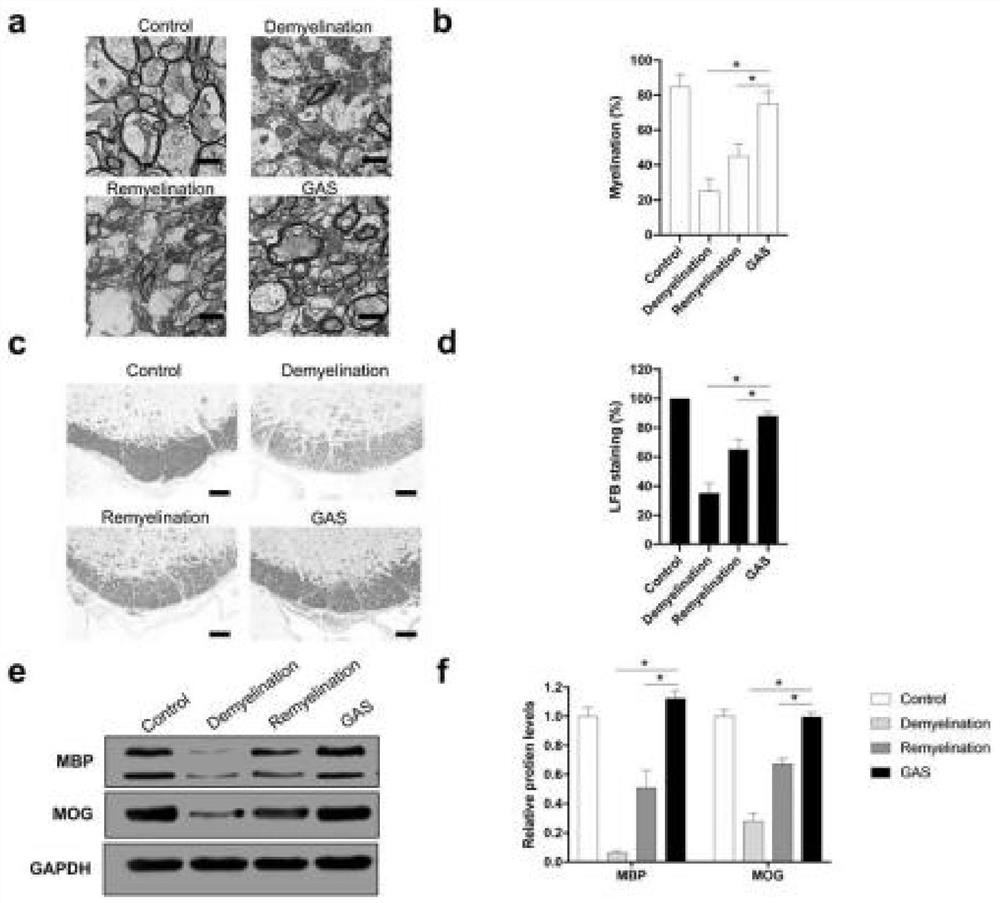
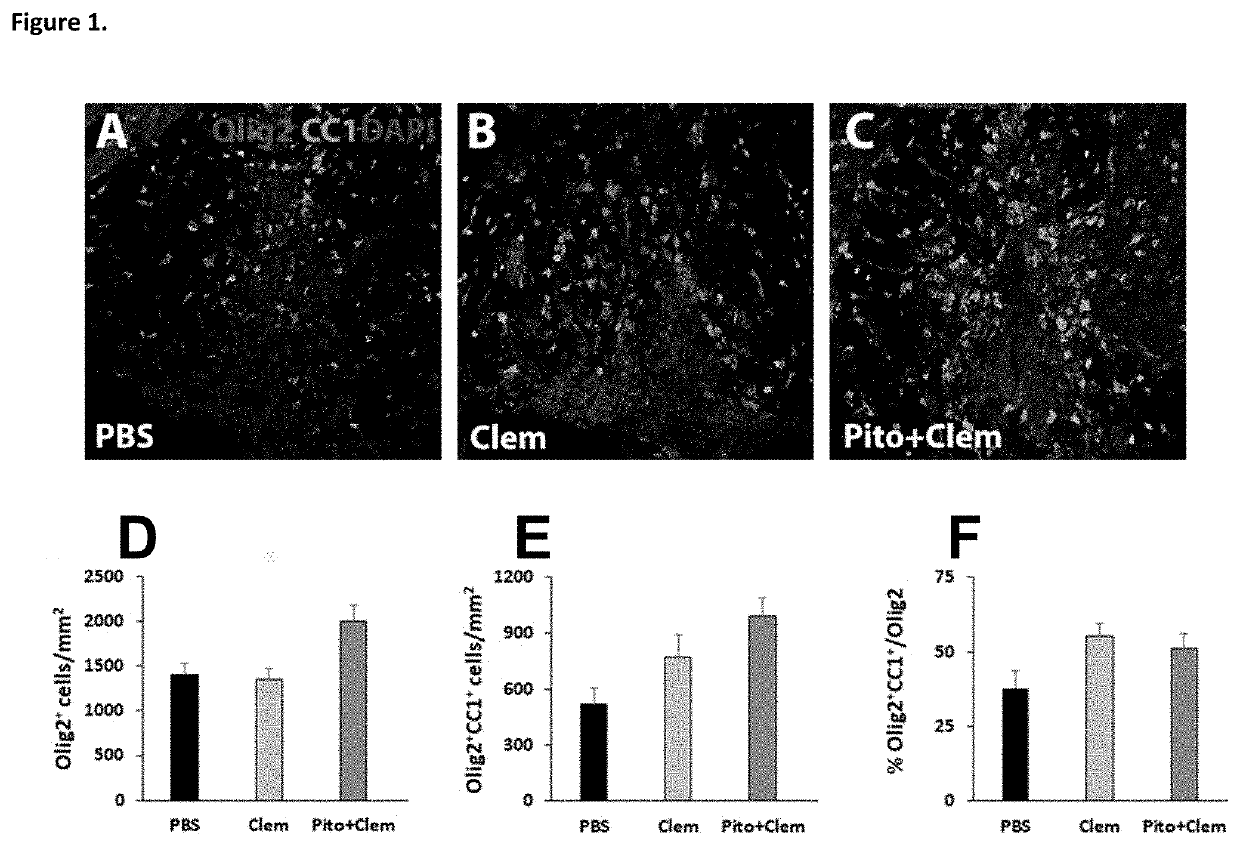
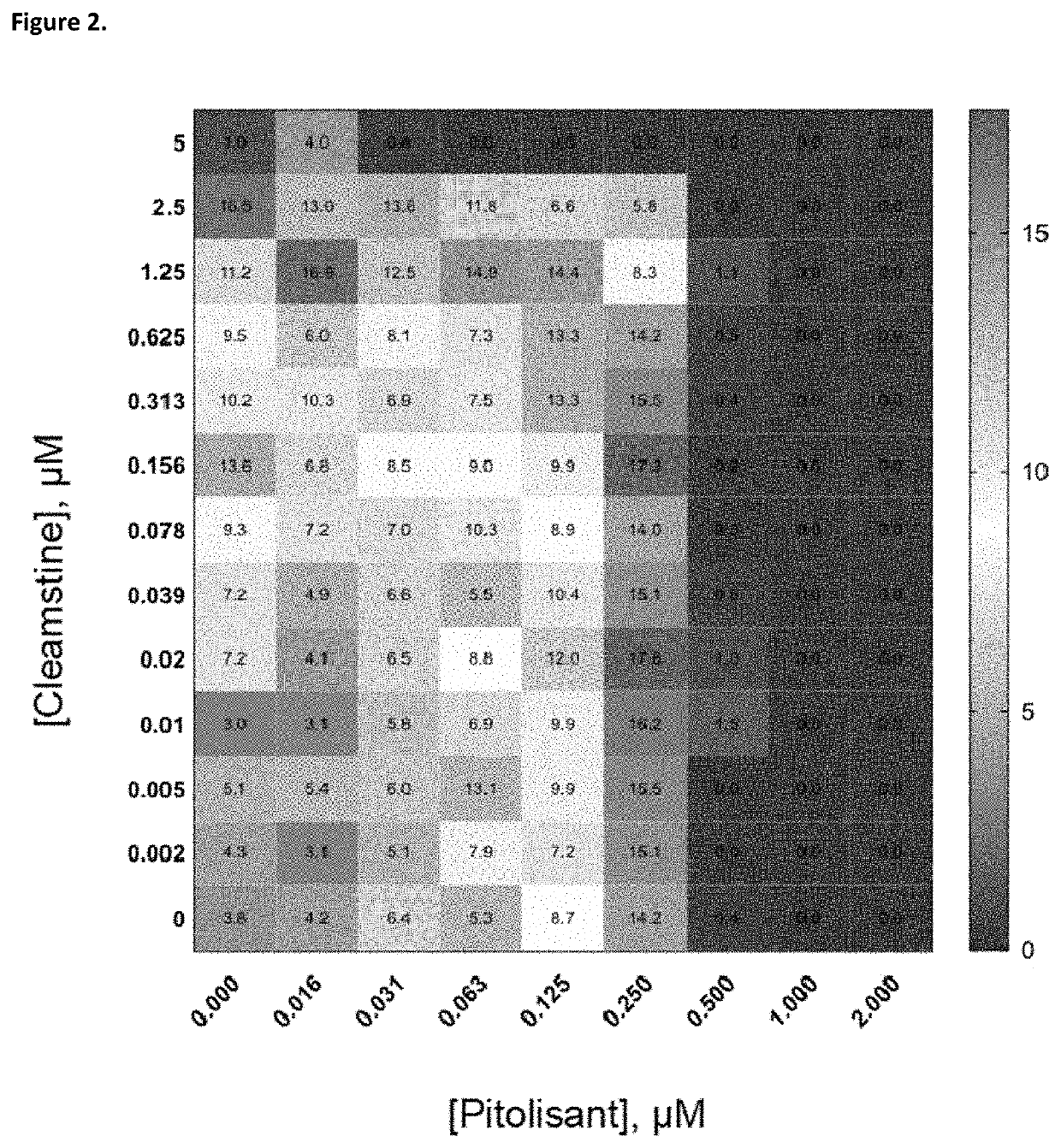
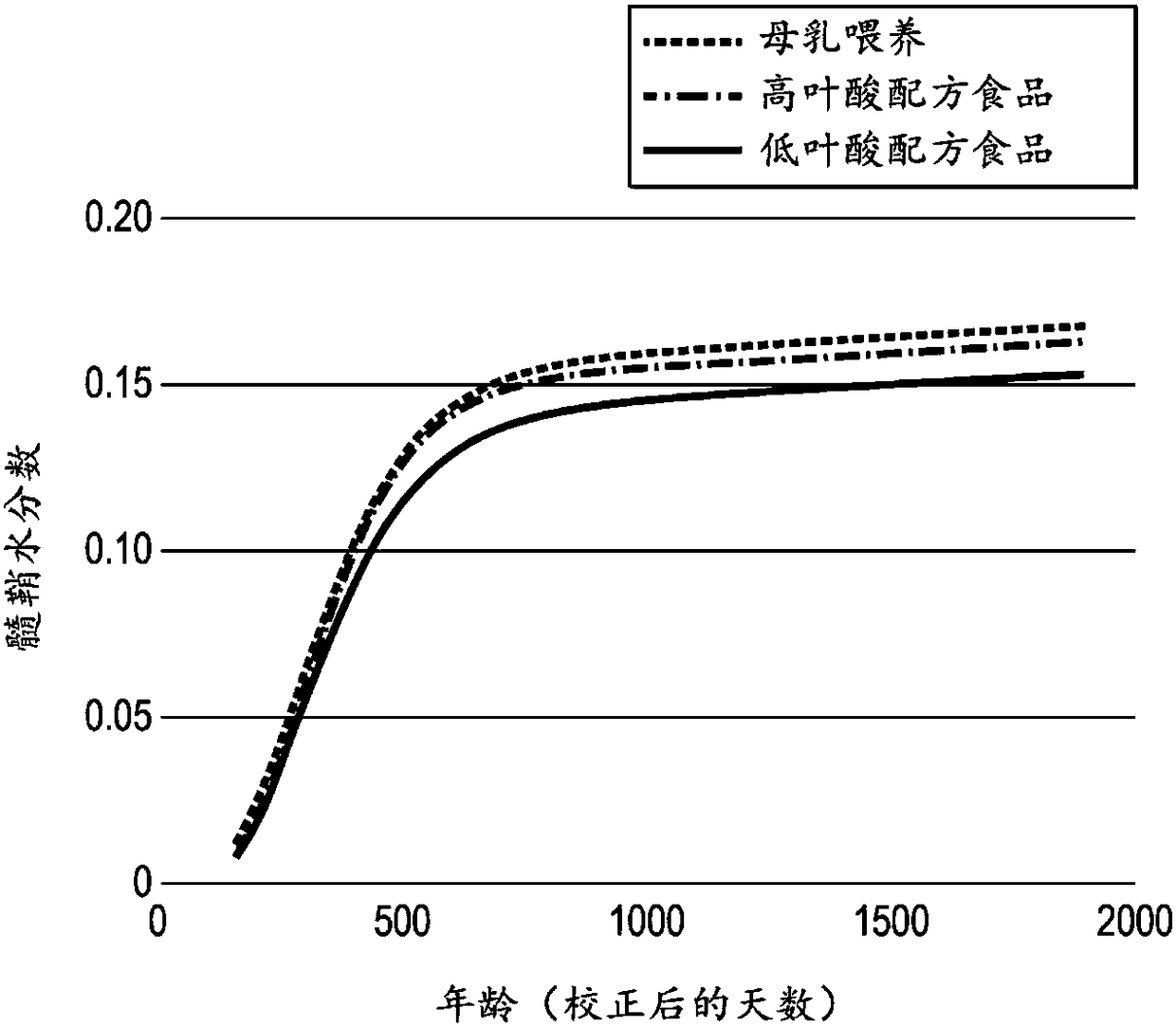
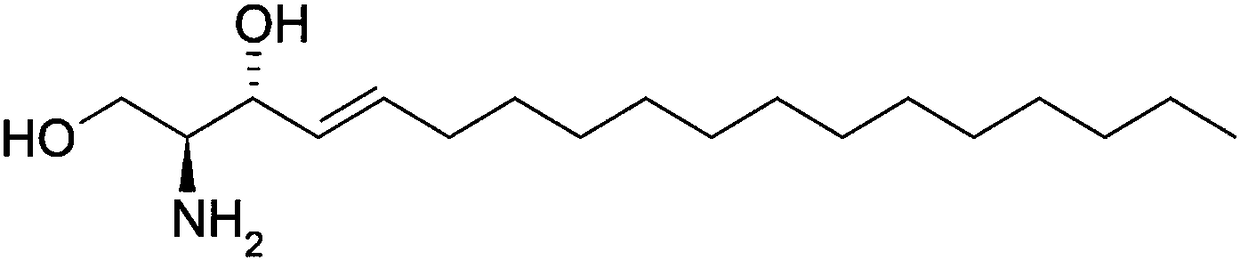
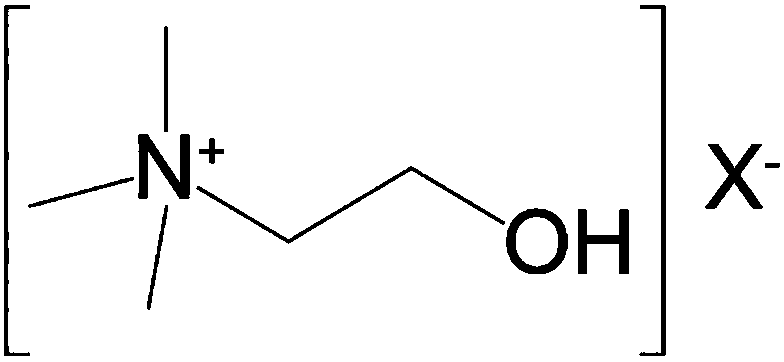
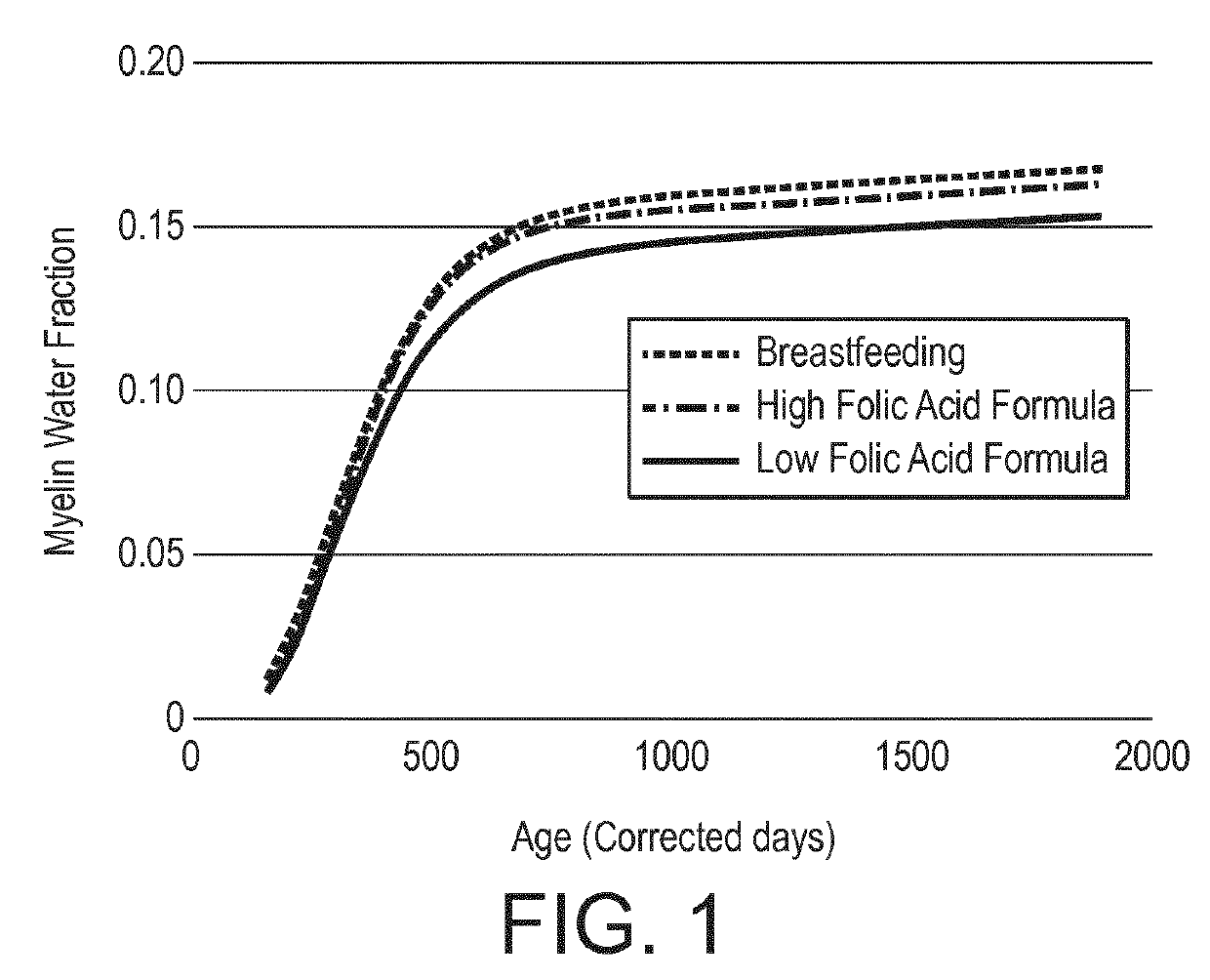
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Myelin body formation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
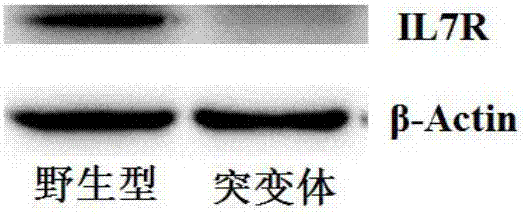
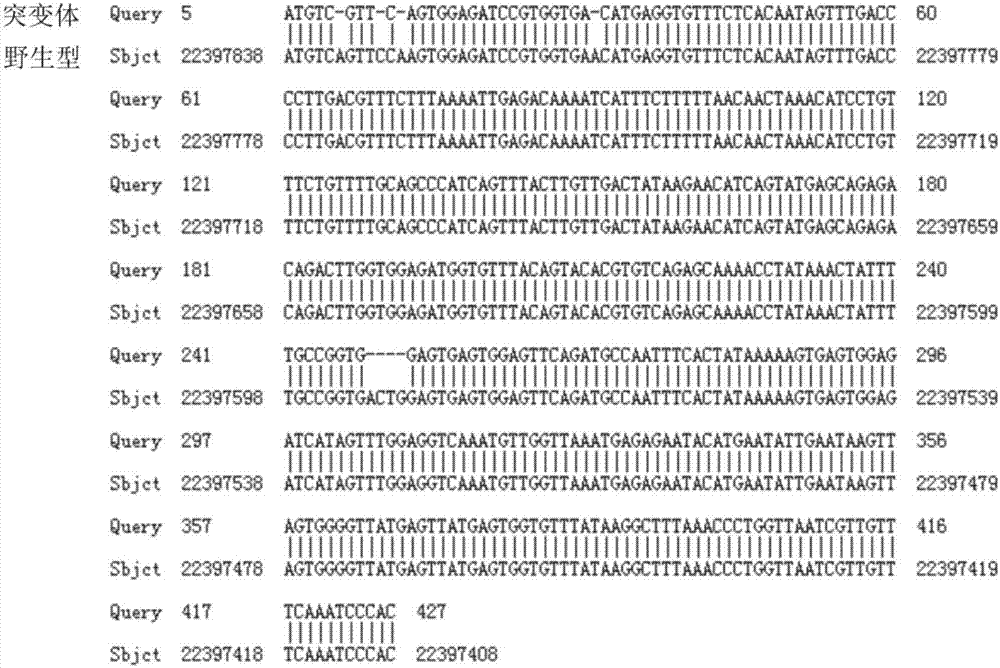
Preparation of IL7R gene-deleted zebra fish mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN107058320AConvenient for in vivo experimental researchGenetic stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesDeveloping nervous systemMutant
The invention discloses an IL7R gene-deleted zebra fish mutant and a preparation method thereof. The construction of the IL7R gene-deleted zebra fish mutant is realized through a CRISPR / Cas9 technology. Moreover, the invention also discloses application of the IL7R gene-deleted zebra fish mutant; a mutant model provided by the invention can be used for studying an effect of IL7R in the nervous system development and myelination.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Compounds and methods of promoting myelination
A method of promoting the generation of oligodendrocytes from oligodendrocyte precursor cells by enhancing their survival and / or maturation includes administering to the cell an effective amount of anagent that enhances and / or induces accumulation of delta8,9-unsaturated sterol intermediates of the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway in the oligodendrocyte precursor cells.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Combination therapies and uses for treatment of demyelinating disorders
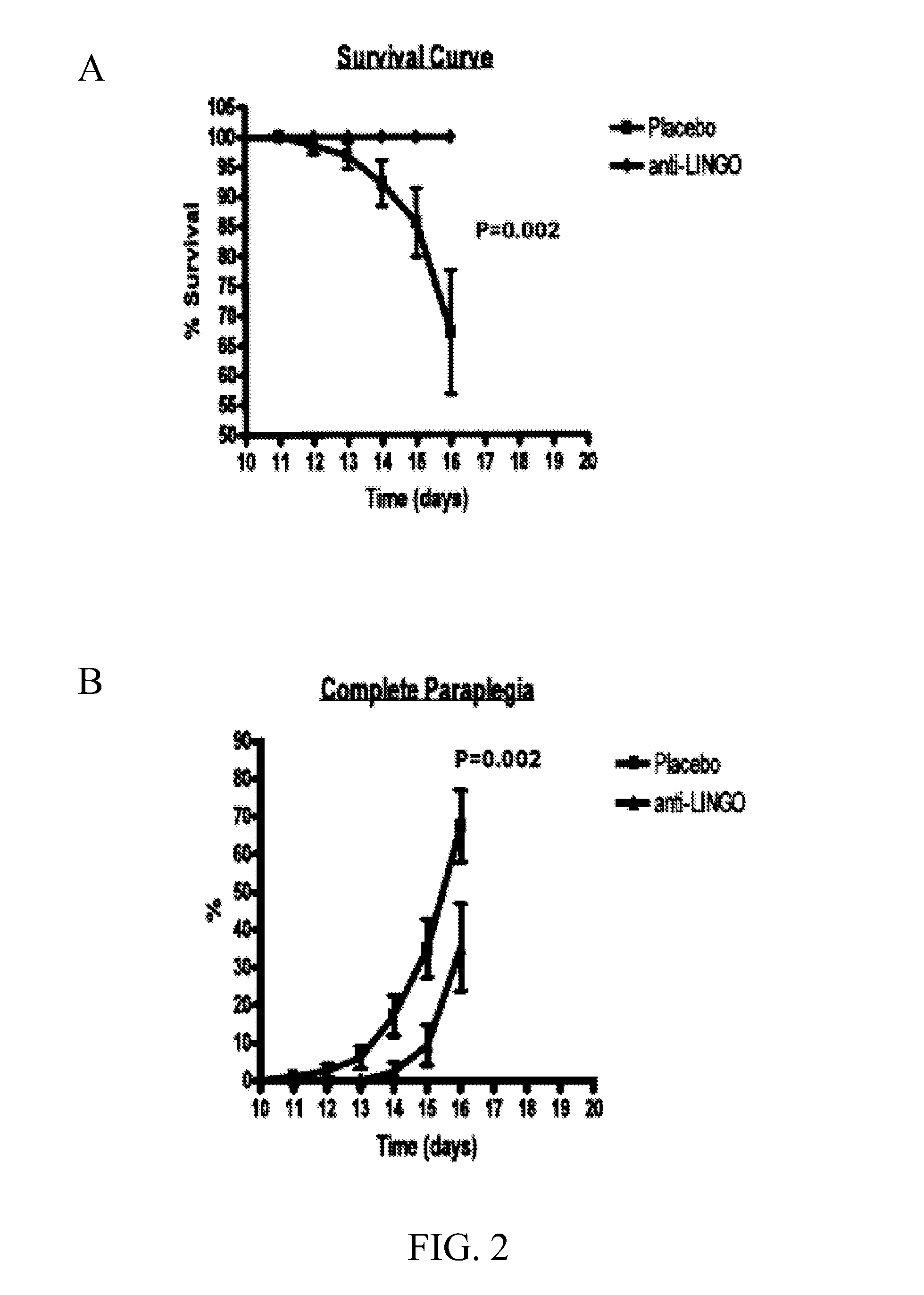
InactiveUS20150238602A1Enhances myelinationPromotes oligodendrocyte numberOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDemyelinating DisorderMyelin body formation
Methods and compositions for enhancing one or more of: myelination, re-myelination, oligodendrocyte numbers, or neuroaxonal protection, while ameliorating an inflammatory condition in a human subject are disclosed. In certain embodiments, the methods and compositions described herein include a reparative agent (e.g., a LINGO-1 antagonist) and an immunomodulatory agent, in combination. Thus, methods, compositions and kits described herein can be useful for treating a CNS demyelinating disease.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Methods of detecting myelin basic protein
ActiveUS20140154178A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsMyelin body formationTissue sample
A method and a kit for detecting myelin basic protein are provided. The method comprises administering an agent, which binds to myelin basic protein (MBP), to a subject at risk of or diagnosed with a myelin-associated neuropathy, and determining myelination by detecting the agent resided in the subject. The amount of the agent present in the subject is indicative of a myelin-associated neuropathy. A method of quantifying an amount of MBP present in a tissue sample is also provided, wherein the method comprises contacting the tissue sample with the same agent, detecting the agent present in the tissue sample; and quantifying an amount of the agent present in the tissue sample.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods of inducing myelination and maturation of oligodendrocytes
The present invention disclosed methods of inducing maturation of oligodendrocyte cells. A method of inducing myelination in a patient suffering from demyelination is also disclosed
Owner:KADIMASTEM
Methods and treatment for certain demyelination and dysmyelination-based disorders and/or promoting remyelination
The invention relates to methods and compositions for treating demyelination and / or dysmyelination and / or promoting remyelination of neurons and / or preventing the development of myelin-related diseases by administering to a subject in need thereof an effective amount (either therapeutic or prophylactic) of an elemental gold crystal nanosuspension.
Owner:CLENE NANOMEDICINE INC A NEVADA CORP
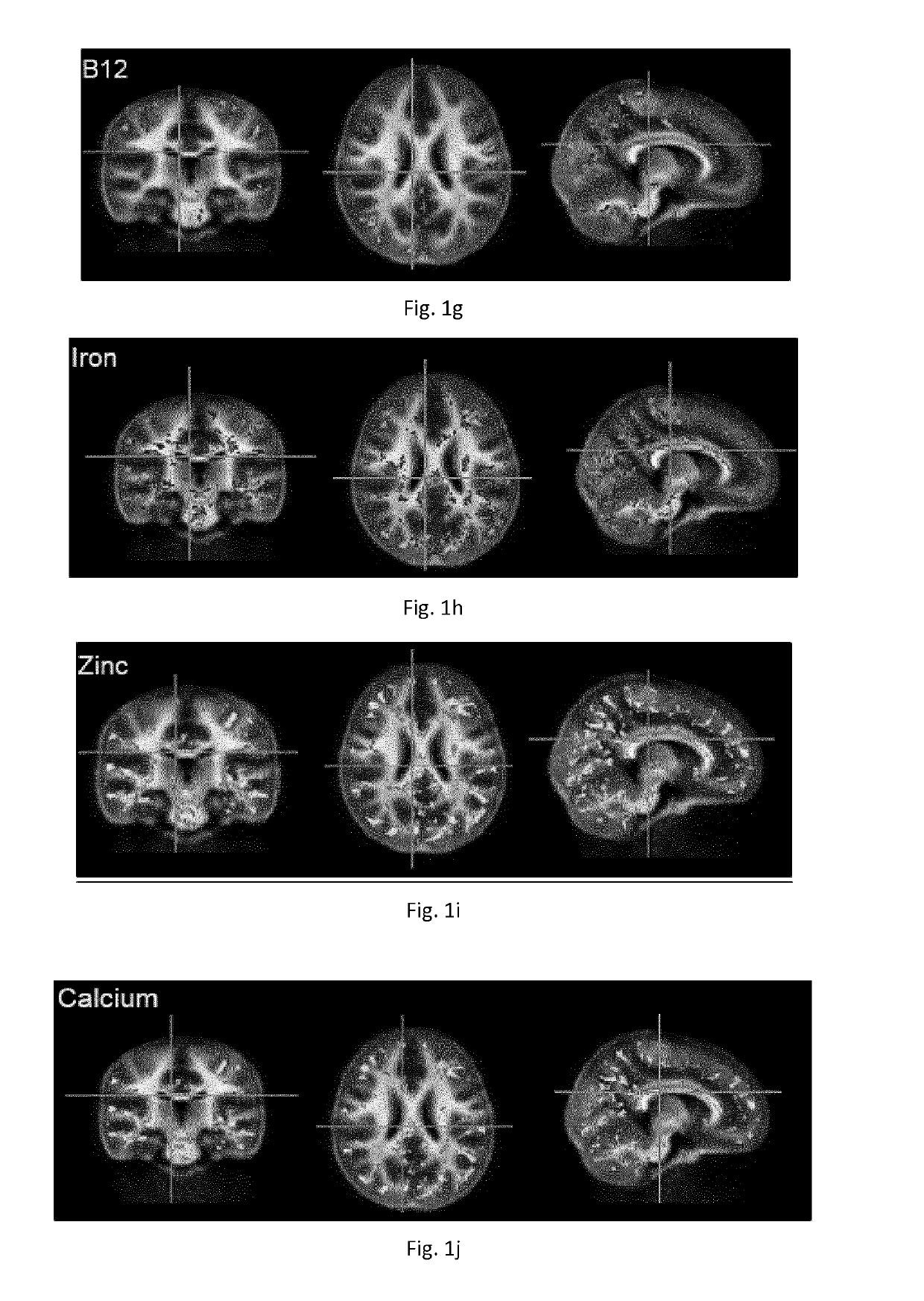
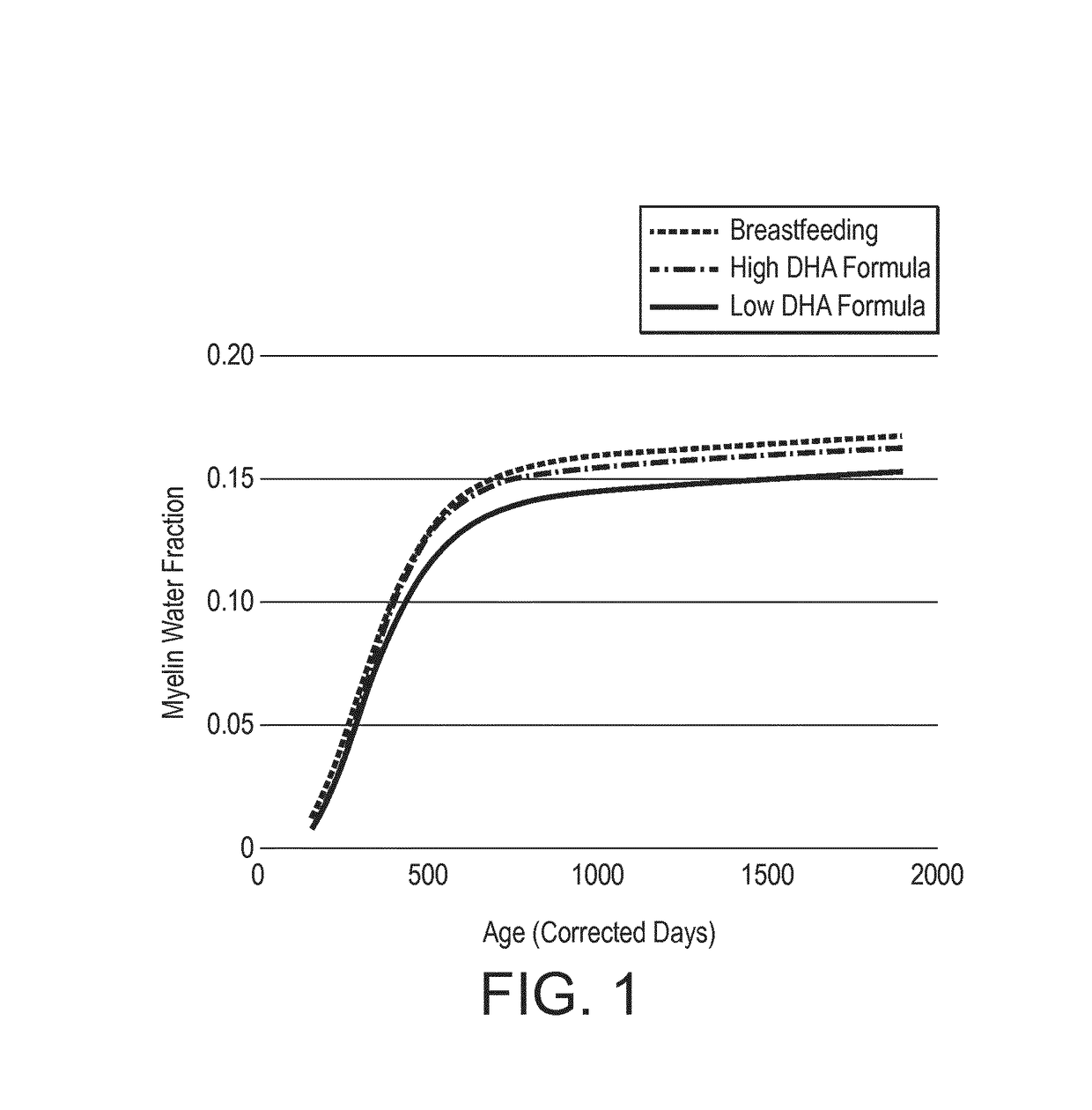
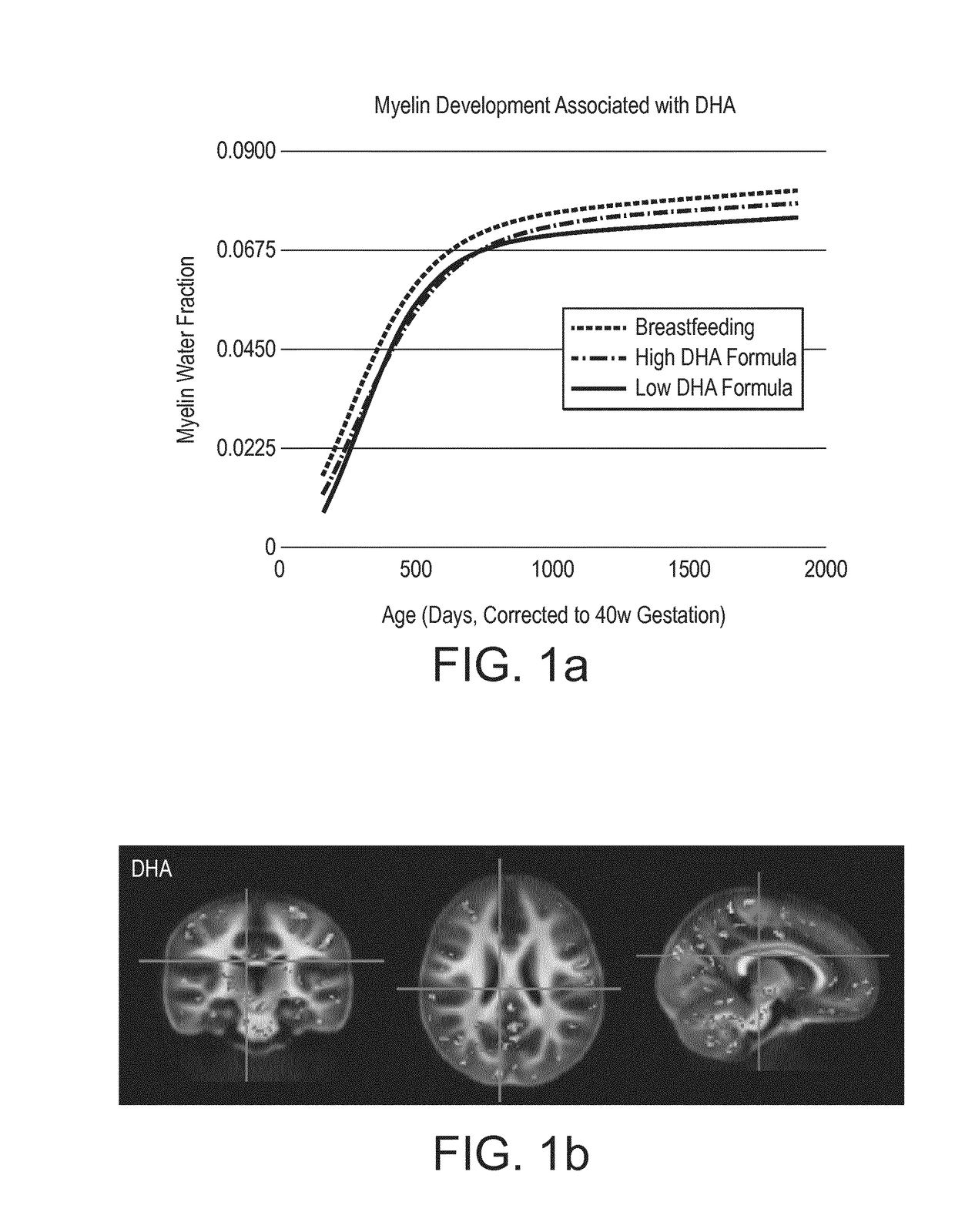
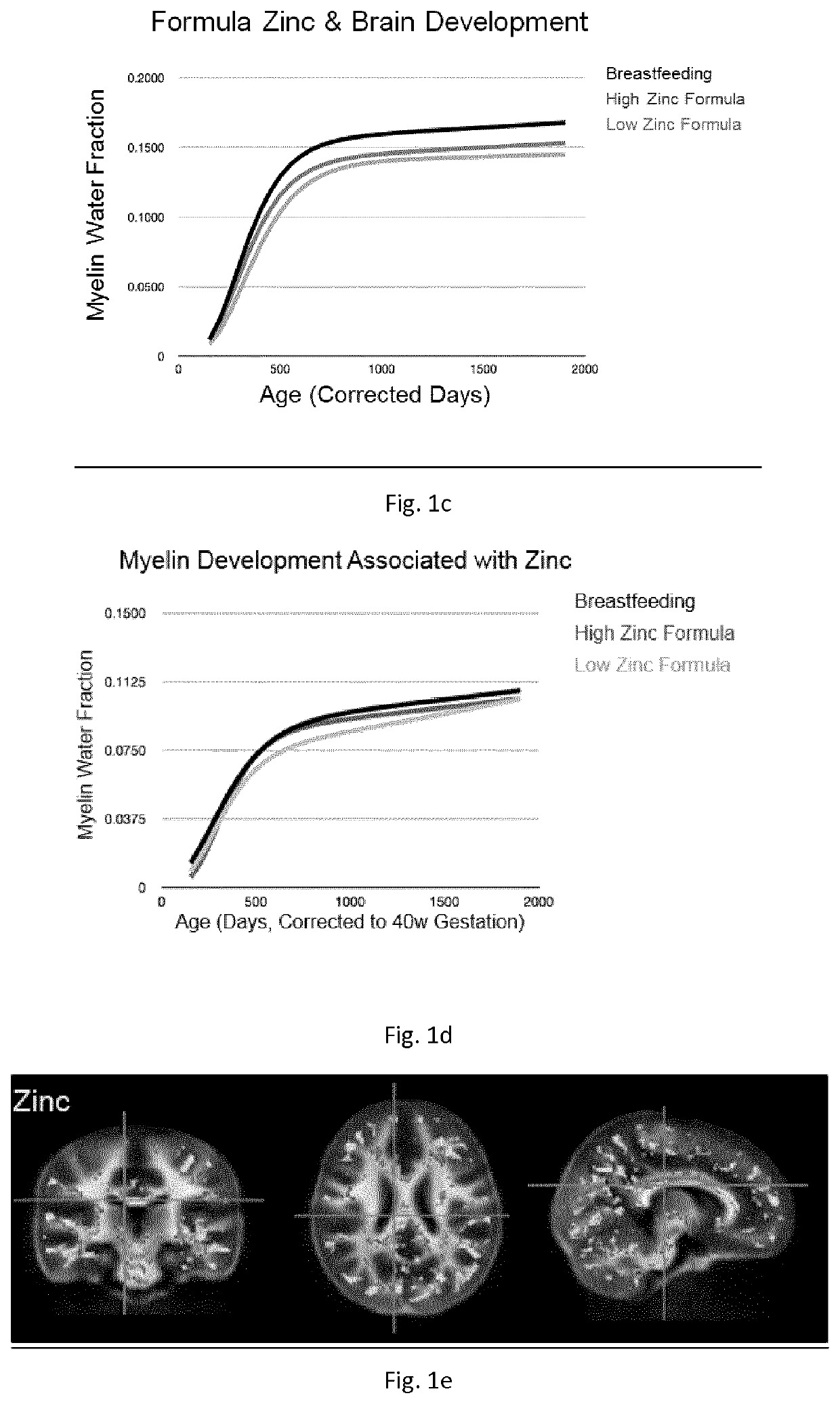
Nutritional compositions and infant formulas to promote myelination in the brain
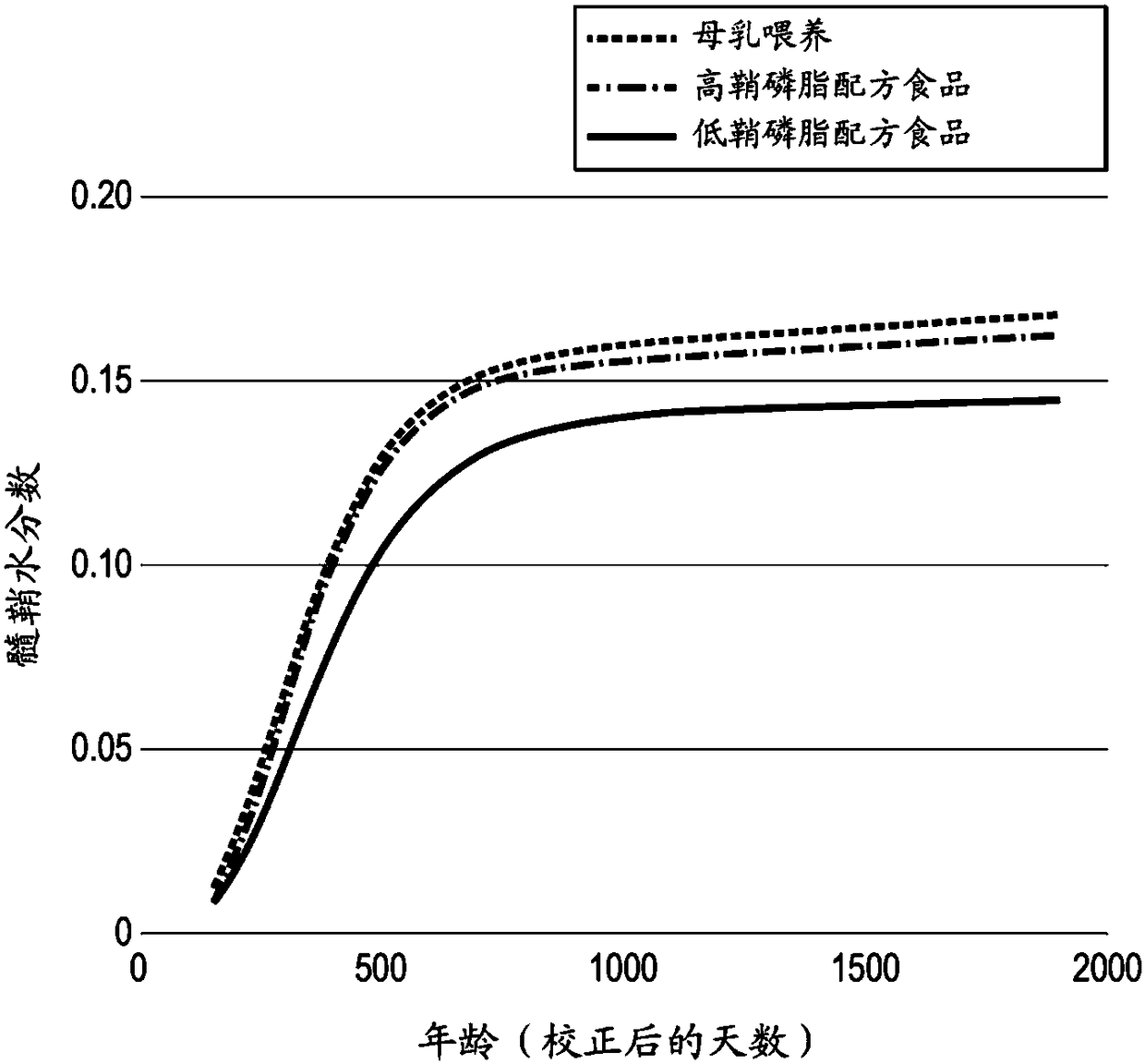
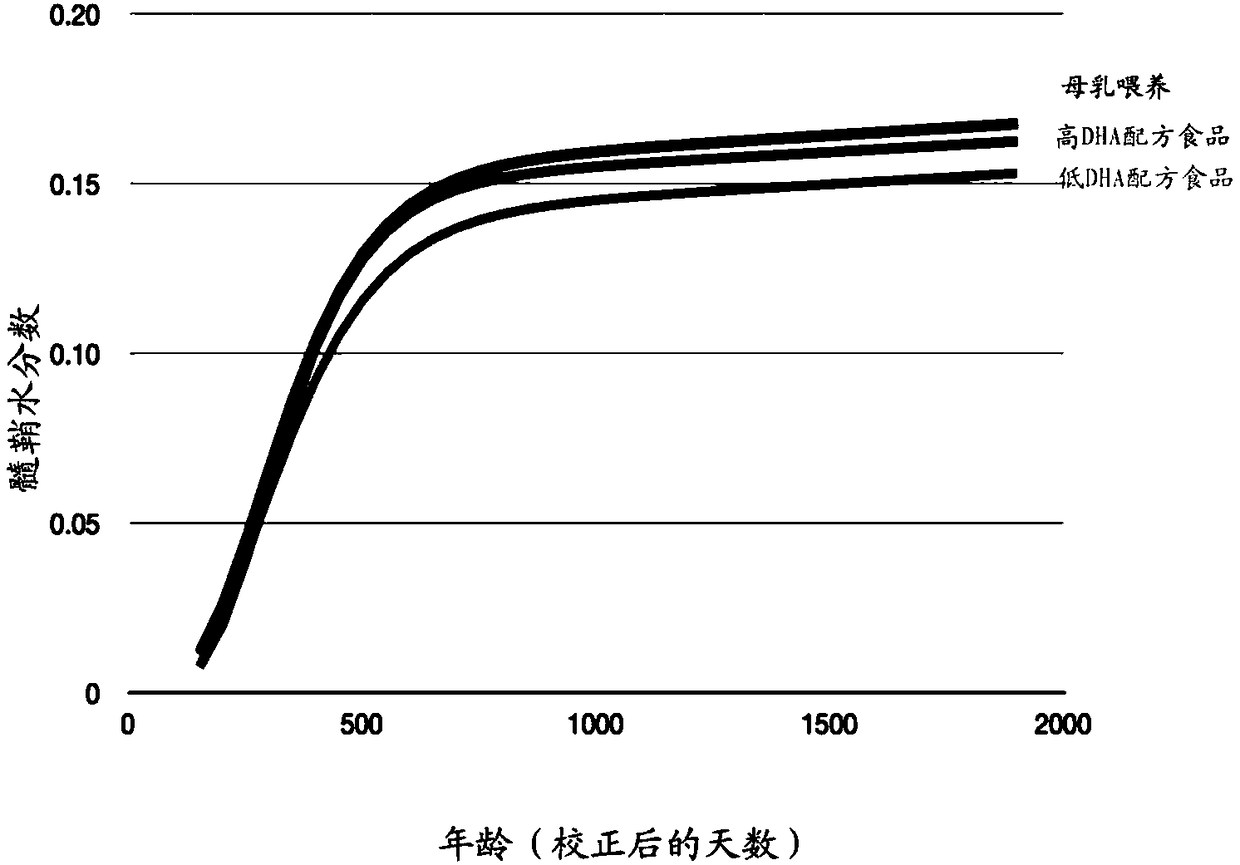
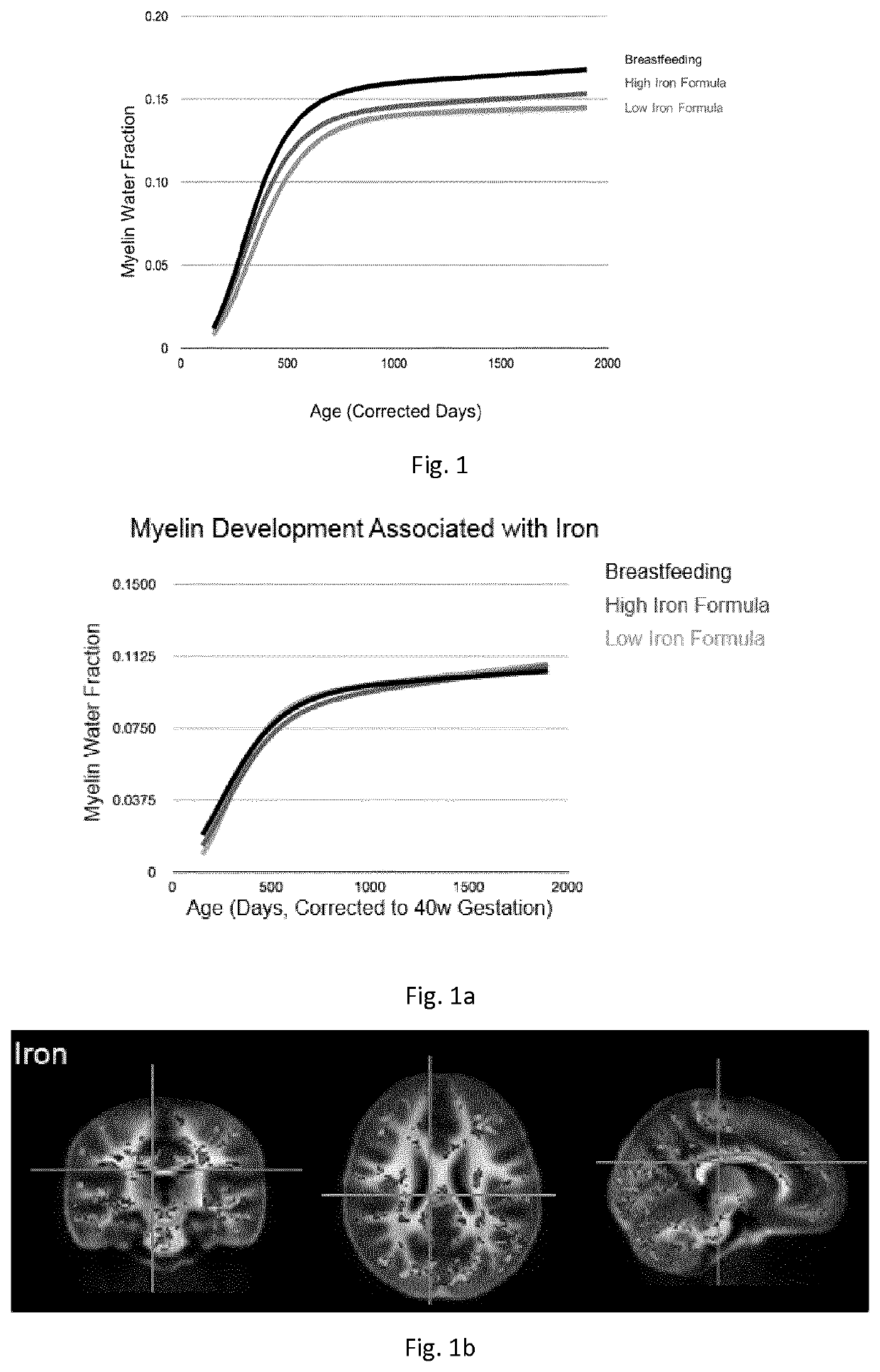
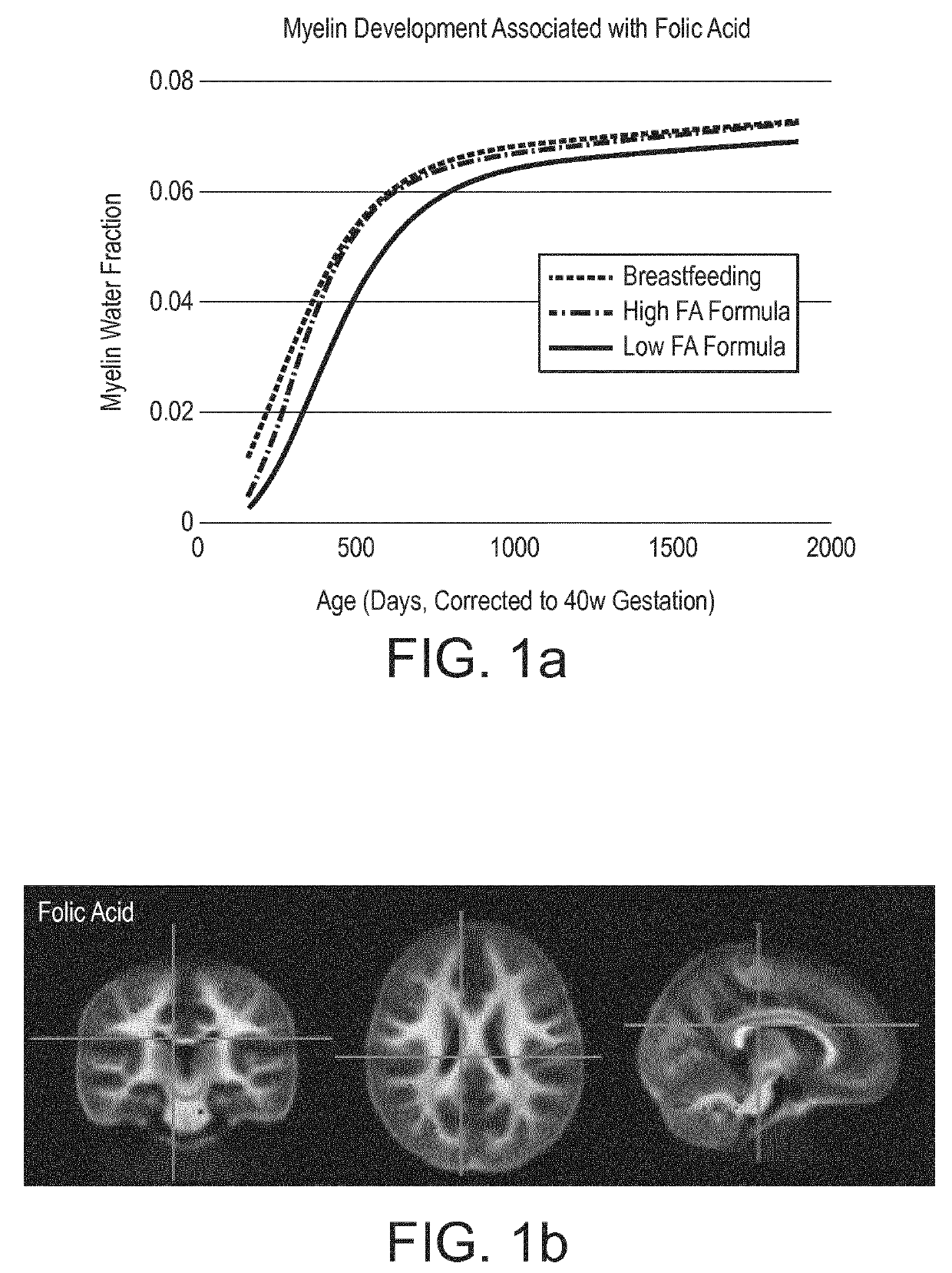
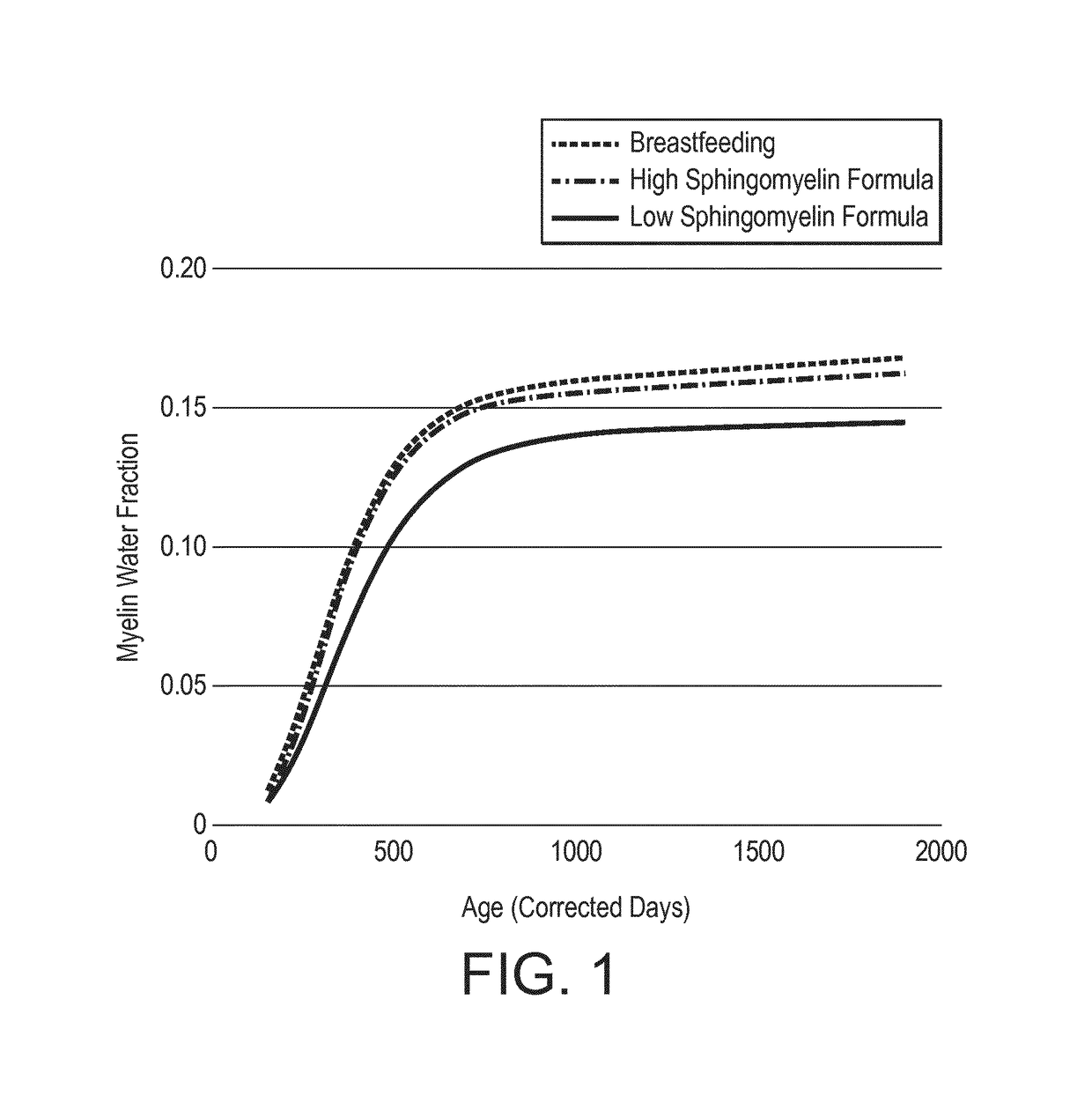
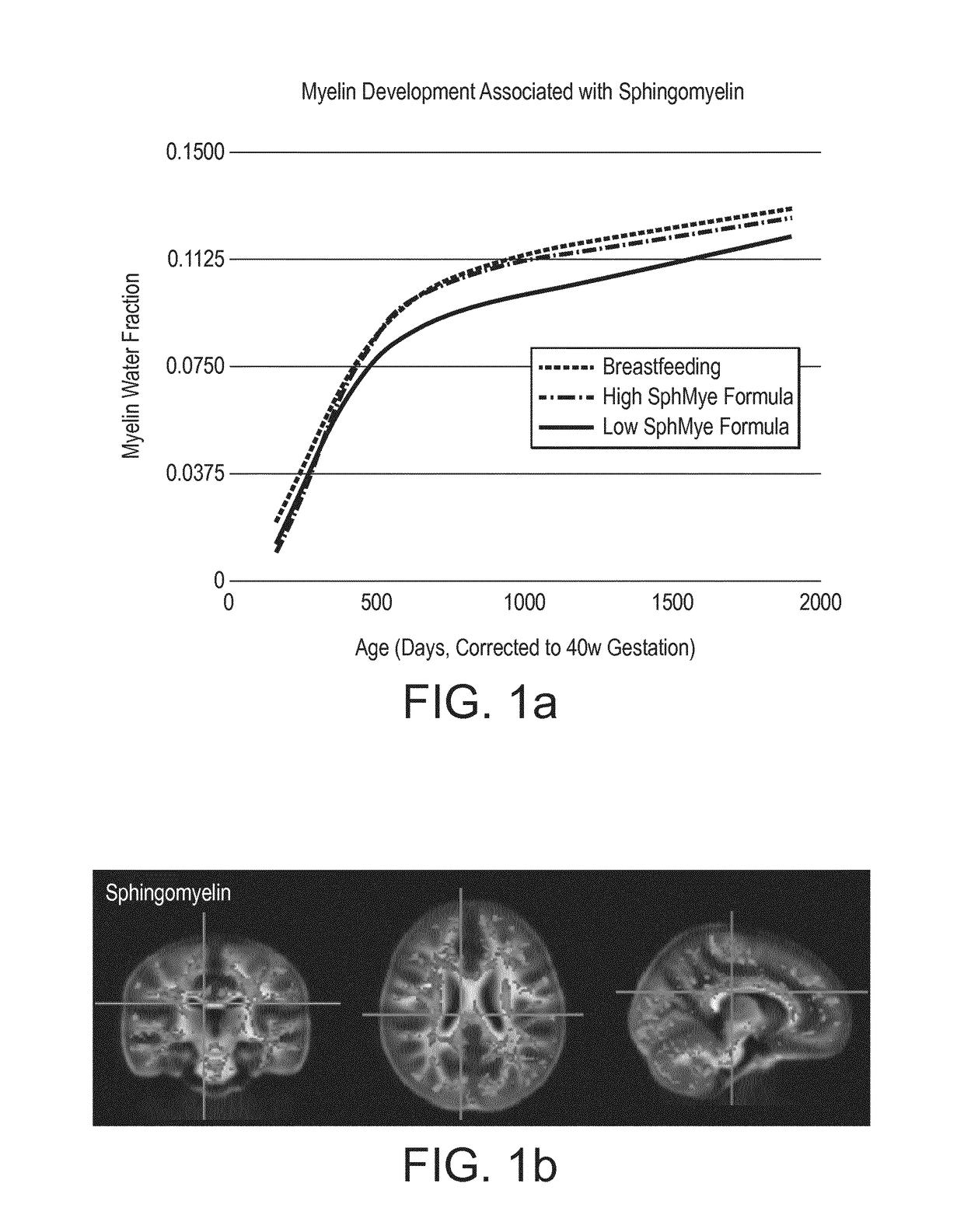
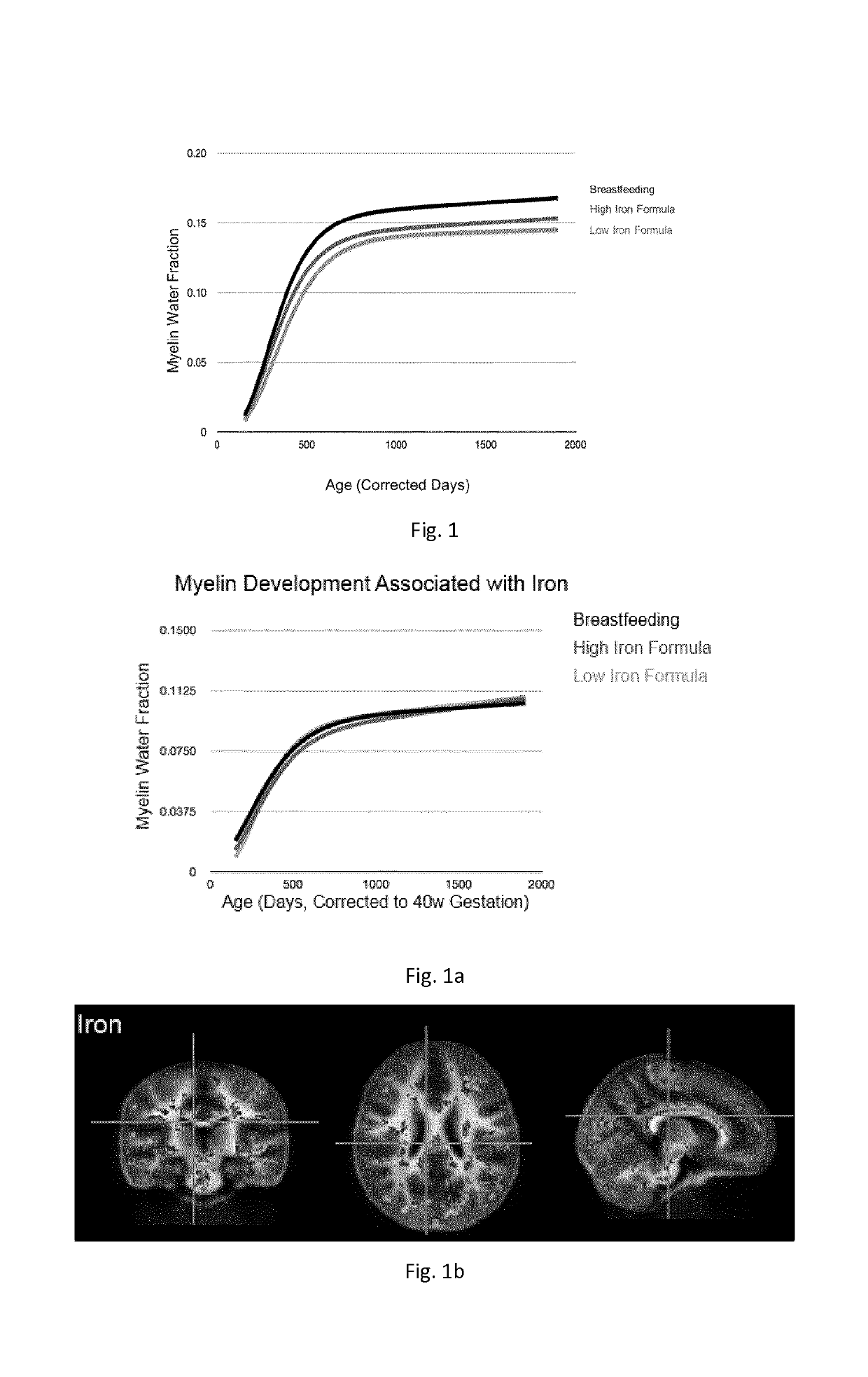
The invention relates to a nutritional composition for infants and young children, such as an infant formula or follow-on formula or growing up milk, preferably an infant formula, and comprising a phospholipid, a metabolic precursor and / or a metabolite thereof. The phospholipid promotes and / or supports an optimal myelination trajectory in the brain, such trajectory being close to that observed ininfants fed exclusively with human breast milk (HBM). The infants or young children can be between 0 and 60 months, preferably between 0 and 12 months of age.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
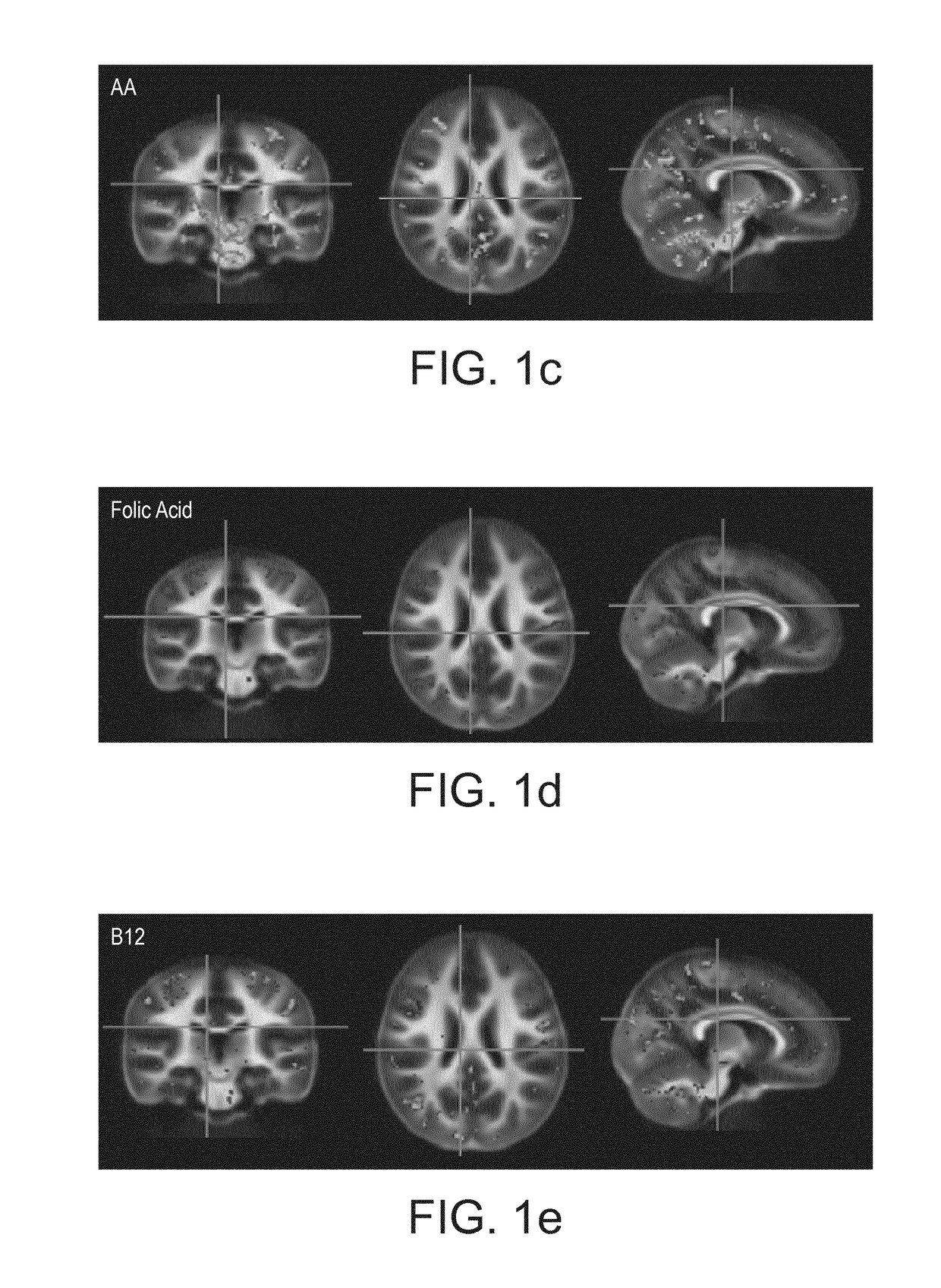
Nutritional compositions and infant formulas to promote myelination in the brain
The invention relates to a nutritional composition for infants and young children, such as an infant formula or follow-on formula or growing up milk, preferably an infant formula, and comprising a fatty acid derivative or mixtures thereof, for example ARA and / or DHA. The a fatty acid derivative or a mixture thereof, for example ARA and / or DHA promotes and / or supports an ideal myelination trajectory in the brain, such trajectory being close to that observed in infants fed exclusively with human breast milk (HBM). The infants or young children can be between 0 and 60 months, preferably between 0and 12 months of age.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Treating optic neuritis with induced pluripotent stem cell-derived oligodendrocyte precursor cells
PendingUS20190151367A1Improve efficiencyEnhance maturationNervous disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDamaged optic nerveProviding material
This document provides materials and methods for treating a damaged optic nerve in a mammal to restore visual function comprising administering a population of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived oligodendrocyte precursor cells. This document also provides materials and methods for determining a remyelination potential quotient of a population of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived oligodendrocyte precursor cells. This document also provides materials and methods for screening factors that enhance maturation or myelination efficiency of an induced pluripotent stem cell-derived oligodendrocyte precursor cell or cells.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Nutritional composition and infant formula for promoting myelination of the brain
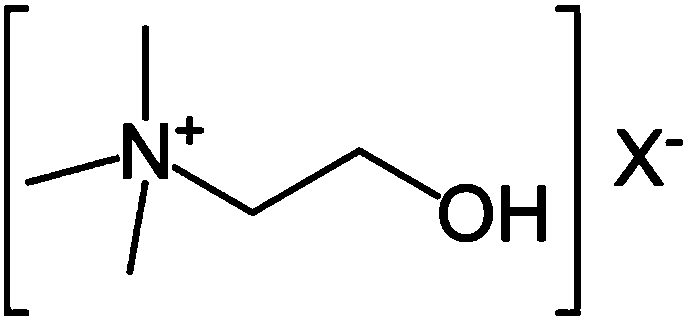
A synthetic nutritional composition comprising choline for use to promote, support or optimise de novo myelination, in particular the de novo myelination trajectory, and / or brain structure, and / or brain connectivity, and / or intellectual potential and / or cognitive potential and / or learning potential and / or cognitive functioning in a subject, in particular a formula fed subject.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Nutritional composition and infant formula for promoting myelination of the brain
ActiveUS20180360789A1Heavy metal active ingredientsNervous disorderFormula fedNutritional composition
A synthetic nutritional composition comprising a fatty acid derivative for use to promote, support or optimise de novo myelination, in particular the de novo myelination trajectory, and / or brain structure, and / or brain connectivity, and / or intellectual potential and / or cognitive potential and / or learning potential and / or cognitive functioning in a subject, in particular a formula fed subject.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Compounds and methods for promoting myelination
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
A kind of measuring method of gm7237 to central nervous myelinization
ActiveCN110542673BPromote formationOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderMyelin body formationMyelin sheaths
Owner:ZUNYI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Compositions and methods for increasing remyelination
InactiveUS20190336490A1Increase differentiationNervous disorderMuscular disorderMyelin body formationHistamine H3 receptor
Provided are compositions and methods comprising a MAChR antagonist / inverse agonist / partial agonist and a histamine H3 receptor antagonist / inverse agonist / partial agonist for increasing proliferation Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells (OPCs) into mature, myelinating oligodendrocytes, and related methods of treating demyelination disorders.
Owner:FREQUENCY THERAPEUTICS INC
Construction method of insufficiency of myelination and myelination aplastic disorder animal model
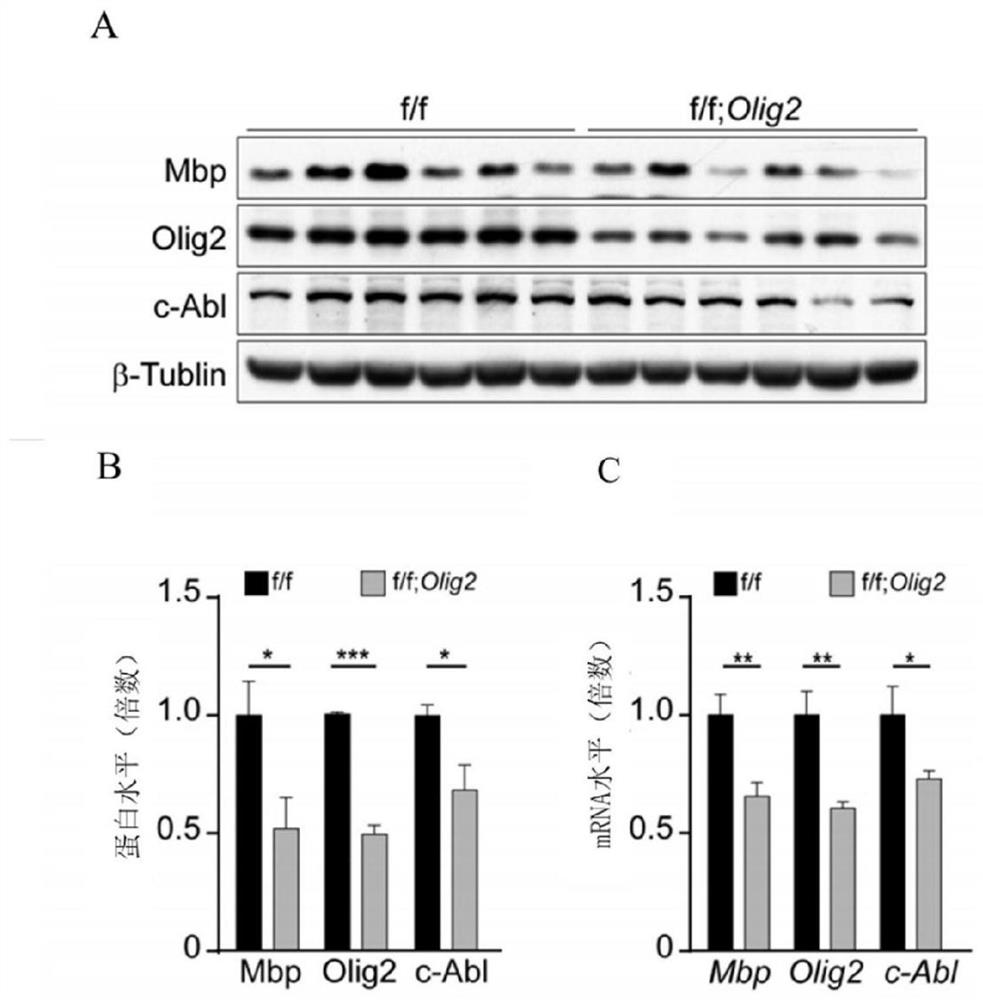
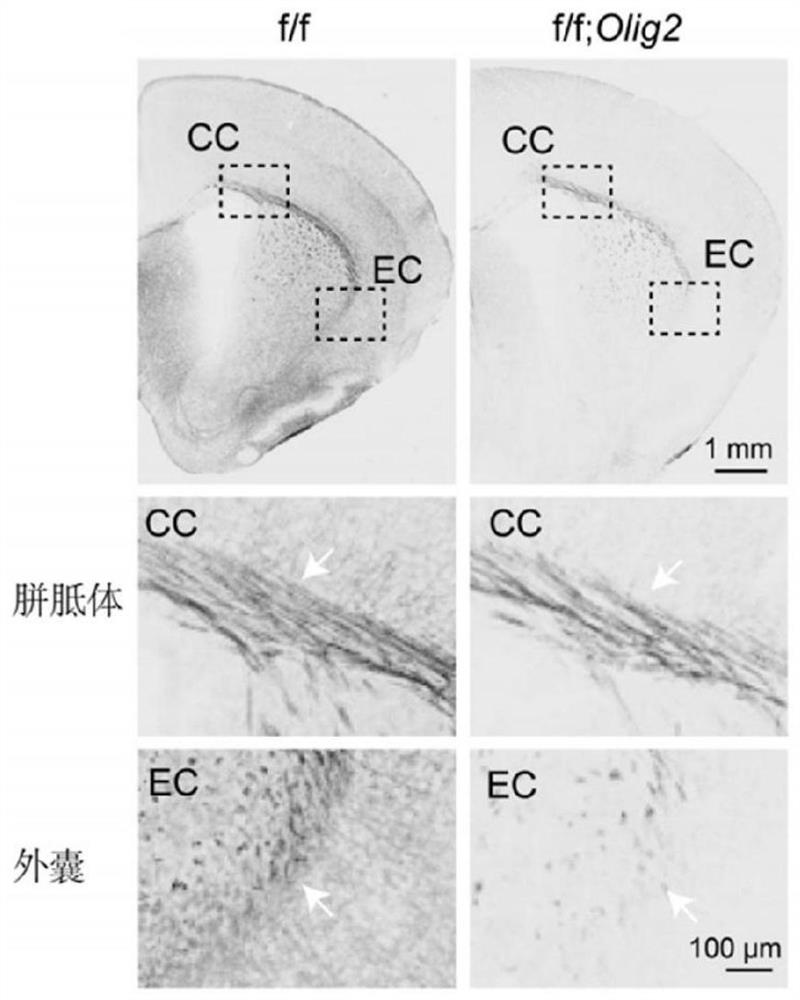
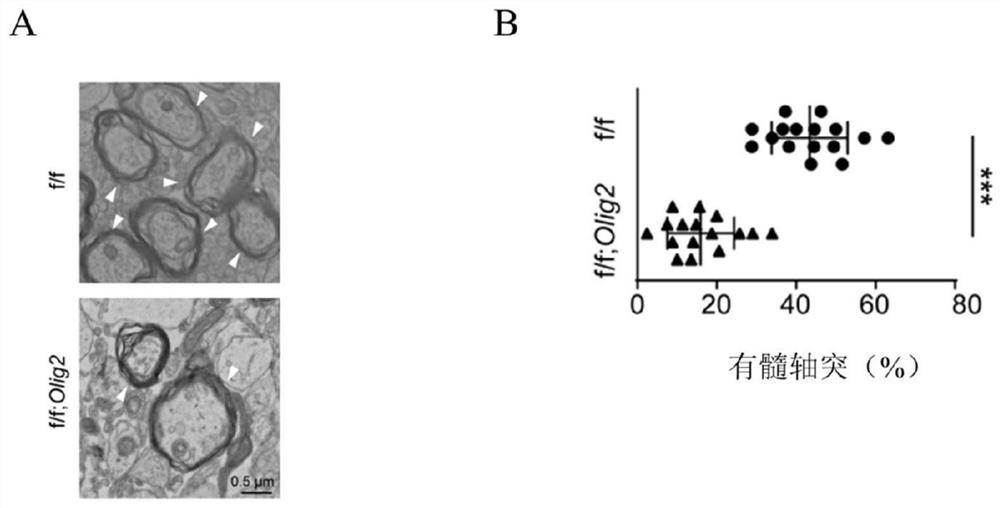
The invention discloses a construction method of an animal model with insufficiency of myelination and myelination aplastic disorder. The research proves that the knockout of c-Abl can cause insufficient myelin sheath formation of mice and delay of myelin sheath regeneration of mice to cause obstacles, and on the basis of the research results, an animal model with insufficient myelin sheath formation and myelin sheath regeneration obstacles can be constructed by knocking out c-Abl, so that a research basis is provided for researching a myelin sheath formation mechanism.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Peripheral nerve injury repairing system
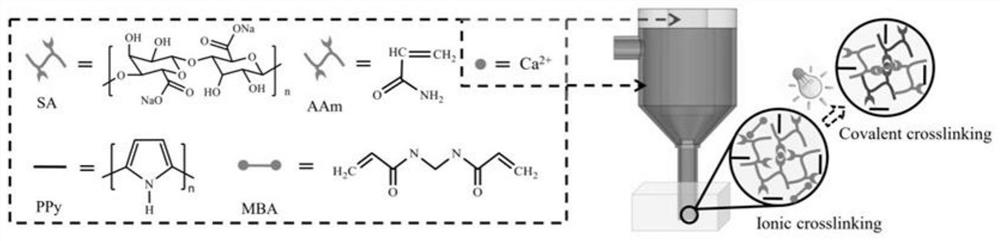
ActiveCN113577382APromote repairElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsMyelin body formationPolypyrrole
The invention discloses a peripheral nerve injury repair system, and belongs to the field of peripheral nerve injury repair. The peripheral nerve injury repairing system comprises nerve conduit preparation, nerve conduit carrying NGF-7S and nerve conduit carrying NGF-7S combined magnetic stimulation application. A triple-network micro-fluidic hydrogel nerve conduit composed of alginate / calcium ions, polyacrylamide and polypyrrole is loaded with NGF-7S, the conductive nerve conduit can be caused to generate variable electromotive force in a pulsed magnetic field generated by an 8-shaped coil, directional growth and migration of Schwann cells are helped, myelin sheath formation is promoted in a non-invasive mode, and the nerve conduit can be used for treating myelin sheath diseases. Growth and differentiation of nerve cells are jointly promoted through slow controlled release of the carried NGF-7S and endogenous secreted nerve growth factors (NGF) of Schwann cells, and nerve regeneration and functional recovery of sciatic nerve defect rats can be promoted through combination of nerve conduit carried NGF-7S and magnetic stimulation.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Topical application of nerve labeling dyes for image-guided surgery
The present invention relates to a topical agent that binds specifically to myelin basic protein and its method of use and determining myelination in the subject by detecting the agent present in the subject. A kit containing the agent or its derivatives for use in detecting myelin basic protein is also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods for promoting myelination and for treating demyelinating diseases
PendingUS20210023218A1Nervous disorderImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseMyelin body formation
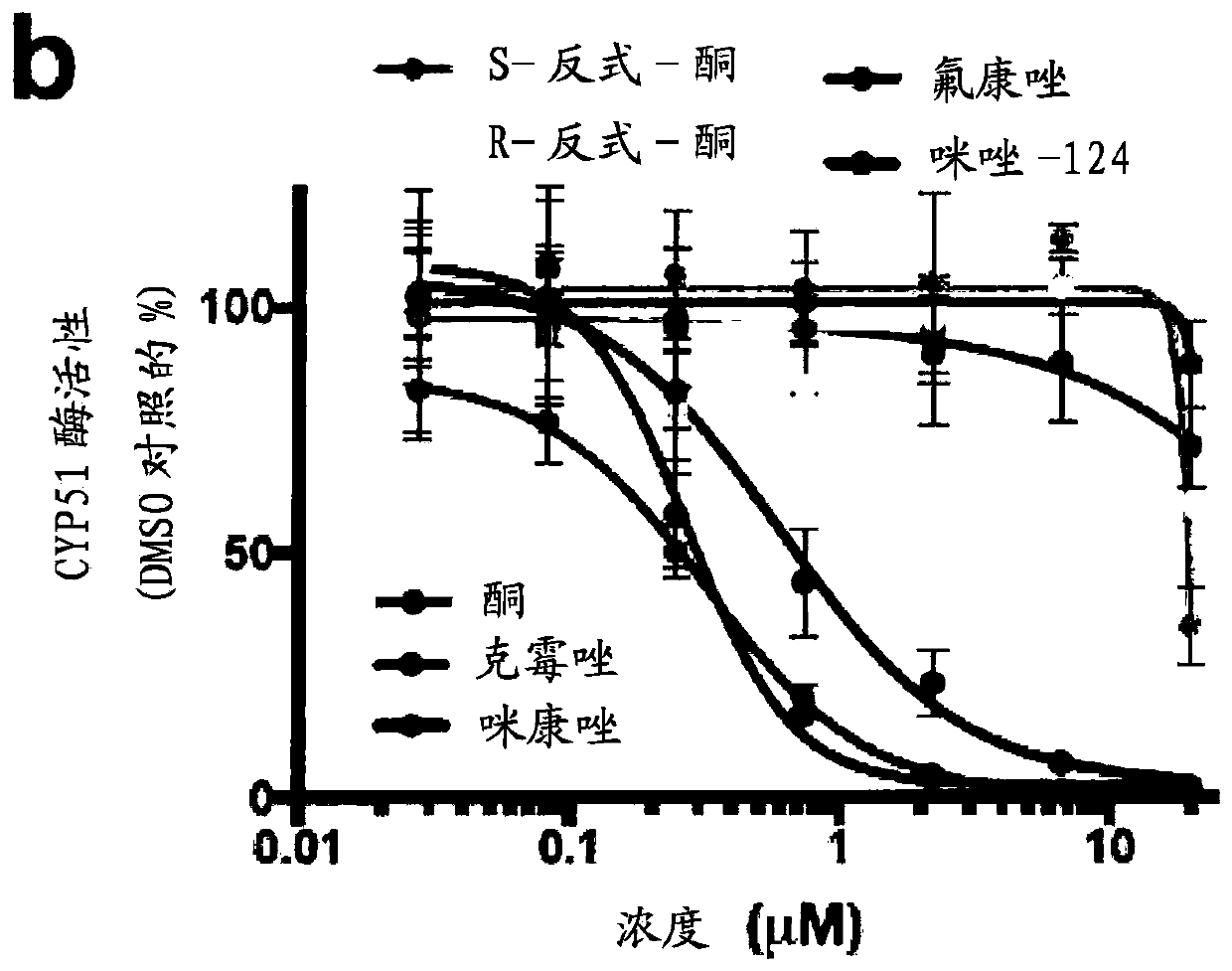
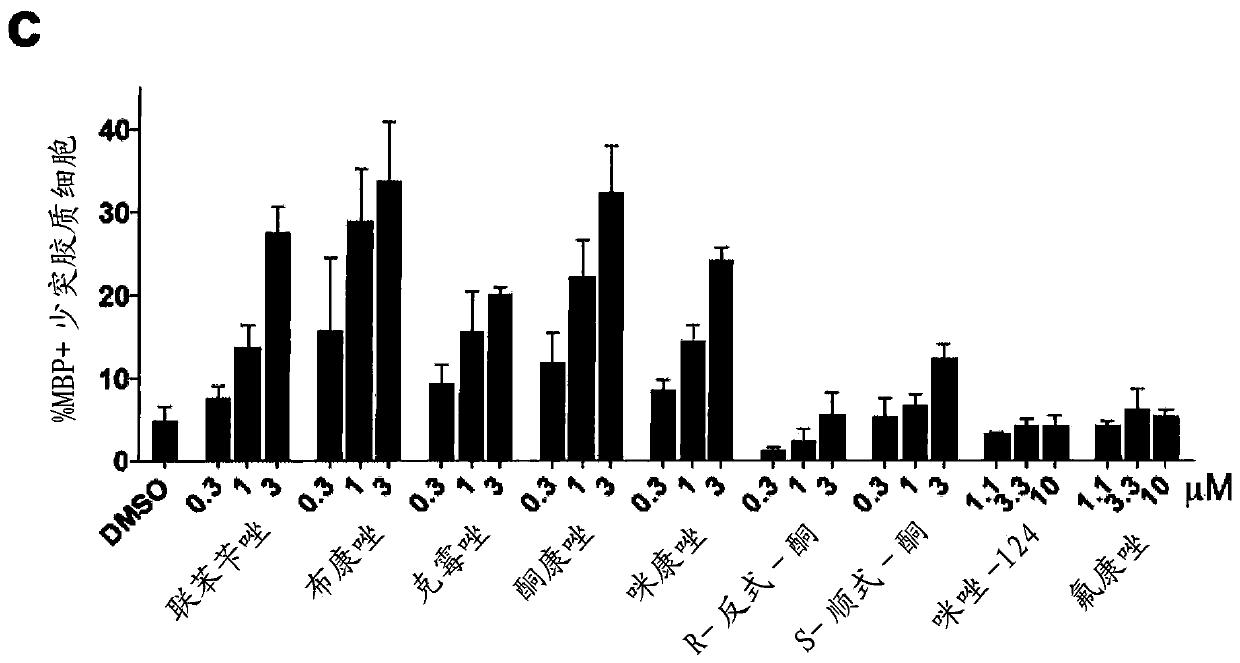
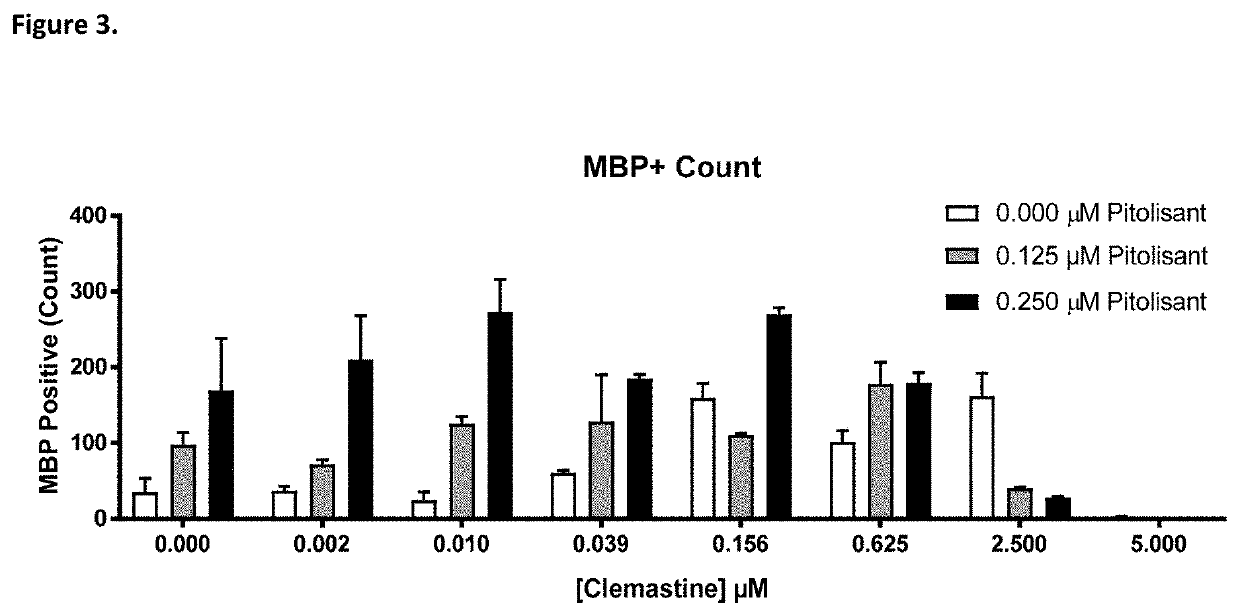
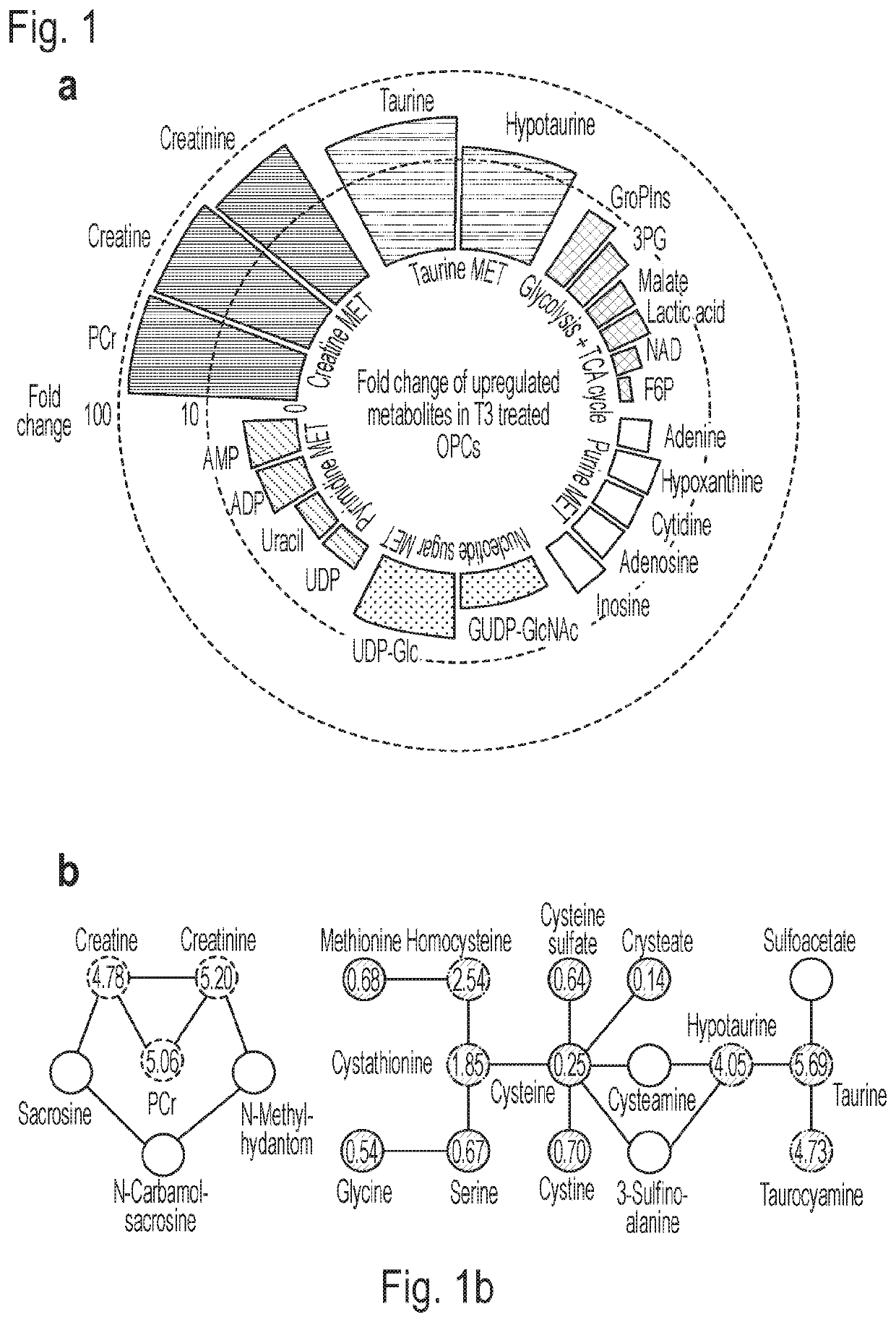
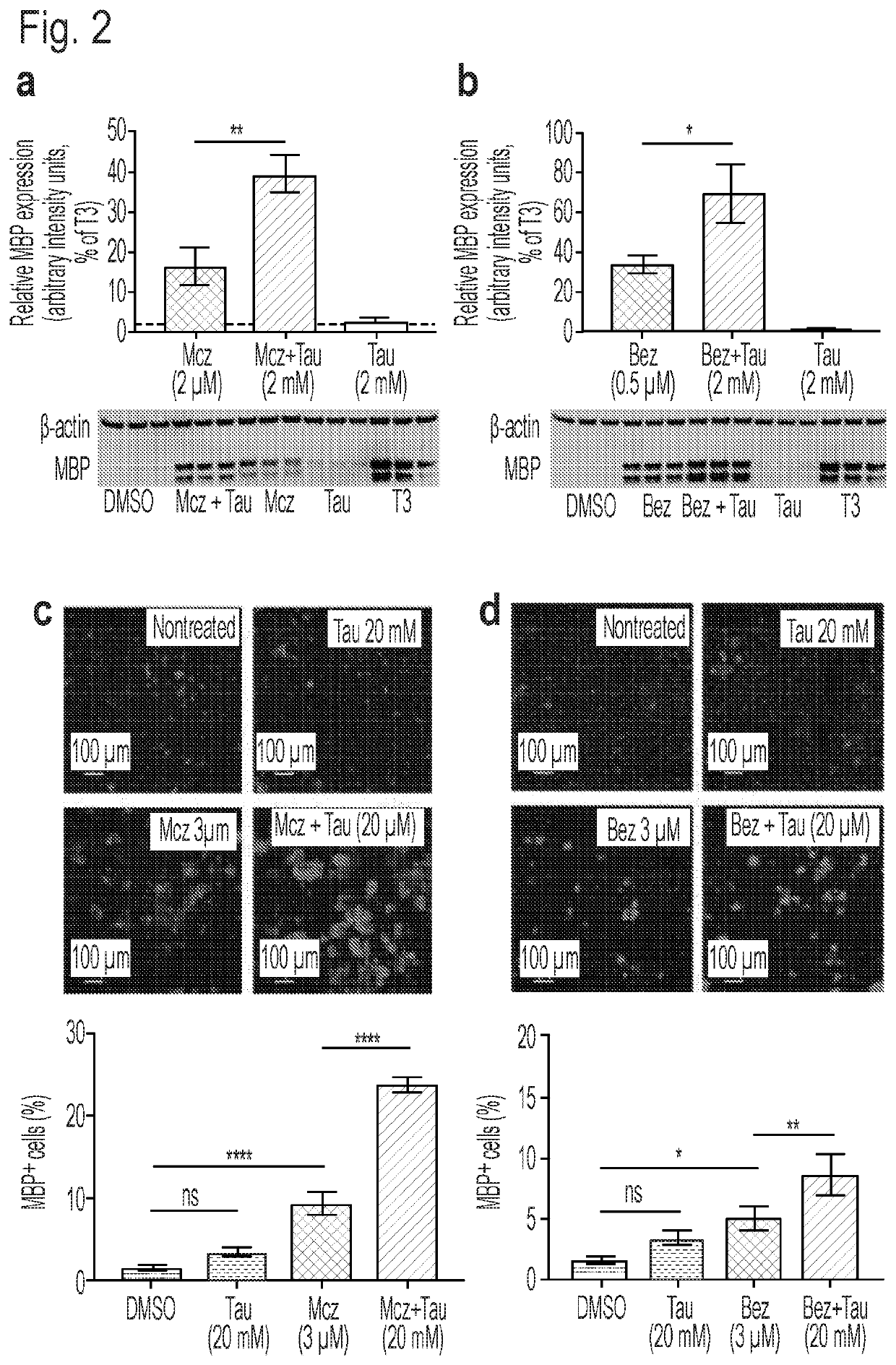
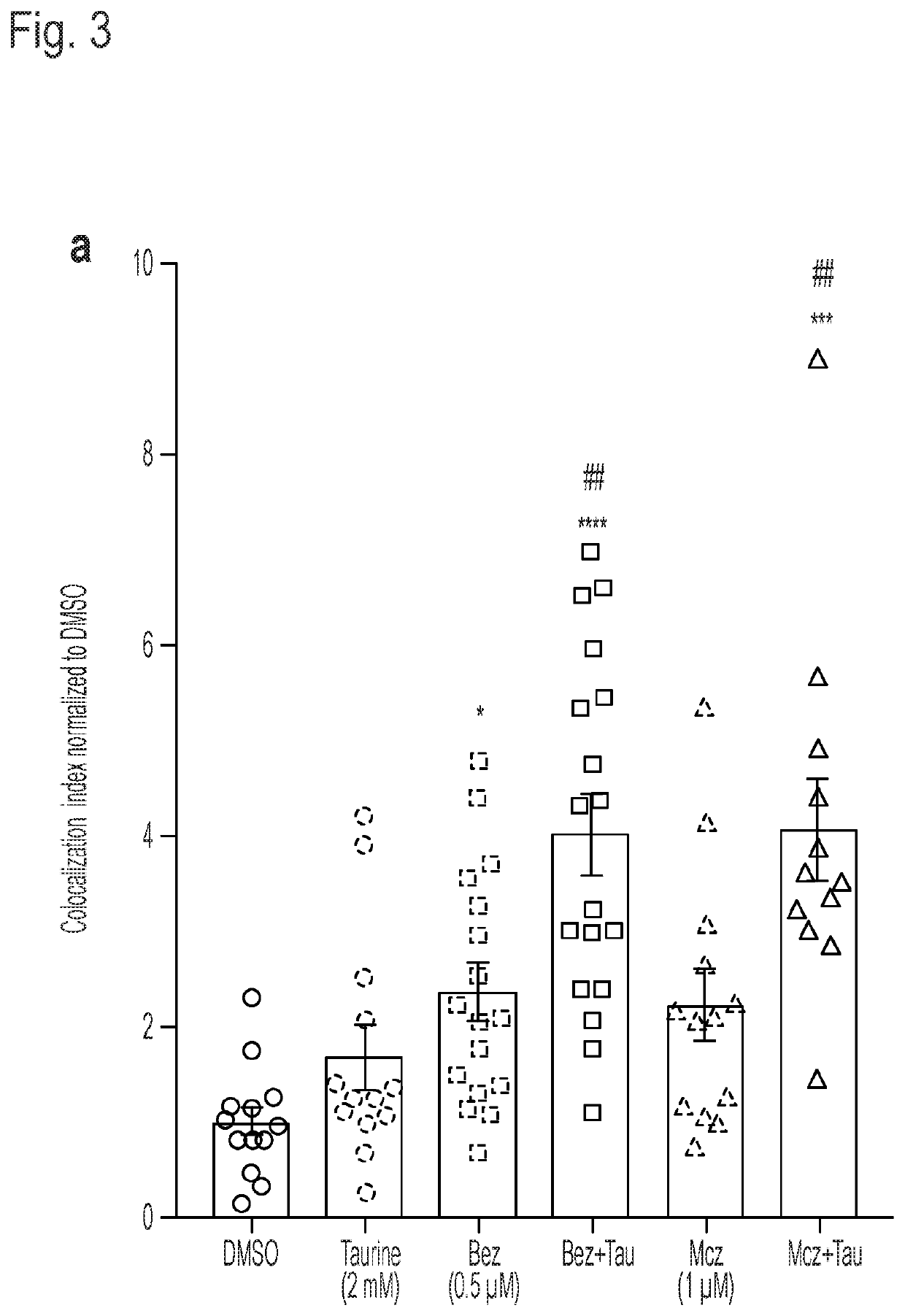
This invention provides novel methods for treating or ameliorating symptoms of demyelinating diseases such as multiple sclerosis. The methods involve administering to subjects in need of treatment a pharmaceutical composition that contains a therapeutically effective amount of taurine and also a compound that induces oligodendrocyte precursor cell (OPC) differentiation (e.g., T3, benztropine, clemastine or miconazole). Some of the methods additionally involve administration to the subject a known agent for treating demyelinating diseases (e.g., SIP receptor agonists) or a known disease modifying drug. The invention also provides methods for increasing myelination and methods for promoting OPC differentiation into oligodendrocytes. These methods entail contacting a population of OPCs with a combination of taurine and a known OPC differentiation-inducing agent such as T3, clemastine, benztropine or miconazole.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Nutritional compositions and infant formula for promoting de novo myealination
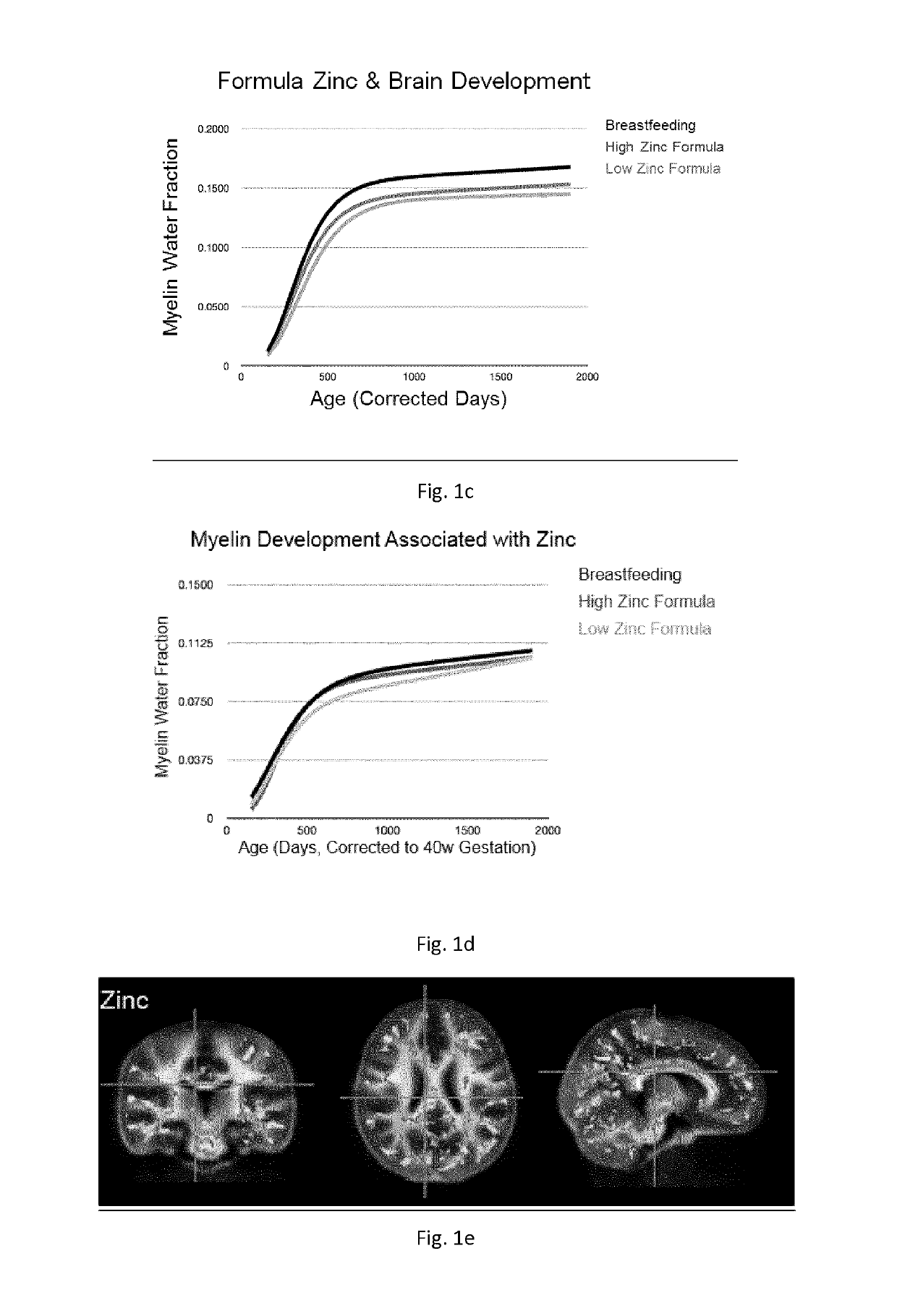
A synthetic nutritional composition comprising a mineral for use to promote, support or optimise de novo myelination, in particular the de novo myelination trajectory, and / or brain structure, and / or brain connectivity, and / or intellectual potential and / or cognitive potential and / or learning potential and / or cognitive functioning in a subject, in particular a formula fed subject.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
SP35 antibodies and uses thereof
InactiveCN101495509BSenses disorderNervous disorderOligodendrocyte differentiationMonoclonal antibody
Endogenous Sp35 is a negative regulator for neuronal survival, axon regeneration, oligodendrocyte differentiation and myelination (Negative Regulator). Molecules that block endogenous Sp35 function, such anti-Sp35 antibodies can be used as therapeutics for the treatment of neuron and oligodendrocyte dysfunction. The present invention provides antibodies specific for Sp35, and methods of using such antibodies as antagonists of endogenous Sp35 function. The invention further provides specific hybridoma and phage library-derived monoclonal antibodies, nucleic acids encoding these antibodies, and vectors and host cells comprising these antibodies. The invention further provides methods of promoting oligodendrocyte survival and myelination in a vertebrate, comprising administering to a vertebrate in need of such treatment an effective amount of an anti-Sp35 antibody.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
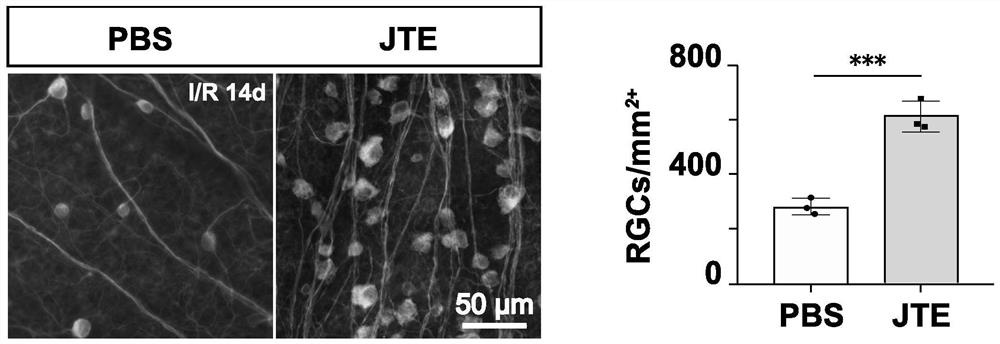
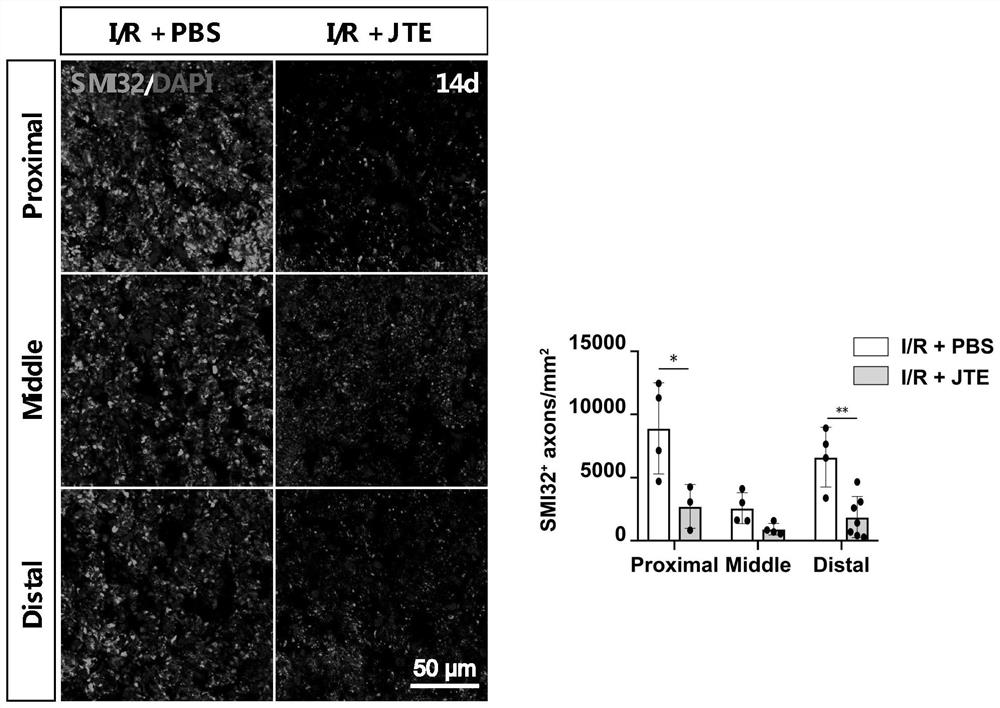
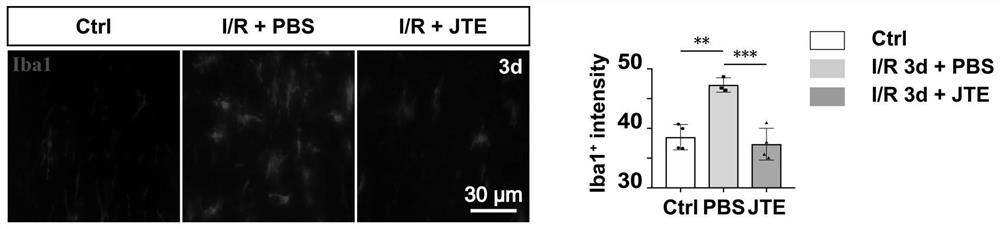
Application of JTE-013 in preparation of medicine for protecting glaucoma optic nerve injury
PendingCN114796213AProtection from damageOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderIntra ocular pressureMyelin body formation
The invention discloses an application of JTE-013 in preparation of a medicine for protecting glaucoma optic nerve injury. According to the application, the JTE-013 is applied to treatment of an ischemia reperfusion model of a glaucoma related animal model for the first time, the treatment effect of the JTE-013 is determined, and the JTE-013 can obviously improve retinal ganglion cell injury caused by increase of intraocular pressure; axonal injury caused by increase of intraocular pressure can be obviously improved; the activation of microglial cells can be obviously inhibited; myelin sheath regeneration and proliferation of myelin sheath formation cell oligodendroglia cells can be obviously promoted; the visual function can be obviously recovered.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN OPHTHALMIC CENT SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Nutritional compositions and infant formulas to promote myelination in the brain
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Compositions and their use
A synthetic nutritional composition comprising a vitamin for use to promote, support or optimise de novo myelination, in particular the de novo myelination trajectory, and / or brain structure, and / or brain connectivity, and / or intellectual potential and / or cognitive potential and / or learning potential and / or cognitive functioning in a subject, in particular a formula fed subject.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Nutritional composition and infant formula for promoting de novo myelination
ActiveUS20180360095A1Effective compositionHeavy metal active ingredientsNervous disorderMetabolitePhysiology
A synthetic nutritional composition comprising a phospholipid and / or a metabolic precursor and / or metabolite thereof for use to promote, support or optimise de novo myelination, in particular the de novo myelination trajectory, and / or brain structure, and / or brain connectivity, and / or intellectual potential and / or cognitive potential, and / or learning potential and / or cognitive functioning in a subject, in particular a formula fed subject.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Novel method and compounds for treatment of cognitive loss associated with adult onset leukodystrophy with axonal spheroids and pigmented glia (ALSP) and other neurodegenerative diseases involving reduced colony stimulating factor-1 receptor (CSF-1R) signaling
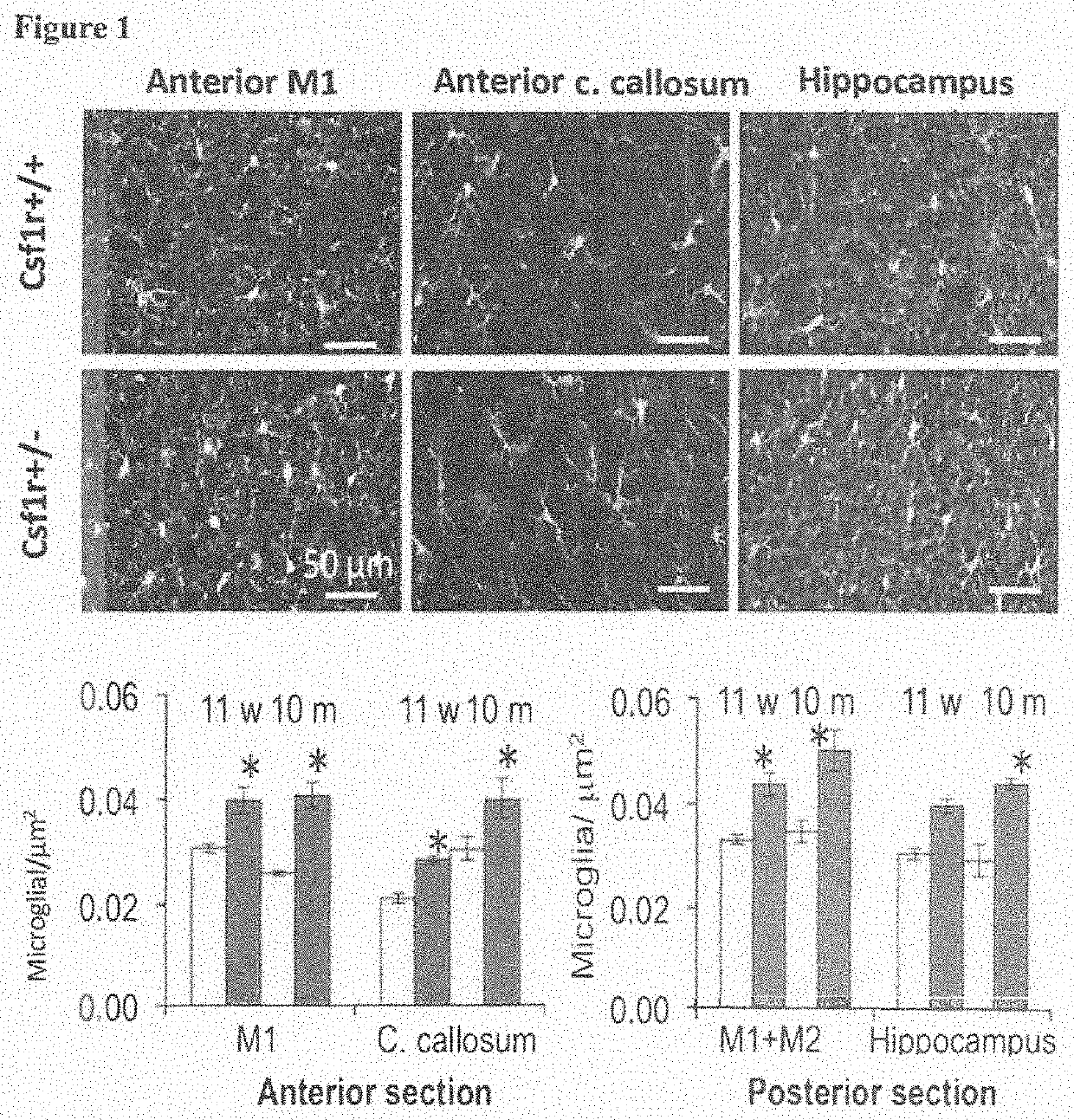
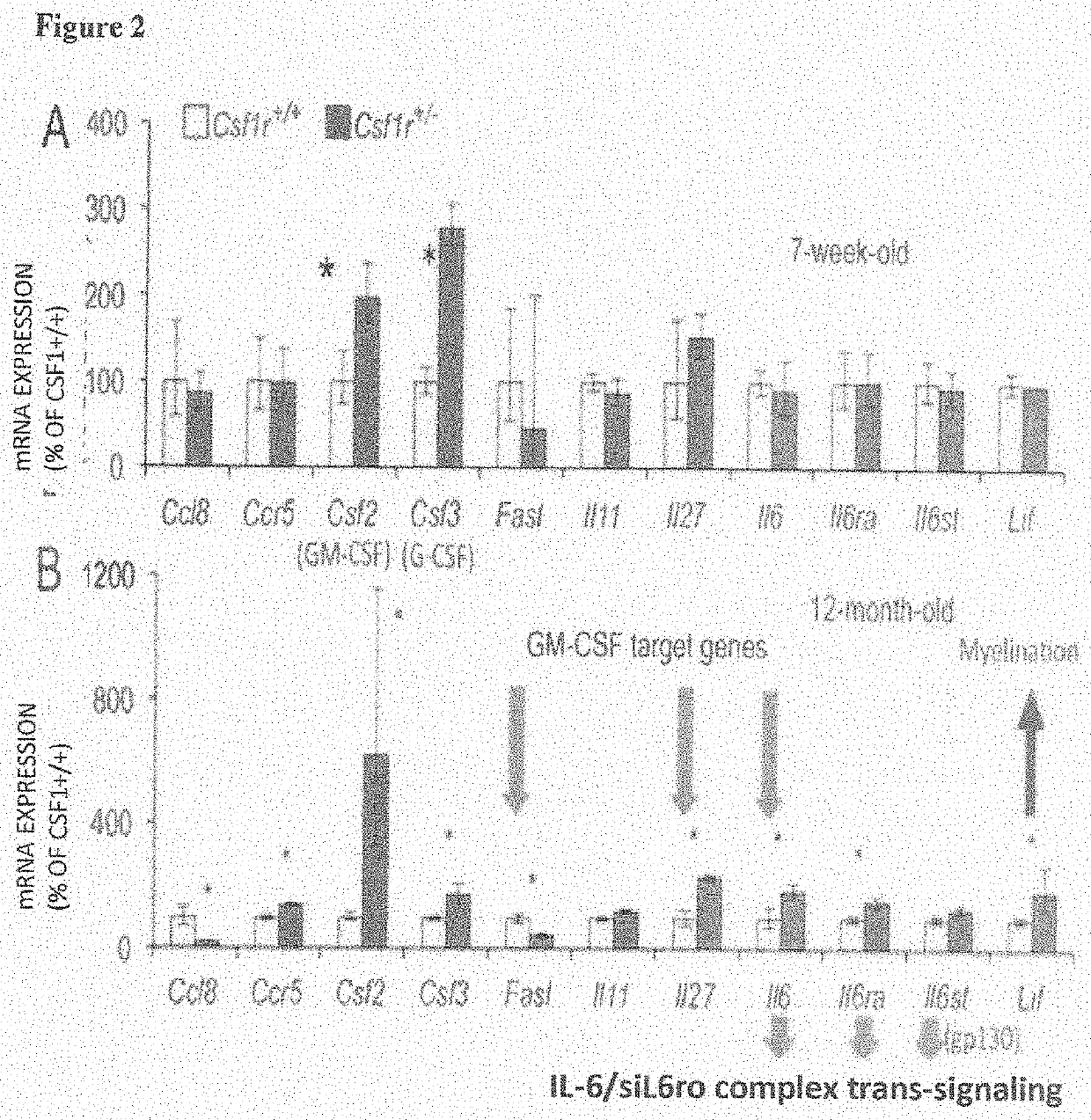
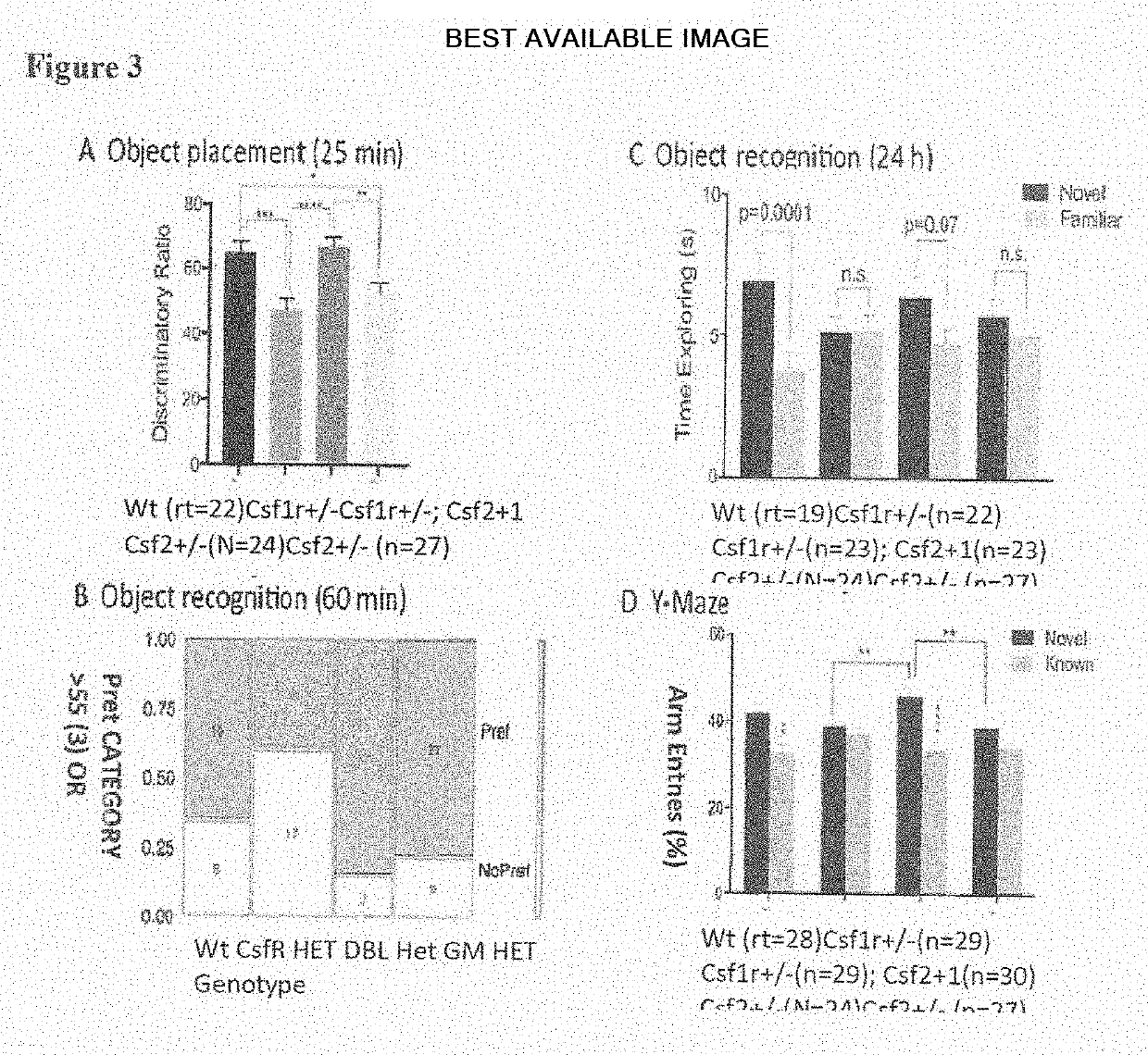
Adult-onset leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids and pigmented glia (ALSP) is caused by dominant inactivating mutations in the colony stimulating factor receptor 1 (CSF1R) kinase domain. GM-CSF haploinsufficiency corrects olfactory, cognitive and emotional functions lost in Csf1r+ / − mice. This correlates with the correction of microgliosis and microglial functions resulting in improvement of myelination and rescue of neurogenesis. However, GM-CSF haploinsufficiency fails to correct the motor deficits of Csf1r+ / − mice and cerebellar microgliosis. The present invention discloses methods and compositions using GM-CSF as a suitable therapeutic target to inhibit in amelioration of the cognitive impairments in ALSP and other in conditions involving inflammatory activation of microglia and macrophages, such as AD, ALS, multiple sclerosis, and hippocampal inflammation following radiation therapy. Treatment with GM-CSF inhibitors is beneficial in ALSP, as adult neurogenesis is important for memory, olfaction and prevention of anxiety / depression and early initiation of such treatment in carriers of CSF1R mutations may increase effectiveness. Balancing the actions of CSF-1R and GM-CSF signaling are necessary to preserve olfaction, cognition and emotional balance in aged mice. This balance is likely altered in many neurodegenerative diseases in which activated microglia contribute to the pathology.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
Lipid biomarker for autism and application of lipid biomarker
PendingCN113444787AReduce thicknessReduce expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisLipidomeDisease
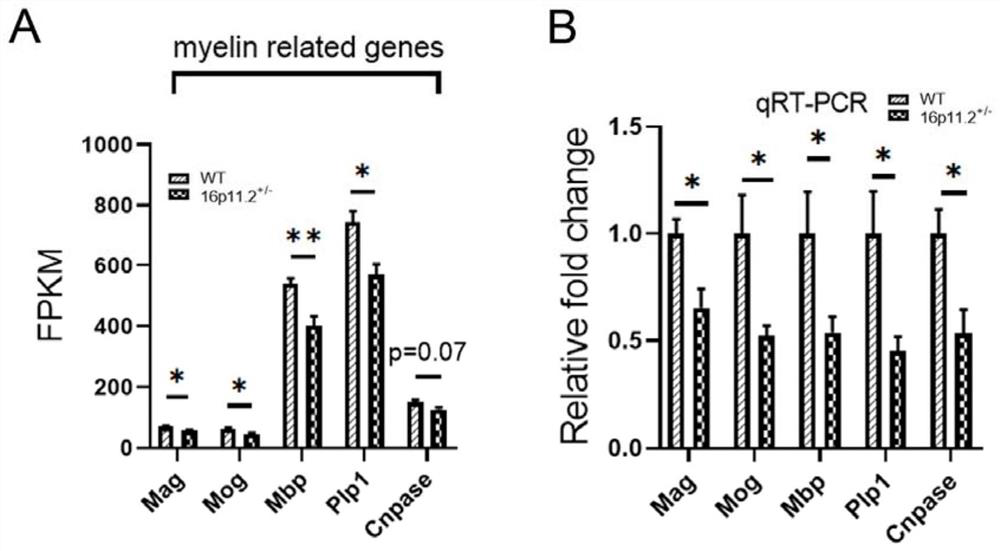
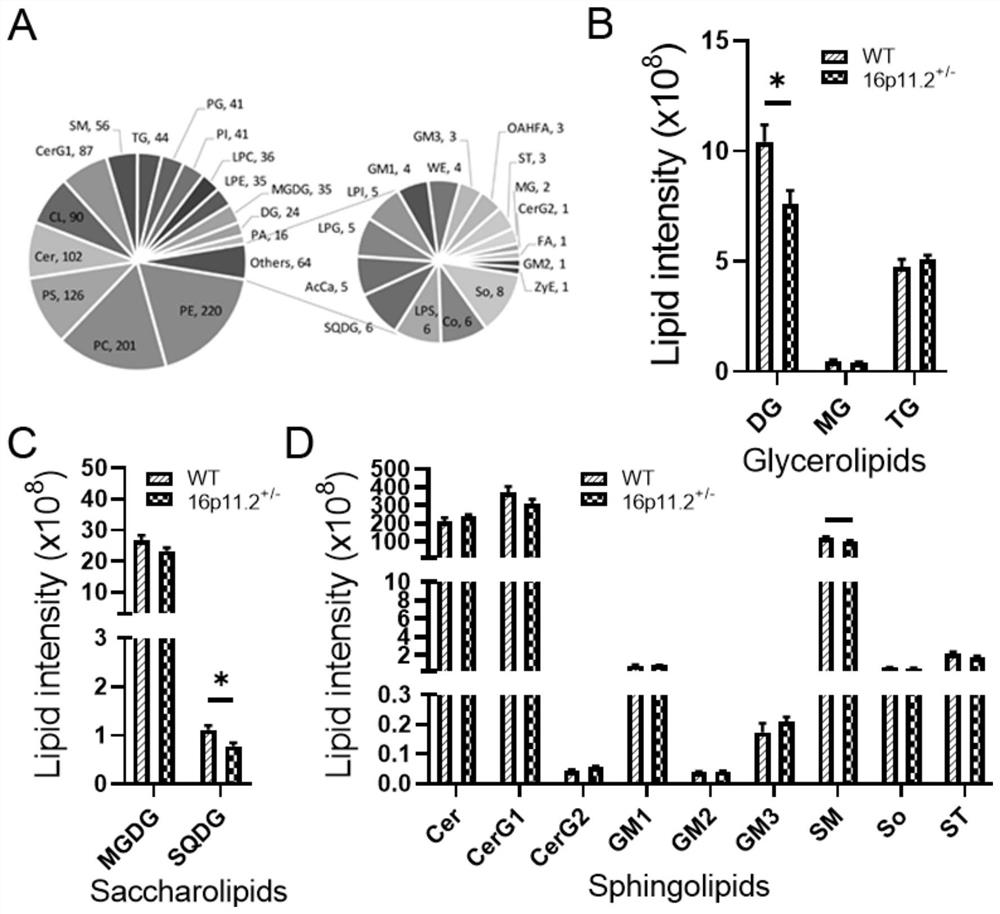
The invention relates to the field of disease diagnosis, in particular to a lipid biomarker for autism and application of the lipid biomarker. The invention discloses the effect of myelination in autism, and the result that reduction of myelination is an important reason of onset of autism possibly is found. Sphingomyelin (SM) and hexosyl ceramide (CerG1) are two types of important lipids forming a myelin sheath; and lipiomics results show that the contents of sphingomyelin and hexosyl ceramide of long acyl chains in autism model mice are significantly reduced. The two lipids can be used as potential biomarkers for autism diagnosis, and have important clinical prospects and economic values.
Owner:THE SEVENTH AFFILIATED HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV SHENZHEN
Nutritional compositions and infant formula for promoting de novo myealination
A synthetic nutritional composition comprising a mineral for use to promote, support or optimise de novo myelination, in particular the de novo myelination trajectory, and / or brain structure, and / or brain connectivity, and / or intellectual potential and / or cognitive potential and / or learning potential and / or cognitive functioning in a subject, in particular a formula fed subject.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
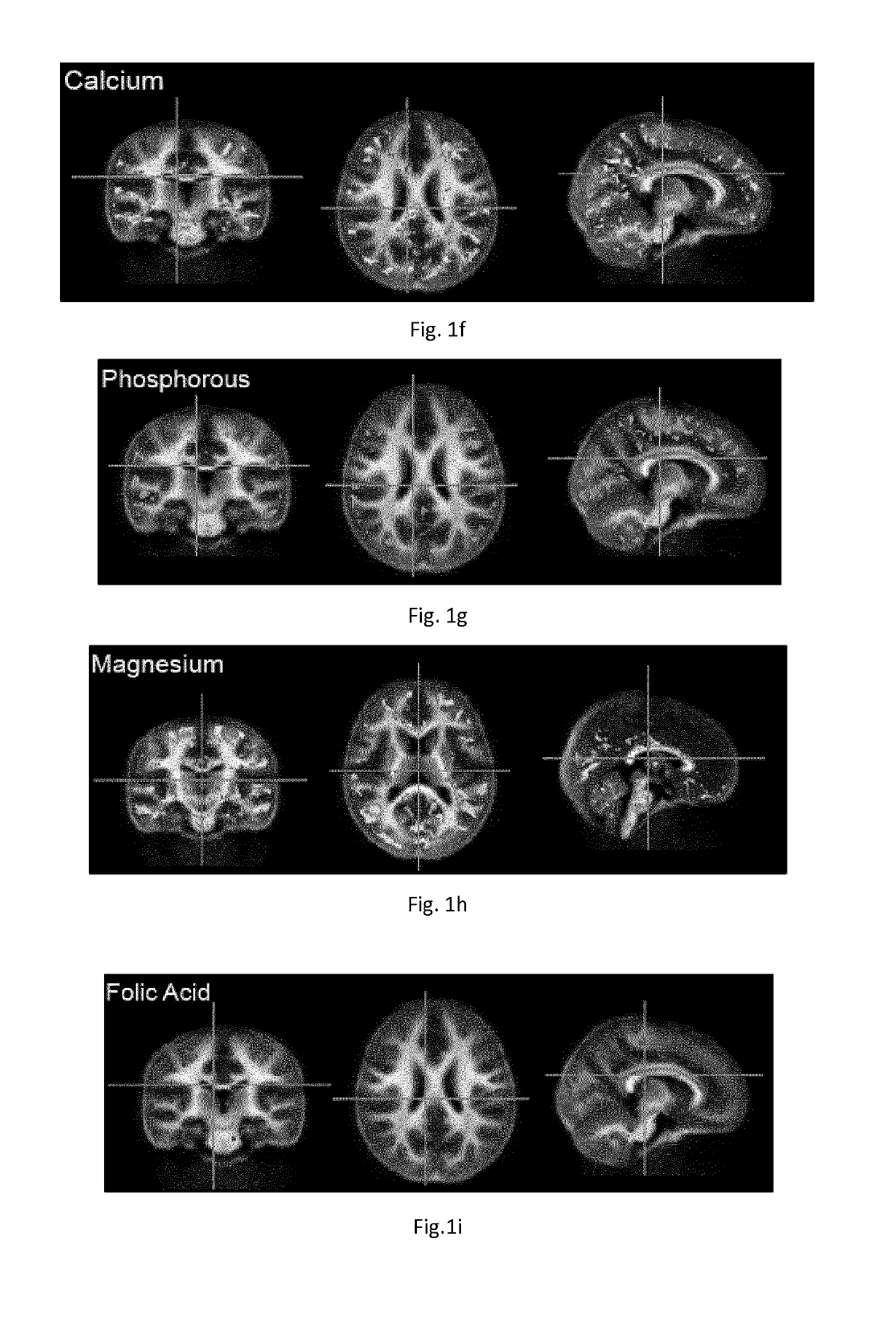
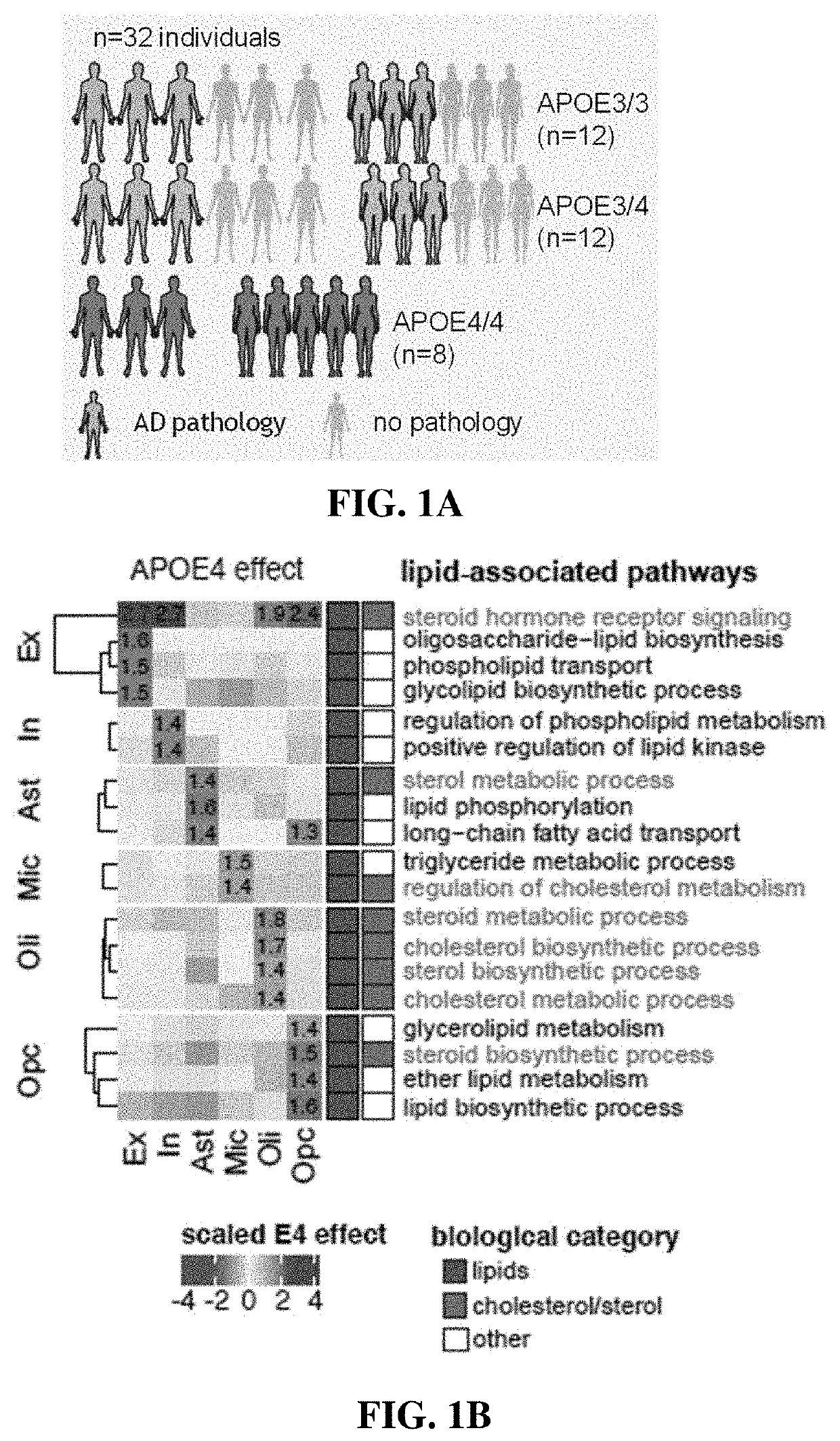
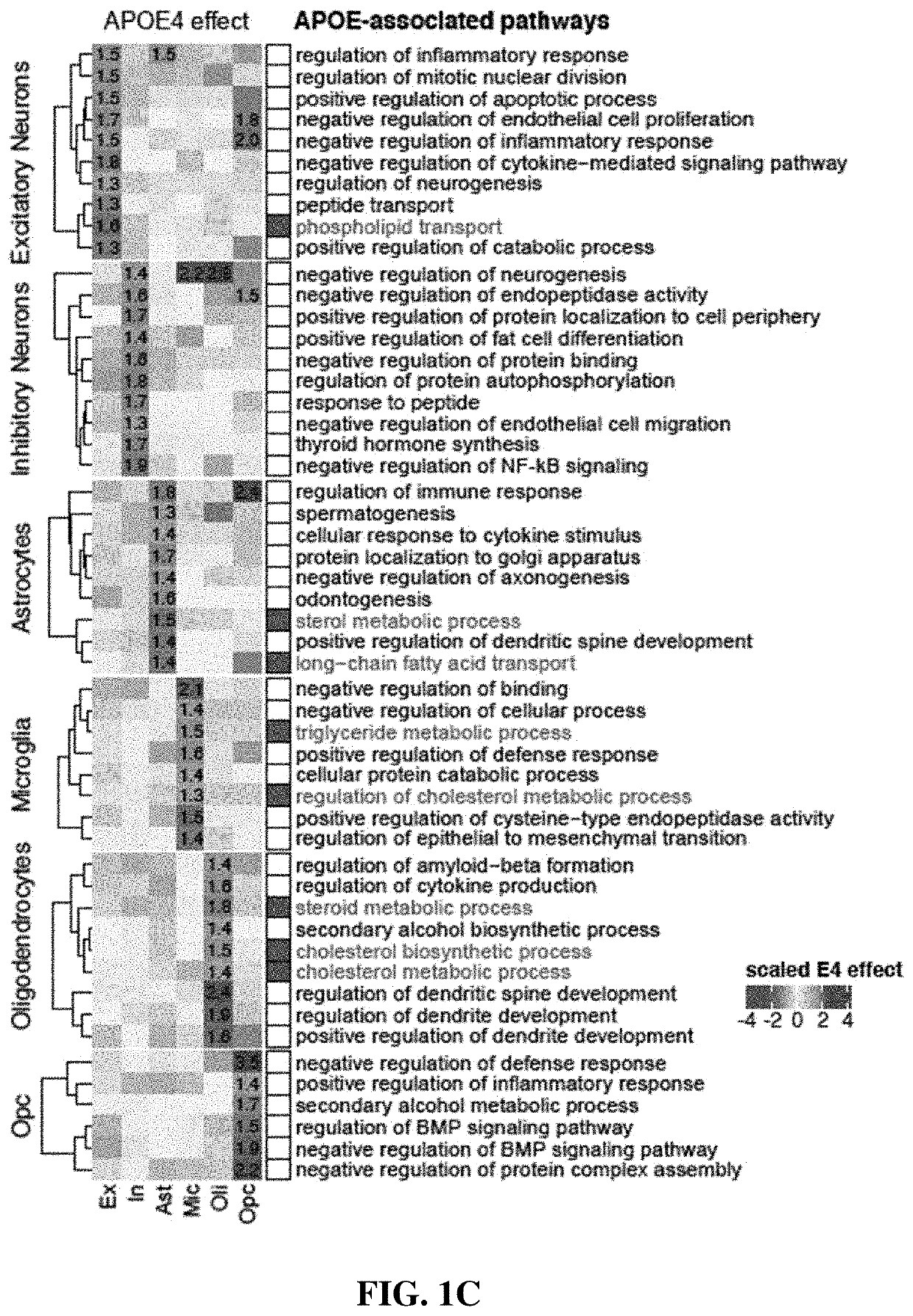
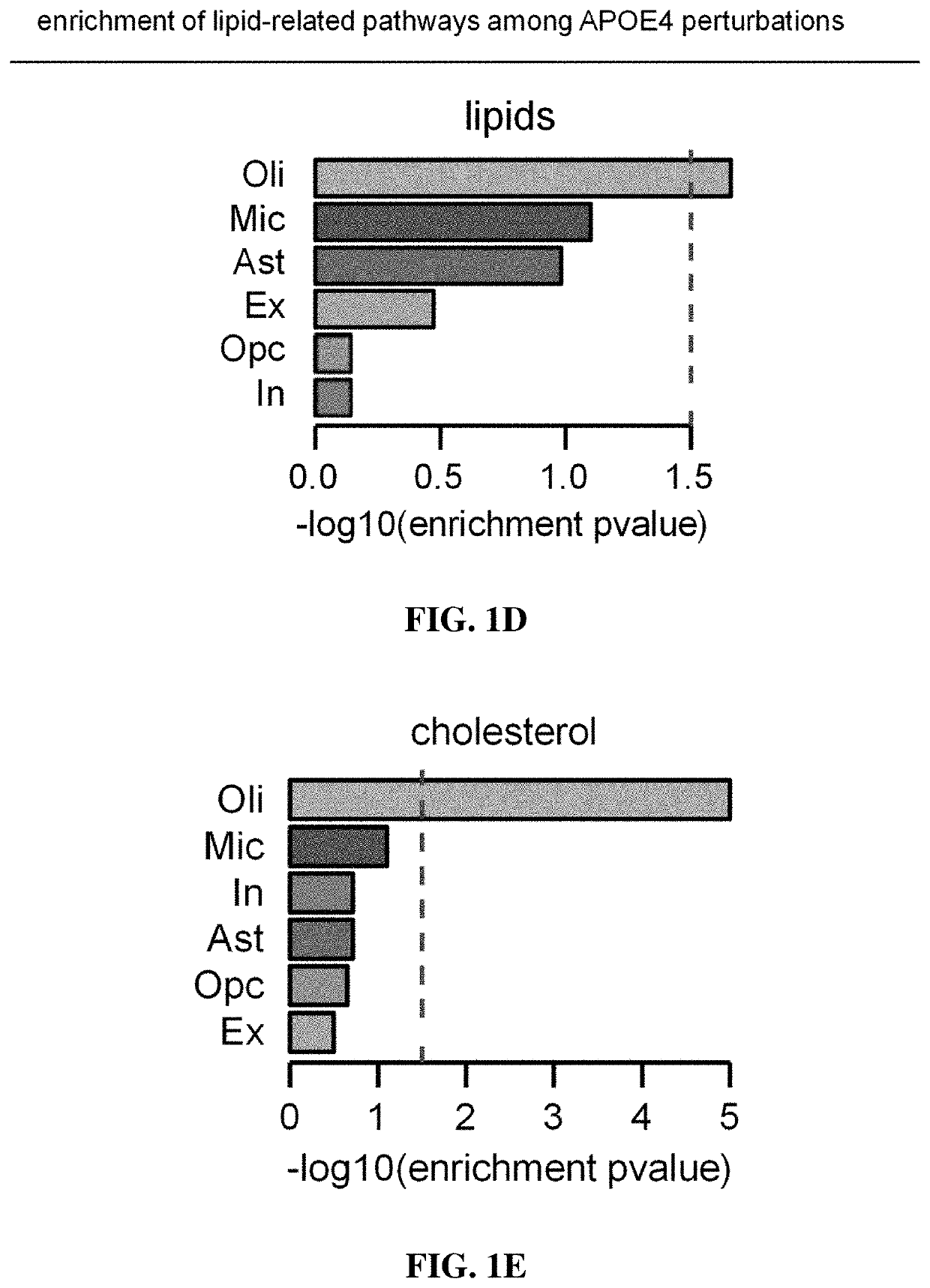
Apoe4 impairs myelination via altered cholesterol biosynthesis and transport in oligodendroglia
PendingUS20220288104A1Enhances myelinationNervous disorderAmine active ingredientsDiseaseMyelin body formation
The present disclosure provides methods of inhibiting amyloid synthesis in a subject using cyclodextrin and analogs thereof. Small molecules (cyclodextrin) reverse APOE4-associated cholesterol phenotypes and lead to significantly improved myelination both human in vitro cultures and APOE4 targeted replacement mice. This demonstrates that APOE4 alters cholesterol synthesis and transport in oligodendrocytes which impairs myelination. Collectively, this work uncovers a pathogenic role of APOE4 in oligodendrocytes and myelination and enables therapeutic opportunities for Alzheimer's Disease.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
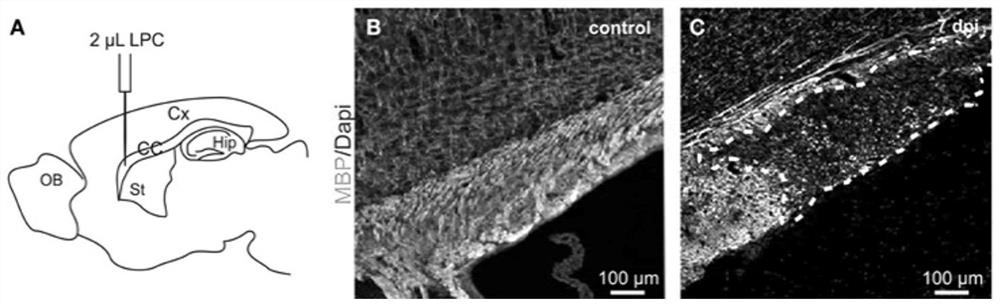
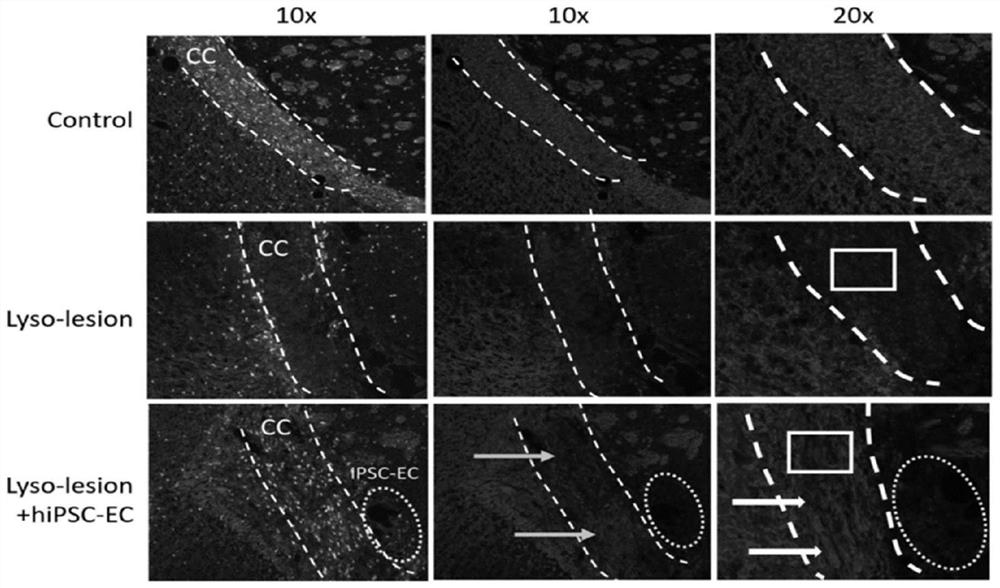
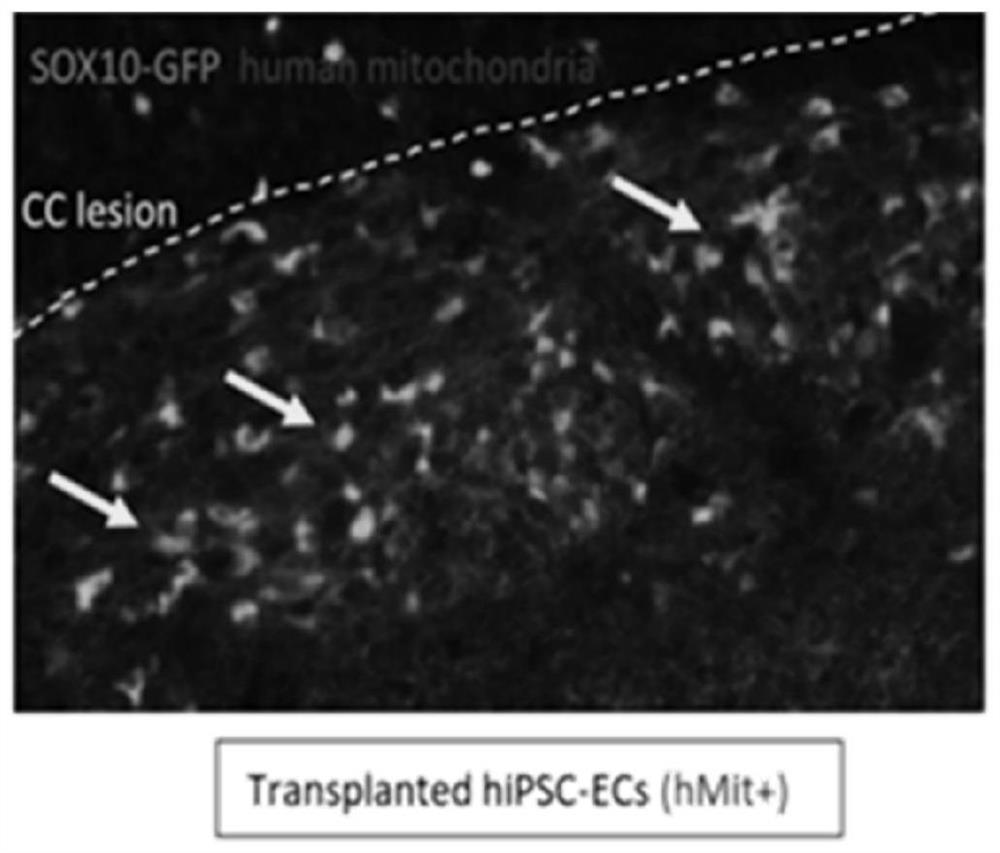
Application of endothelial cells and precursor cells thereof in treatment of demyelination diseases
PendingCN113846052ADelay progressProgress delayNervous disorderNeuregulinsMyelin body formationBiochemistry
The invention discloses an application of endothelial cells and precursor cells thereof in treatment of demyelination diseases. The research finds that the endothelial cells and the precursor cells thereof can promote OPC cell proliferation, migration and maturation, promote astrocyte reaction and promote microglial cell / macrophage activation so as to promote myelin sheath formation, regeneration and repair. The research result of the invention provides a method for actively regulating and controlling myelin sheath formation and regeneration for clinic.
Owner:呈诺再生医学科技(北京)有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com