Data sharing apparatus and processor for sharing data between processors of different endianness
a technology of data sharing and processors, applied in the direction of micro-instruction address formation, memory adressing/allocation/relocation, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of hindering the speed of other processors and posing a barrier to high-speed memory access
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0071] (First Embodiment)
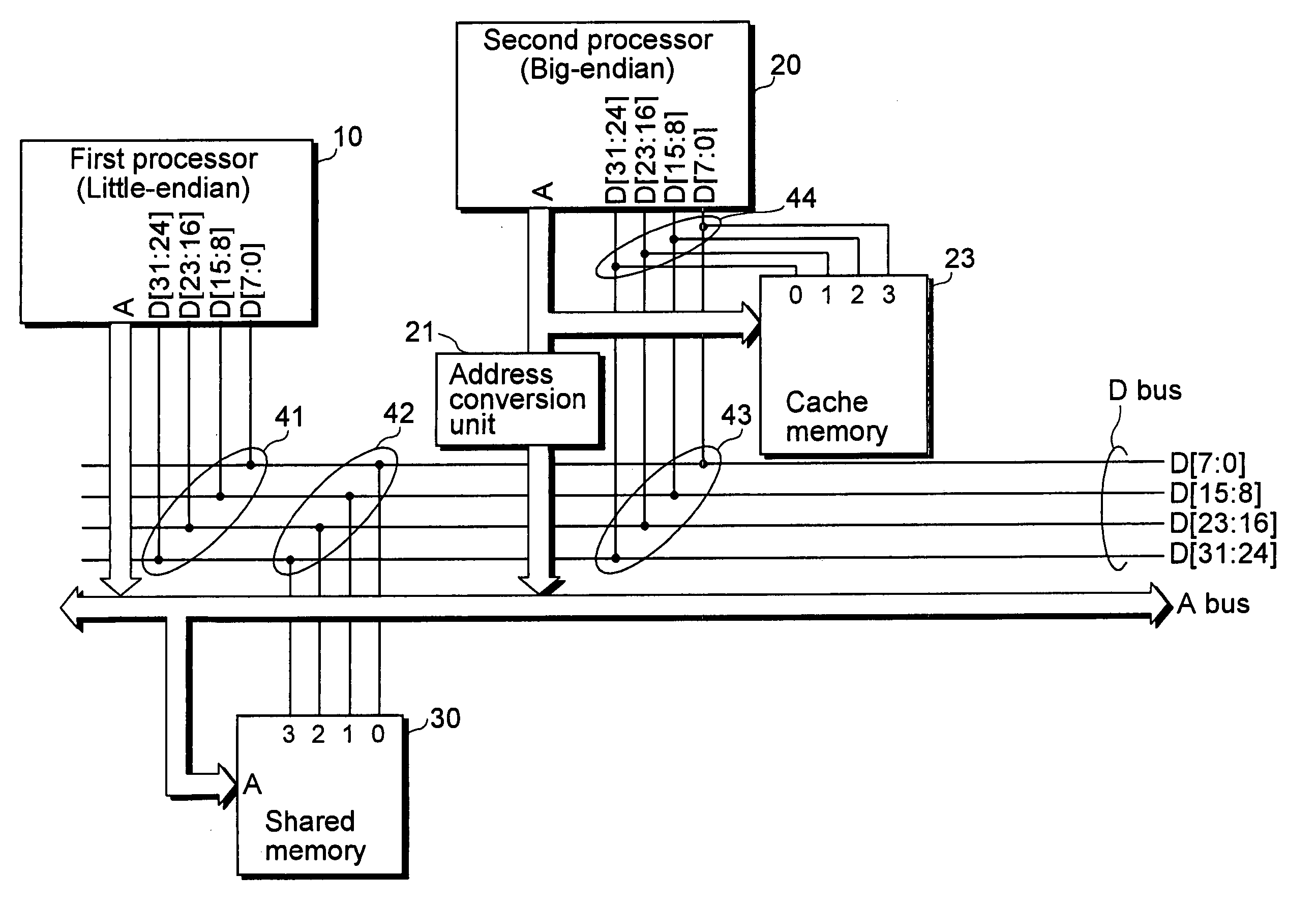
[0072] FIG. 7 is a block diagram showing the structure of a data processing apparatus in the present embodiment. As in the diagram, the data processing apparatus includes a first processor 10, a second processor 20, a shared memory 30, an address conversion unit 21, and a cache memory 23, that are connected to each other via a data bus (D bus, in the diagram).
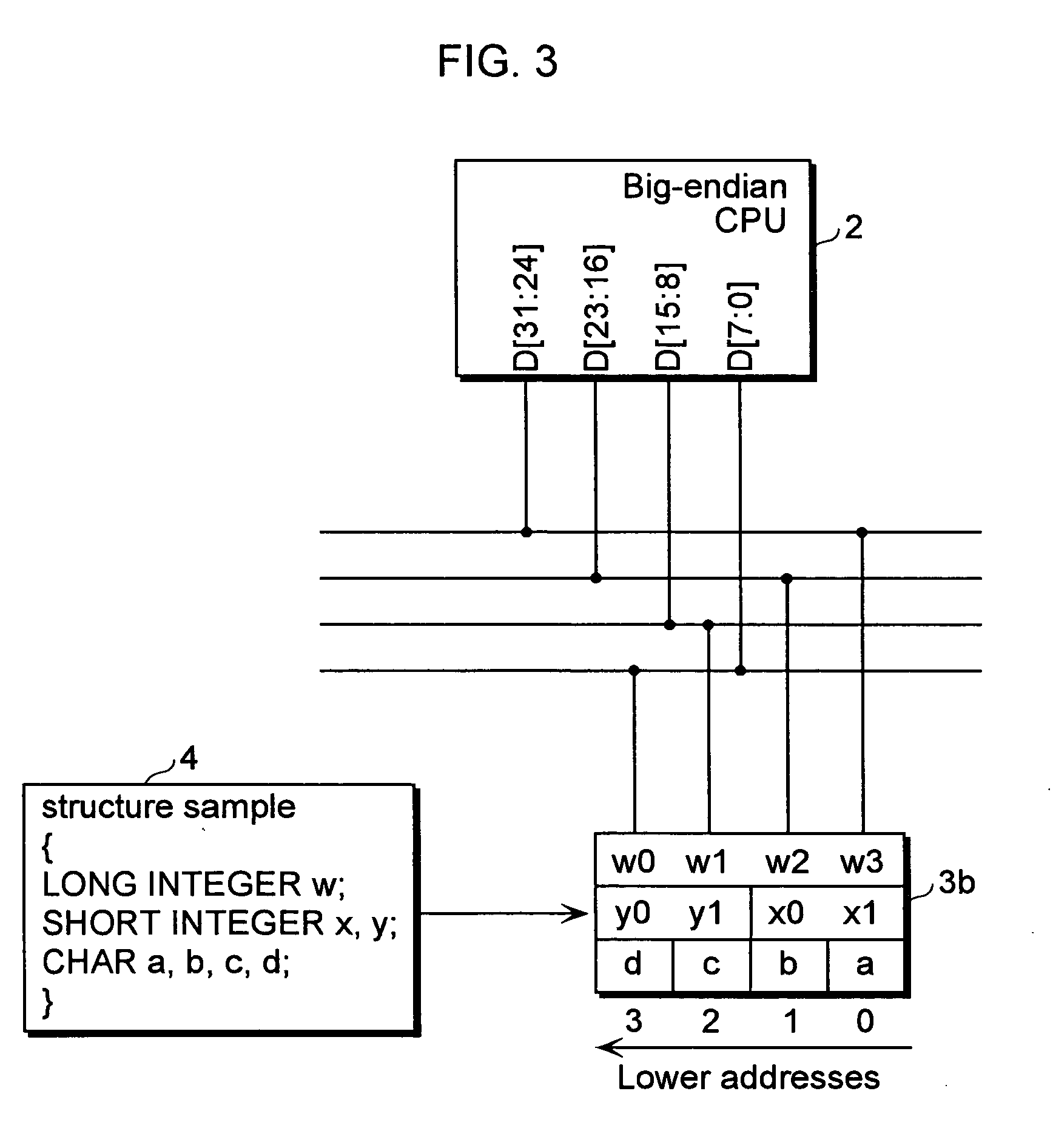
[0073] This data processing apparatus achieves the sharing of data in a memory in an extremely simple structure, through the following three points: (A) the big-endian-type second processor 20 is connected to the shared memory 30 with the same byte order as the little-endian-type first processor 10, (B) the address conversion of the second processor 20, and (C) the respective methods in which structures of data in a program are defined by the first processor 10 and the second processor 20, where (A) and (B) are hardware structures, and (C) is a software structure.
[0074] (A. Bus Connection)
[0075] In FIG....
second embodiment
[0111] (Second Embodiment)
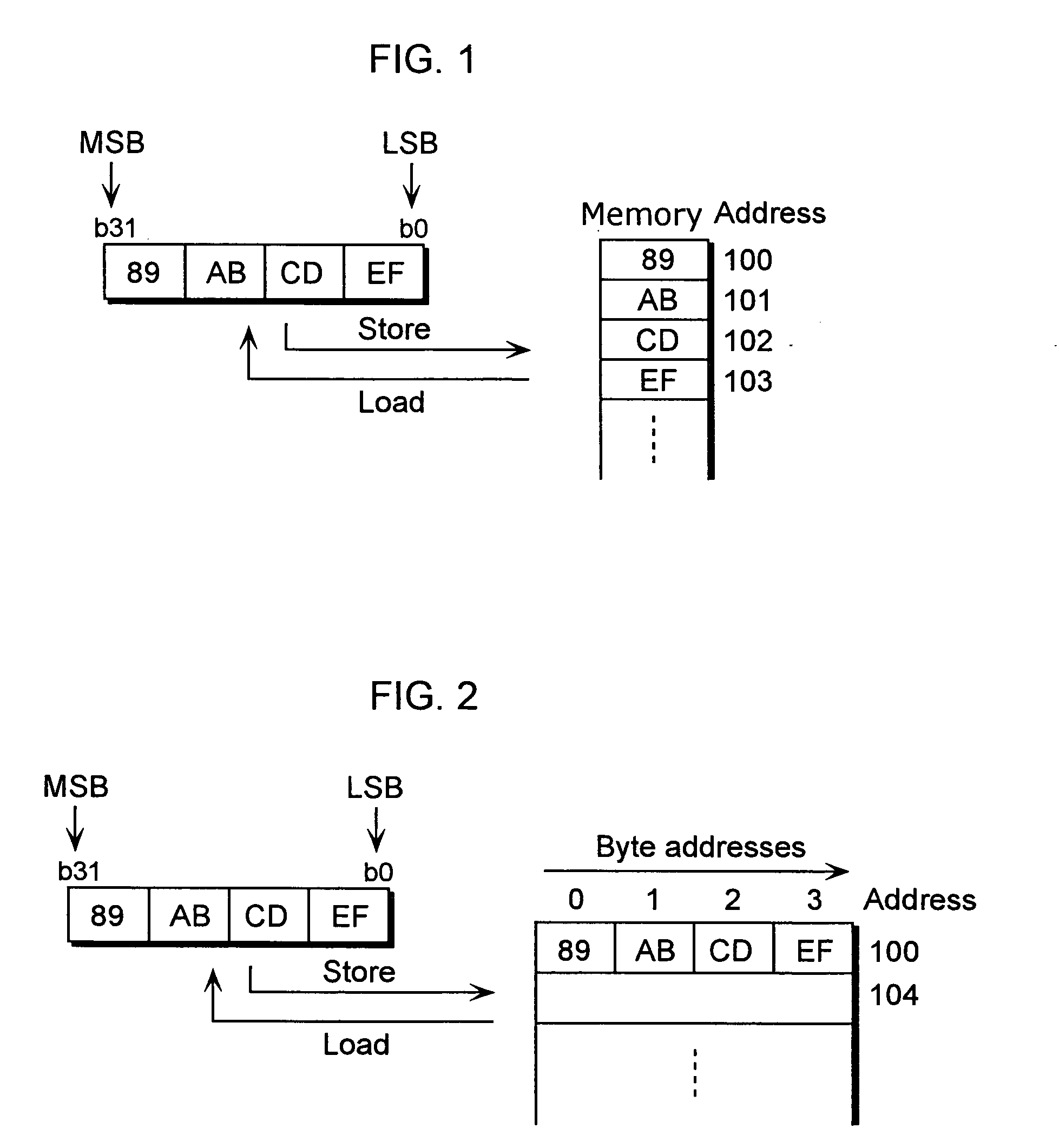
[0112] In the above-mentioned embodiment, the issue of mismatches in half-word addresses and byte addresses arising in (A) and (B), when data in the shared memory 30 is taken from perspective of the first processor 10, and when it is taken from the perspective of the second processor 20, is resolved through the above-mentioned (C). In the present embodiment, a structure for resolving this mismatch by DMA transfer, without using (C), shall be explained.
[0113] FIG. 16 is a block diagram showing the structure of a data processing apparatus in the second embodiment of the present invention. The data processing apparatus in the diagram is different from that in FIG. 7, in having a Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory (SDRAM) 31, a Direct Memory Access Controller (DMAC) 32, an Input / Output device (I / O) 33, and I / O 34, added. Structural elements identical to those in FIG. 7 are assigned the same numerals, and explanations will not be repeated. Explanations wil...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com