Wire grid polarizer with double metal layers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0032] First Embodiment
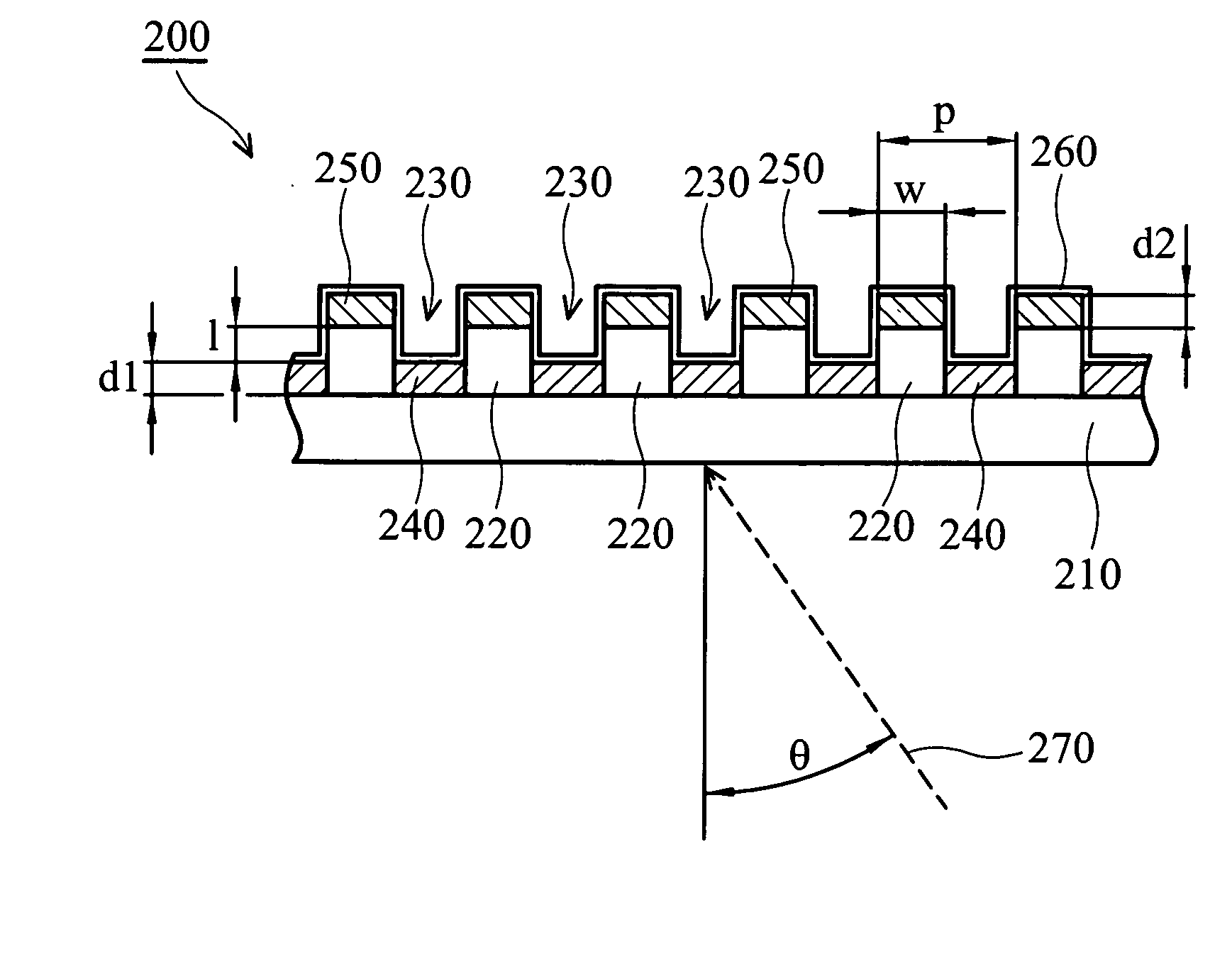
[0033]FIG. 2 is a sectional view of a wire grid polarizer 200 with double metal layers, according to the first embodiment of the present invention. The wire grid polarizer 200 comprises the following elements.
[0034] An insulating and transparent substrate 210 is provided. The transparent substrate 210 can be a glass or plastic substrate, wherein the plastic material is PC (polycarbonate), PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate), PS (polystyrene) or the like. The width of the transparent substrate 210 can be 500˜1500 μm. The refractive index (R.I.) of the transparent substrate 210 is, for example, about 1.5.
[0035] An array of parallel and elongated dielectric layers 220 overlies the transparent substrate 210, wherein the dielectric layers 210 have a period (p) and a trench 230 is located between adjacent dielectric layers 220. In the first embodiment, the transparent substrate 210 is exposed in the trench 230. The material of the dielectric layers 220 can be polymer, ...
second embodiment
[0042] Second Embodiment
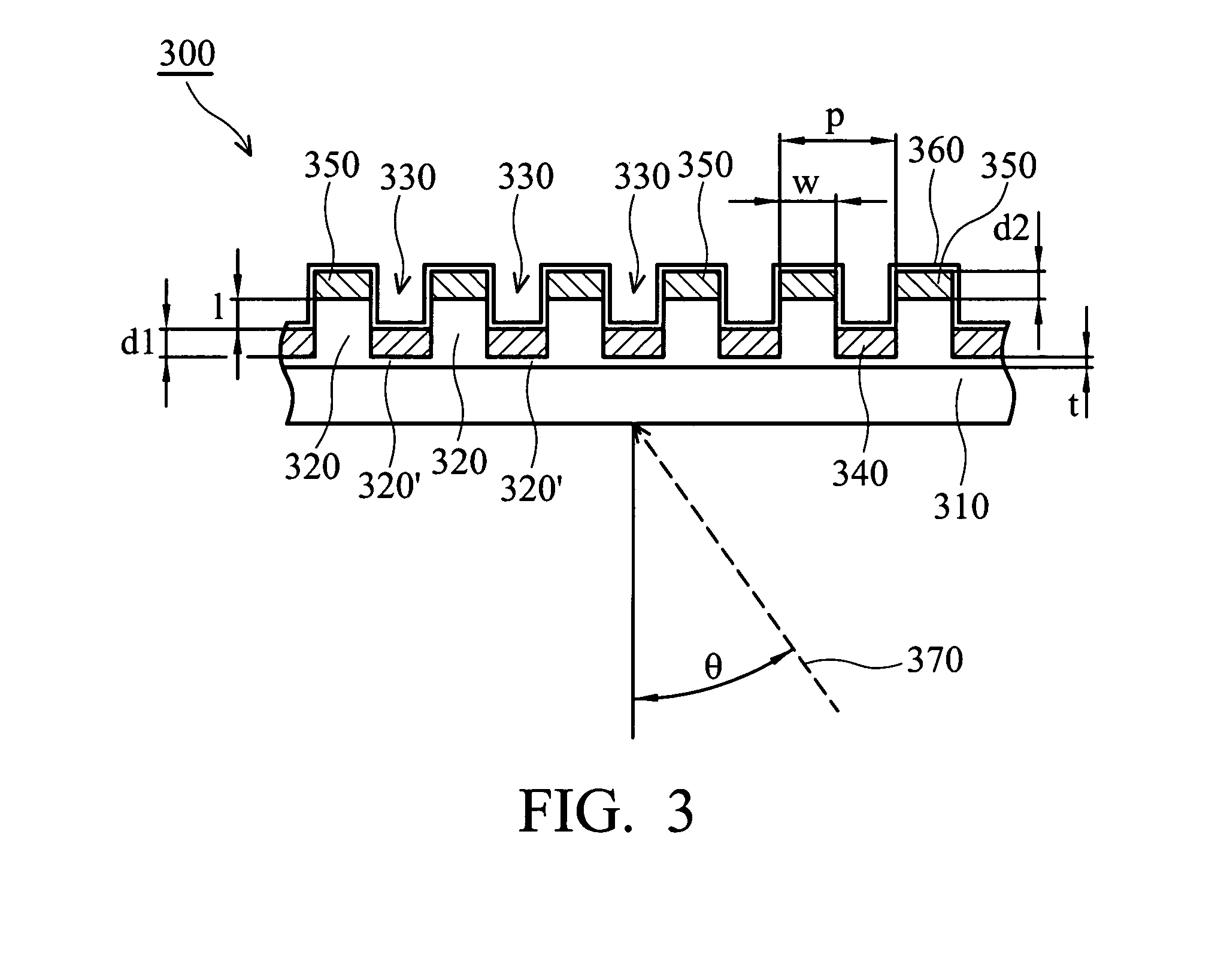
[0043]FIG. 3 is a sectional view of a wire grid polarizer 300 with double metal layers, according to the second embodiment of the present invention. The difference in the second embodiment is that the trench does not expose the transparent substrate. That is, a remaining dielectric layer is left in the trench. The wire grid polarizer 300 comprises the following elements.
[0044] An insulating and transparent substrate 310 is provided. The transparent substrate 310 can be a glass or plastic substrate, wherein the plastic material is PC (polycarbonate), PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate), PS (polystyrene) or the like. The width of the transparent substrate 310 can be 500˜1500 μm. The refractive index (R.I.) of the transparent substrate 310 is about 1.5.
[0045] An array of parallel and elongated dielectric layers 320 overlies the transparent substrate 310, wherein the dielectric layers 310 have a period (p) and a trench 330 is located between adjacent dielectric laye...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com